To begin work on the Cabinet with the construction of the slipway. Prepare two blocks of wood a cross section of 50×100 mm and a length of 2880 mm, position them parallel to each other at a distance of 300 mm and fasten with three or four crossbars. Now you can start making cross-recruiting. It consists of three frames – the nose, the mid-bulkhead and the transom Board. Each of them must be drawn life-size on a sheet of plywood and, using this sheet as plazom, collect frames of pine boards with a thickness of about 20 mm. Connection of individual elements – vpoldereva, waterproof glue and screws.
The housing Assembly. Install the frames on the slipway. To strengthen their best screws. The fact that the result in the case would be “extra” holes shouldn’t bother you they can be later repaired wooden stoppers on glue.
Cut the grooves for the keel timber and temporarily attach it with one screw to the mid-bulkhead. Further, consistently turning keel beams, dock it to the forward bulkhead and transom. After adjustment, the temporary fixture is removed and the beam finally is put in its place. Used epoxy glue and screws with countersunk heads.
Now it is necessary to cut the slots in the frames under the remaining parts of the longitudinal set. The sequence of fit and the rails is the same as that for the keel timber. After final gluing to the frames armalcolite the outer face of the longitudinal and transverse set. Finding that line is adjacent to the set not completely, prostrogat Reiki a plane, and cleared a rasp.
The hull of the Dinghy:
1 – corner cnica (plywood s8); 2 – the nose of the Bank; 3,4 – steps of the mast (plywood); 5 – mast; 6 – mounted additional parts (plywood or pine Board 18×200); 7 – frame banks (pine 18×45); 8 – seat banks (plywood s8); 9 – snake keel (oak rack s18); 10 Kil; 11 – feed of the Bank; 12 – steering pen (plywood s10); 13 – loop linkage of the steering of the pen; 14 – a lining (plywood s8); 15 stop; 16 – rumple (oak rake 1875, L1200); 17 – rowlocks; 18 insert (oak); 19 – Klondike (plywood s8); 20 – a lining svarca (plywood s8); 21 – cross member for mounting sverzov; 22 – bearing mast; 23 – outer stringer (pine 18×45); 24 – cladding the front of the transom (plywood s5); a 25 – frame front transom (pine s18); 26 frame, mid-frame (pine s18); 27 – bolts M6; 28 – keel beams (pine 18×90); 29 Kil (oak rail); 30 – hull bottom (plywood s6); 31 – a sealing joint (GRP); 32 – the corner stringer pine (18×30); 33 – sheathing Board (plywood s4…6); 34 – fender (semi-circular oak rail); 35 – internal stringer (pine 18×45); 36 – support banks (plywood s6); 37 – seat (plywood s8); 38 – support seat (plywood s8); 39 – frame transom (pine s18); 40 – pad (plywood s8); 41 – the covering of transom (plywood s6…8)
The pattern of hull plates:
1 – bottom; 2, 5 – casing flanges; 3 – the covering of transom; 4 – the skin of the nose; 6 – the rest of the plywood for the brackets, rails, linings
Installation of the frames on the slipway:
1 – crossbar; 2 – the longitudinal bars of the bench; 3 – the frame of the front transom; 4 – midship-frame; 5 – transom
The shell plating is best to start from the bottom. A sheet of plywood prihvatyvaya clamps and outlined with a pencil outline with an allowance. After cutting and pre-fit cladding is fixed using screws and epoxy glue. Screws are best to use brass or galvanized steel. After curing of the adhesive edge trim, handle plane.
Similarly, the sheathed side. After finishing this work, the case can be removed from the pile and proceed to frame interior stringers, which are the trim and increased top side. It is necessary to carefully calculate their length or use the method of successive approximations (to paraphrase a famous saying – cut it seven times!). Between the outer and inner stringers are glued spacers with a thickness of 20 mm with step of 300 mm, Two spacers need to be strengthened – they will be used as the basis for rowlocks.
The joints between the sides and transom and between the sides and the nose frame reinforced angular brackets, sawn from plywood with thickness of 6 – 8mm and secured to the housing section by screws and glue.
Additional parts are cut from pine boards or plywood with a thickness of 15 to 18 mm. Their cross-section resembles a biconvex symmetrical profile of the aircraft wing. At the top of sverzov on both sides of each must be affixed to the plywood (8mm thick) pads. The steering is feather sailboat – desyatiletnego of plywood; a tiller pivotally connected with the pen from the oak of the bar.
Sealing the sides:
1 – strut (pine 20x45x50); 2 – outer stringer; 3 – inner stringer; 4 – RUB rail; 5 – casing; 6 – screw
Cross member to install sverzov:
1 – nut-“lamb”; 2, 6 – washers; 3 – a washer-pad (glued with epoxy glue); 4 – swiercz; 5 – pin M12; 7 – a bolt of M6 with nut; 8 – plate (steel, sheet s3, 90х125); 9 – handle (oak or beech 20×90); 10 – a bolt of M6 with nut
Install the crossmember on body:
1 – crossbar; 2 – inner stringer; 3 – panel (plywood s8, 55х100); 4 – M6 bolt; 5 – side; 6 – spacer (wood)
Cross – bearing for the mast:
1 – mast; 2 – pad (plywood s8, 175×175); 3 – crossbar (pine 20×90); 4 – inner stringer; 5 – panel (plywood s8, 55×150); 6 – bolts M6; 7 – plating side; 8 – strip (tree)
At the end of these works you can start to finish. It is preferable to hang it outside on fiberglass epoxy glue, but it is not restricted just to luted, primed and painted in the desired color. Steering pen, additional parts and banks should be impregnated with hot drying oil and to ulcerate.
Sailing rig of a Dinghy -Latin, with an area of 4.5 m2 . The mast is fixed at a distance of 760 mm from the nose (additional parts in this case are located at a distance of 1220 mm from the nose). To determine the center of the sail and the centre of lateral resistance, you can use the following methods. For triangular sails (which is Latin) its center is determined as the intersection point of median lines dividing the side opposite the corresponding angle in half.
The center of lateral resistance of the hull of the Dinghy is the easiest way to find empirically. For this, the estimated (purely roughly!) the center of lateral resistance Board attached to a rope and pull the boat sideways through the water. If the position changes, the candidate center is selected incorrectly and the anchor point should be changed to ensure that the Dinghy was moving strictly sideways. The place of attachment of the rope will be a true centre of lateral resistance.
Geometrical method of finding the CPU
A practical way of finding TSBS:
1 – the attachment point of the rope behind the selected CBS; 2 – anchor point ahead of CBS; 3 – anchor point coincides with the TSBS
The relative positions of the center of the sail (CPU) and the centre of lateral resistance (MKS) Dinghy:
1 – sail; 2 – body; 3 – swiercz (dash-dotted line shows the way of changing CBS to turn sverzov)
Sailing rig of a Dinghy:
1 – jaw; 2 – solitaire head points of the angle of the sail with a grommet; 3 – pocket Hafele; 4 – Klondike solitaire the tack angle with grommets; 5 – gik; 6 – mast; 7 – the pocket geek; 8 – solitaire Shkotovo corners with grommet
With the installation of the mast and sverzov need to ensure that the centre sail were located at 100 – 150 mm closer to the nose than the center of lateral resistance.
Mast height – 3200 mm. Diameter near the base – 60 mm, in the upper part is 40 mm. the Gaff and boom sails – aluminum tubes diameter 30 – 40 mm and length 3000 mm. it is possible to make them of pine sticks of appropriate length. The gaff and boom are connected with a sail with pockets sewn to the main panel.
A small area of the sail allows to do without a complex system of blocks. You will need only one unit, mounted on a swivel on Kileva the Board, and two to three meters of vegetable or nylon rope (for the geek-sheet).
I. SERGEEV
Recommend to read COMPRESSOR FROM A REFRIGERATOR The advantage of a paint sprayer is well known: it provides quality coverage. Moreover, achieving smooth transitions from one color or tone to another can only be done by spraying. And for... ATV FOR ALL SEASONS Before proceeding to the description of the snowmobile "Turtle-2", will tell about the history of his birth. And it happened thanks to the ATV — the predecessor of the same name, only... Scroll back to top
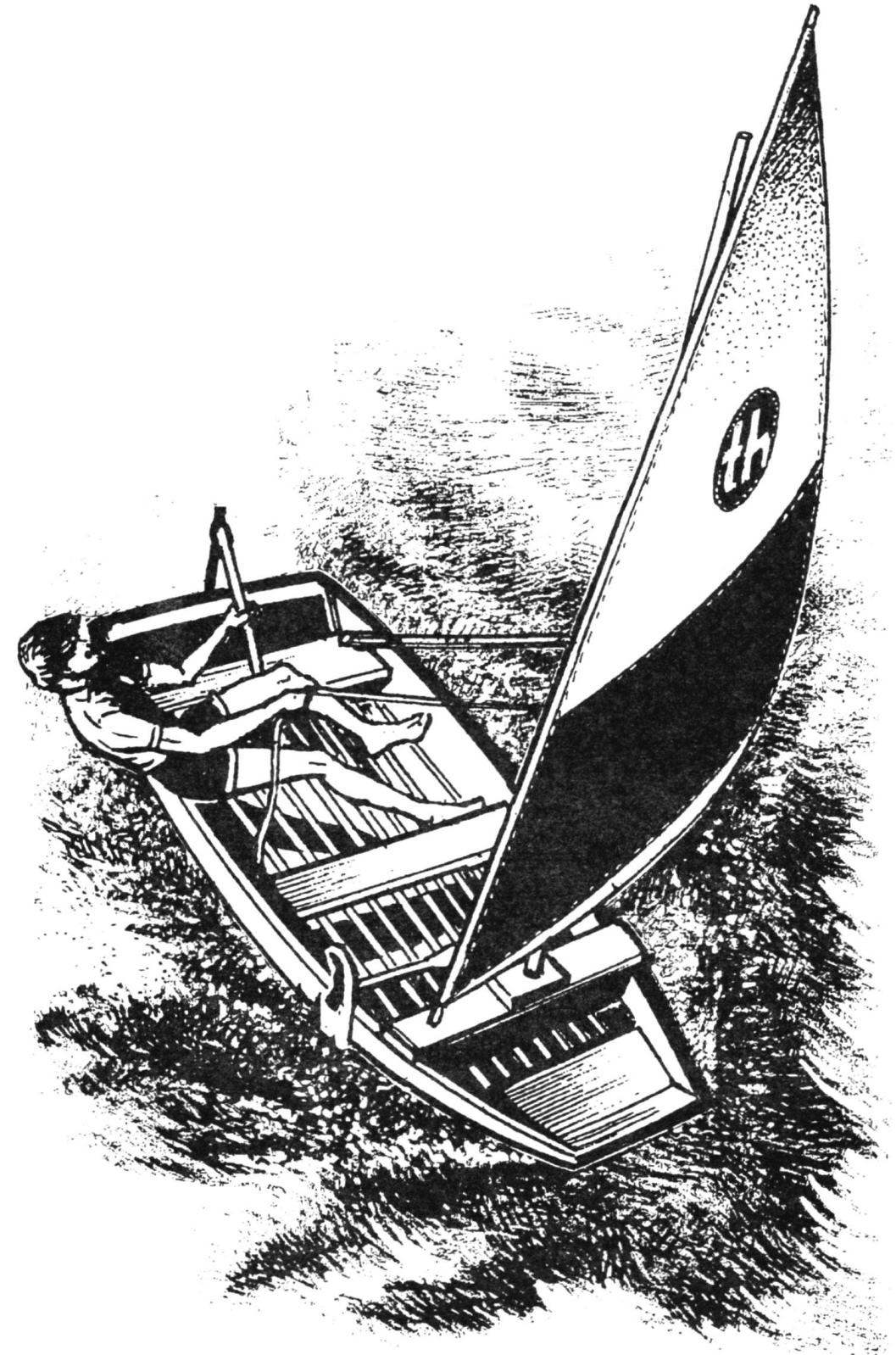 If you live not too far from the pond, make our drawings Dinghy, and you will experience all the delights of sailing. But if this ancient engine is not too attract you, the body of the Dinghy can be used as the basis for small motor boats or rowing Dinghy. Materials for it will require only two sheets of plywood and pine slats.
If you live not too far from the pond, make our drawings Dinghy, and you will experience all the delights of sailing. But if this ancient engine is not too attract you, the body of the Dinghy can be used as the basis for small motor boats or rowing Dinghy. Materials for it will require only two sheets of plywood and pine slats.