A tasty and healthy product—sauerkraut. Practical housewives prepare it in autumn both in rural areas and in the city. And the most labor-intensive operation here is shredding the heads. For this, both sharp long knives and special shredders are used. But no manual one can compare in convenience and productivity with an electric one, which you can make with your own hands, taking some parts and components from an old washing machine.
The general design of the electric shredder is simple: on a metal frame welded from 20X20 mm steel angles, an electric motor and a bearing unit of the working disk with three knives are mounted. Rotation is transmitted to it from the motor by a belt drive. The shredder body, which encloses the working disk, has an inlet opening with a loading hopper and an outlet window. For convenience of operation, the frame is installed on support legs welded from steel angles so that the working disk is tilted 30° from the horizontal. This simplifies loading the hopper and feeding the cabbage under the knife.
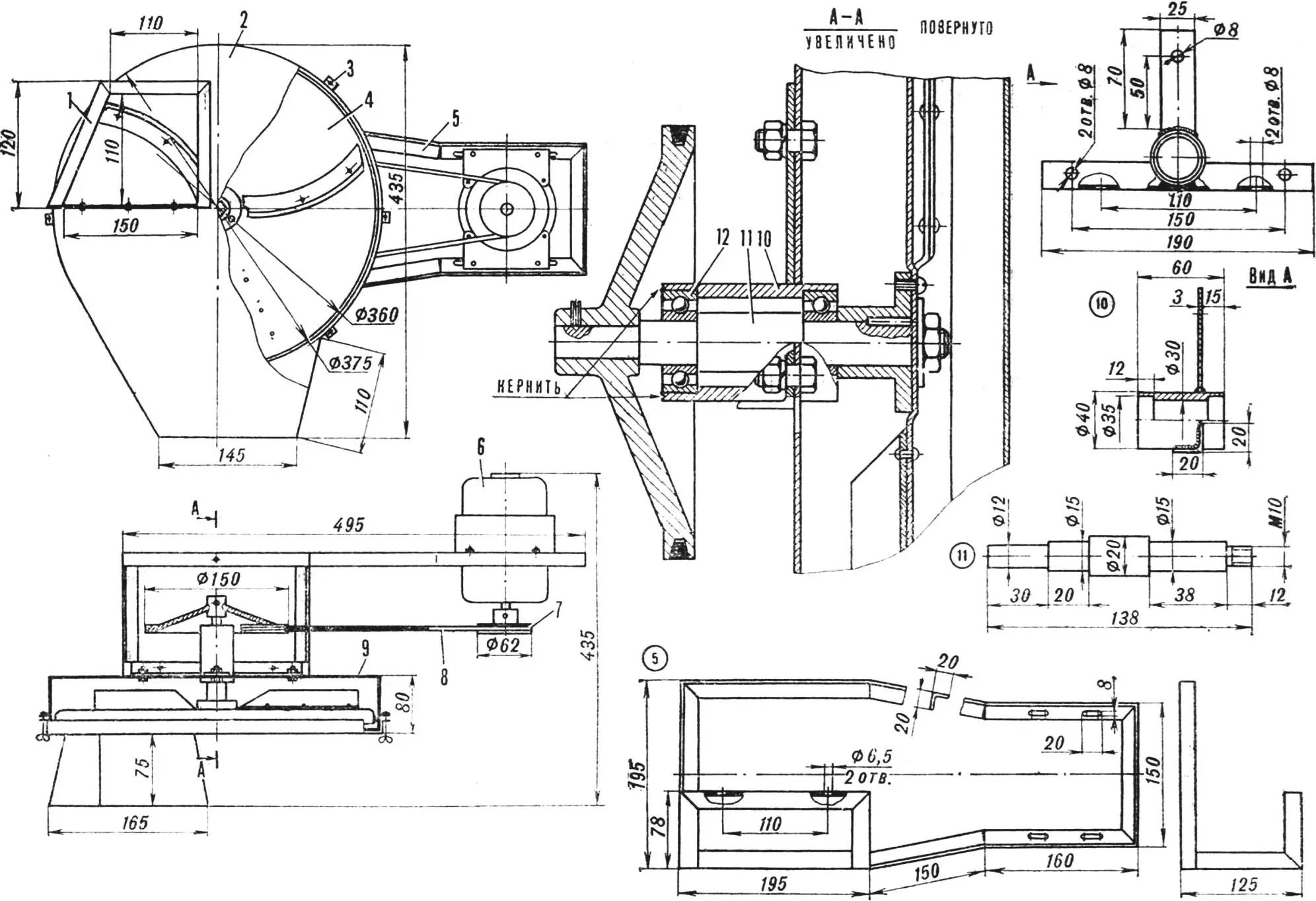
1 — loading hopper, 2 — cover, 3 — tie bolt, 4 — working disk, 5 — frame, 6 — electric motor, 7 — drive pulley, 8 — belt, 9 — working disk housing, 10 — bearing unit housing, 11 — working disk shaft, 12 — bearing No. 80202.
The most critical part of the shredder is the working disk with three knives. It is cut from a 2 mm thick duralumin sheet. To increase rigidity, its edge is flanged at a right angle by 10 mm. Having marked the knife mounting locations, three crescent-shaped windows are cut in the disk, and then the cut edges are extruded 6 mm above the disk plane, as shown in Figure 2. Crescent-shaped knives are mounted on the resulting platforms with three rivets. The best material for them is a mechanical hacksaw blade or a scythe blade. It is somewhat simpler to make a straight knife, but a saber-shaped one works better. Three duralumin angles riveted on the opposite side of the disk from the knives will help remove the cabbage “noodles” from under the disk.
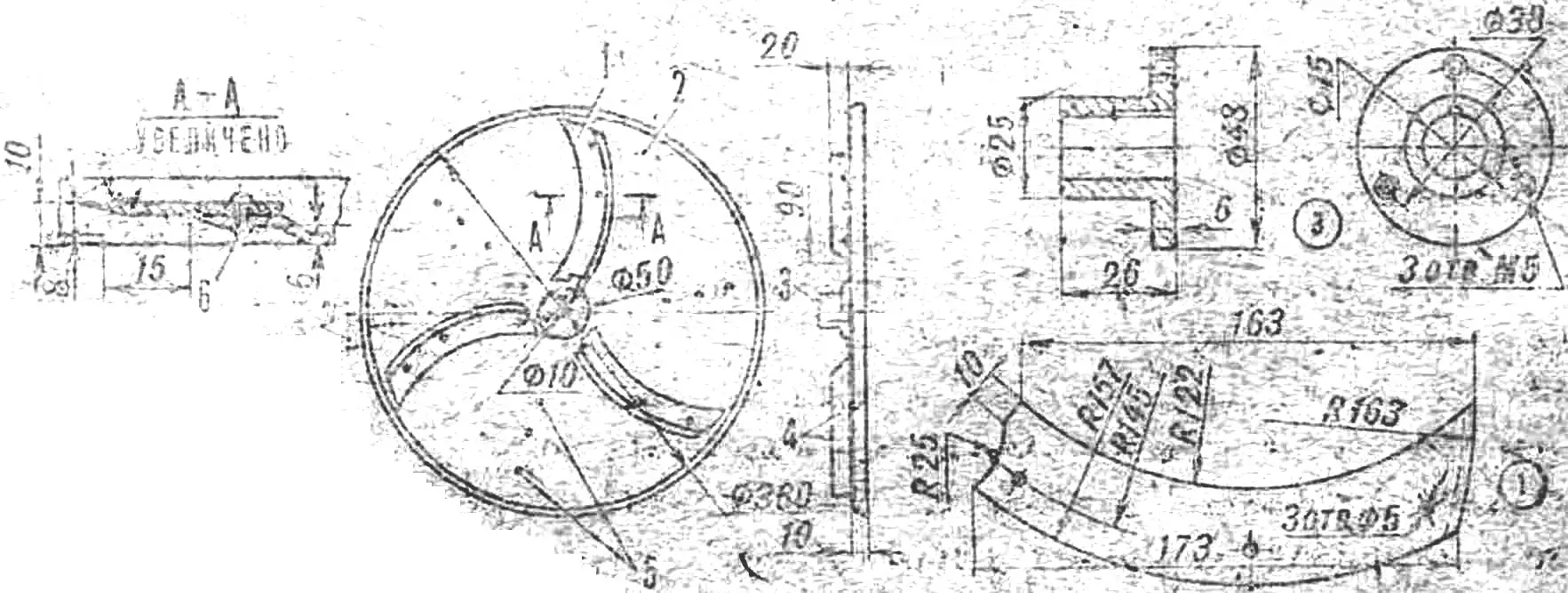
1 — knife, 2 — disk, 3 — disk hub, 4 — angle, 5 — angle rivets, 6 — knife rivet.
The shredder body consists of two parts: the working disk housing and the cover with the loading hopper. Both parts can be made either from 0.75 mm thick steel sheet, joining the seams with gas welding, or from washing machine body material with aluminum rivets, or from aluminum sheet with a rolled edge connection.
The bearing unit of the working disk consists of: a housing, a shaft, and two bearings No. 80202. A 20X20 mm angle is welded horizontally to the housing and a vertical 3 mm thick steel plate. Two holes in the lower angle flange are for mounting the unit to the frame, and two in the vertical flange and one in the upper plate are for connecting the protective housing of the working disk.
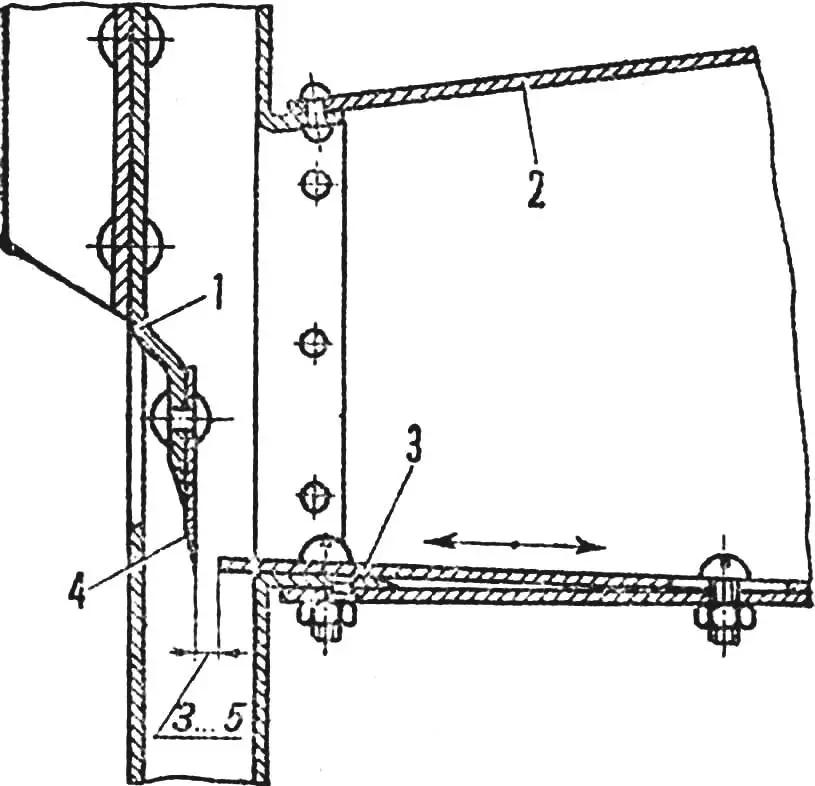
1 — working disk, 2 — loading hopper, 3 — adjustable support plate, 4 — knife.
The parts of the V-belt reduction drive from the motor to the working disk are borrowed from a washing machine. Belt tension is adjusted by the motor position: slots of its mounting bolts on the frame allow changing the center-to-center distance within small limits.
Adjustment of the working mechanism comes down to setting a gap of 3—5 mm between the support plate of the feed hopper and the knives, and the cut thickness is determined by the working disk design: the height of the knife blade positions relative to the disk.
An electric shredder with sharpened knives handles a head in seconds, so to avoid injuries, feeding the vegetables to be shredded to the rotating disk should be done with a wooden pestle.
V. MALYSHEV