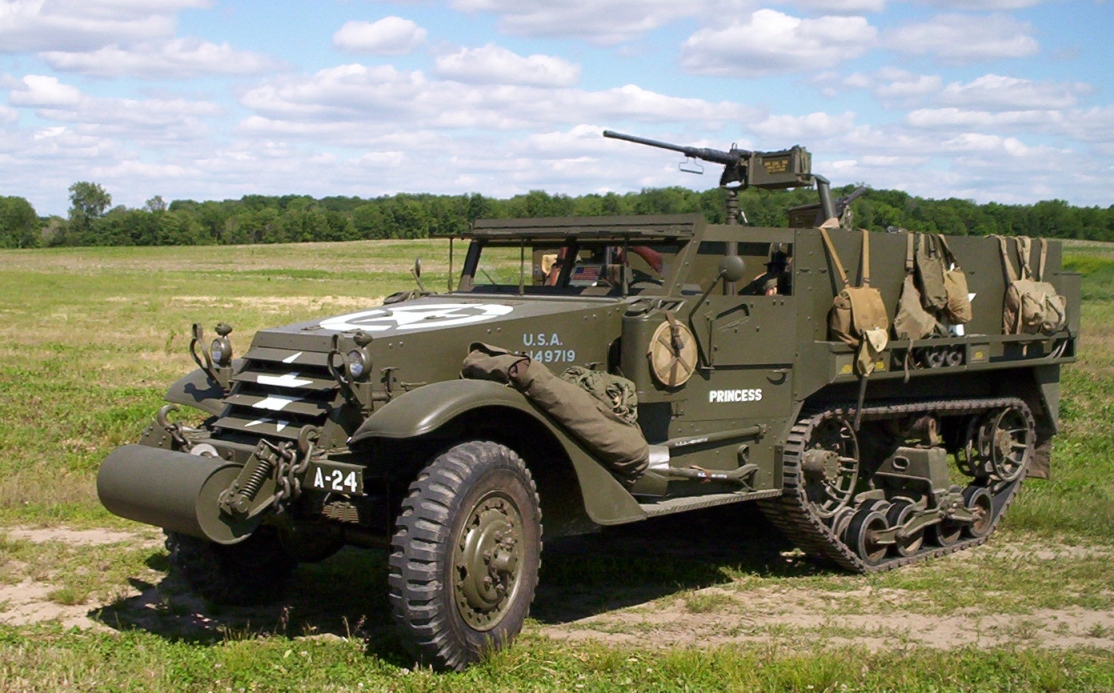
A family of half-track armored “half-tracks”, one of the most famous and popular among the fighting machines of the allies during the Second world war, began to be developed in the United States since 1932. Their design started from four firms: James Cunniagham and Sons, Linn, GMC and Marmon-Herrington. As the prototype was used the chassis of the French Citroen-Kegresse С417, several samples of which were purchased a year earlier. In the next five years was developed and tested experienced polupustyne options from T1 to Т9Е1. The latter, recognized as the most successful, was based on the chassis of the truck Ford V-8 wheel formula 4×2. Rear axle was replaced by a tracked vehicle of the company Timken with rubber caterpillar.
A family of half-track armored “half-tracks”, one of the most famous and popular among the fighting machines of the allies during the Second world war, began to be developed in the United States since 1932. Their design started from four firms: James Cunniagham and Sons, Linn, GMC and Marmon-Herrington. As the prototype was used the chassis of the French Citroen-Kegresse С417, several samples of which were purchased a year earlier. In the next five years was developed and tested experienced polupustyne options from T1 to Т9Е1. The latter, recognized as the most successful, was based on the chassis of the truck Ford V-8 wheel formula 4×2. Rear axle was replaced by a tracked vehicle of the company Timken with rubber caterpillar.
In 1938, the propeller equipped armoured car reconnaissance Scout Car M3, which pushed the firm Diamond T Motor Company to the creation in 1940 of prototypes T14 and T8. The rapid development of events in Europe, the fall of Poland, Belgium, Holland and France forced the Americans to speed up the work. As a result, in October 1940 the prototypes of T8 and T14 was standardized (i.e. adopted by the US army) as a Half-Track Car M2 and the Half-Track Personel Carrier M3, respectively. The first was a half-track artillery tractor, and the second armored vehicle.
Mass production of Half-Track Car M2 began in the spring of 1941 and continued until 1943. White Motors and the Autocar was manufactured during this time and 8423 2992 tractor, respectively.
The M2 design was based on automotive units. The machine had a classic bonnet layout. The case is a simple box shape with a vertical side and aft walls assembled from rolled armor plates on the frame from the corners. Sheets with a frame connected with screws. The front part of the body, including the hood and the cab was borrowed from the armored reconnaissance Scout Car М3А1. Compared to the last M2 had a significantly greater amount of body. In the back housed a gun crew of six and there were two boxes for the gun shots, to which access is opened from the outside, for which the sides of the machine were folding doors. The door at the rear of the body for boarding and alighting of calculation was absent. Inside the case, on its perimeter, mounted rail for mounting machine guns. In the standard weapons of the machine consisted of a 7.62-mm machine gun Browning М1919А4 and 12.7-mm machine gun Browning М2НВ. Armored vehicles of the early editions can be equipped with 7.62 mm machine gun Browning M1917A1 water-cooled. Machine guns were attached to the rail moving machines M22, allows firing at air targets.
The car was equipped four-stroke 6-cylinder petrol engine White 160АХ 147 HP at 3000 Rev/min the Main clutch Spicer, dry, single-plate. Transmission four-speed. Transfer box at the same time were the dual and mounted within the Carter gearbox had two gears — straight and slow. It provides transmission of torque to the front and rear leading axles, and a PTO winch.
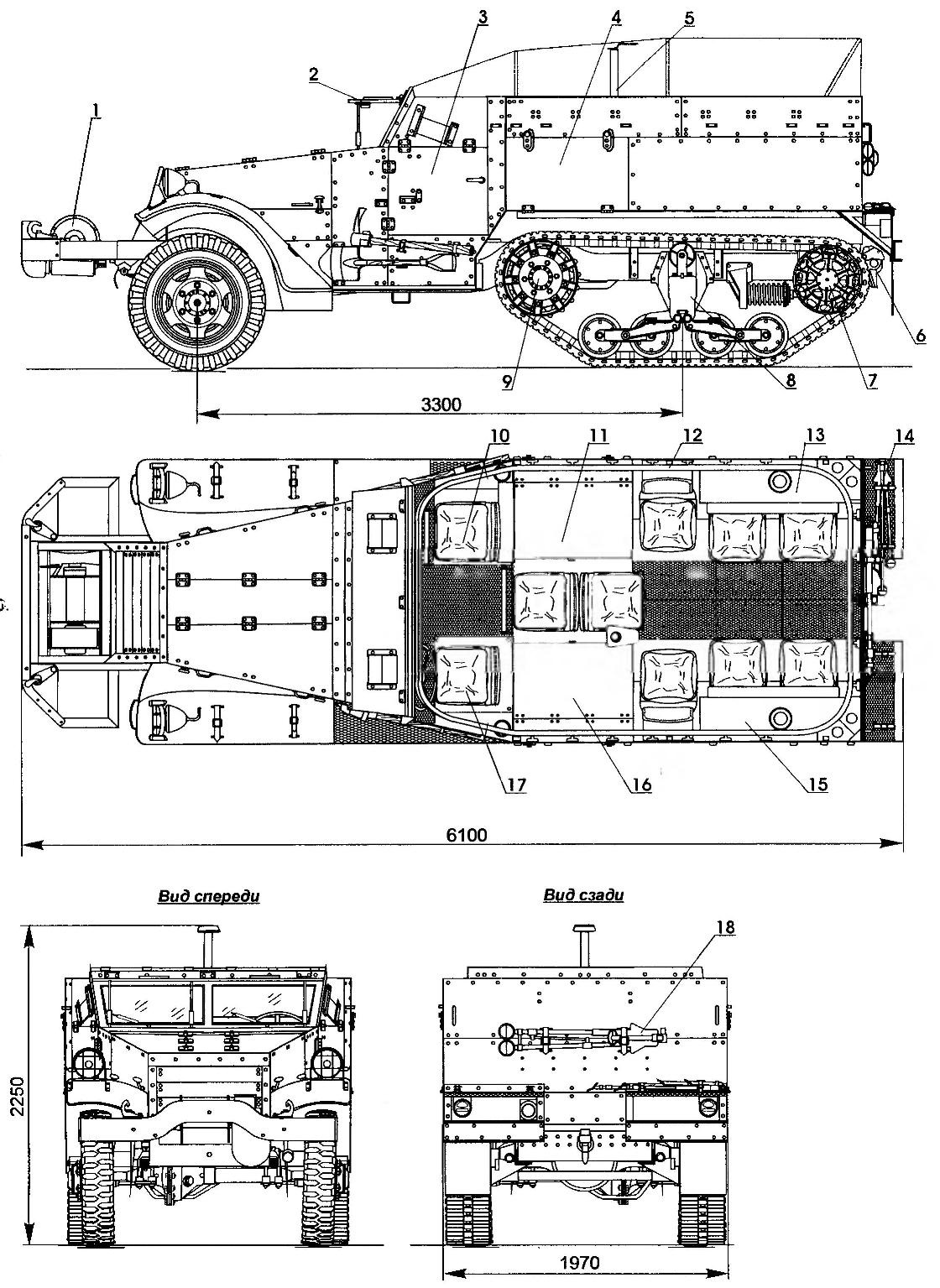
M2 half-track armored personnel carrier:
1 — hoist; 2 — armor windscreen; 3 — the driver’s door; 4 — lid of the ammunition box; 5 — front mount antenna; 6 — towing device; 7 — guide wheel; 8 — truck suspension; 9 — driving wheel; 10— the commander’s seat; 11,16 — boxes of ammunition; 12 — rail-bus; 13,15—fuel tanks; 14 — tripod machine gun Browning М1919А4; 17 — seat; 18 — tripod machine gun Browning М2НВ
Unlike German half-track tractor front axle armoured personnel carriers M2 brand Timken F-35-HX-1 was not only manageable, but also leading. This factor significantly improved the maneuverability of the cars. Rear axle Timken 56410-BX-67 — leading, crawler. Differentials front and rear axles automotive type with completely interchangeable parts. The front wheels of the car, tyre size 8,25—20”, suspension front axle on semi-elliptic leaf springs with hydraulic shock absorbers.
Caterpillar mover each side consisted of four dual rubber rollers, connected in pairs in two tandem that combined in a common unit. The right balance unit connected with the left cross tube. Therefore, these units can be rolled together after disconnecting them brackets from the frame of the armored vehicle. Suspension of caterpillar tracks equalizer, the tape springs of the buffer type, upright. Drive wheel front location was completed with a steel drive sprocket, the two guide flanges and the hub. Guide wheel located on the rear. To prevent sagging of the tracks on the bracket beam Assembly mounted supporting roller. Brakes — drum-type with hydraulic drive.
Caterpillar — rubber-to-metal, one-piece 300 mm wide with ridges of the engagement, which was at the same time the guide tracks. To increase the cross on it was attached the special lugs, and front-wheel — skid chain folding type.
In front of the vehicle housed a single-drum winch. On some machines instead of the winch mounted buffer has a diameter of 310 mm to facilitate overcoming such barriers, such as moats and escarpments. Armored personnel carriers equipped with the buffer drums and has overcome trench width of up to 1.8 m.
At a combat weight of 7.99 t Half-Track Car M2 was able to tow the guns weighing up to 3.5 tonnes (e.g. a field howitzer M1 105mm) with an average road speed of up to 36 km/h Maximum speed without a trailer reached 69 km/h, range of 290 km.
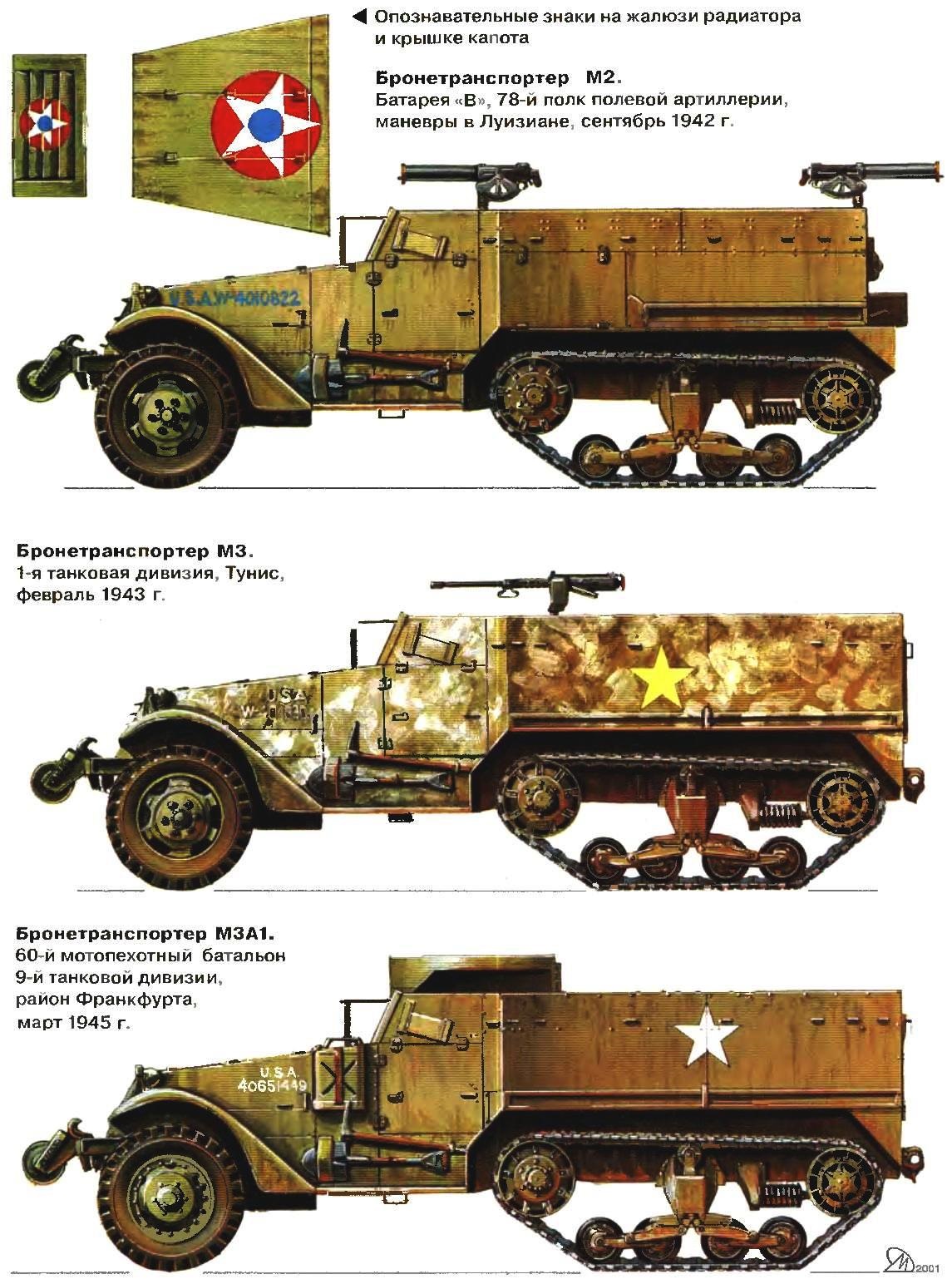
In October 1943, production machinery modifications М2А1. From the M2 it was distinguished by a turret installing large-caliber machine gun mounted in the right side of the driver’s compartment above the commander’s seat. Rail for mounting machine guns were dismantled and 7.62-mm machine guns installed on one of the three brackets on the sides and at the rear of the hull. Until March 1944, the firm White Motor Company released 1643 armored М2А1, 5065 more of these machines were converted from M2.
As for the M3 armored personnel carrier, running in series simultaneously with the M2, its body was longer than 250 mm. Instead of boxes of artillery shells in the back set a ten seat landing (back to sides). Rail for mounting machine guns were absent, and the regular 7.62-mm machine gun Browning М1919А4 mounted on the bar in front of the body. At the rear there was a door for the boarding and landing, the rest of the M3 was identical to M2. Virtually unchanged the weight and dynamic characteristics. From 1942 to 1943 the firm of White, Autocar and Diamond T manufactured 12 499 armored personnel carriers.
In the modification МЗА1 were made exactly the same changes as in М2А1. They touched mainly the structure and distribution of weapons. In 1943-1944 factory shop >- left 2862 cars of this brand. In addition, a significant number of M3 upgraded to the level of М3А1.
The first M2 were transferred to the U.S. army in may, and M3 in June 1941. They commissioned fourteen emerging mechanized infantry regiments.
Combat debut of armored vehicles took place in December 1941 in the Philippines. In part 192 and 194, the American tank battalions, there were 23 machines of this type, which were used mainly in the military headquarters and intelligence units. During the fighting with the Japanese on Luzon island they were all lost. Even then, there was a lack of their reservation.
Massive baptism of fire took place in November 1942 during operation Torch — landing of American troops in North Africa.
According to the state of the American armored division in 1942, in each of its two tank regiments had up to a hundred “Hoftrac” mechanized infantry regiment — 230. The total number of half-track vehicles, taking into account staff, artillery, engineering and intelligence units, reached 733. The first military unit to enter the fray on these machines, 6th infantry regiment (6th Armored Infantry) of the 1st armored division. During fierce fighting in January — February 1943 in repelling the German offensive through the Kasserine pass, this regiment was almost completely destroyed.
Subsequently, Half-Track Car M2 and the Half-Track Carrier M3 Perconnel, as well as their improved versions М2А1 and МЗА1, used by the Americans in all the military operations of world war II in the European and Pacific theaters of war.
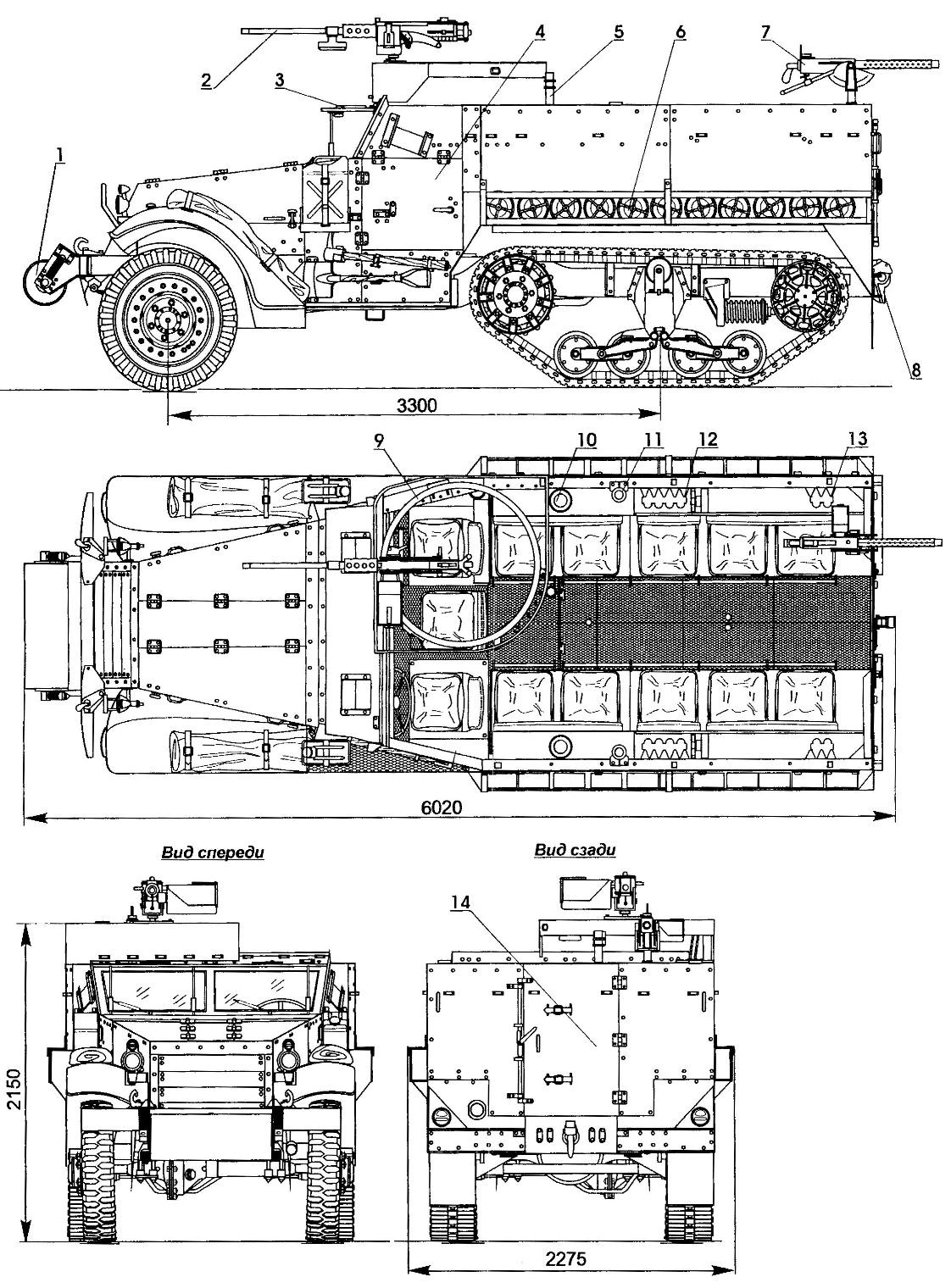
M3A1 half-track armored personnel carrier:
1 — the buffer drum; 2 — Browning M2HB machine gun; 3 — armor windscreen; 4 — door; 5 — front mount antenna; 6 — anti-tank mine; 7 — Browning machine gun M1919A4; 8 — towing device; 9 — turret; 10 — neck of the fuel tank; 11 — bracket gun; 12,13 — frame for rifles; 14 — door assault
American half-track armored personnel carriers were supplied to the allied Nations via lend-lease. Moreover, as the basic version of the M2 and M3 and later M5 and M9. The latter was developed by the firm International Harvester Company in 1942, after the program was approved production of “half-tracks” until 1944, providing for the release of 188 404 military vehicles. It became apparent that the capacity of the three major manufacturers is not enough. When prototyping М2Е1 and МЗЕ1 International Harvester Company made in their design, some changes compared to the base versions.
Thus, increased armor protection of the vehicle’s body was made of 8-mm homogeneous armor, which was a 7.92-mm German armor-piercing bullet from a distance of over 200 yards (one yard is equal to 0,9144 meters). The M2 and M3 armor provides protection from this bullet at a distance of over 300 yards. Was established “brand” of components and assemblies chassis: engine International RED-450-B with a capacity of 141 HP, the combat tyre size of 9.00—20″, front axle IHC 1370 and rear — RHT-1590, new transmission, etc. in General, However, neither the layout nor the overall design of combat vehicles has not changed. Outwardly, they differed only rounded nodes on the rear of the hull and wings of a more simple form. The machine was standardized under the designations M5 and M9, and in December 1942 began mass production. Firm International Harvester Company produced and 2026 respectively 4625 units. In may 1943, both machines were redesigned and sold under the designations m5a1 variants and М9А1 (made respectively 2959 and 1407 units), being analogues М2А1 and МЗА1.
However, the us army, these armored vehicles were not included. In 1943, the program was revised polukonteynerov. For reconnaissance units of the preference given to the M87 armored vehicles, and artillery — tracked high-speed tractors M5. The need for a “half-tracks” dropped right up to 87 302 cars! In order not to confuse the units of cars of different brands, M5 and M9 declared “limited standard” and began to export. Almost half of their total number — 5238 units sent to Britain, where they fell to the troops of the Commonwealth countries, as well as in Polish and Czechoslovak part of the West. In the English army polupustyne not used to transport infantry because of this role played the British armored Universal Carrier. Their main task was towing 6 and 17 pounder anti-tank guns. They were used in engineering parts, as well as staff and ambulances.
The second largest export batch polukonteynerov got movement “Free France”, headed by General De Gaulle: 176 M2 machines/М2А1, 245-MZ/МЗА1, 1196 – M5/m5a1 variants and 603 – M9/М9А1.
Combat vehicles of these types were in the part of the 1st Brazilian infantry division fought in Italy. However, there were very little: eight units — M2/М2А1, three – MZ/МЗА1 and twenty — M5/m5a1 variants. A small number of “half-tracks” were used in the Chinese tank group in Burma. In the years of world war II, several armoured personnel carriers were transferred to the armed forces of Chile and Mexico.
As for the Soviet Union, according to American data, he was transferred 1158 polukonteynerov. Including: 342 units M2, two M3,401 — 413 M5 — M9. According to the latest data published by Russian researchers, the USSR was 1200 half-track armored personnel carriers, of which armored and mechanized forces of the red Army directed at only 118.
All of them were shipped in 1942 and was distributed among the intelligence units and the command of the armored corps and armies. The bulk of these machines were sent to the artillery (mostly anti-tank), where it was used to tow guns, 85-mm anti-aircraft gun 52K sample 1939 and 100-mm anti-tank guns BS-3 sample 1944
On the basis of M2 and M3 in the US had created a large number of self-propelled artillery, self-propelled mortars and anti-aircraft self-propelled units, many of which were produced in large quantities and was in service with American and other allied armies.
Full analogue of the armoured personnel carrier M3 in the Wehrmacht — polupustyne Sd.Kfz.251 (see “modelist-Konstruktor” No. 9,’99), as well as his American “brother”, intended for transportation on the field of battle mechanized infantry branch. With slightly less weight (8 tons versus 9.3 from M3) Sd.Kfz.251 had thicker armor — 15 mm in the frontal part of the hull and 8 mm sides (M3 — 12.7 and 6.3 mm, respectively). Even more the security of German cars increased the location of the hull sides at an angle of 35° to the vertical. However, this arrangement significantly reduces the volume of the troop compartment, where ten Marines were close. American car, although he had in the basic version of the standard weapons one 7.62 mm machine gun, usually armed with two, one of which was heavy. Without prejudice to embed Marines the number of machine-guns could bring to three, and even four, providing a “half-track” overwhelming fire superiority over the “albtelecom”. The better M3 have different dynamic characteristics. In particular, because of the higher specific power and leading of the front axle patency of American cars exceeded the permeability of the German armored personnel carrier. Latest in this regard is not rescued even the metal tracks, which, unlike the rubber was more durable and had no inclination to slip. The design of caterpillar tracks offered by the Americans was German easier, more convenient operation and repair.
No coincidence that after the Second world war, a considerable number of “half-tracks” was in service with many countries of the world. They were widely used in local wars in Korea, Algeria, and Indochina. The IDF used these machines, however in modernized versions, in the Arab-Israeli wars of 1948, 1956, 1967, 1973 and 1982. In service with the Israeli military police they were until most recently.
M. BARYATINSKY
Recommend to read
 OH, THE SLEIGH – RIDE THEMSELVES
OH, THE SLEIGH – RIDE THEMSELVES
Perhaps, in the memories of every adult baby winter fun be sure to contact the sled. And it's safe to say that in a rare home today will not meet them: they still serve the kids and... RADIO MIC
RADIO MIC
We are talking about miniature and low-power VHF transmitter that operates at a distance of only a few tens of meters. The contractor, using a wireless microphone, can move freely around...
 A family of half-track armored “half-tracks”, one of the most famous and popular among the fighting machines of the allies during the Second world war, began to be developed in the United States since 1932. Their design started from four firms: James Cunniagham and Sons, Linn, GMC and Marmon-Herrington. As the prototype was used the chassis of the French Citroen-Kegresse С417, several samples of which were purchased a year earlier. In the next five years was developed and tested experienced polupustyne options from T1 to Т9Е1. The latter, recognized as the most successful, was based on the chassis of the truck Ford V-8 wheel formula 4×2. Rear axle was replaced by a tracked vehicle of the company Timken with rubber caterpillar.
A family of half-track armored “half-tracks”, one of the most famous and popular among the fighting machines of the allies during the Second world war, began to be developed in the United States since 1932. Their design started from four firms: James Cunniagham and Sons, Linn, GMC and Marmon-Herrington. As the prototype was used the chassis of the French Citroen-Kegresse С417, several samples of which were purchased a year earlier. In the next five years was developed and tested experienced polupustyne options from T1 to Т9Е1. The latter, recognized as the most successful, was based on the chassis of the truck Ford V-8 wheel formula 4×2. Rear axle was replaced by a tracked vehicle of the company Timken with rubber caterpillar.