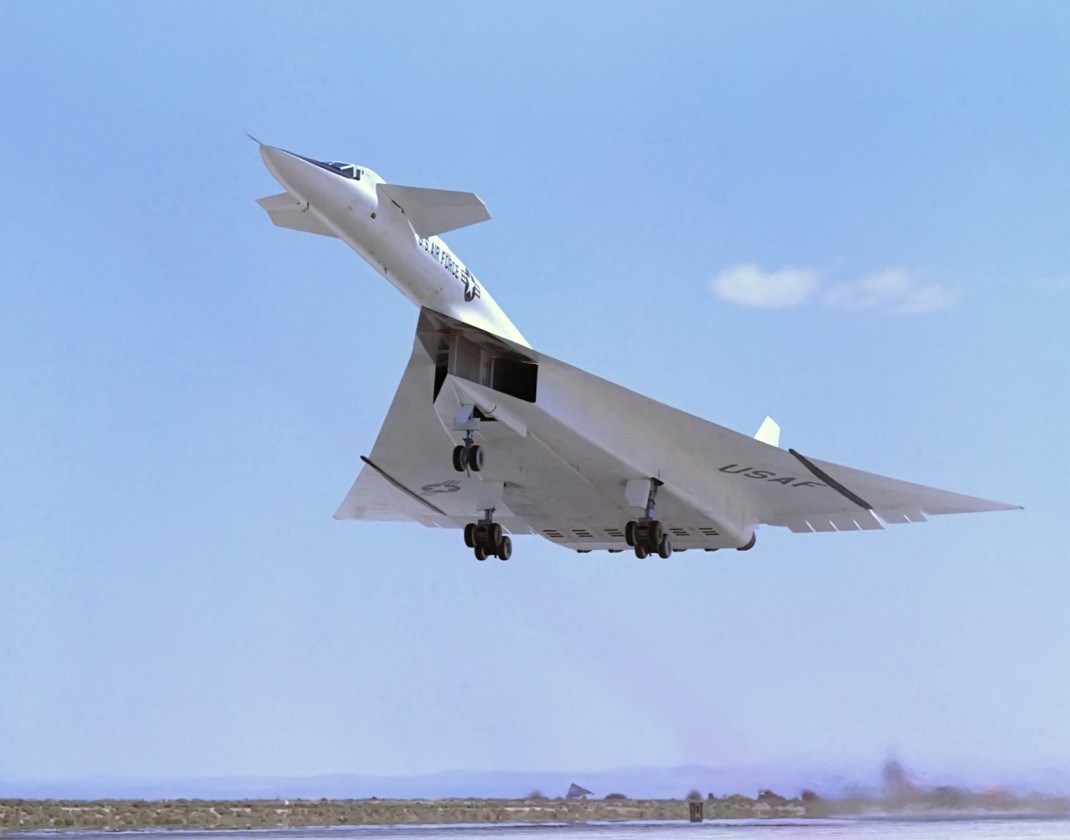
Bomber XB-70 VALKYRIE. The first jet bomber the BOEING b-47 came to the command of the U.S. air force in late 1951. However, the aircraft with maximum payload of about 10 tons could carry in their sections, not all types of bombs from the nuclear Arsenal of the United States at the time and thus became just a huge addition to the piston b-36. This circumstance was the cause of the development of the heavy bomber b-52, the first modification which was twice higher than the b-47 take-off weight in the range of about 5500 km, and, most importantly, could carry a hydrogen bomb MK.17 weighing 21 tons with a TNT equivalent of 20 megatons.
Bomber XB-70 VALKYRIE. The first jet bomber the BOEING b-47 came to the command of the U.S. air force in late 1951. However, the aircraft with maximum payload of about 10 tons could carry in their sections, not all types of bombs from the nuclear Arsenal of the United States at the time and thus became just a huge addition to the piston b-36. This circumstance was the cause of the development of the heavy bomber b-52, the first modification which was twice higher than the b-47 take-off weight in the range of about 5500 km, and, most importantly, could carry a hydrogen bomb MK.17 weighing 21 tons with a TNT equivalent of 20 megatons.
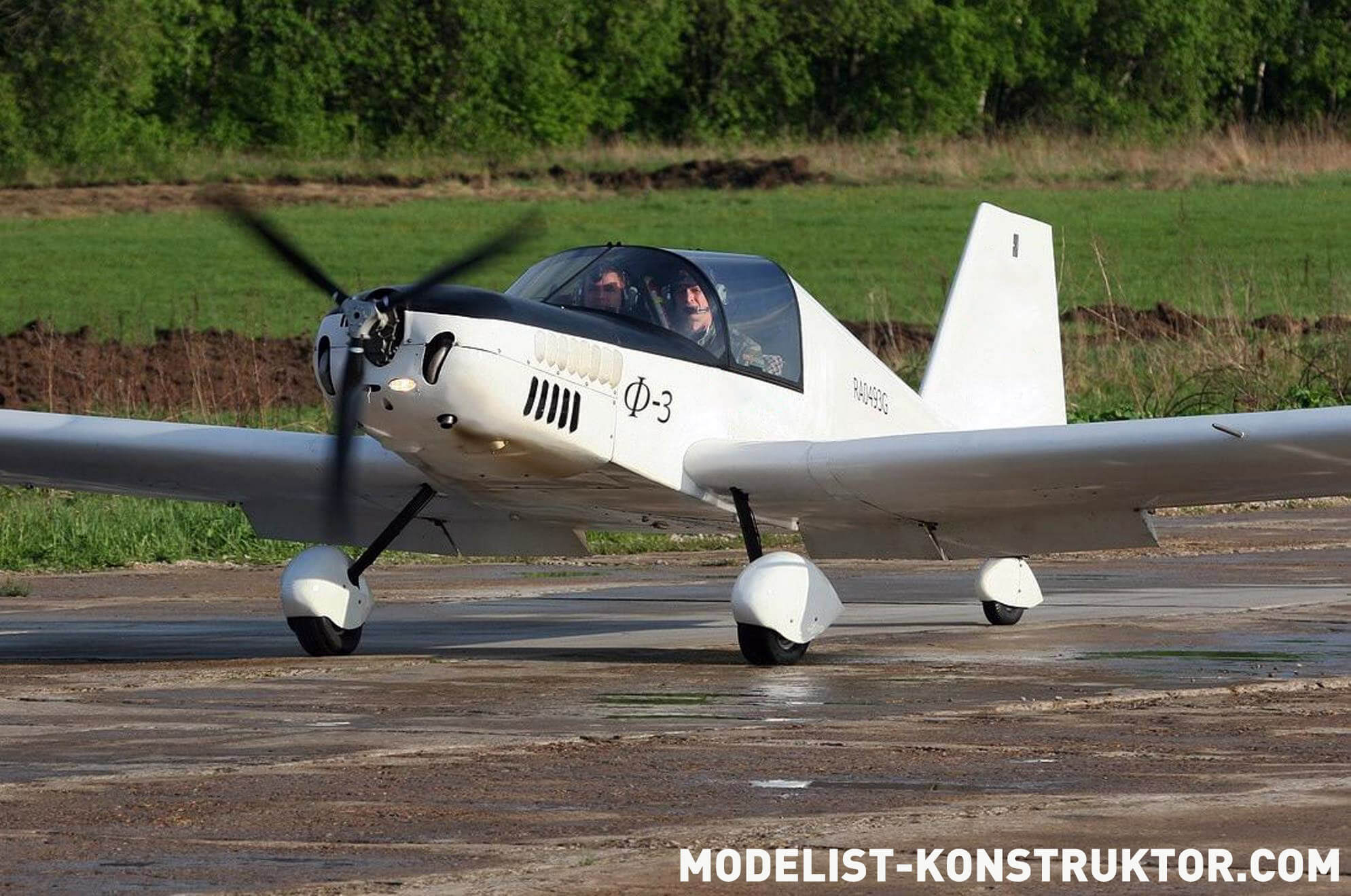
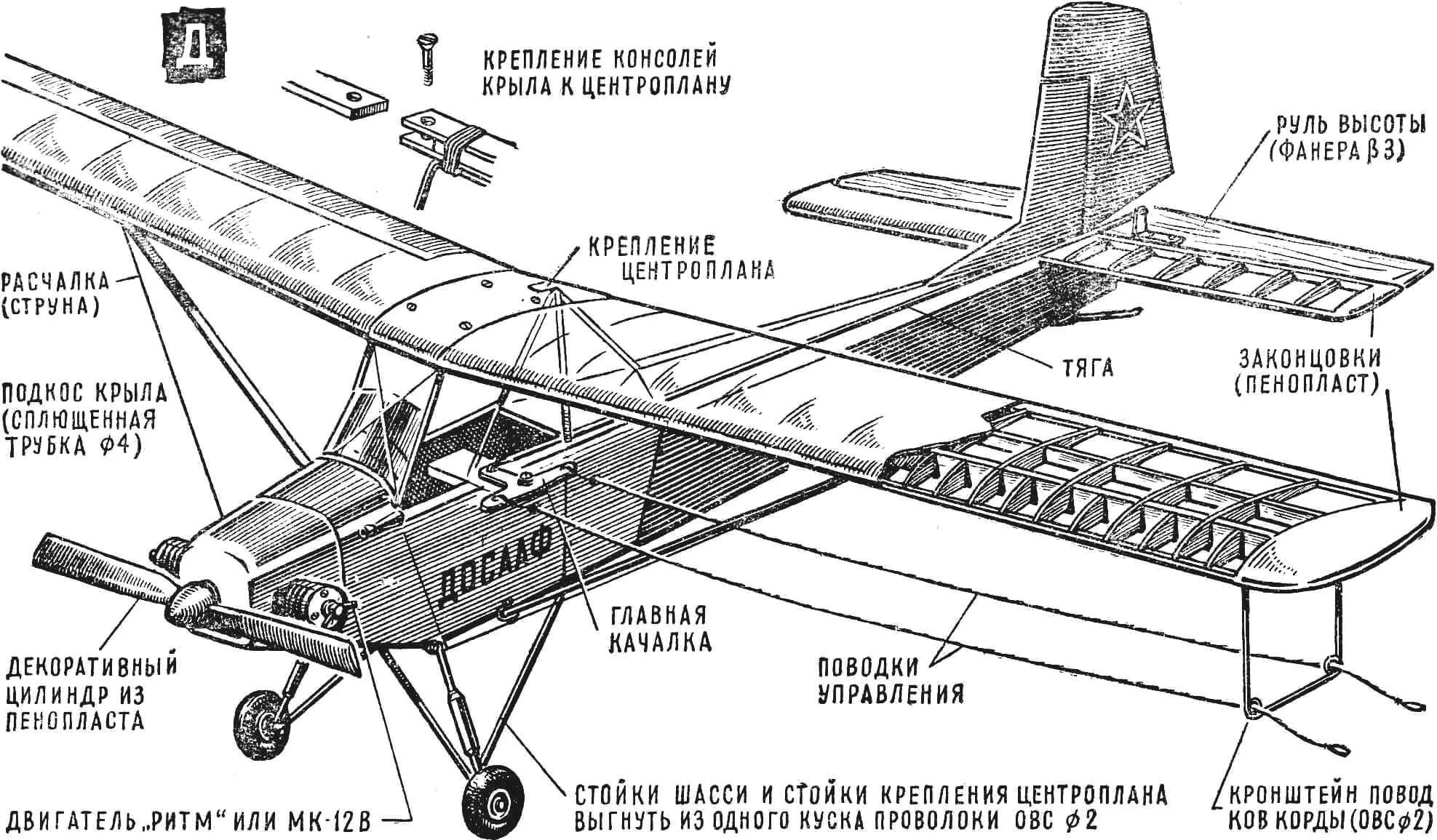
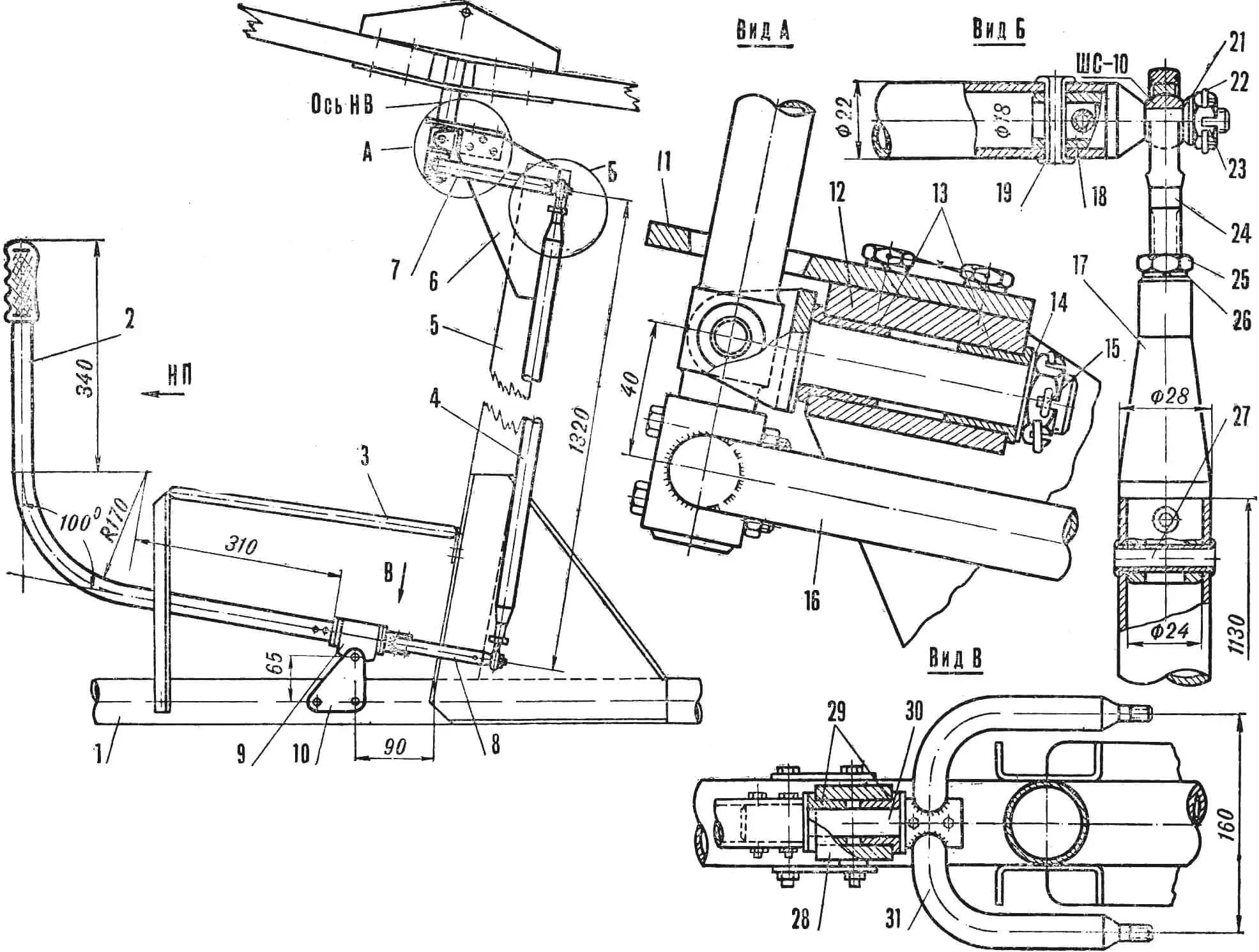
“Wasp” — the first all-metal one
What is the microplane “Wasp” created by Kronstadt craftsmen? At first glance, it seems there is nothing new in it. A strut-braced high-wing monoplane, a scheme that has become the most popular among amateur designers. This very scheme was the basis for the microplanes “Leningradets” by N. Tatsiturny, “Malysh” by L. Komarov, “Sputnik” by V. Read more…