But the main complication was represented by Dots. Many of them had thick concrete walls, up to 2 m and 1.5-meter roof. The most powerful was a reinforced concrete structure consisting of recessed in the ground combat casemates, connected by an underground shelter-barracks. The number of machine-gun embrasures could reach 4 to 6, and one or two gun 76-mm guns. Of them shoots near and direct approaches, were flanking the fire, blocking the path to the adjacent firing points. From the front to break such facilities available means was virtually impossible. Needed were powerful tools of destruction.
In mid December the red army was adopted by 48-ton heavy tank KV “Klim Voroshilov” with 76-mm cannon. Prior to this the prototype tank took part in the fighting: he was sent to the Karelian isthmus to check in the front line, immediately removing field and plant tests. The first fight he took on 18 December 1939 and showed excellent fighting qualities.
Among the tasks performed by them on the field of battle, consisted, in particular, “the destruction of concrete structures.” However, combat reports, “shooting for Border positive results has not given.” Therefore, the Military Council of the northwestern front recognized the need to strengthen the armament of the new tank gun up to 152 mm. According to military experts, this caliber could “deal” with serious fortifications.
In January 1940, SKB-2 of the Leningrad Kirov factory received the order of the government to perform this task.
Tank tower must match the settings 152-mm guns, recoil device and the breech must be placed in it. The internal volume of the tower of the KV-1 proved to be insufficient for that purpose. Therefore, the designers had to create a new tower with a large living space. It was called “the big tower”, as opposed to standing on the KV-1 “small turret”. It mounted a howitzer M-10T with a barrel length of 23.1 per PBC. Tower with a howitzer received index MT-1.
A full-sized mockup of the KV-2 with authentic items in the Museum of military equipment “Battle glory of the Urals”. Verkhnyaya Pyshma, Sverdlovsk oblast
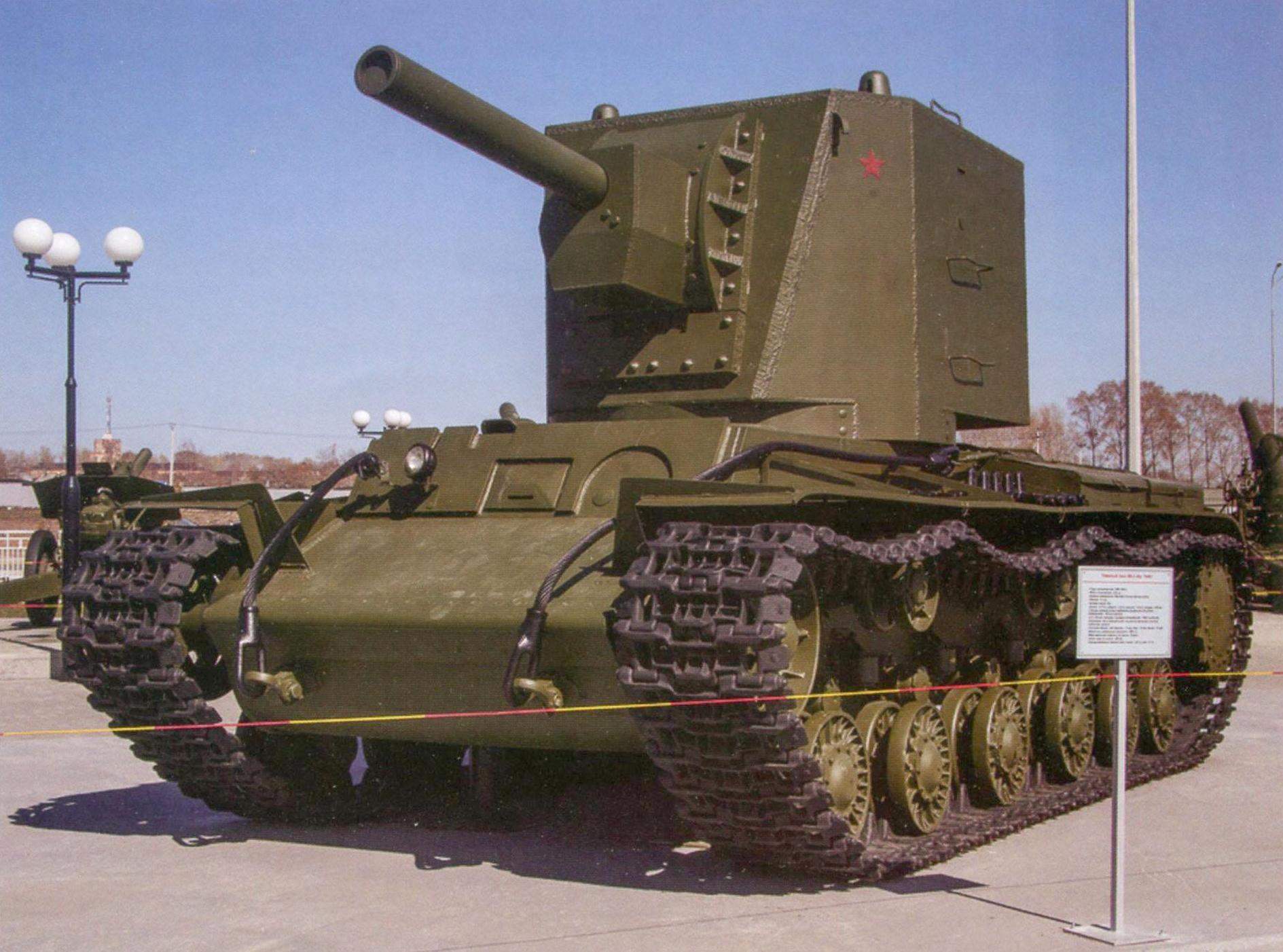
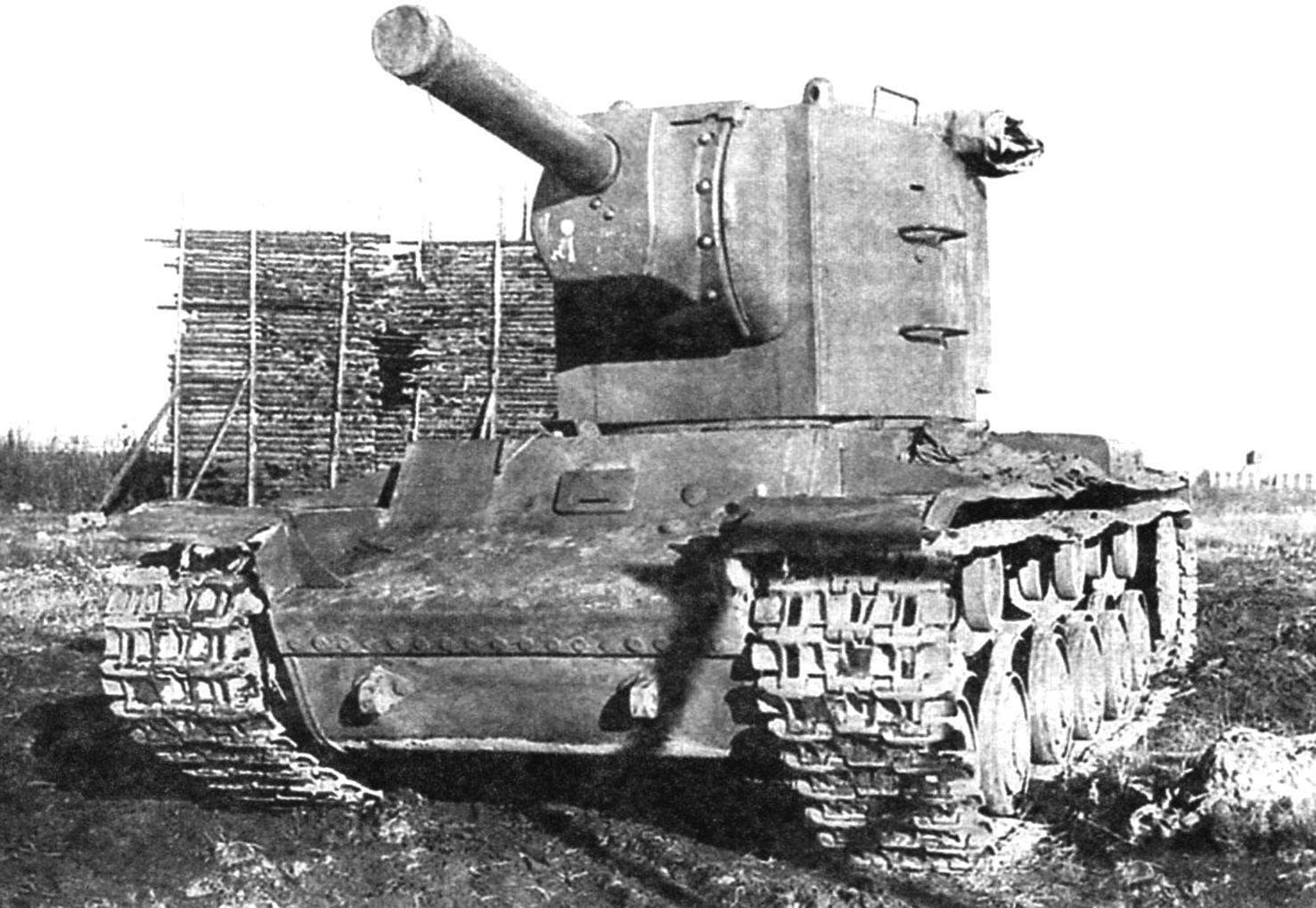
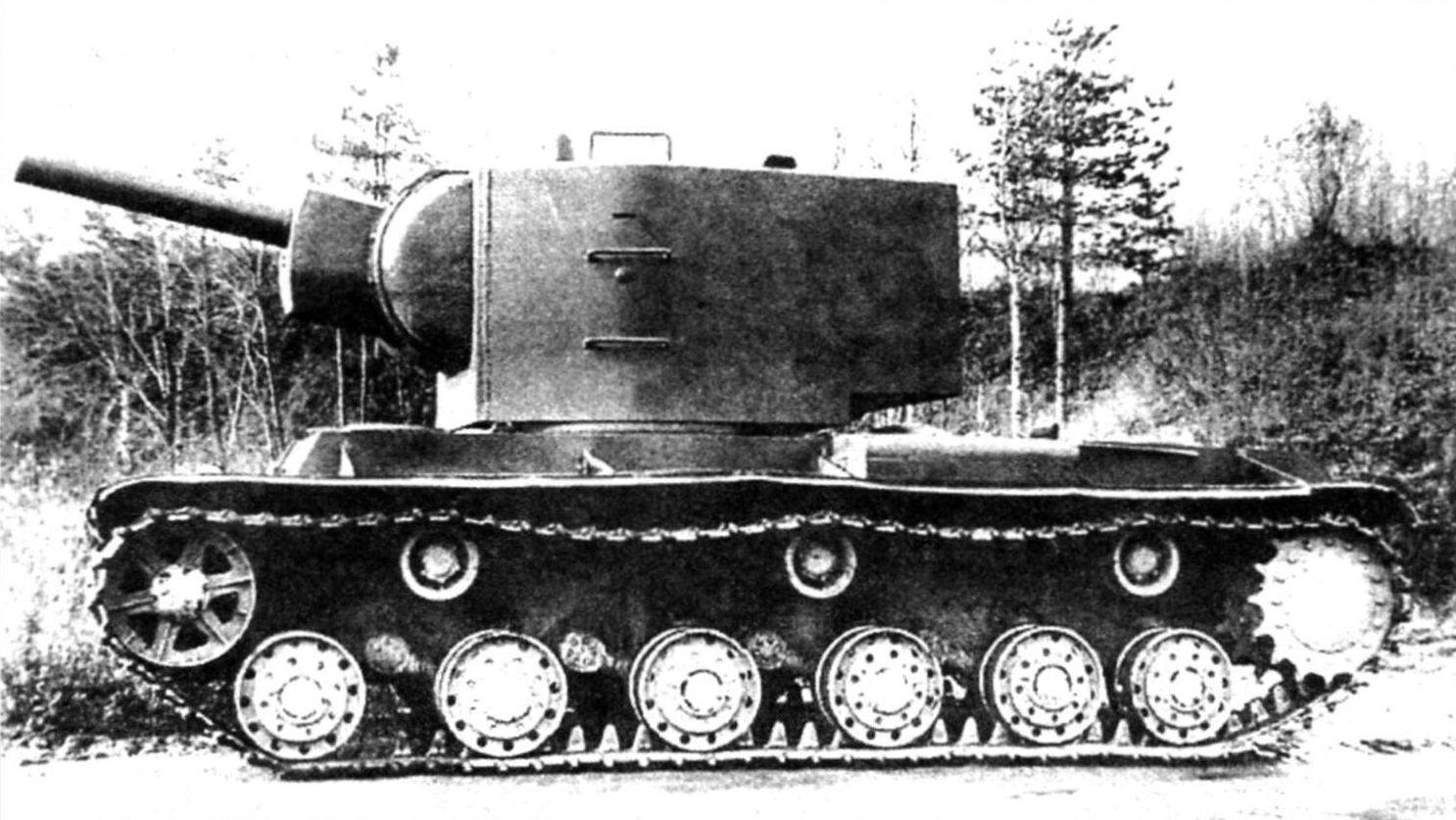
Heavy breakthrough tank KV-2. Weight – 52 tons, booking frontal part and the sides of the hull, turret – 75 mm Armament: 152-mm gun-howitzer M-10T, three 7.62-mm machine gun DT
KV-2:
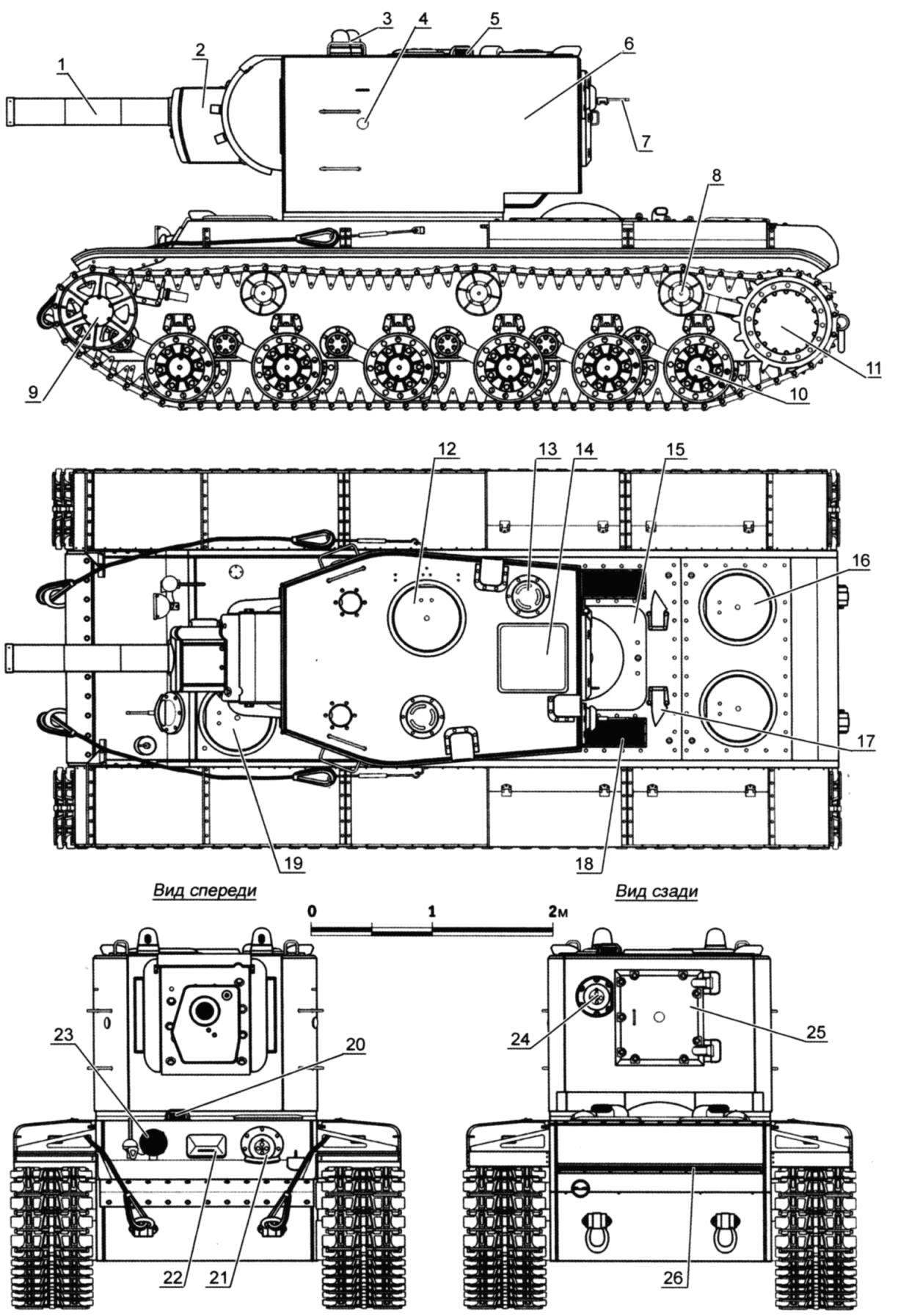
1 – 152-mm gun M-10T; 2 – gun mask; 3 – the armored covers of the sight; 4 – hole for firing personal weapons; 5 – description of the surveillance device; 6 – turret; 7 – aft 7.62-mm machine gun; 8 – supporting the roll; 9 – a steering wheel; 10 – support roller; 11 – driving wheel; 12 – turret hatch; 13 – the armored covers of the fan; 14 – Luke download ammunition; 15 – Luke the engine compartment; 16 – an access hatch to the powertrain; 17 – exhaust pipe; 18 – louver air intake; 19 – cover radio operator-gunner; 20 – a surveillance device of the driver; 21 – the frontal recess 7.62-mm machine gun; 22 – inspection hatch of the driver; 23 – front outer headlight; 24 – recess aft machine gun; 25 – the aft hatch of the gun; 26 – closed blinds air
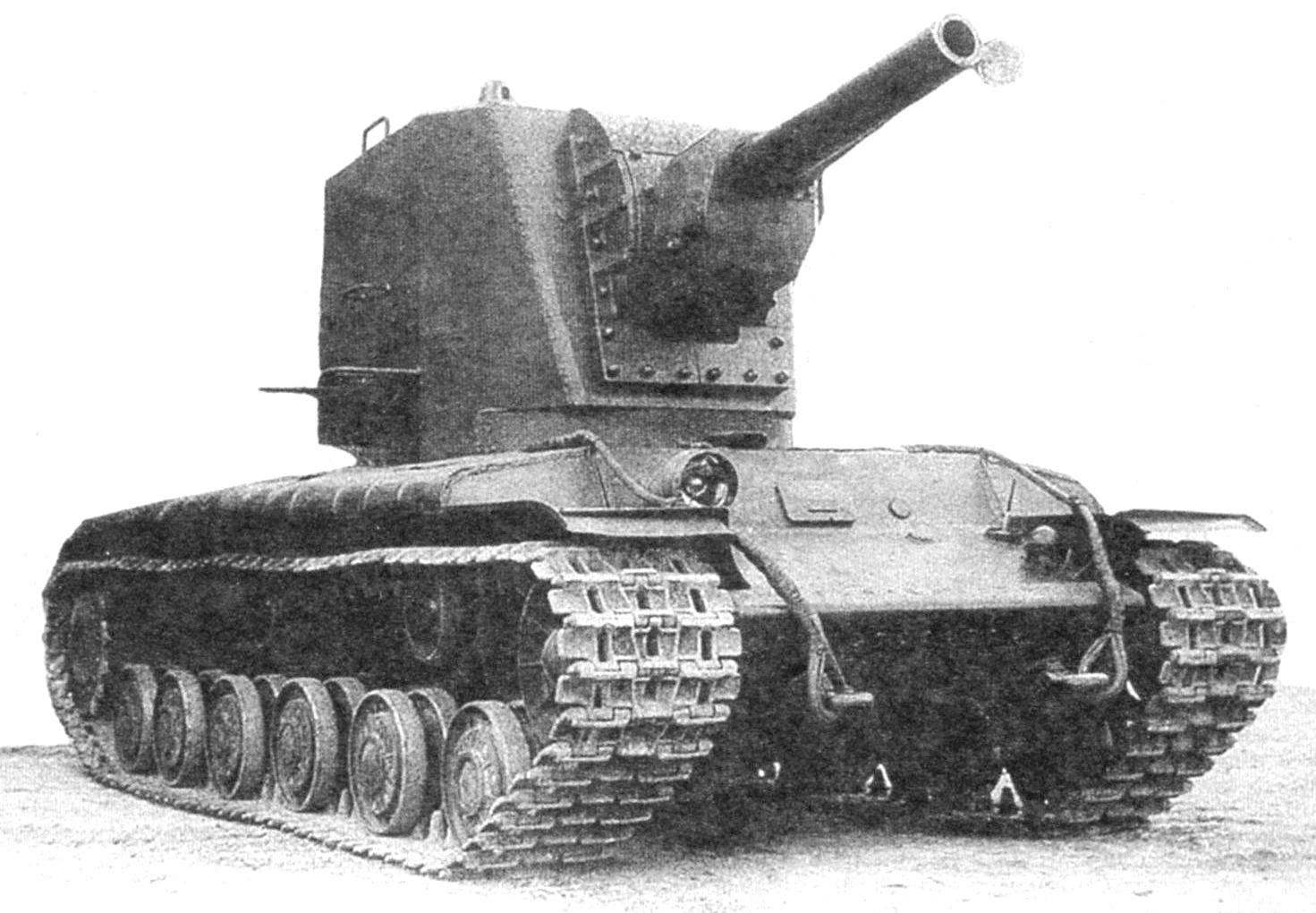
A prototype of the KV-2. Is slope of the front armor plate of the tower. The gun barrel with a cover to prevent being hit by bullets and shrapnel
Tower prototype and the first series of the KV-2
Already on the 10th of February produced pilot shooting, which proved very successful, and soon a few prototypes of a new tank the KV-2 was sent to the front. They participated in combat operations from 18 December until the end of the war.
In a report generated by the command at the end of “combat testing” was mentioned in particular, that KV-2 “is a powerful means of destroying anti-tank guns, field artillery and other emplacements that are in shelters… Able to do passes in nadabah of stone, dug into the ground, artillery fire direct fire”. And then noted: “…the armor of tanks did not break armor-piercing projectiles with a very close range of 100 – 250 m”.
The decision of Sovnarkoma of the USSR and the CPSU(b) № 548-232сс 5 March 1941 the vehicle entered into production at the Leningrad Kirov plant. According to the plan in 1940 was required to produce 50 such machines in the next year had to move to high-volume production of 250 units.
The military command, the KV-2 was considered as a breakthrough tank heavily fortified front lines and for amplifying heavy artillery fire involved in combat operations divisions of medium and light tanks. So the KV-2 armed with a howitzer, with hinged trajectories shooting, which is so important in offensive combat when the opponent is defending and you have to destroy his building, out of the trenches, dugouts, unlike the defensive actions when necessary grazing trajectory counter-fire at close range. In the end, on the tank, put a powerful gun-howitzer M-10T.
High-explosive projectile OF-530 weight of 40 kg this gun at a distance of 1500 m past the 72-mm armor at an angle meeting of 60°. When the high-explosive explosion in soil average density of the formed crater with a diameter of 3.5 m and a depth of about 1.2 m. When you install Fuze for shrapnel effect fragments scattered on the area of 2100 m2, up to 70 m wide and 30 m deep. Cumulative shell 53-BP-540 punched 250 mm armor at an angle of meeting of 90°, 220 mm at 60°, 120 mm at 30°. Ammunition howitzers consisted of 36 shots separately-tubular loader.
Military sources have different opinions about using when firing KV-2 concrete-piercing shells G-530. Indicating that the tanks in the period of “Winter war” is successfully applied as when shooting at long-term firing points, and when making passages among obstacles, destroying them. Other publications objected, citing the possibility of the rounds jamming towers because of the large impact and rollback, in addition, from concussion could suffer components and assemblies engine-transmission group. However, in General, according to the service manual, the firing could be conducted only on a reduced charge W-536, and the full charge is strictly forbidden. But the weight and PF-530, G-530 was identical – 40 kg.
For the same reason, shooting was allowed only at stops.
Gun M-10T was developed on the basis of field howitzer M-10; if fine-tuning to the tank gun its barrel shortened to 23.1 klb, that is, it was short. The gun had a piston stopper, which had to specifically enter “the castle”, which became the sixth member of the crew. His duties included the loading of the gun: first, open the breech, the projectile was laid on the cradle, then dvigala in the breech of the gun and goilala prisojnica – gate was shut.
Horizontal guidance produced by the rotation of the tower, and in a fixed position by a few degrees in the horizontal sector could “bring” to the purpose of the gun itself. Vertical angle pickup guns – from -3° to +18°. The rate was 2 to 3 RDS./min.
When firing, the crew used a telescopic sight TOD-9, with a straight tip and a periscope PT-9 – when firing from the closed position, the commander could also use a commanding panorama of PT-K At night, the devices had a backlight.
The weight of the swinging gun parts -2300 kg. Its axle mounted in bearings of the frame, fixed in the embrasure of the tower. The turret in the roof of the fighting compartment was equal to 1535 mm.
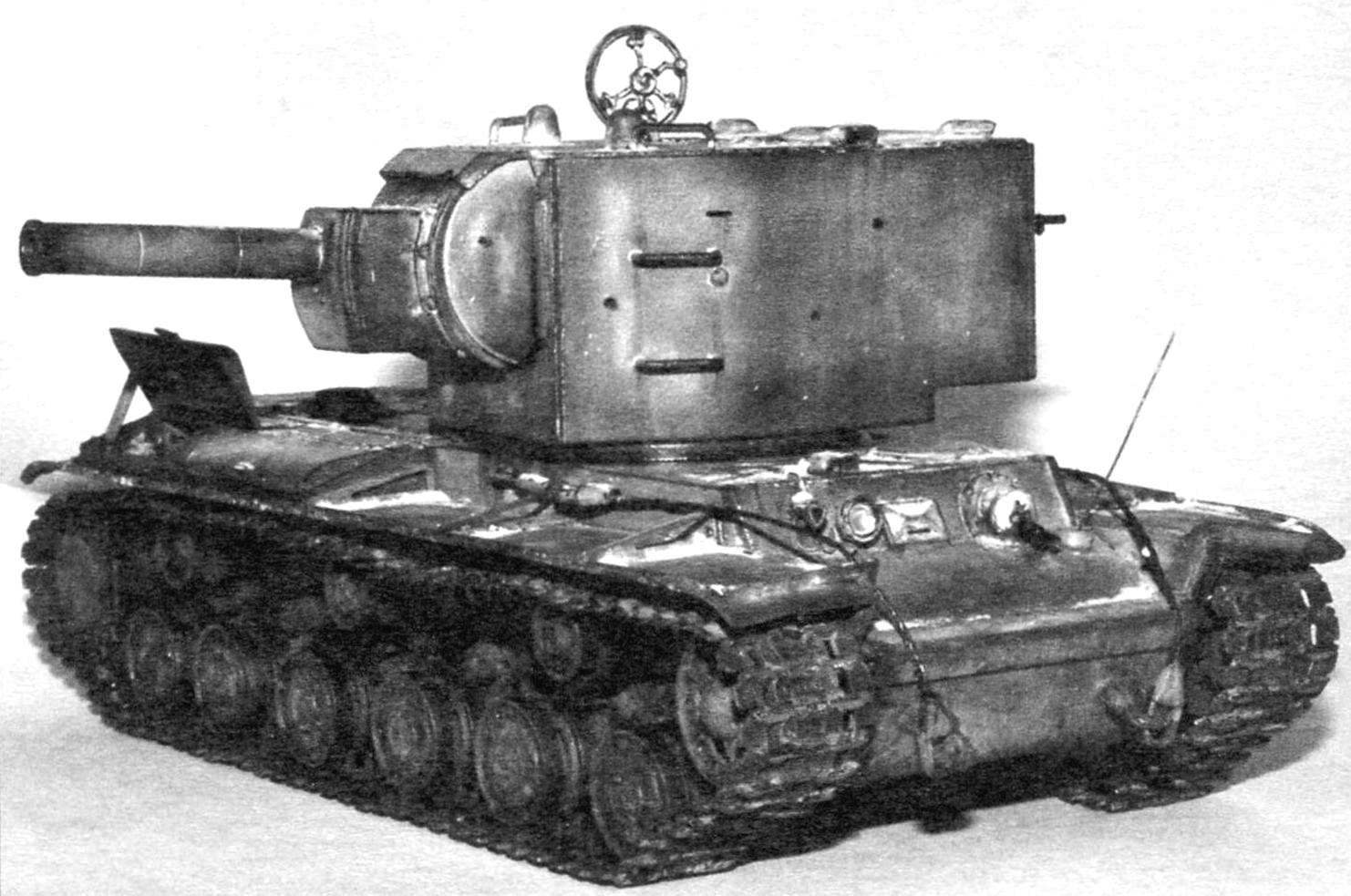
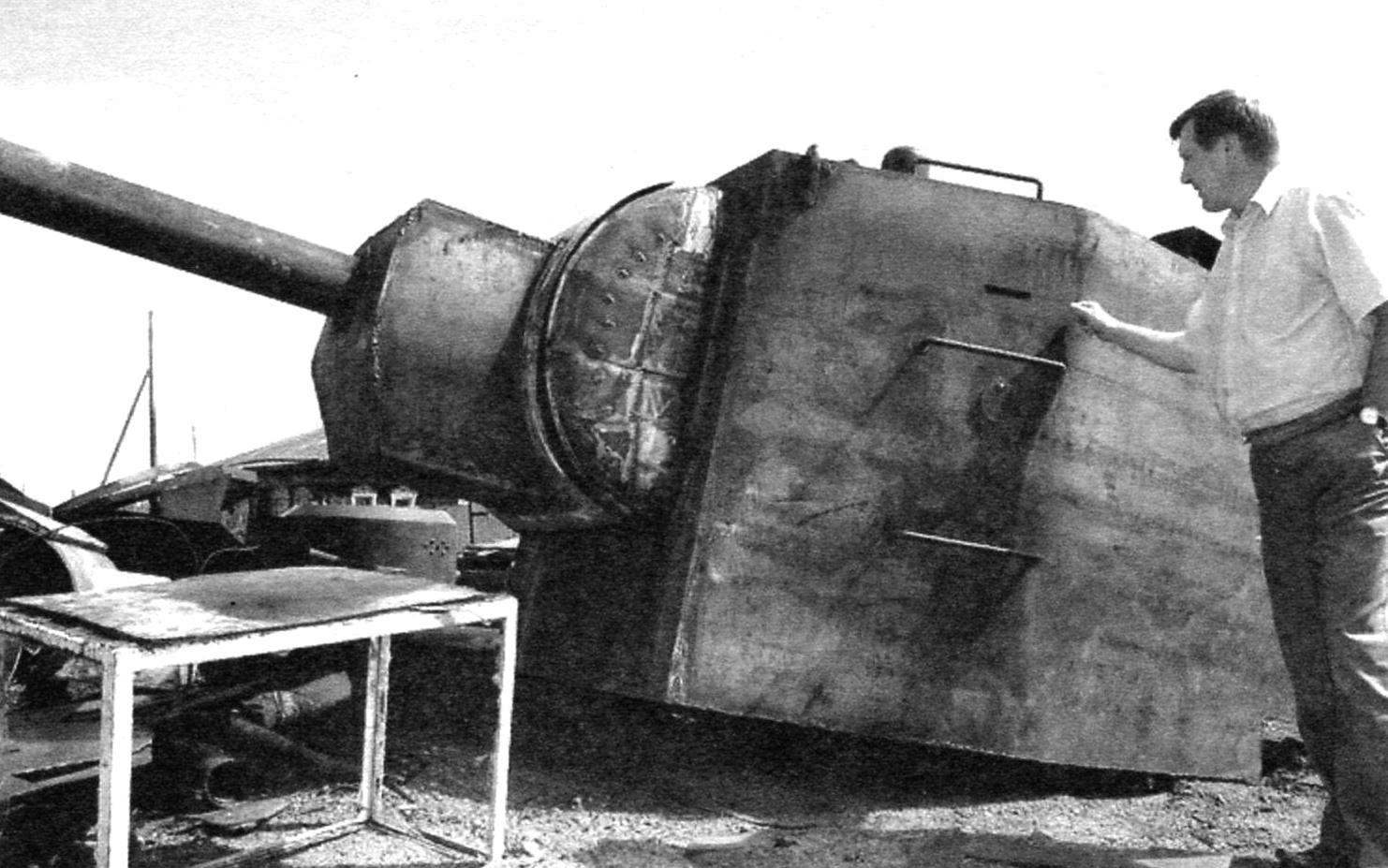
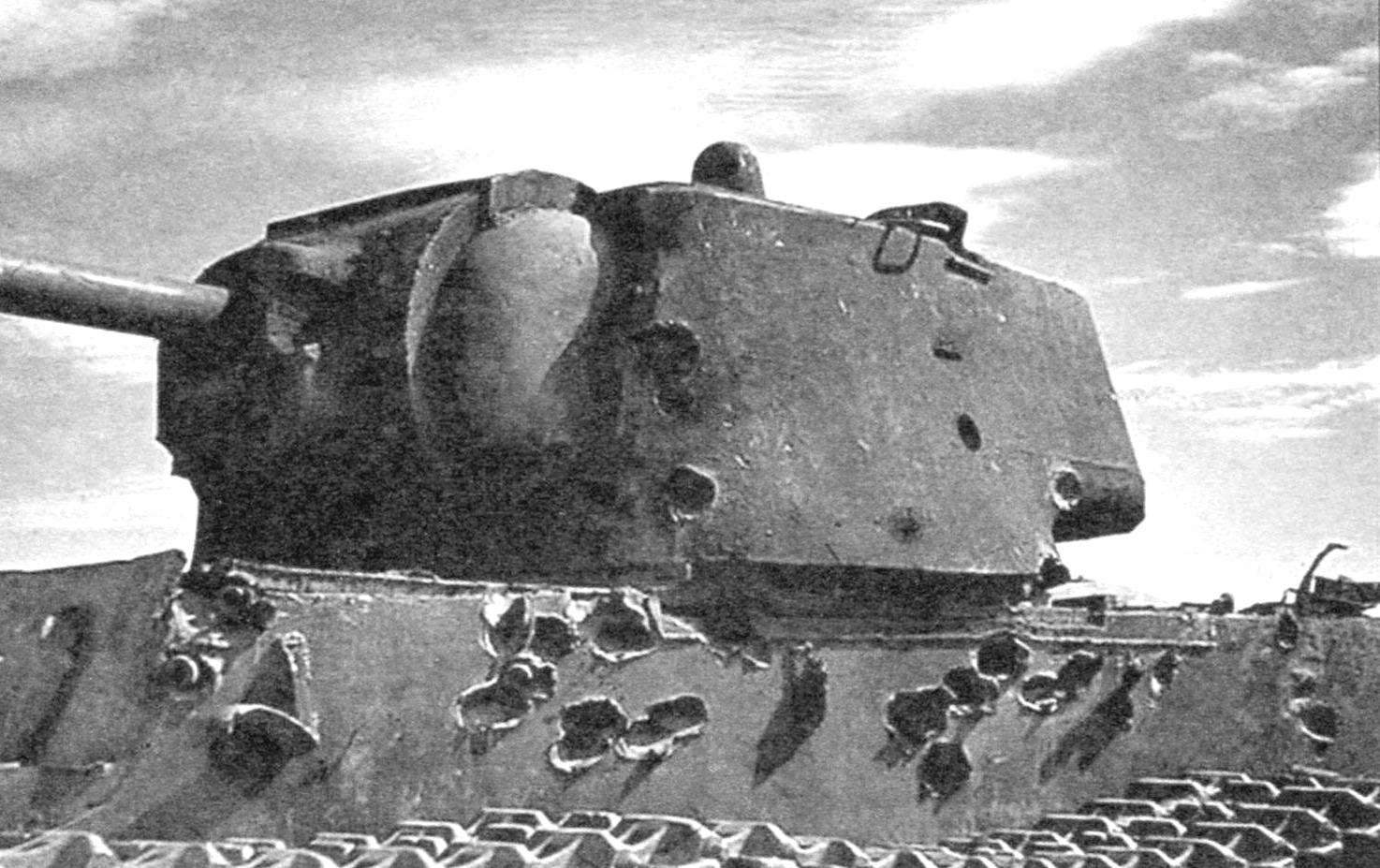
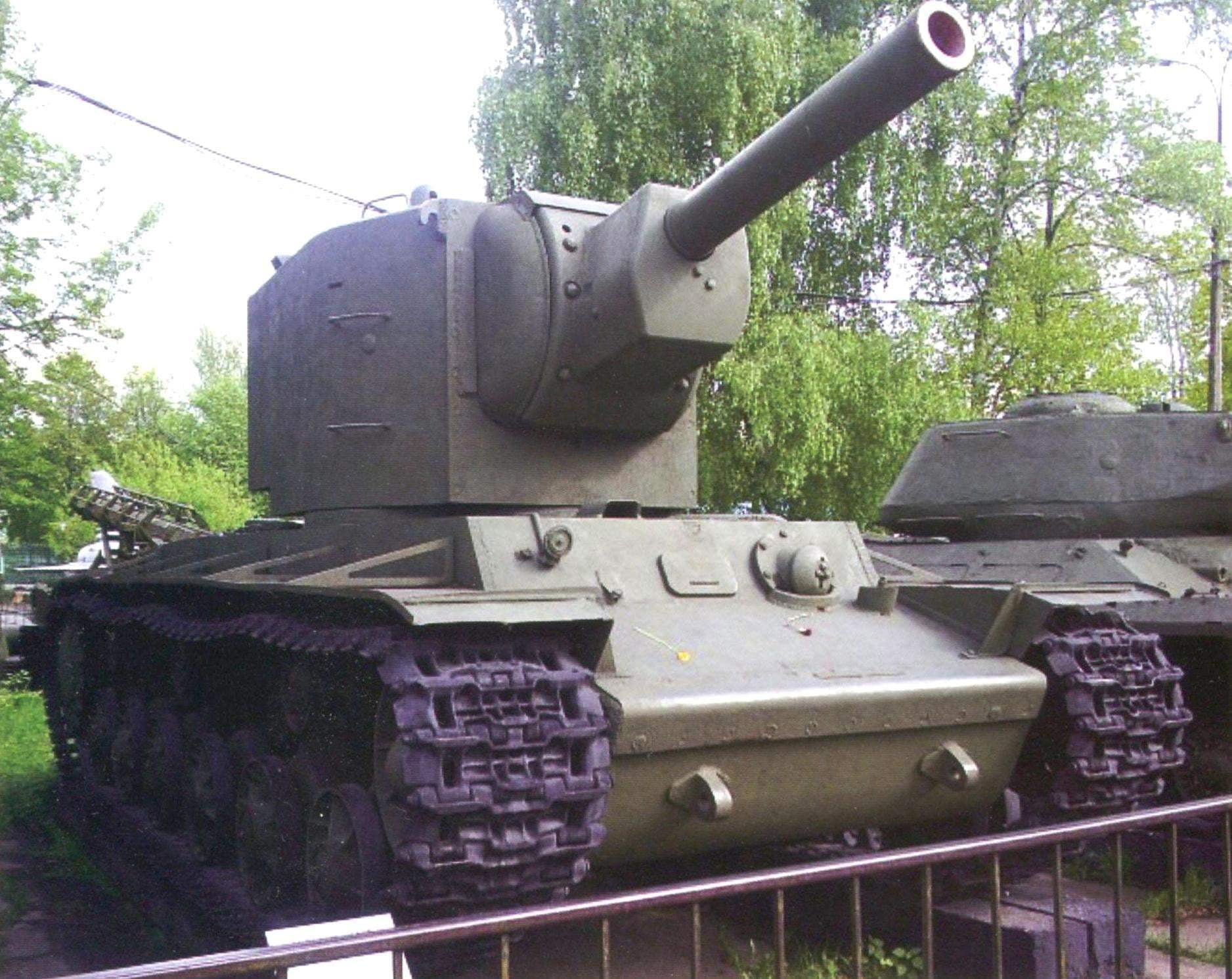
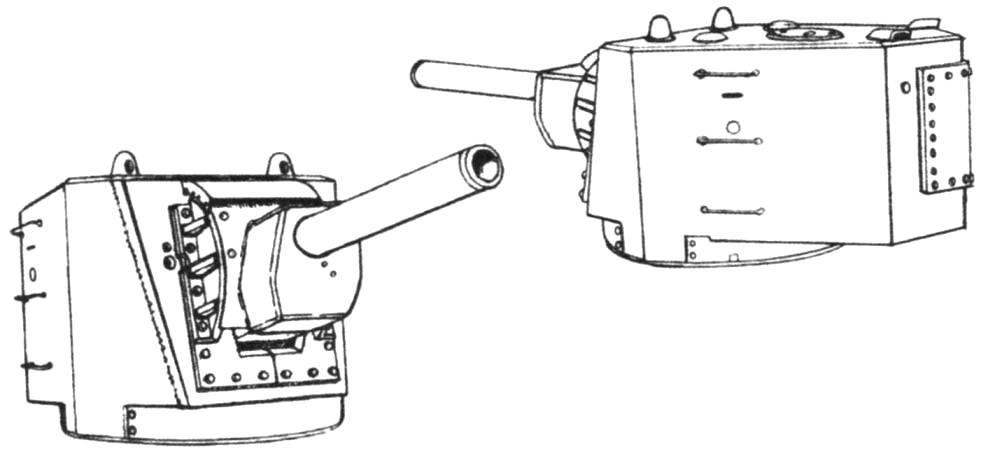
Tower serial KV-2 was somewhat different in configuration from each other. Originally established MT-1 “Motovilikha tank first”, designed and manufactured at the Motovilikha plant in Perm. It was huge for the tank size, height in human height – 1790 mm. Side was sealed by a 75-Milli-meter of rolled armor plates, a roof thickness of 30 mm, and the mask of the gun – 110 mm. A tank with a heavy turret and a powerful gun was heavier than the original nearly 10 tons and had a mass of 52 t
The tower housed four members of the crew: left of the gun were the gunner and loader on the right – the commander and castle, assistant loader. In the roof of the tower there was a hatch release and landing in the stern – hatch for loading ammunition in the rear wall of another for installation and disassembly of guns, armor closed the lid on the bolts. Observation of the terrain could be conducted through the two observation slits with protective “triplexes” in the sides of the tower and mirror monitoring devices in her aft. Were covered with armored plugs the hole for the firing of personal weapons.
All three 7.62-mm machine gun DT was not fixed and transported in the pilings. When fighting two of them mounted on the brackets in the hatches of the tower – alone, paired with a gun, in front, the other in the stern. Another course was placed in the frontal turret box to the left of the driver. On the hatches there were holes in the armor for aiming. The guns were fitted with PU scopes from a sniper rifle with a three-fold increase.
Shots of ammunition was divided into parts. The shells are packaged in cassettes, placed on the floor of the fighting compartment, and the charges to them – in a niche of the tower and in the Department of management.
Later, from November 1940-began to apply the so-called “lower” the tower, slightly smaller in mass and size, but they still remained impressive. So, the tower had an internal volume with such dimensions: length – 2400 mm, width – 1745 mm, height – 1550 mm, the length of the rollback when a shot was equal to 810 – 860 mm.
The tower from the ground defended almost “at the level of the second floor” -the roof it was at the height of 3250 mm, and the height of the line of fire of the gun was 2510 mm.
Reduced tower differed from the original vertical armor plates front, while from the former they were inclined.
In addition to occupying its place in the tower, crew members, two were placed in front of the tank. The driver is centered in front of the tower, and gunner – to the left of it; it was another round hatch entry and exit. There was also an emergency hatch in the floor for emergency escape from the car.
In a combat situation a driver could use a viewing device in an armored hatch on the front broneliste. When driving on the March hatch of the device moved forward and did not prevent him from watching the road.
Gunner worked for short wave telephone and Telegraph radio station 71-TK-H operating in the frequency range of 4.0 MHz -5,625. It was a connection with a phone at ranges up to 30 km away in the Parking lot and 15 km on the move and in CW in the Parking lot – up to 50 km, a receiver and a transmitter are performed in separate apparatuses. The antenna is a retractable whip, a height of 4 m. the mass of the whole set was 60 kg.
The crew could use the internal intercom system TPU-4бис that allowed connection to the radio for external communications.
Tank turned toward the stern gun. Right in the hull is a course of machine gun gunner-radio operator in the centre – hatch with a surveillance device of the driver. In the rear of the turret is visible aft machine gun
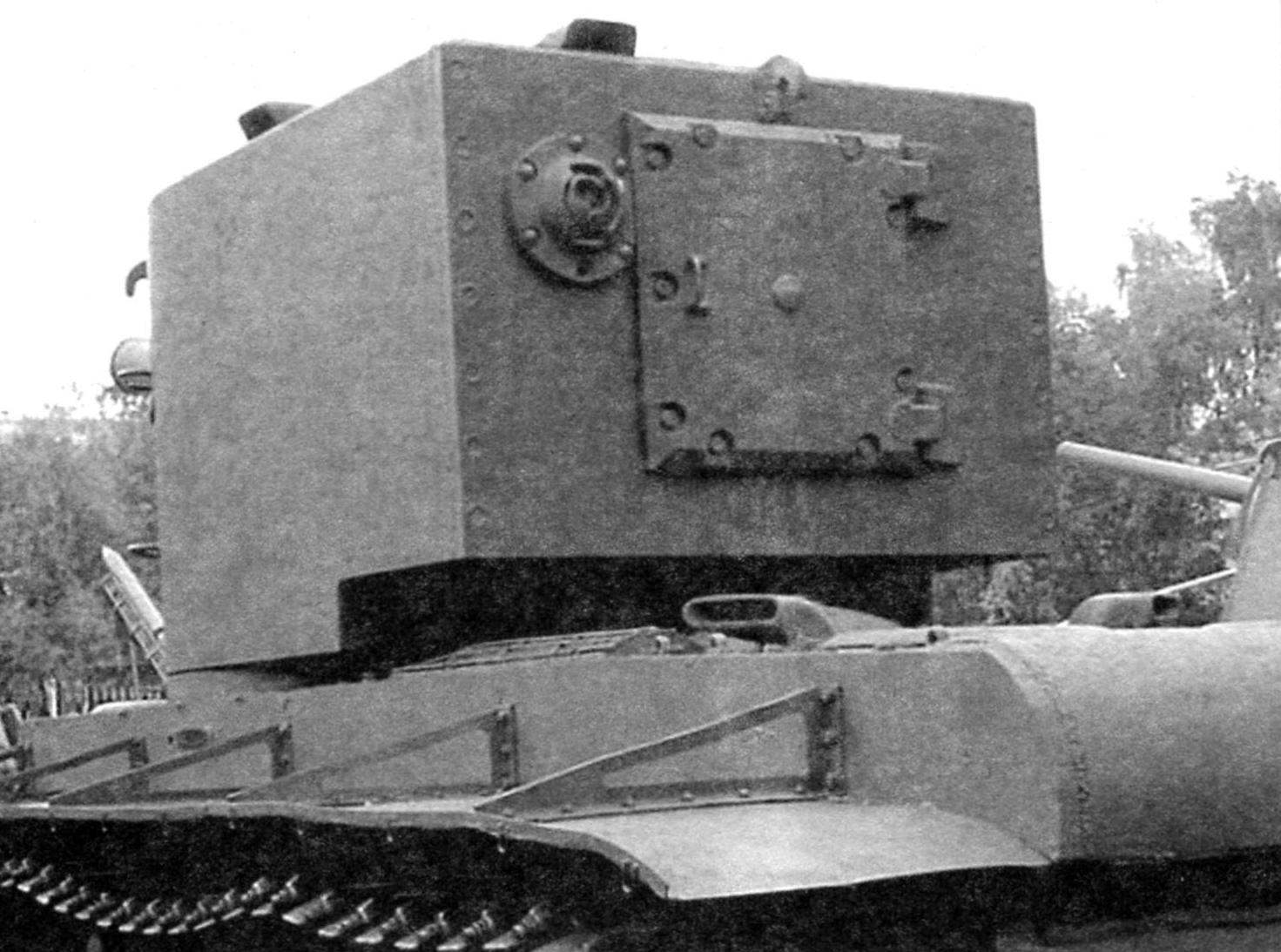
The tower feed. In the center is the hatch for mounting the cannon to the left of him – the breach aft 7.62-mm machine gun. Under the tower – the exhaust pipe of the engine
One of the first samples of the tank before testing. 1940
The turret of the KV-2 was already struck by its size – its height was equal to 1.79 m. the Internal dimensions of the tower: lenght – 2400 mm, width -1745 mm. For comparison, standing next to a man had a height of about two meters. Turret – a private Museum exhibit designer V. Verevochkin, Novosibirsk
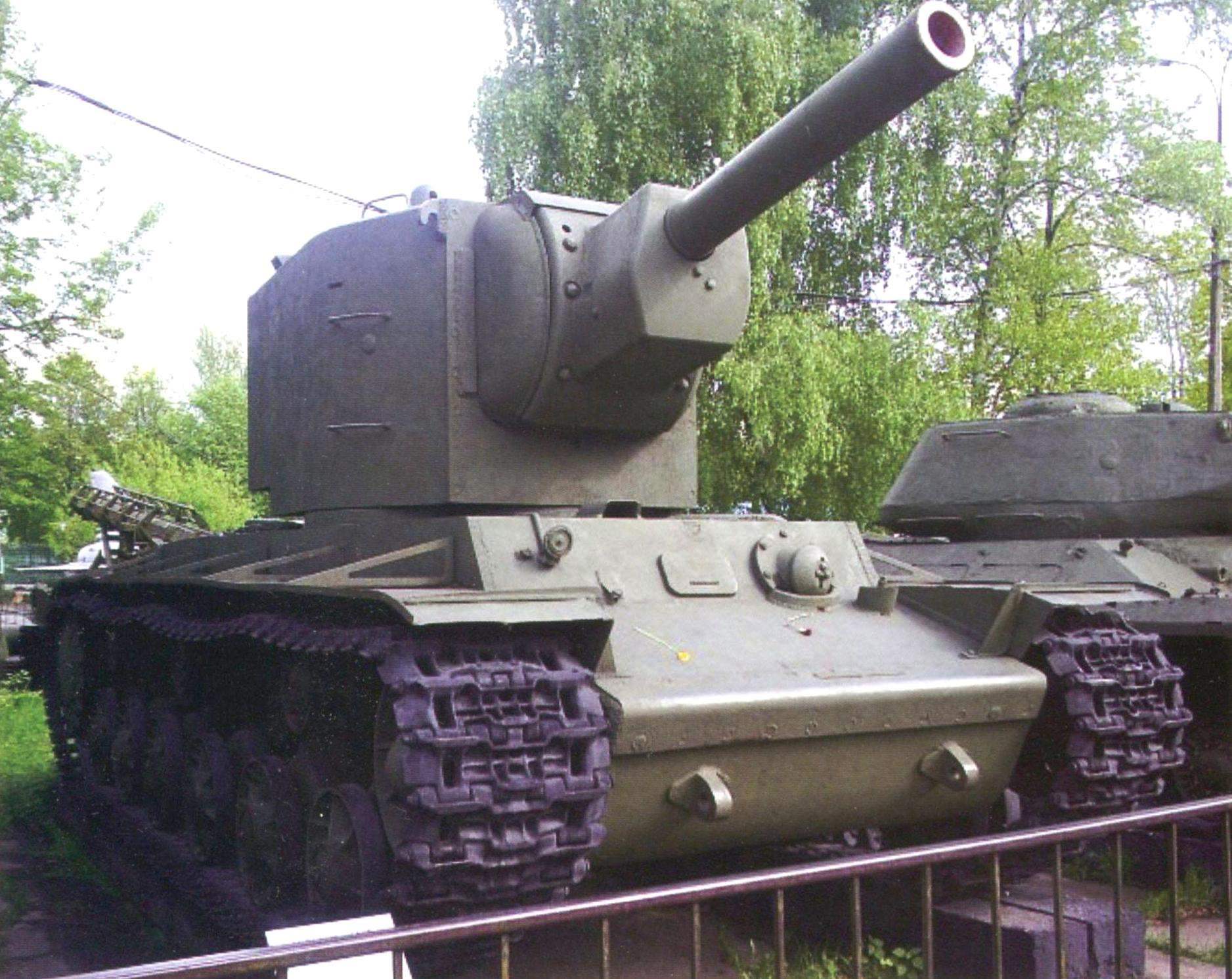
The turret of the KV-2 with traces of numerous hits. However, the shells of German anti-tank guns 47 mm Pak 36(t) 50-mm Pak 38 could not cause her any harm. Threat was only 88-mm shells of anti-aircraft guns Flak 18
Engine and transmission the tank was installed in the aft part. Diesel V-2K were the same as on the KV-1: 12-cylinder water-cooled, four-stroke /-shaped. Its maximum power is 600 HP at 2000 rpm, operating slightly below -500 HP at 1800 rpm.
Fuel tanks with a total volume of 615 litres were in the fighting compartment and the aft compartment.
KV-2 had a mechanical transmission with a main multi-plate friction clutch, the two are also multi-plate clutch side, two side planetary gearboxes. Transmission – manual with five forward gears and one back. Brake – band floating.
Tank suspension – torsion, consisted of six gable support and three support rollers on each side. Drive wheels with removable toothed crowns were rear guides respectively is found. Track had a 90 odnoklubnik tracks width 700 mm.
The case of the KV-2 is not much different from the KV-1. Also going on the basis of rolled armor plates with thickness of 30 – 75 mm.
In may 1941, the tank decided to provide a long-barreled gun, thereby increasing the power of weapons. Tried to install 107 mm gun f-32 (ZIS-6) V. grabina, originally developed for tanks KV-3 and KV-5. Its armor-piercing projectile with an initial velocity of 830 m/s at a distance of 600 m past the 120-mm armor plate with a slope of 60°. However, due to the poor accuracy of fire, low vitality of the barrel, due to the fact that the gun had a unitary shots with their large mass and length, the test was not successful.
Tank KV-2 were produced at the Leningrad Kirov factory in 1940 – 1941 there were produced 330 – 344 units (various sources). They all participated in the fighting on the fronts of the great Patriotic war and was a very effective weapon. They just were not a worthy opponent. Their fire struck tanks have any armor available at that time in the Wehrmacht. Falling German shells anti-tank guns 47 mm Pak 36(t) 50-mm Pak 38 did not cause them any significant harm. To fight them was capable of only 88-mm anti-aircraft gun Flak 18.
Of all the issued Kirov plant KV-2 to the present day survived only one. This tank is an exhibit of the Central Armed forces Museum in Moscow. In the village of Safonovo near Murmansk Museum of the Air forces is full-scale model of the KV-2, built on the basis of the KV-1 for the filming of the film “Tank Klim Voroshilov”. In Verkhnyaya Pyshma (Sverdlovsk oblast) in the Museum of military equipment “Battle glory of the Urals” is a full-sized layout with genuine elements of the KV-2.
THE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GUN M-10T
The mass of the oscillating parts, kg……………2300
Barrel length, CLB…………………………….23,1
The length of the rollback, mm……………………..810 – 860
The initial velocity
the projectile OF-530, m/s…………………………436
Maximum range, m………….14 000
The rate of fire, RDS./min………..2 – 3
The angles of vertical guidance,
grad………………………………………….-3 – +18
Ammunition………………………..36 shells
Projectile weight, kg……………………………….40
Penetration OF 530
at 1500 m, mm……………………………….72/60°
Loading……………..dual core
Shutter………………………………….piston
THE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF KV-2 TANKS
Crew…………………………………………..6
Weight, kg……………………………………….52 000
Length, mm………………………………………..6950
Width, mm……………………………………..3320
Height, mm………………………………………3250
Ground clearance, mm………………………………………430
Booking, mm:
the frontal part…………………………………..75
Board………………………………………………..75
stern………………………………………..60 – 75
bottoms………………………………………..30 – 40
roof……………………………………….30 – 40
The tower, mm:
the frontal part…………………………………..75
Board………………………………………………..75
stern……………………………………………….75
roof………………………………………………40
of the mask tool…………………………………..110
Weapons:……..152-mm tank howitzer
M-10T OBR 1938/40, 3×7,62 mm machine gun
Ammunition……………………..shells – 36,
7.62 mm cartridges – 3087
Engine………………………diesel V-2K,
12-cylinder
four-stroke V-shaped liquid cooling
Power, HP.:
maximum……………………………600 HP
at 2000 rpm
operating……………………………500
at 1,800 rpm
Fuel…………………………….diesel DT,
gas marks “a”.
Suspension……..individual torsion-bar
Transmission………………the main clutch
dry, multi-disc, (ferrodo steel), steering clutches -multi-disc, dry final drives – planetary five-speed transmission
Brake……………….tape floating
ferrado
Speed km/h:
on the highway…………………………………………..34
cross country………………16
Capacity of fuel tanks, l……………….615
Cruising range, km:
on the highway…………………………………………250
cross country…………….150
Overcoming obstacles in m:
the vertical wall……………………….0,87
the width of the pit………………………………………2,7
Ford…………………………………………………1,6
ascent, hail……………………………………..36
Radio……………………………..71 -TK-3
 The Soviet-Finnish war began on 30 November 1939 and ended on 12 March 1940. All this time our units had to overcome the fortifications of the “Mannerheim line”, created on the Karelian isthmus. This “line” became the most significant fighting. Rasstalas front is 135 km, it had a depth of defense around 95 km, and the Main defense line consisted of strong points, just within which it was built 800 wooden-earthen fire facilities Bunkers and 280 long-term firing installations (Pillboxes). All of them, as well as the other positions were covered by the first anti-personnel obstacles of the dozens of rows of barbed wire on concrete base. They were followed by anti-tank obstacles, saturated ditches and scarps. Space between them in huge quantities were made nadybali in several bands. Tanks could not pass, and the Marines had to overcome many roadblocks often three or four layer fire to undermine them. Such a difficult task sometimes allowed T-28 tanks, fire their 76.2 mm guns destroying dragon’s teeth. They could also deal with small Bunkers.
The Soviet-Finnish war began on 30 November 1939 and ended on 12 March 1940. All this time our units had to overcome the fortifications of the “Mannerheim line”, created on the Karelian isthmus. This “line” became the most significant fighting. Rasstalas front is 135 km, it had a depth of defense around 95 km, and the Main defense line consisted of strong points, just within which it was built 800 wooden-earthen fire facilities Bunkers and 280 long-term firing installations (Pillboxes). All of them, as well as the other positions were covered by the first anti-personnel obstacles of the dozens of rows of barbed wire on concrete base. They were followed by anti-tank obstacles, saturated ditches and scarps. Space between them in huge quantities were made nadybali in several bands. Tanks could not pass, and the Marines had to overcome many roadblocks often three or four layer fire to undermine them. Such a difficult task sometimes allowed T-28 tanks, fire their 76.2 mm guns destroying dragon’s teeth. They could also deal with small Bunkers.