In 1934 Germany began work on a new light armored vehicle with higher performance characteristics. The first step in this direction was the creation of a standard chassis for heavy army vehicles.
This chassis had to have a wheel formula 4×4, controls, acting on all four wheels, small mass, small specific ground pressure, high strength, simple construction, convenient access to components and the consequent ease of repair. The requirements were so high that excluded the possibility to use serial commercial chassis. Therefore, all collaborated with the Ministry of arms of the company received an order to develop a completely new design. The best samples were in 1936 in Berlin demonstrated at the exhibition of the means of motorization. The military has opted for the prototype, created at the Horch factory in Zwickau owned by group Auto Union AG. Was issued in two versions of chassis. The first option, known officially as the Einheitsfahrgestell I für schwerer Personenkraftwagen, had the engine in the stern and was designed specifically for the installation of an armored body. The second option is Einheitsfahrgestell II für schwerer Personenkraftwagen — a differed from the first in that the engine was placed on the front. This chassis is more suited to passenger cars heavy class.
The first variant had the designation Horch 801/EG I, had a mass of 1965 kg. Chassis equipped with engine of Horch/ Auto-Union V8-108 volume of 3.5 liters and output of 75 HP at 3600 rpm gear Box provided with five gears forward and one back. In accordance with the requirements of the military, the drive was carried out on all wheels. The steering is also operated to all four wheels, but when driving on the highway at speeds over 35 km/h rear wheel was fixed in a neutral position. Suspension is independent on two vertical helical springs. Continental tyres size 210-18 had an air chamber low pressure. Foot hydraulic brake operated on all wheels of the chassis.
On the chassis 801 /EG I created a new armored vehicle with a long name mit Leichter Panzerspaehwagen fur Einheitsfahrgestell I sPkw. The work on the machine led firm Eisenwerke Wesserhutte of bad Oynhausen. The armored car was produced in several modifications, differing in armament and equipment.
First formed reconnaissance units of the Wehrmacht began to receive light armored vehicles Leichter Panzerspaehwagen (MG) (Sd.Kfz.221). From 1936, they began to gradually replace the old Kfz 13.
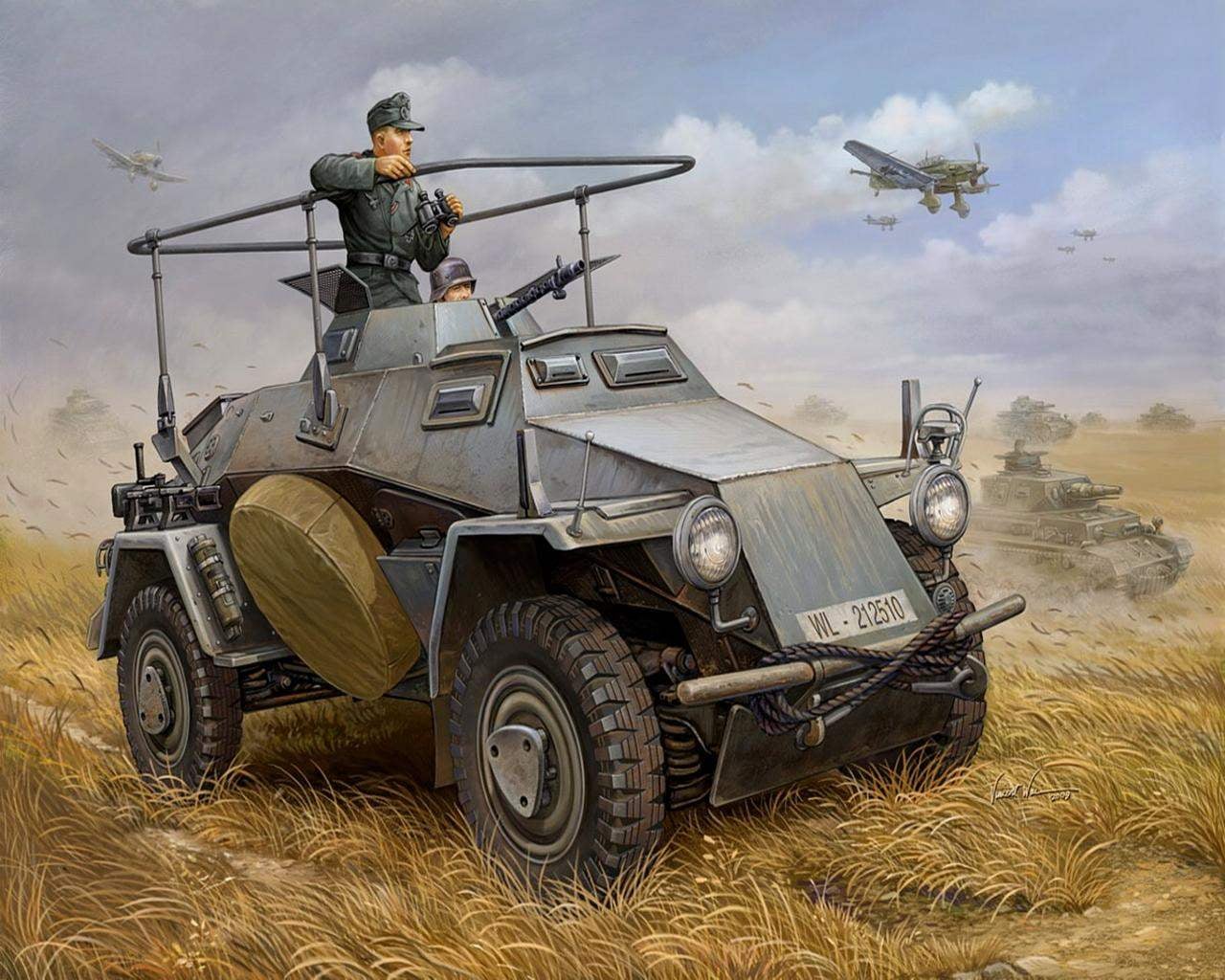
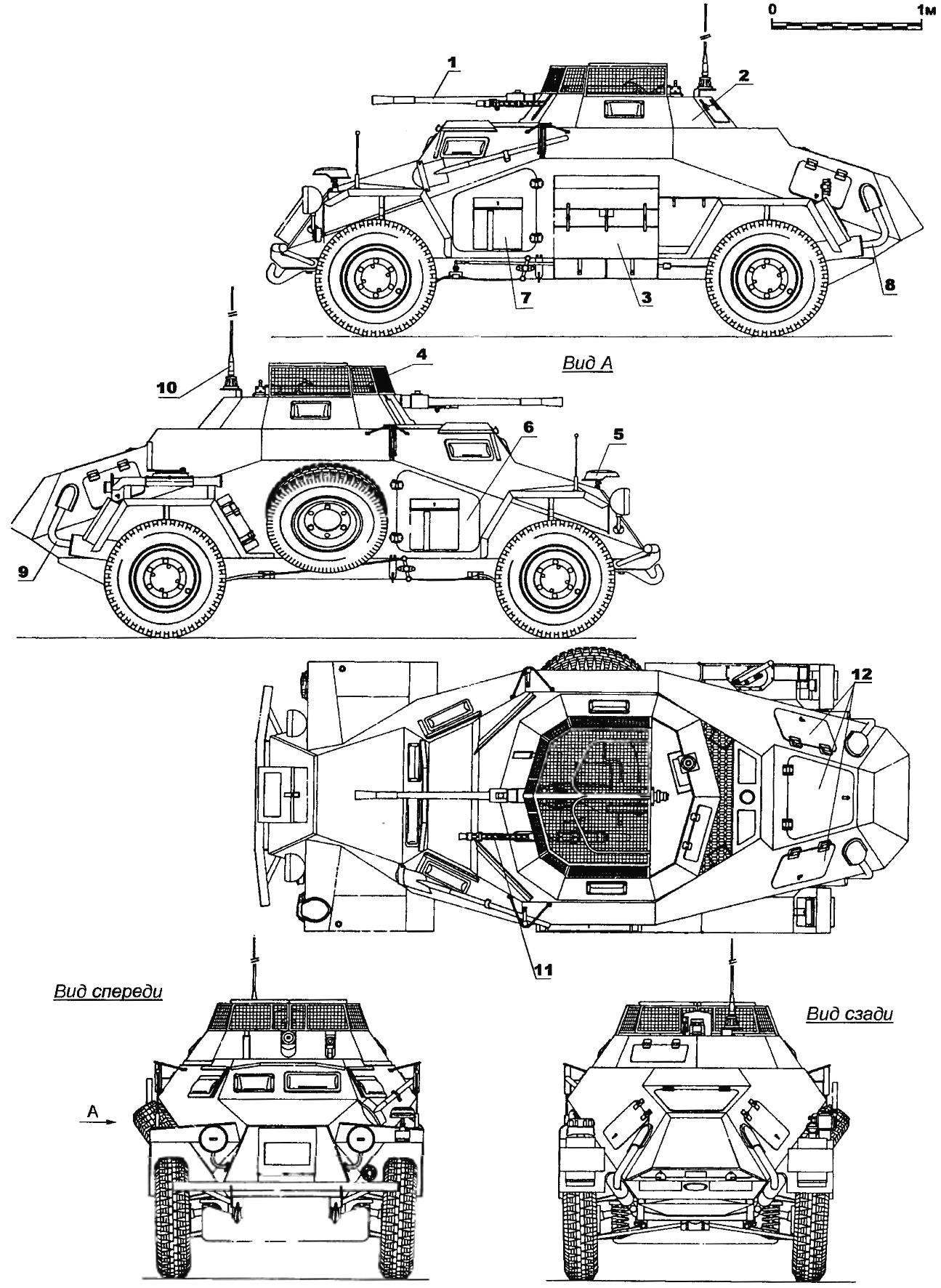
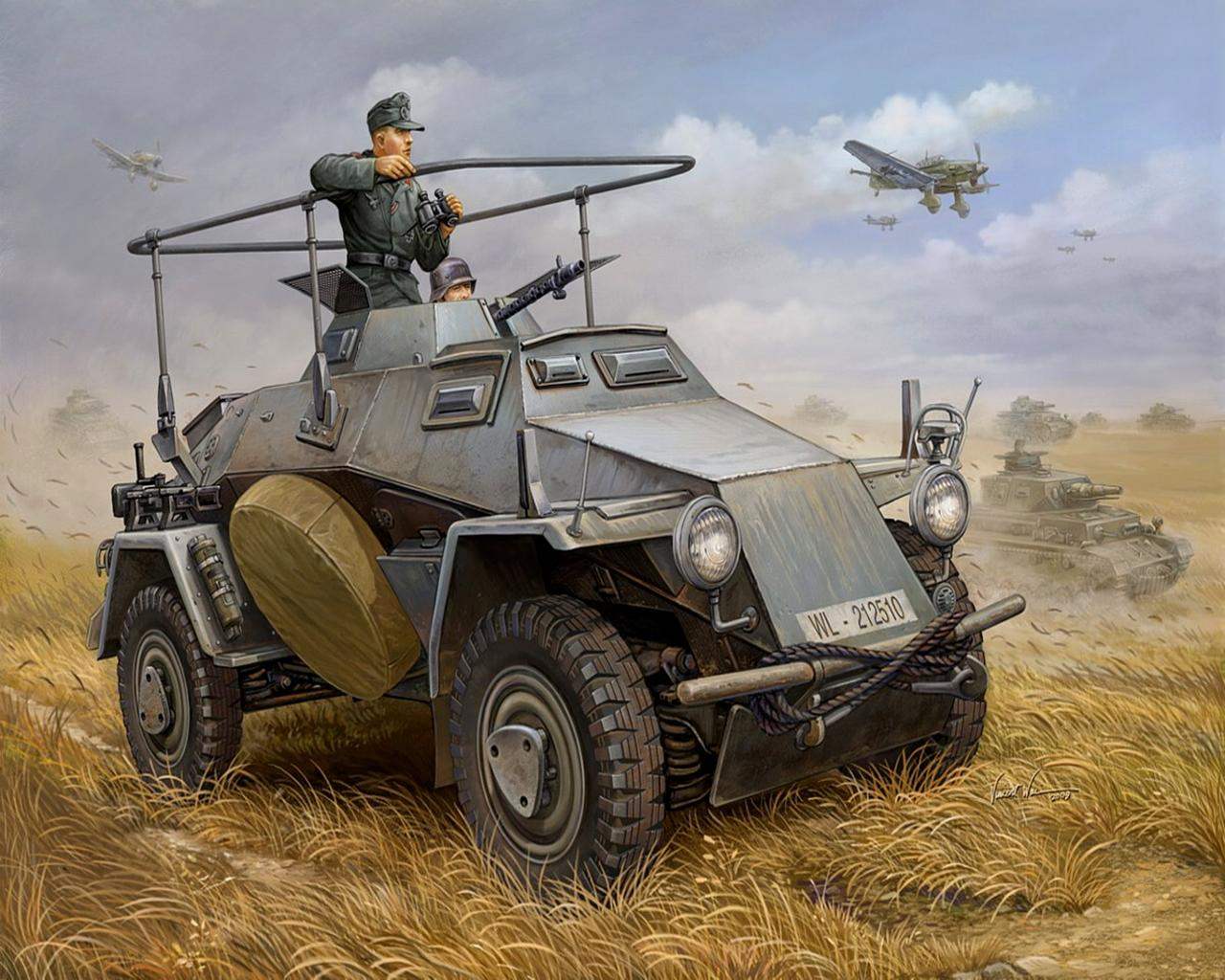
Sd.Kfz.221 had a body, welded from armor plates with a thickness of 14.5 mm. armor plates located at an angle, increasing their effective thickness. The armor is enough to protect against shrapnel and rifle bullets, including with a steel core.
The driver was watching the road through a rectangular access hole cut in the front sheet. Similar hatches are a little smaller there was in the left and right sides of the body. During the battle they were closed by armored shutters with narrow observation slits.
Access to the engine was carried out using three rectangular hatch. Behind the bulkhead that separated the fighting and engine compartment, there were two fuel tanks with a capacity of 55 L.
The crew got into the car via doors in the sides of the body. The spare wheel hung to the starboard side of the machine.
Armored Car Sd.Kfz.221 was armed with one 7.92-mm machine gun mounted in a rotating turret, which had the shape of a truncated pyramid fold. The tower had a solid roof. Instead, on top of the fighting compartment was protected by two hinged screen of wire mesh. In the sides of the tower were peepholes.
The prototypes were installed the old machine guns MG 13, but production vehicles received a new MG 34. Ammunition for the machine gun was 1050— 1200 rounds. The turret could rotate 360° and the machine gun provided vertical aiming angles from -10° to +69°. This allowed us to fire from the gun, not only at ground targets, but low-flying aircraft.
The crew of the armored car Sd.Kfz.221 consisted of two people: a driver and commander who simultaneously performed the functions of the arrow. Standard weapons of the crew consisted of one machine gun MP 38 or MP 40 and six hand grenades.
Radio stations on the car was the relationship was maintained with the help of signal flags.
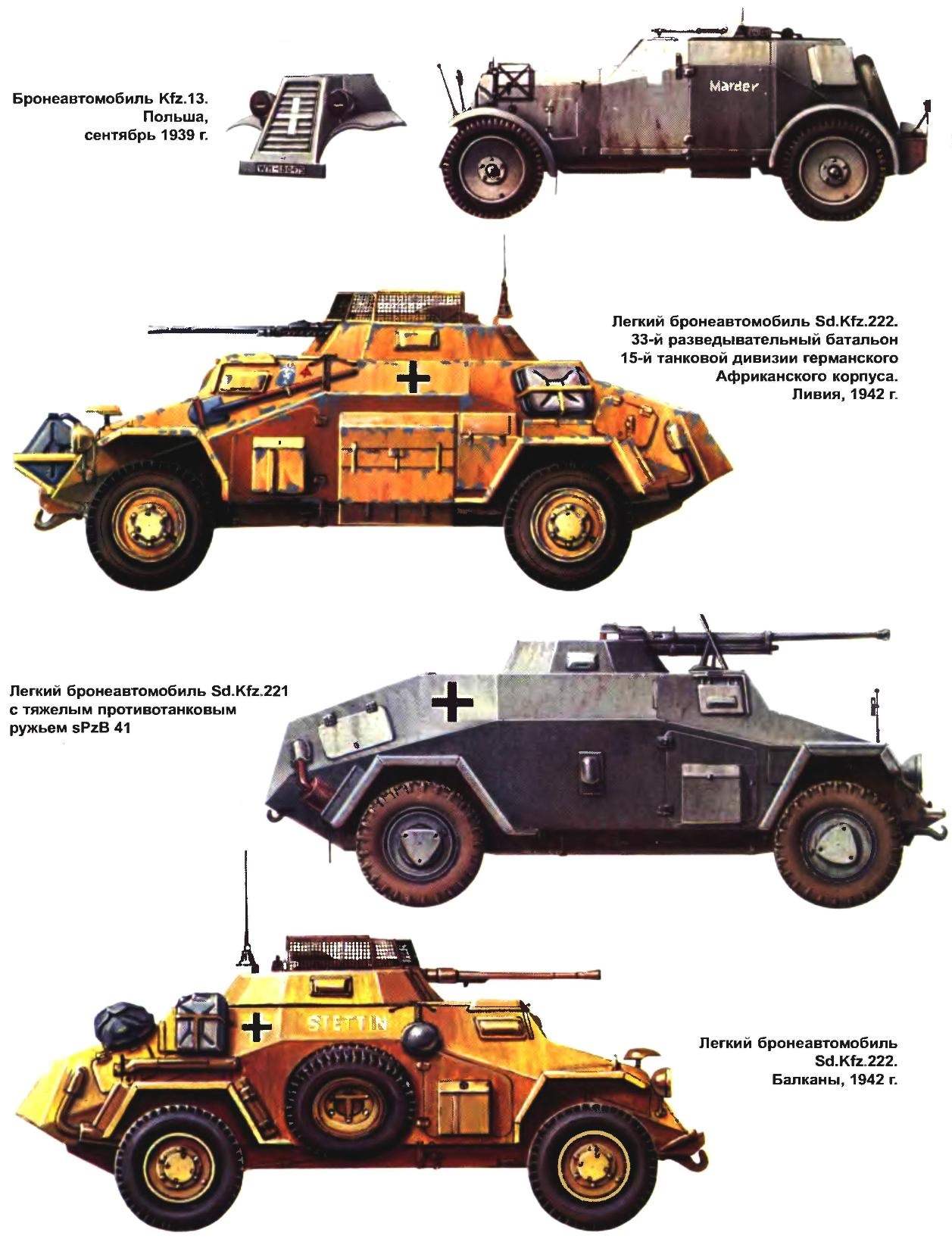
In the form of armored car Sd.Kfz.221 (released 339 units) reconnaissance units of the Wehrmacht received fast and maneuverable car. She had one serious drawback — weak arms. After the outbreak of the Second world war, armored cars were fitted with the more heavy weapons. In particular, additionally they are armed 7.92-mm anti-tank gun PzB 39, which was placed in the tower next to the regular machine gun. The gun was allowed to fight the enemy armored vehicles only at extremely close range.
A better solution was the installation of HaSd.Kfz.221 heavy anti-tank guns 2,8 cm sPzB 41. This modification of the armored car appeared in 1941. Instead of the MG 34 machine gun the machine was armed with heavy anti-tank gun of calibre 20 — 28 mm conical barrel. New weapons were required to slightly change the design of the tower (to reduce the height of the front wall). Anti-tank gun installed in the tower along with the flap, slightly increased height of the armored car.
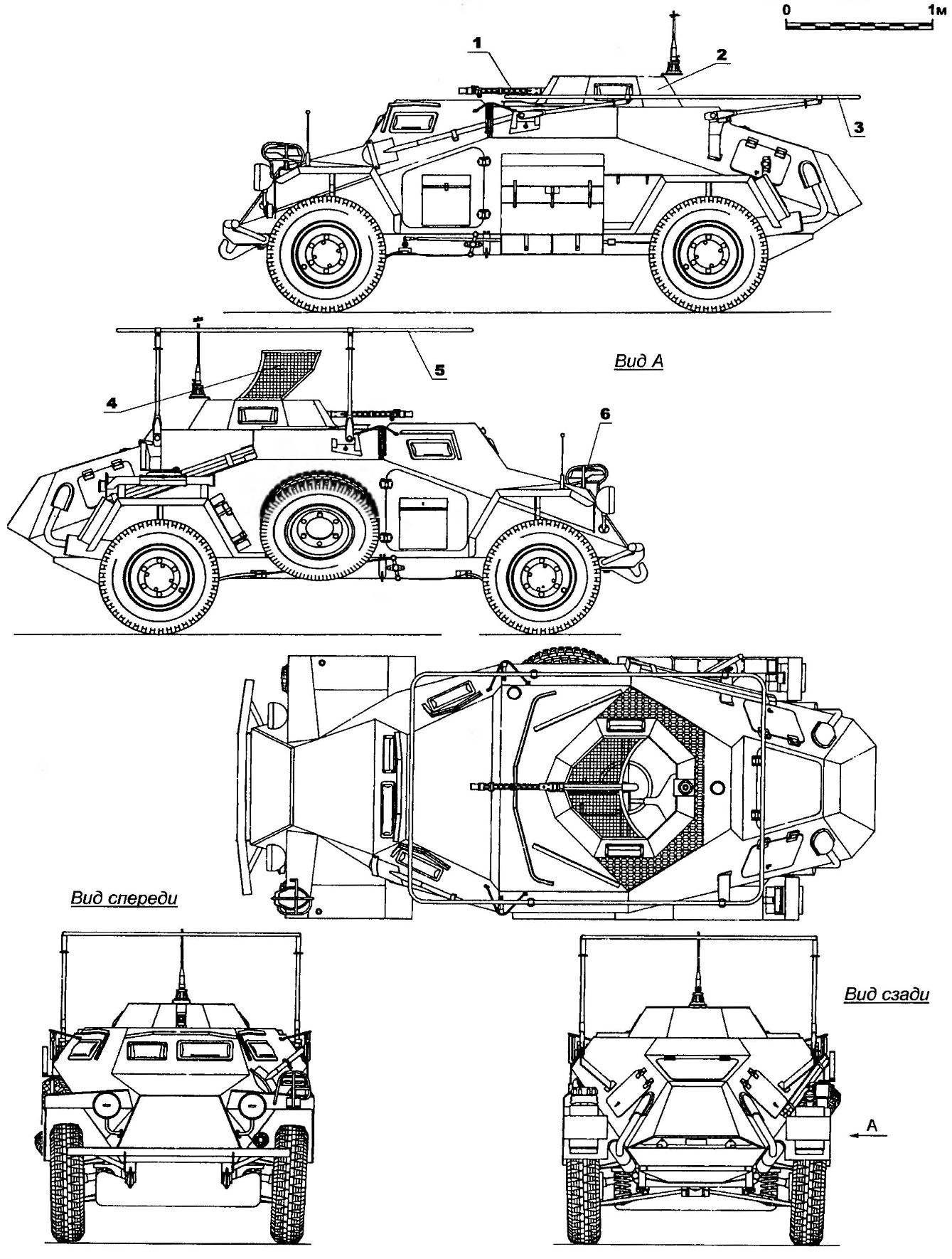
The most popular and successful modification of the armored car became the Sd.Kfz.222. This machine was armed with 20-mm automatic gun KwK 30 (parts of machines KwK 38) gun and coaxial machine gun MG 34 set in desativando open top of the tower. The ammunition consisted of 180 shots and 1050 rounds. The angles of elevation of the gun and the gun allowed to fire at air targets. Armored Cars Sd.Kfz.222 was manufactured 989 units.
Along with the reconnaissance versions were produced and special. We are talking about the Sd options.Kfz.223 and Sd.Kfz.260/261.
The first was radiomacher for communication intelligence units. She was equipped with radio Fu10 or Ful9, and later Ful2 framework with a folding or whip antenna. Tower with weapons preserved from modification Sd.Kfz.221. Combat weight increased to 4.4 T.
Armored Cars Sd.Kfz.260/261 — machine communication for armored and motorized units, differing only in the type of radio station. On Sd.Kfz.260 installed Fu 7 radio with telescoping whip antenna, Sd.Kfz.261 — Fu 12 with a loop antenna. Each crew consisted of four people.
Radiomacher Sd.Kfz.223 and Sd.Kfz. 260/261 was made respectively 550 and 493 units. All in All, from 1935 to 1944, the factory shops of the firms Horch, MNH and Weserhutte left 2371 machine of all modifications.
Military career of light biaxial armored cars began with the annexation of the Sudetenland of Czechoslovakia in autumn 1938. On 1 September 1939 in the army, there were about 1200 cars of this type.
The composition of the Panzer division on the average up to a 90 light armored vehicles, and about 60 of them were concentrated in the reconnaissance battalion. Even more had their divisions in the lungs. In the reconnaissance regiment of the 3rd light division, for example, was listed 121 armored vehicle.
Radiomaria Sd.Kfz.260/261 were used as staff vehicles communication link in the “regiment — division” and consisted on arms of the respective units in the compounds of all types.
By the beginning of operation “Barbarossa” in the German army, there were 961 armored car Sd.Kfz.221, 222 and 223. In conditions of Russian off-road very soon it became clear that light armored cars, despite the presence of two major bridges, have limited tactical mobility. By the end of 1941 on the Eastern front was lost 341 machine. Much more effective was their use in North Africa in the intelligence battalion of the 5th light division Afrika Korps.
During the war, 20 armored cars Sd.Kfz.222 and the Sd.Kfz.223 received the Bulgarian army. Armored cars participated in operations against Yugoslav partisans in the territory of Macedonia occupied by the Bulgarian troops. With the end of 1944 they were used in combat against German troops.
In 1938, Germany supplied China 18 Sd.Kfz.221 and 12 Sd.Kfz.222. These machines took part in the battles with the Japanese.
M. BARYATINSKY
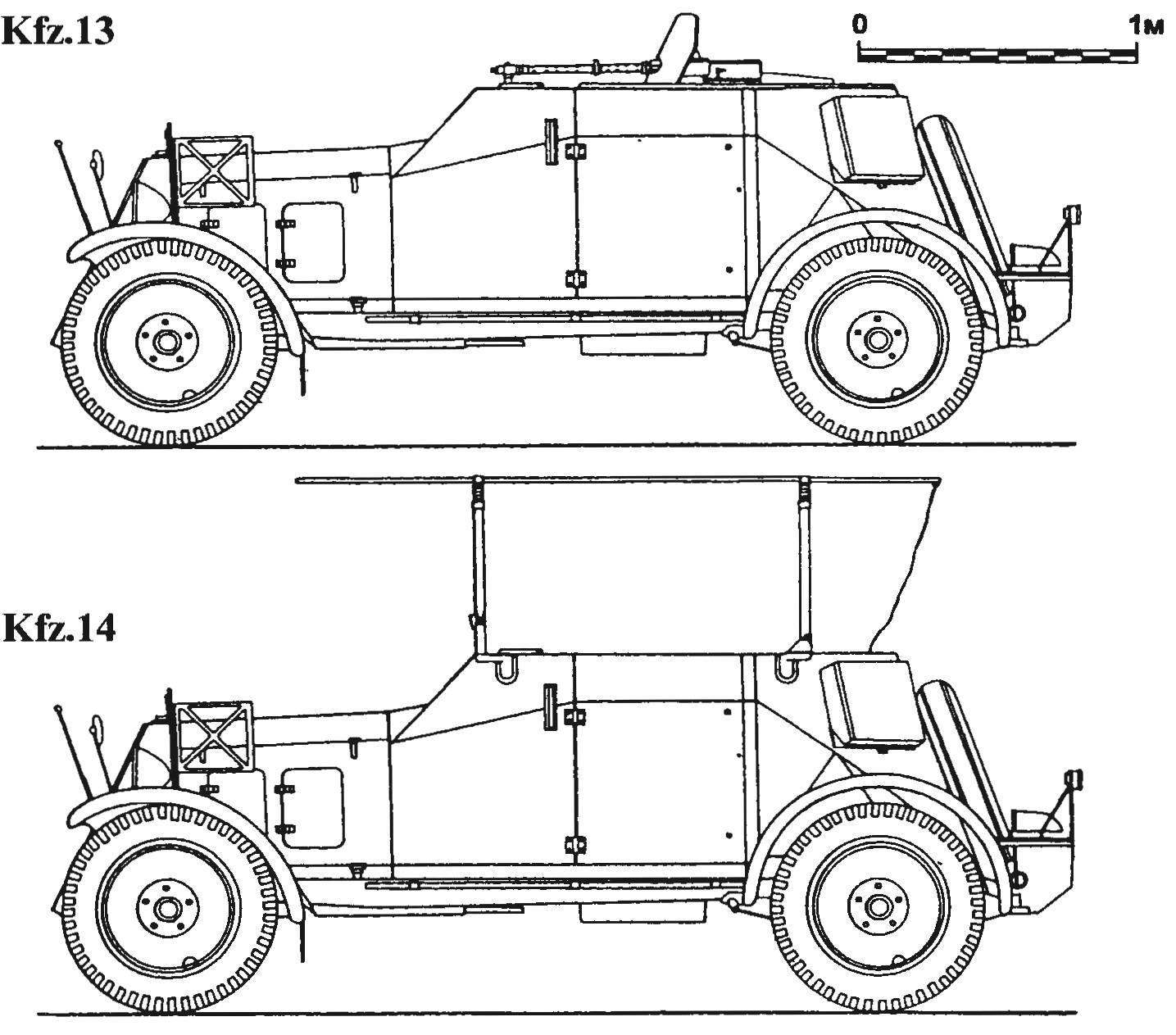
 the First German armored vehicle, created in the 1930-ies, was developed by order of the Supreme command of the Reichswehr on the chassis of the car Adler 3Gd. This rather primitive combat vehicle intended to accompany cavalry and intelligence. It had a welded open top hull of the 8-mm armor. Armament consisted of a 7.92 mm MG 13 machine gun mounted in the middle of the body behind the shield and having a limited arc of fire. Carbureted 6-cylinder engine Adler 6S power 60 HP at 3200 Rev/min dispersed heavy (2,1-t) combat vehicle up to a speed of 50 km/h. Armored car had rear wheel drive and steer front wheels, suspension on semi-elliptic leaf springs and hydraulic brakes. The crew of the armored car consisted of two people: the commander and the driver. Radio stations on the car was and the crews maintained communications via signal flags. As such, the armored car was accepted into service of the Reichswehr under the designation Kfz.13.
the First German armored vehicle, created in the 1930-ies, was developed by order of the Supreme command of the Reichswehr on the chassis of the car Adler 3Gd. This rather primitive combat vehicle intended to accompany cavalry and intelligence. It had a welded open top hull of the 8-mm armor. Armament consisted of a 7.92 mm MG 13 machine gun mounted in the middle of the body behind the shield and having a limited arc of fire. Carbureted 6-cylinder engine Adler 6S power 60 HP at 3200 Rev/min dispersed heavy (2,1-t) combat vehicle up to a speed of 50 km/h. Armored car had rear wheel drive and steer front wheels, suspension on semi-elliptic leaf springs and hydraulic brakes. The crew of the armored car consisted of two people: the commander and the driver. Radio stations on the car was and the crews maintained communications via signal flags. As such, the armored car was accepted into service of the Reichswehr under the designation Kfz.13.