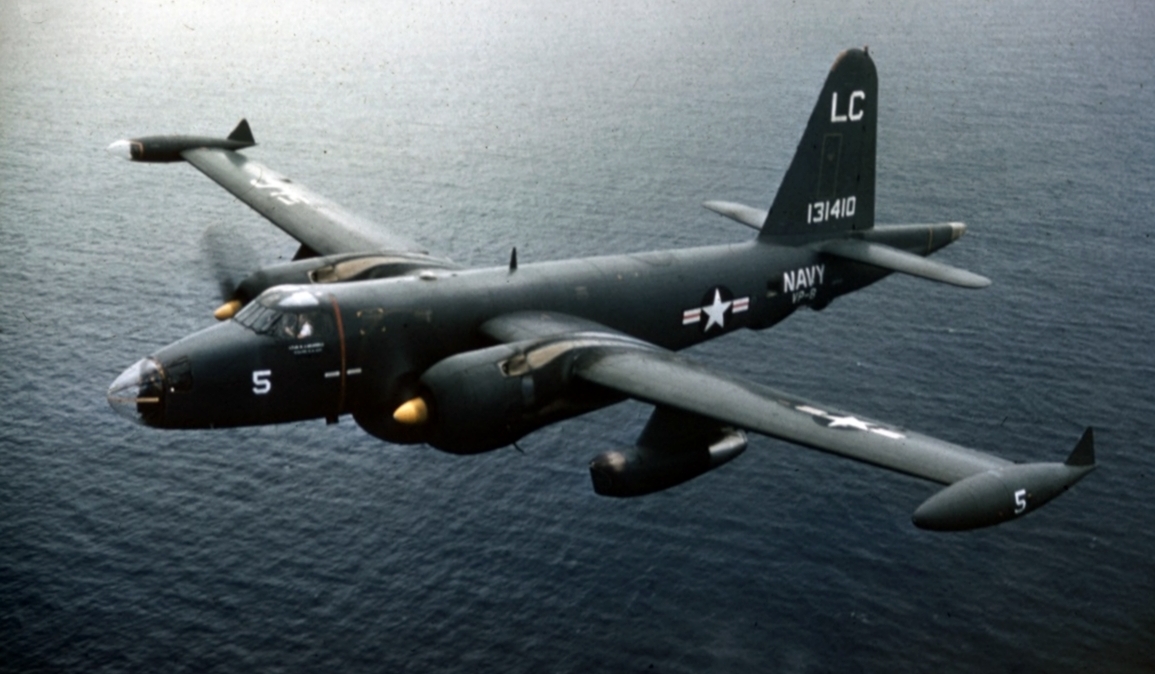
 Bomber P2V NEPTUN. In the late 30-ies of the leadership of the U.S. Navy began to develop the requirements for patrol aircraft anti-submarine escort convoys and deep sea exploration. New aircraft with long range flight was to carry the weapon systems of a wide range from conventional bombs to sea mines and torpedoes. To develop for this purpose flying boat did not make sense, because its pressurized fuselage are not satisfied with the capacious bomb Bay and external weapons worsens the already poor aerodynamics of a floatplane, reducing the maximum range and speed of flight.
Bomber P2V NEPTUN. In the late 30-ies of the leadership of the U.S. Navy began to develop the requirements for patrol aircraft anti-submarine escort convoys and deep sea exploration. New aircraft with long range flight was to carry the weapon systems of a wide range from conventional bombs to sea mines and torpedoes. To develop for this purpose flying boat did not make sense, because its pressurized fuselage are not satisfied with the capacious bomb Bay and external weapons worsens the already poor aerodynamics of a floatplane, reducing the maximum range and speed of flight.
The military has opted for a plane airfield basing and approached Lockheed with a proposal for a new patrol aircraft.
Work on schematic design began on 6 December 1941, while the car was assigned the working title “Model 26”. Leading engineer appointed Jack Weisel. In the first drawings of the plane looked like a normal bomber with machine-gun turrets on the top and bottom of the fuselage, high wing and T-tail. The war with Japan dramatically slowed work on the project, and the management of the fleet returned to the idea of a new patrol aircraft until the spring of 1944, and 4 April signed a formal contract with Lockheed for the production of two prototypes and fifteen pre-production cars. The new aircraft was assigned the military designation for P2V NEPTUN.
During the design the main objective was the reduction of aerodynamic drag, which held 5470 purging bomber models in wind tunnels. Carefully studied, and the breakdown of aircraft on components and assemblies to ensure maximum access to them during Assembly.
The first prototype XP2V-1 (serial number 48237) collected in the spring of 1945. It was already signalen with a single-fin tail and tricycle landing gear with controlled nose wheel. It established engines R3350-8 CICLONE company Wright maximum power of 2300 HP Maximum take-off weight of the aircraft reached 24 715 kg. Bombs, naval mines and torpedoes with a total weight of up to 3700 kg was placed in the bomb Bay. Under the wing can be hung four large-NUR “tiny Tim” or sixteen NUR HVAR caliber 127 mm bomber Crew — seven people. Defensive armament consisted of six coaxial 12.7 mm machine guns with ammunition 446 rounds per gun, two machine guns located in the nose of the fuselage, two in the rear and two in the upper transparent rotating turret.
As the aircraft was designed for long flights at low altitude and in bad weather, the designers have tried to create conditions that reduce the fatigue of pilots. For maximum effectiveness of control of the aircraft they provide a neutral compensation for the rudders, then in the process of flight tests to adjust to the desired values of the force on the wheels, thus extending the trailing edge of the rudder and using a variety of trimmers that can be easily replaced during the tests.
Given the military experience, the designers paid much attention to the handling of the machine when flying at low speed on one engine while landing. The main difficulty consisted in selection of the optimal value of the square of the keel (P2V it amounted to eighteen percent of the wing area) and the horizontal tail. Designers managed to develop a horizontal tail with variable curvature of the profile due to the deflecting surface between the stationary part of the stabilizer and Elevator. It is possible to reduce the area of the horizontal stabilizer and efforts on aircraft control.
The first flight of an aircraft with the pilots by Joey Coelom and Harold Johnson took place on may 17, 1945, with a strip of factory airfield in Burbank.
Flight tests and additional venting in the pipe showed that the stabilizer had a reduced effectiveness. When changing the curvature of the Elevator, deviating from the specified pilot position, acted as an independent surface.
Test flights took place mostly successful, although there were incidents. When flying with a large horizontal velocity (gauge — 410 km/h) needed to obtain the maximum possible slip angle of the plane Ripped off the front edge of the keel and right on the side of the bomb Bay, and aft fuselage were deformed, breaking several ribs. The car miraculously managed to land. It turned out that to hold it in the desired position the pilot had to apply to the pedals considerable effort. The angle of deflection in the presence of a spring of the trimmer turned enough to slip angle and aerodynamic loads on the vertical operanew higher than estimated. After this incident, the front edge of the keel and the aft fuselage significantly strengthened, and further tests were carried out without the spring trimmer.
More than a hundred flight hours spent on checking the anti-icing system and the study of performance in icing conditions-rotor, antenna farms, and other equipment. The fact that the first vertical type wire antenna broke off due to gravity and vibration generated by this ice. The location of the antenna has been completely revised. Further testing showed that in certain atmospheric conditions when using wire antennas without coating static electricity make the almost impossible job of low-frequency radio equipment. Had to install the antenna with a plastic coating that ensured the smooth operation of all radio equipment.
In one of the flights second copy of the aircraft XP2V-1 was in icing conditions at low altitude for two hours. Glass canopy, nacelles and some other unheated part of the plane was quickly covered with a thin layer of ice. On the wing ice formed behind the front edge only in the region of the nacelle. Ice covered and the surface of the keel, which caused a slight shaking of the rudder. But on the stabilizer and the leading edges of wing and tail ice did not appear. To maintain a constant airspeed the pilots had to gradually increase the engine speed.
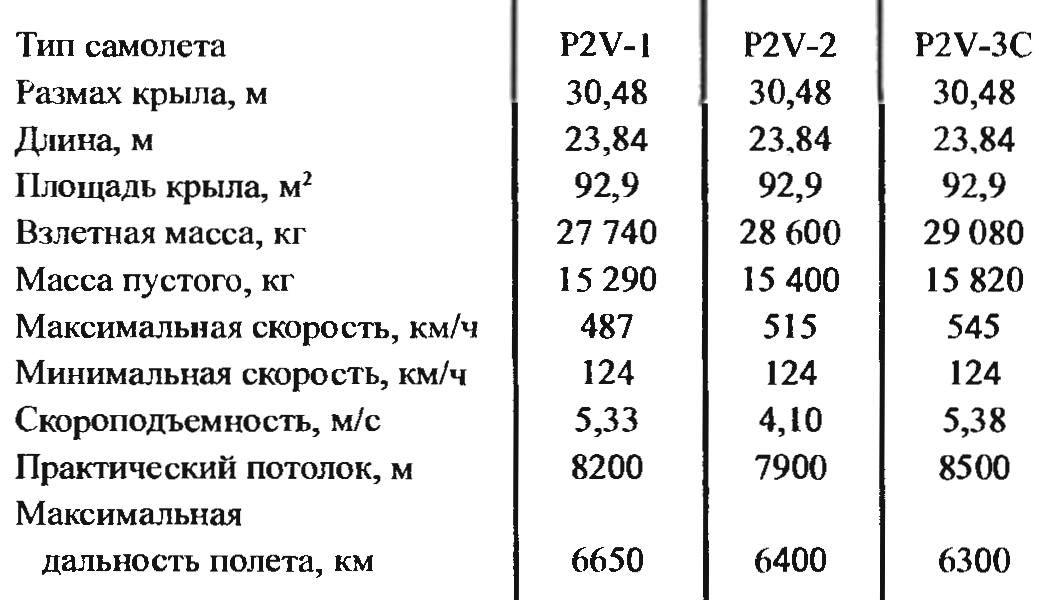
Flight testing was completed in July 1946. The first prototype aircraft was transferred to the Navy and began production of the fifteen pre-production vehicles. Compared to the prototypes they had more powerful engines (3000 HP), maximum speed increased by 21 km/h and reached 486 km/h, service ceiling reached 8230 m.
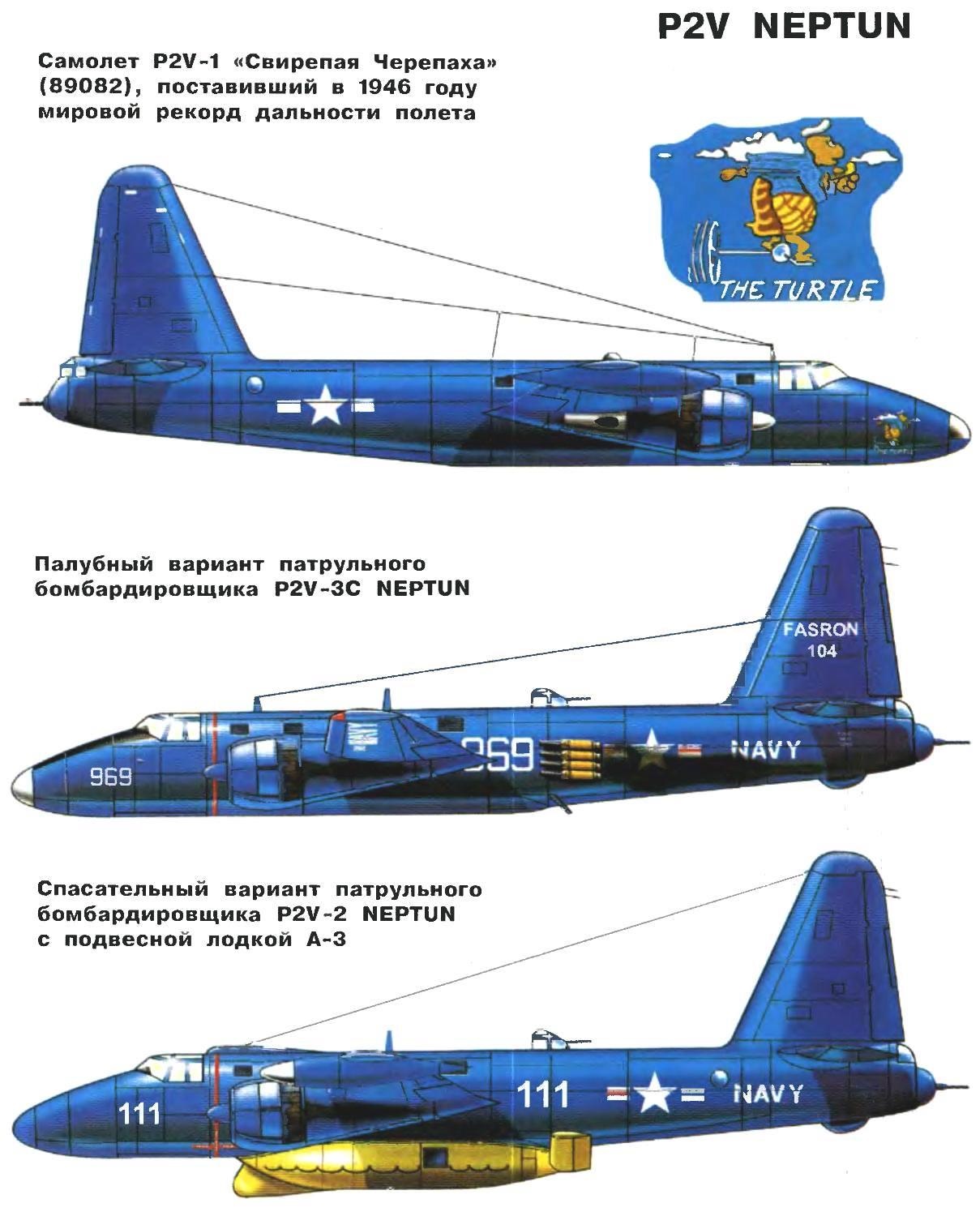
The military expressed some concern that the maximum range was reduced by more than a hundred km to km 6645 Designers company Lockheed promised to install additional fuel tanks on the wing tips serial machines and in the bomb Bay. As proof, they converted the third series P2V-1 (serial number 89082), then the maximum amount of fuel on Board was 33 054 L. On the plane besides remade clumsy nose of the fuselage.
The leaders of the U.S. Navy, always jealously related to the success of the air force, decided to use this plane to break records-range non-stop flight established by the bombers of the air force b-29. In the best military traditions machine is assigned its own name Truculent Turtle (“Truculent turtle”) and drove it on the Australian air base in Perth.
On the morning of 29 September 1946 pilot Thomas Davis led the Truculent Turtle from Australia to USA. For takeoff peretyagina machine used four starting powder accelerator Jato reduced the run-up to 1828 meters. After 55 hours and 17 minutes of flight Turtle overcame 18 082 miles and landed at the airport in Columbus (Ohio), breaking all imaginable world record of range of flight for piston aircraft without refueling for decades to come.
In March 1947, the first production aircraft entered service with patrol squadron VP-ML2.
The direct heir of the Truculent Turtle was a new modification to the P2V-2 (original designation “Model 126”), released in January 1947. It was distinguished by a characteristic record of the plane pointed nose part of the fuselage, which has posted six 20-mm guns M2. For engines set a new three-bladed propellers. The length of the aircraft increased by 760 mm, maximum takeoff weight increased to 28 590 kg. the Distance of the flight was again reduced to 6405 km Serial production of this modification is continued until the summer of 1948, the issue volume amounted to 81 aircraft. Two of them have been converted into Arctic variant with ski / wheel landing gear.
Patrol bomber P2V NEPTUN and its modifications:
1 — cabin aft arrow; 2 — directions; 3 — turret gunner-radio operator; 4— wire antenna: 5— blister astrocompass; 6 — the glazing of the cockpit; 7— cockpit glazing of the Navigator; 8 — twin machine gun mount Navigator; 9 — antenna search radar; 10 — additional fuel tanks; 11 — the bomb Bay leaf; 12 — antenna of the radar; 13,14 — coaxial machine gun; 15—trimmer of the rudder; 16 — exhaust pipe; 17 — louvers of the air cooling channel of the engine; 18 — blade propeller; 19 — spinner; 20 maintenance access doors; 21 Aileron; 22 — trimmer Aileron; 23 — air-gap flaps; 24 — boosters; 25 — multi-steering wheel height; 26 — trimmer pitch control; 27 — the aft gun mount, a 28 — fold niches nose landing gear; 29 — section retractable slotted flaps; 30 — tiltable part of the fairing of the nacelle; 31— fold niches main landing gear; 32 — main landing gear; 33 — wheel main landing; 34 — the nose landing gear; 35 — wheel nose landing
On the basis of the P2V-2 developed by rescue modification. Under the fuselage could be suspended RC 15-local rescue boat A-3 length of 9.15 m, which was dropped by parachute in a given area. In addition to rescue equipment and food on it there was a supply of fuel to overcome the distance of 1280 km. After landing the boat operator from the aircraft failed its saving directly to and held in a stable position during the landing Board, and then asked her the rate, which further supported by the gyrocompass. The boat had manual controls so they could enjoy themselves saved.
In 1948 he started producing modifications P2V-3 engines R3350-26W power 3200 HP With this modification the Navy Department of the United States had a very high expectations. In an effort to capture leadership in the armed forces of the United States in the beginning of the cold war and seeing the enormous potential inherent in the design of the P2V, the Navy wanted to turn it into a carrier-based nuclear bomber. To this end, the firm Lockheed was ordered eleven aircraft P2V-3C carrier-based NEPTUN.
Of course, that a plane with such dimensions and weight as the P2V-3 NEPTUN, to take off from the aircraft carrier could not. And here is incidentally reminded of the “Fierce turtle”, which was launched with the help of powder accelerators. For an early experiment on a similar take off from the deck of the ship has chosen a production P2V-2. It was loaded on the aircraft carrier “coral sea” and 17 April 1948, he made a successful takeoff with eight propellant boosters, who for 12 developed a total thrust of 35 tons.
Serial P2V-3C was different from the standard P2V-3 the possibility of a suspension of a nuclear bomb with a mass of 4532 kg. the flight pattern was assumed the following: taking off from the deck of an aircraft carrier, the flight to the target, drop bombs, flying to a given airport and landing.
Soon built of the eleven bombers were a special group of FASRON 104. The pilots of this group received training on the use of nuclear weapons and the UPS with accelerators. The first pilot who has mastered nuclear bomber, was John Hayward. On the plane, a P2V-3C NEPTUN with mock nuclear bombs on Board on 7 March 1949 took off from the deck of the aircraft carrier “coral sea”, crossed the U.S. from East to West, dropped over the target, the layout of the bombs and planted the car on the base at Patuxent river in Maryland. In October of the same year another BUILDING after taking off from the aircraft carrier “midway”, spent 25 hours in the air, overcoming 7724 km. In February 1951, three nuclear P2V-3C NEPTUN flew to Morocco, where he joined the group of carrier-based bombers, “the curious savage”.
Operation deck the P2V-3C NEPTUN lasted about two years. Firm Locrheed led an intensive search for solutions to their landing on the deck of the ship. This aircraft was planned to equip the boarding hooks, reversible propellers and more powerful wheel brakes. But after the failure of the construction of aircraft carriers of the series “United States”, which wanted to arm these bombers, the development was discontinued.
Serial production of the patrol aircraft NEPTUN has continued in the US until the mid 50-ies of the last century. Last modification of machine P2V-7 was removed from service in late 1966, replacing it with a new patrol aircraft P-3 ORION.
DESIGN DESCRIPTION
Patrol bomber P2V NEPTUN was a monoplane with a mid-wing and single-fin tail. The fuselage — semi-monocoque. The center section of the wing and the middle part of the fuselage the bomb Bay had a constant section design, which reduced the number and nomenclature of parts and assemblies basic elements of design, as well as the number of devices and stamps. To simplify dismantling the fuselage is made of six sections, connected by bolts, and piping and wiring with detachable connections in the planes of the connector. A large part of the fuselage skin had a curvature in one plane only, which allowed her to apply for flat sheets.
The airplane wing with modified profile NACA 2419. The wing was mounted with a transverse V equal to 3°. Wing used the minimum number of all kinds of cut-outs and connectors. The main wheel gear retracted forward into the engine nacelle. The wing box passes through the fuselage without connectors. The wing provided aircraft temporary buoyancy when landing on water. In the front with the edge of the wing located electrical deicing devices. The ailerons are equipped with an inner wind and the weight compensation. To get the lowest landing speeds, the wing was equipped with modified Fowler flaps, deflected at the angle of 32°. For a uniform distribution of load along the span of the wing when the flaps are rejected at the same time (10°) deviated and ailerons.
The first airplane the rudder to provide a small force when control of the aircraft in flight at low speed (on one engine) was equipped with a spring trimmer.
Was installed on the P2V R3350 engines of various series with the capacity from 2300 to 3800 HP Each engine had a separate fuel system, but in special lines, all the fuel could be directed at meals one of them. The fuel tanks of the aircraft were tested; two with a capacity of 2650 l was located in the center section and two 1800 l — in consoles. Tanks installed in the center section, was removed through hatches on the surface of the center section, closed by a removable power panels. Fuel tanks consoles were taken out through the front spar when removing nasal sections and section wall of the front spar. To increase the range of flight in the bomb Bay installed four additional interconnected tanks with a total capacity 3785 liters, which, if necessary, reset. Auxiliary control panel the fuel system is located on the cab floor between the seats of the pilots.
Flight performance of airplane modifications NEPTUN
Access to the units motor is opened through a niche of the main chassis, which in the fire wall had a removable hatch. Hood motor installation with adjustable skirts consisted of four easily removable panels. At low temperatures the cooling was decreased by using the front blinds. For engine replacement took only 30 minutes to install the new propeller can be was in 22 minutes.
N. Food reserve was, A. CHECHIN, Kharkov



