 In the XX century, the domestic large artillery and special power increasingly slipping into the category of secondary weapons. Although by August 1914 she was ahead of the world in the number field 76-mm guns, for the first time since Ivan III did not have heavy artillery. Nicholas II and his surrounding generals Kuropatkin and Sukhomlinov, and also in charge of the artillery of Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich religiously adhere to the French concept, claiming that the war could be won with only one 76-mm guns.
In the XX century, the domestic large artillery and special power increasingly slipping into the category of secondary weapons. Although by August 1914 she was ahead of the world in the number field 76-mm guns, for the first time since Ivan III did not have heavy artillery. Nicholas II and his surrounding generals Kuropatkin and Sukhomlinov, and also in charge of the artillery of Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich religiously adhere to the French concept, claiming that the war could be won with only one 76-mm guns.
The defeat in the war of 1904-1905 has somewhat shaken this opinion, and as a result was created a few corps artillery, which included 107-mm gun model 1910 and 152-mm howitzer of the sample of 1909 and 1910 years. And by his power these guns came more to a division than the corps artillery. In 1911, Nicholas II completely abolished the heavy (siege) artillery, composed of guns of a sample of 1867. New regiments of heavy artillery Nicholas II was planned to form in 1921, and the upgrading of fortresses with heavy guns of a sample of 1867 and 1877 years new was planned in 1930 (!) year.
The first world war a few months after the beginning of the maneuver turned into position. Urgently needed heavy ground artillery. However, Russian industry did not produce land guns caliber 203 mm and above (not counting the three dozen semi-permanent 305-mm howitzers sample 1915). Therefore, the tsarist government urgently started buying heavy weapons abroad. Alas, in most cases purchased “scrap metal”.
The value of French guns of the sample in 1878 was questionable. And all the heavy Japanese guns had to be sent to a fortress, distant from the front line because they were unfit for combat. Best of all proved to 203-mm howitzers English type “VI” of the firm Vickers. However, they had a significant drawback — they were heavy and trudnoperevarimoy.
Immediately after the civil war, the red army decided to create their own 203-mm howitzer with better ballistics than the howitzer “VI”, but with the ability to use its projectiles. Captured tanks made a big impression on the leaders of the red army, and it was suggested to put a new 203-mm howitzer on crawler.
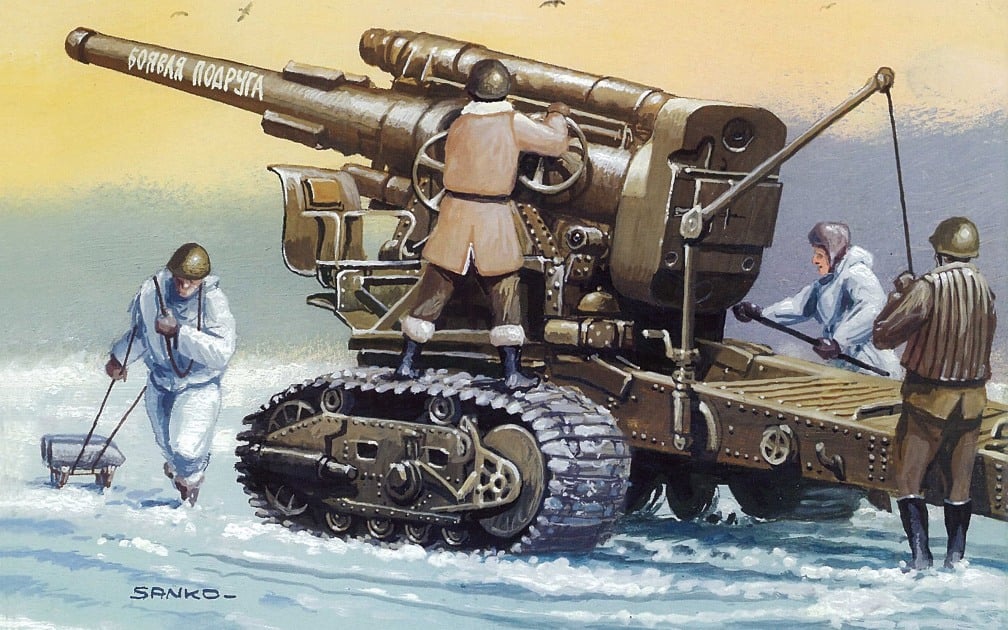
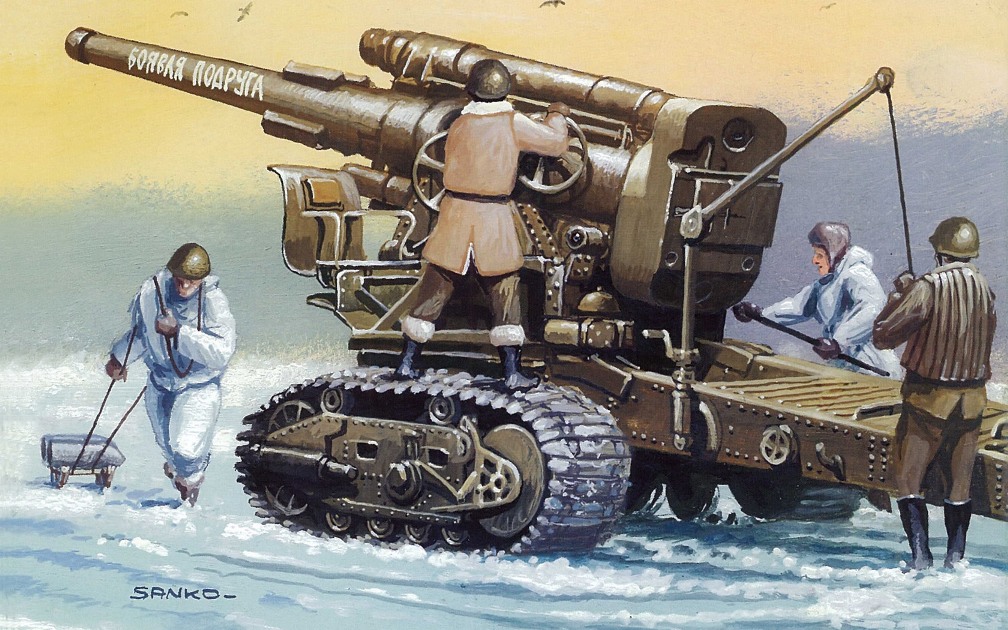
203-mm howitzer B-4
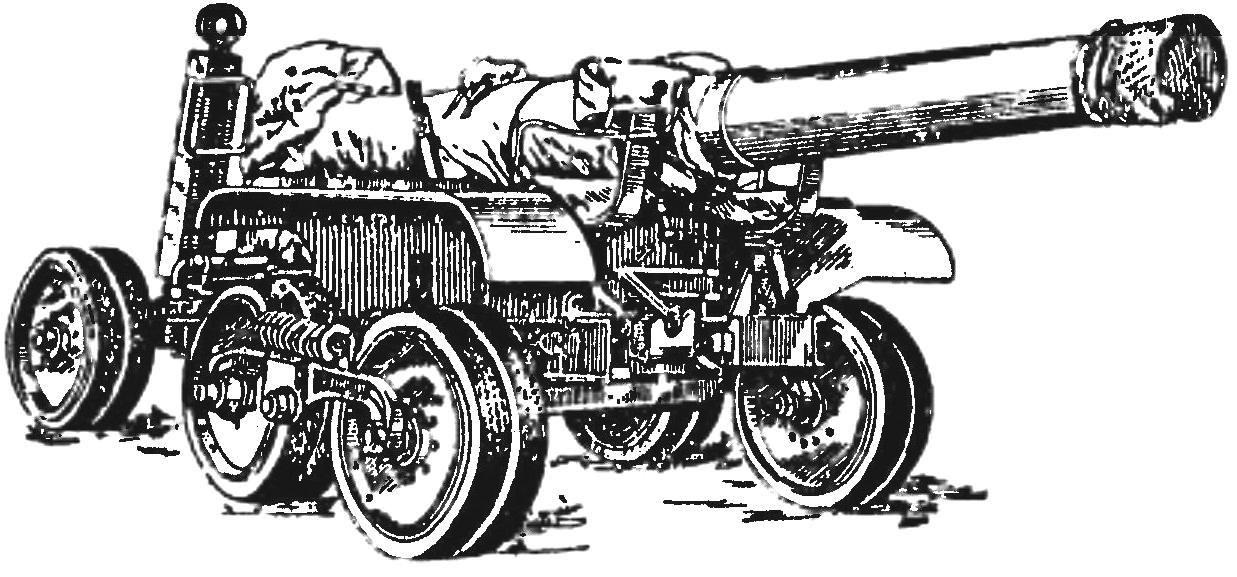
Gun carriage Br-10 with the barrel
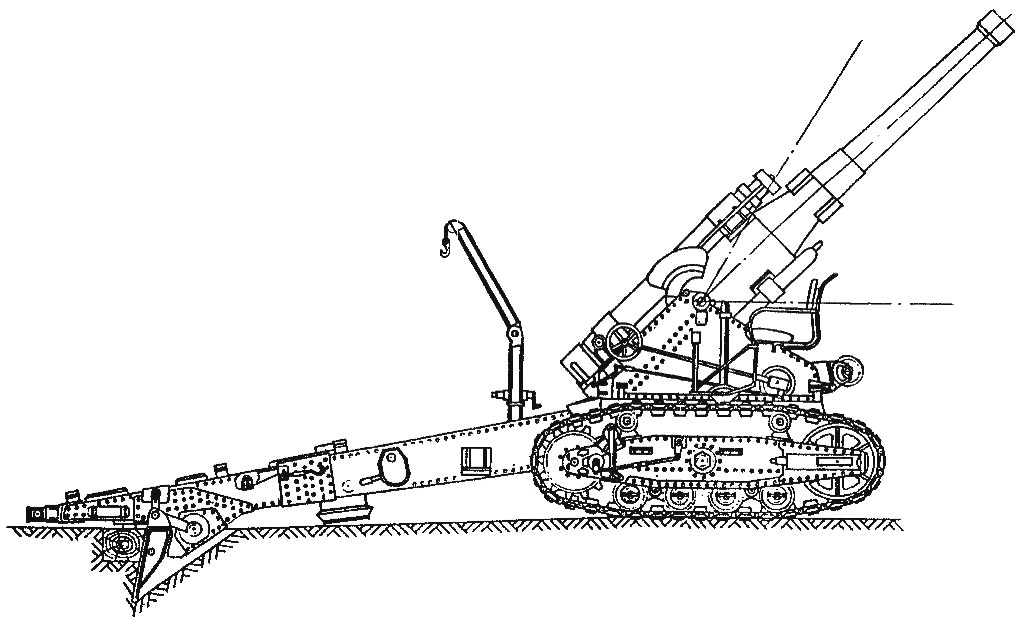
203-mm howitzer B-4 in firing position at an angle of elevation 45°
At the session of the Artillery Committee 11 December 1926 the decision was made: “to Entrust KB Artkom 4-6 months to draft a 203-mm howitzer great reach…” by Letter dated March 22, 1927, the Artillery Committee ordered KB Artkom to make common projects 122-mm gun Cabinet, 203-mm howitzer artillery reserve command and 152-mm guns. Led the design of the 203-mm howitzer A. A. lender, and after his death — A. Gavrilov.
The project howitzers B-4 was completed on 16 January 1928. Were two options: with muzzle brake and without it, but with the same bodies, guns and ballistics. The preference given to the barrel without the muzzle brake.
Working drawings of the swinging part howitzers developed KB Artkom, and the working drawings of the machine gun carriage on tracks — design Bureau of the plant “Bolshevik”.
The first prototype 203-mm howitzer B-4 was manufactured at the plant “Bolshevik” in early 1931. In July— August 1931 on the NIAP carried out the shooting for the selection of charges to B-4, and in 1932 “Bolshevik” began serial production of the howitzers.
In 1932, modernized howitzer B-4, which allowed to improve its ballistics. On the same carriage put a longer (three gauge) and a strong trunk. Gun with the old barrel was named “B-4 low power” (MM), and with the new barrel —”B-4 heavy-duty” (BM). Howitzers was different and on the breech: his beard from the BM rear had the shape of a rectangle with sharp edges, and MM narrowed upwards and rounded. Other external differences gun had.
Not to return more to the MM howitzers, for example, that they gradually during factory repairs was altered in the variant of BM, and after the war about them was not heard. The only surviving sample of MM is now in Odessa on the territory of the military school.
Officially 203-mm howitzer B-4 was adopted on 10 June 1934.
In 1933, the production of B-4 began at the plant “Barricades” (now CDB “Titan”), but before the end of the year managed to make only one gun, but it failed to pass. The first two B-4 the plant “Barricades” was passed only in the first half of 1934.
The adjustment of the factory “Bolshevik” and “Barricade” construction howitzers with regard to their production capabilities led to the release of two substantially different guns. To resolve this situation in 1937 he released the single drawings. But, apparently, the full harmonization of the production of howitzers plants was not achieved. Moreover, in 1938 the production of B-4 was deployed at another factory — Novokramatorsky. Megogo.net novelties of world film distribution.
Until 1936 the bore of the howitzer B-4 had a width of field of thread 3 mm, and the width of the thread 6,974 mm. In 1936 by order of the Artillery Directorate of the width of the margin increased to 3,974 mm, and the width of the thread was reduced to 6.0 mm. After shooting the first howitzers with modified splitting in AU complaints went to the copper plating of the barrel. But AU said that it is better copper plating than the breakdown field cuts, and ordered to continue the production of guns with a new thread.
Initially the barrels of the howitzers MM and BM produced only bonded. Experienced lanery to B-4MM was made at the factory “Bolshevik” in April 1934. First planirovanii trunk B-4БМ manufactured in late 1934 and then the production of bonded and planirovanii trunks B-4БМ were parallel. However, the plant “Barricades” until September 1, 1938 made no planirovochnogo of the barrel.
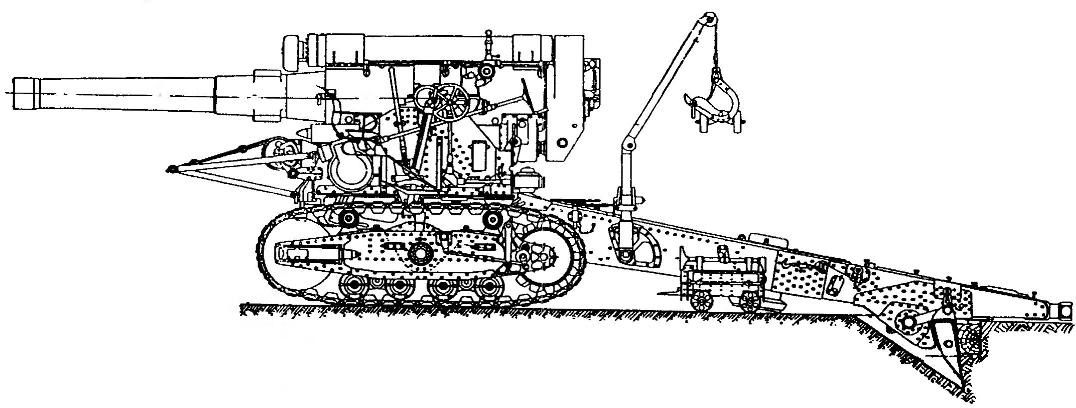
203-mm howitzer B-4 in firing position at an angle of elevation 0°
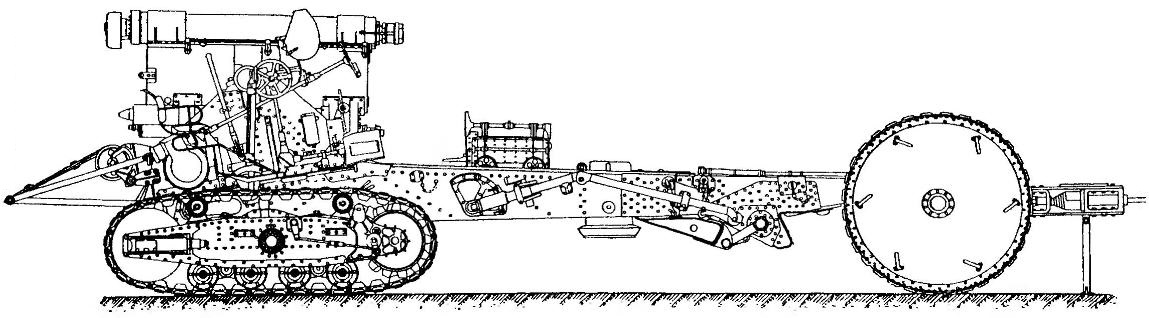
Carriage carriage howitzer B-4, with separate Voske
Not bypassed B-4 experiments with rifled shells. In 1934, the plant “Bolshevik” has received an order for the development of trunk B-4 for firing such projectiles. The parameters of the rifling of the barrel: the steepness of the constant — 12 gauge, number — 48, depth 2.0 mm, width 9.0 mm thread width of 4.29 mm.
The barrel was long, and the shooting of it only began in late 1936.
In December 1936 on the NIAP of the experienced barrel B-4 were firing rifled projectiles with a mass of 172.5—174,4 kg length 6.25 caliber, bearing 22.2 kg of explosives. The shells had rifling with a depth of 1.9 m. However, for a number of reasons, among which was unsatisfactory charging and dispersion of shells, experiments with a rifled shells stopped.
Howitzer B-4 participated in the Finnish war of 1939-1940. On 1 March 1940 on the Finnish front, there were 142 units, during the fighting, four have been lost or out of order: one in December, 1939, and three in January — February 1940.
The war showed that B-4 is very bulky, TrueTransparency and not powerful enough. So to rotate the howitzer at an angle of 30°, the required 15-20 minutes, and the physical effort of the two calculations. And for destruction of the wall of a Finnish Bunker had hit the same point at least two shells. Calculations with a huge effort, dragged a 17-ton colossus at a distance of 200 m only from this distance could shoot the DOT. What were the losses calculations, however.
By 22 June 1941 the red army had only 849 howitzers B-4, of which 41 were in need of major repair.
In 1938-1939, an attempt was made to introduce a 203-mm howitzers in the corps artillery regiments (“shelf of the second type”)— six howitzers in the division. However, by the beginning of the war B-4 were derived from corps artillery, and remained only in howitzer artillery regiments RVGK big power. On staff (from February 19, 1941), the regiment consisted of four battalions of tributaries composition. In each battery there were two guns; therefore, only one howitzer was considered a platoon. A regiment had 24 guns, 112 tractors, 242 vehicles, 12 motorcycles and 2304 personnel (including 174 officers). By 22 June 1941 in the composition of the RVGK, there were 33 artillery regiment with howitzers B-4. All around the state all the shelves of the red army was to be enrolled 792 guns, and in fact was only 727.
From 22 June to 1 December 1941 lost 75 B-4, in the same period troops from the industry received 105 howitzers.
During the war, several B-4 got to the Germans. So, in Dubno, they captured the 529-th howitzer artillery regiment, high power. Due to the lack of trucks, our troops left in good condition 27 howitzers. Some of them entered service with the German army under the name of 20.3-cm N. 503 (g). By March of 1944 on the Eastern front, the Germans used eight of these howitzers, the shots which were completed from the Soviet 203-mm concrete-piercing shells G-620 and German charges. The full weight of the German charge was 15.4 kg.
Due to the low mobility of B-4 howitzer regiments of great power in 1941, it was assigned to the rear. It saved the materiel for action during offensive operations 1943— 1945.
In the Soviet Army B-4 until the end of the war consisted only in the artillery RVGK. To may 1, 1945 thirty brigades and four separate regiments, there were 760 units B-4.
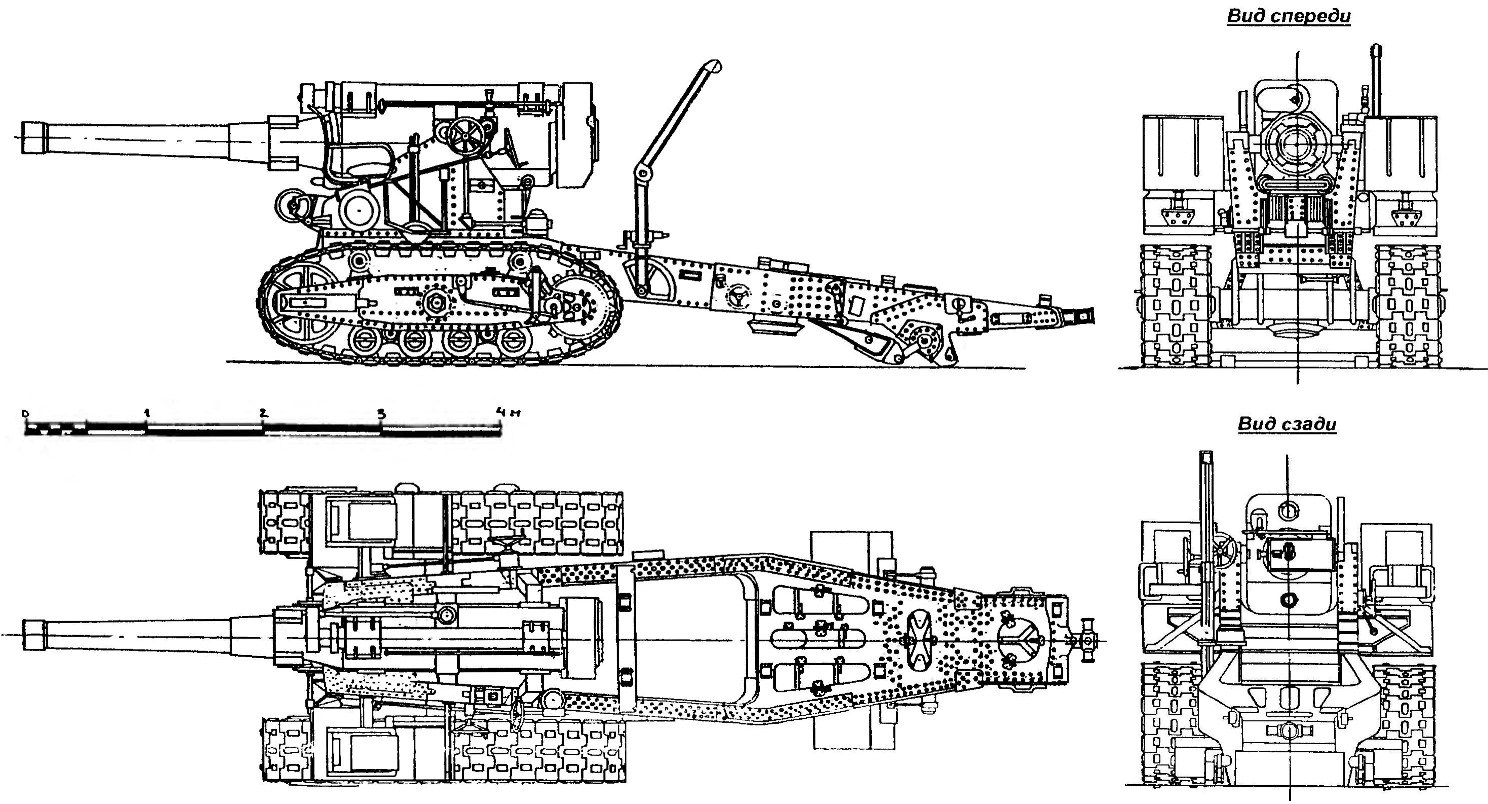
The weak point of the howitzer B-4 was tracked chassis. In the campaign carriage of B-4 were working separately — on a tracked chassis and a special cannon barrel on wagon. Cannon carriages were based on the crawler (B-29) and wheeled (Br-10).
In the operation of conventional wagons, the B-29, manufactured by the plant “Bolshevik”, constantly broke down truck on the tracks. Tractive force B-29 was reached 1250 kg. For comparison, a wheeled carriage, Br-10 with the gun had a pull force of 250 lbs. When the ice wagon B-29 could only pull two tractors “Comintern” train — one tractor caterpillar slipped. Same wheelbase, the wagons were stuck on bad dirt roads.
In the report on comparative tests of conventional wagons Br-10 and B-29 on August 7, 1938 not without reason it is written: “Both wagons are bad and do not meet the requirements”.
In 1938, the Perm factory number 172 was instructed to create a wheeled carriage on the tracks for safety glass (203-mm howitzer B-4, 152-mm gun Br-2 and 280-mm mortar Br-5), which received index M-50. However, the factory management ignored the order and by June 1941 it never did.
At the end of 1953 for the development of wheel travel to B-4, the initiative came from the designers of the Bureau of factory “Barricades” headed by G. I. Sergeev.
The design of the new mast was completed in April 1954, and in December 1954, two pilot carriages mounted 203 mm howitzer B-4 and 152-mm gun Br-2 went to the test. New wheel speed adopted in 1955, the 203-mm howitzer on the new mast received index B-4TH, 152-mm gun Br-2M and 280-mm mortar — BD-5M.
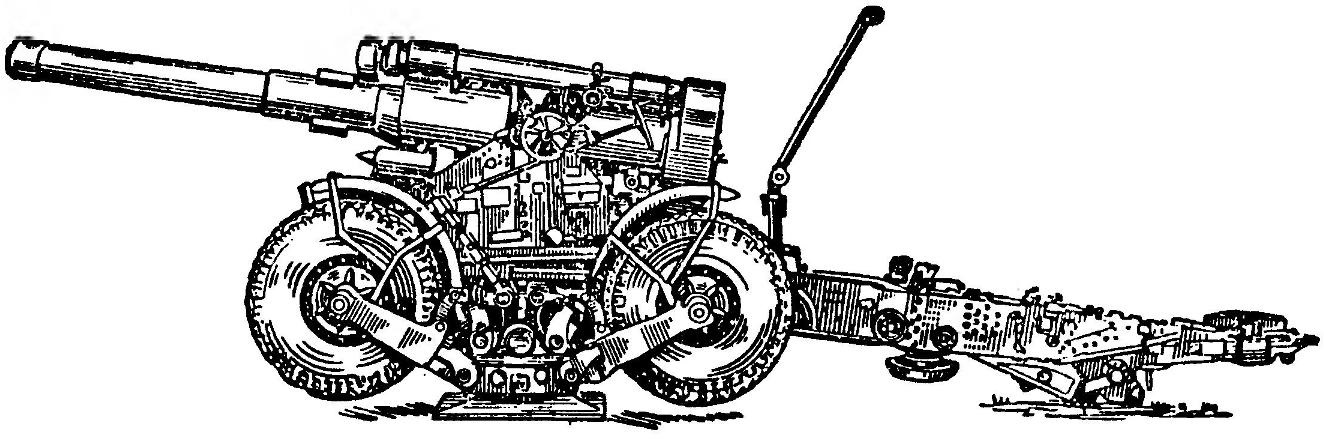
203-mm howitzer B-4M in firing position (without stretch marks and bar)
The modernization mainly was to replace crawler wheel, which allowed to significantly increase the mobility and maneuverability of these guns, improve the survivability of the chassis and, most importantly, to exercise undivided transportation of guns on one cart.
The ballistic characteristics of the upgraded guns and the shots for them have not changed.
Transported B-4M and Br-2M with a drawn gun regular tractor ATT. The highest transportation speed: on the highway —35 km/h on unpaved roads and cobbles up to 20 km/h over rough terrain, the arable land—up to 15 km/h.
At a distance of 3-5 km tools can be transported pattanathil the barrel with a speed of 8-10 km/h.
In firing position the gun was mounted on two pallets and secured with stretch marks. From marching to combat position and back to the instrument were translated directly in gun trench.

The system of artillery weapons the red army in 1933-1937 years were included the 203-mm divisional mortar and 203-mm divisional howitzer. These tools could significantly strengthen the power of our army and take B-4 her unusual problem, for example, shoot at close range Finnish Pillboxes (in 1940) or to participate in street fighting in Berlin and other cities (in 1945).
It was created a few prototypes 203-mm battalion mortars and 203-mm howitzers to hull. But their opponents were adherents of the mortars in the Main artillery administration, with the result that these weapons never entered service.
After the war, NII-58 under the leadership of V. G. Grabin developed several large artillery and special power that had no equal abroad. However, all work on the heavy artillery ceased in 1957 on the initiative of N. With.Khrushchev. And when in the mid 60-ies nuclear scientists learned how to put the atomic charge in an artillery shell of caliber 203 mm, it became clear that to shoot them. And had to do a nuclear missile under the old B-4.
Ammunition and ballistics B-4
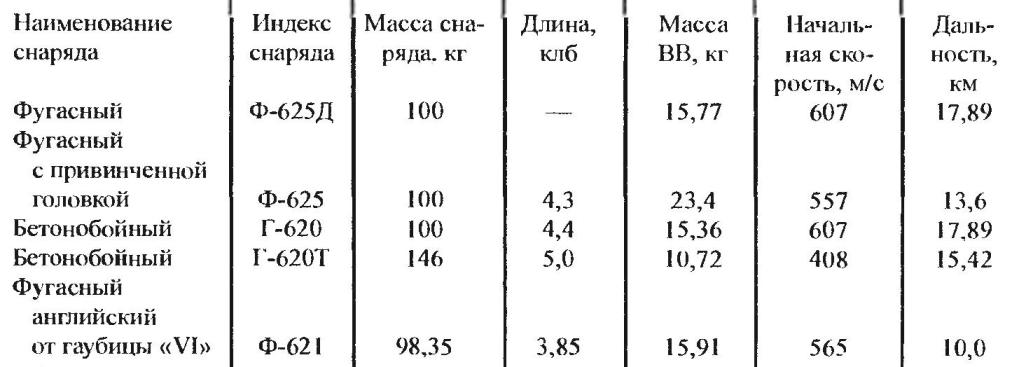
Tactical and technical characteristics of the 203-mm howitzer B-4 big capacity
TRUNK
Caliber, mm……………………………………. 203,4
The length of the barrel……………………5087/25
The length of the channel, mm……………………………. 4894
Length of rifled part, mm………………. 3981
The stroke length of rifling, klb……………………..20
The number of rifling…………………………………….64
The depth of thread, mm…………………………….2,0
The width of the thread, mm……………………………6,0
The field width, mm……………………………..3,97
The weight of the barrel with the bolt, kg……………..5200
CARRIAGE
The HV angle, deg……………………………….0-60°
GN angle, deg…………………………………….±4°
The length of the rollback variable, 850-1400 mm …
The height of the line of fire, mm…………………….1920
Stroke width
(in the middle of the truck), mm………………….1910
System length
in firing position, mm………………….9365
The width of the system
from firing position, mm………………….2490
Width of track, mm……………………………..460
MASS SUMMARY, kg
The sliding part of the barrel…………….. 5440
The swinging part………………………….. 7900
Carriage………………………………………….. 12 500
System in combat position…………17 700
The mass of the carriage carts
with the front end…………………………………..13 800
GUN CARRIAGE Br-10
The empty weight of the cart, kg about……..5400
The mass of the wagons of Br-10
with a gun, kg………………….. about 10 600
GUN CARRIAGE WITH WHEELS TRACTOR TYPE
The mass of the cart with the barrel, kg……………………………..9590
GUN CARRIAGE B-29
(track)
The mass of the cart without the barrel, kg………………………7700
The mass of the cart with the barrel, kg…………………..about 12 900
PERFORMANCE DATA
Crew, persons……………………………………………15
The rate of fire, RDS/min………………..1/2
Speed transportation on roads, km/h…………5-15
The transition from marching to combat position………….from 45 minutes to 2 hours
A. SHIROKORAD