The 1960s, often called a time of change. In this decade changed all the styles and fashion, presidents and General secretaries, and the Soviet Union over Khrushchev’s thaw and Brezhnev’s stagnation began. Varied and principles of automotive design — Empire-style, artsy-rounded turned into Gothic, sharp-faceted…
The 1960s, often called a time of change. In this decade changed all the styles and fashion, presidents and General secretaries, and the Soviet Union over Khrushchev’s thaw and Brezhnev’s stagnation began. Varied and principles of automotive design — Empire-style, artsy-rounded turned into Gothic, sharp-faceted… The first victim of the changes fell “Moskvich” — between the “four third” and “four hundred and eighth” ran the line of demarcation between two eras of automotive style. Next was destined to change the “Volga” — from the “twenty-first” “twenty-four”.
Cars Gorky automobile plant was originally intended for the officials of middle rank — factory Directors and the Secretary, military chiefs, and chief designers, heads of administrations and Deputy Ministers. A large proportion of the cars meant for taxis, well, and to purchase for personal use “m”, “Victory” or “twenty-first” “Volga” is not an outstanding citizen of our country was virtually impossible.
The car GAZ-21 “Volga” Gorky automobile plant was released in 1956. It was quite modern for its era passenger car, differed by a number of original design and design solutions, which, incidentally, was confirmed by a quite stable demand abroad. But in the early 1960s, he became significantly lag behind foreign models — both in design and construction.
Work on the creation of a new model to replace aging, “twenty-first” was launched in 1961 — a project Manager was appointed the leading designer of cars GAZ-A. M. Nevzorov, designers (now such specialists are called designers) — L. I. Tsikolenko and N. I. Kireev.
The car was supposed to produce a whole range of engines, which included upgraded from a four-cylinder GAZ-21, V-shaped six – and eight-cylinder and four-cylinder diesel. There was also an idea to bring to mind the automatic transmission, which initially tried to equip the “twenty-first” “Volga”. Subsequently, however, the idea of equipping the machine with automatic transmission, and a six-cylinder engine, the designers had to be abandoned, and a series of car went with two engine options — inline 2.5-liter “four” and 5.5-liter V-shaped “eight”, the latter produced a very small series as so-called “the escort” (escort high-ranking party and government people) or “catch-up” (KGB). Well, the diesel engines of foreign manufacture were installed by the factory only on special order, a small car export series.
As already mentioned, the creation of the “twenty-fourth” were in a period of change, so when a designer design the shape of the body of the new car designers “thrown” from the American automotive style of the late 1950-ies, with its peculiar fins and chrome moldings to a purely utilitarian with a suitcase-flat contours of the hood, trunk and roof.
From 1962 to 1965, the designers have created six full-size search models, which differed significantly in appearance. In 1965 the appearance of the car finally decided it had been approved at the highest level. Almost simultaneously completed the construction of the aggregate, and a year later was ready the first running prototypes.
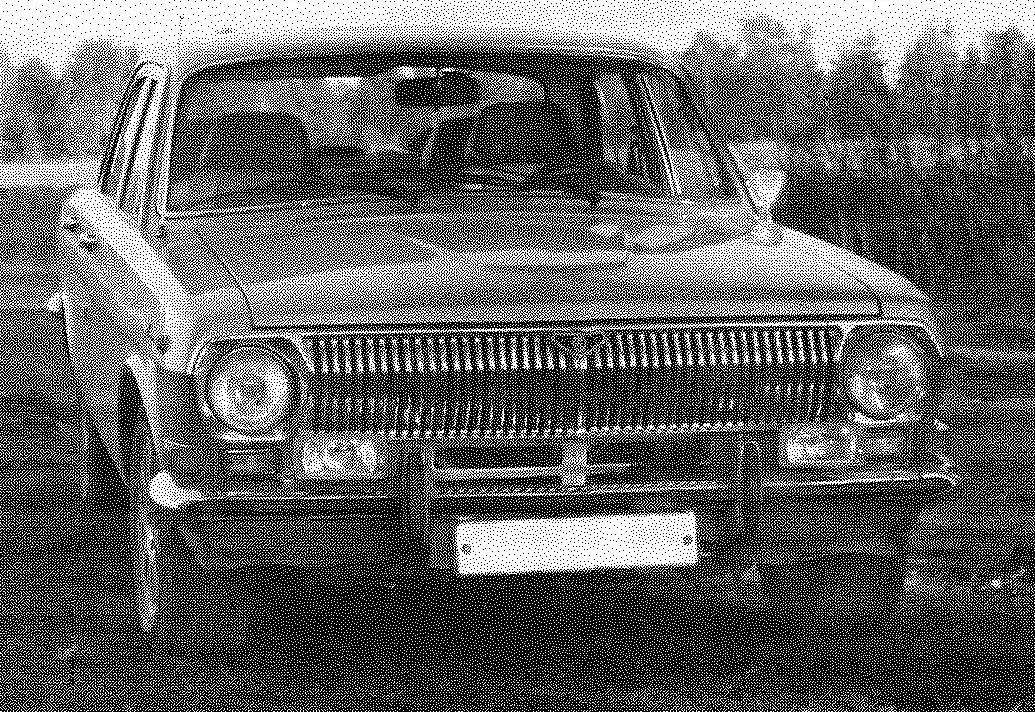

The car “Volga” GAZ-24.
In parallel with the vehicle’s design work was carried out on the preparation of serial production. GAZ-24 contain more complex aggregates than the “twenty-first”, “Volga”, which forced the workers to significantly increase requirements for the accuracy and quality of their production. By the way, for this purpose in 1962 was built the country’s first shop precision casting and running automatic line molding molding, in 1967, built the plants dies and moulds, and in 1968 the production plant transmission.
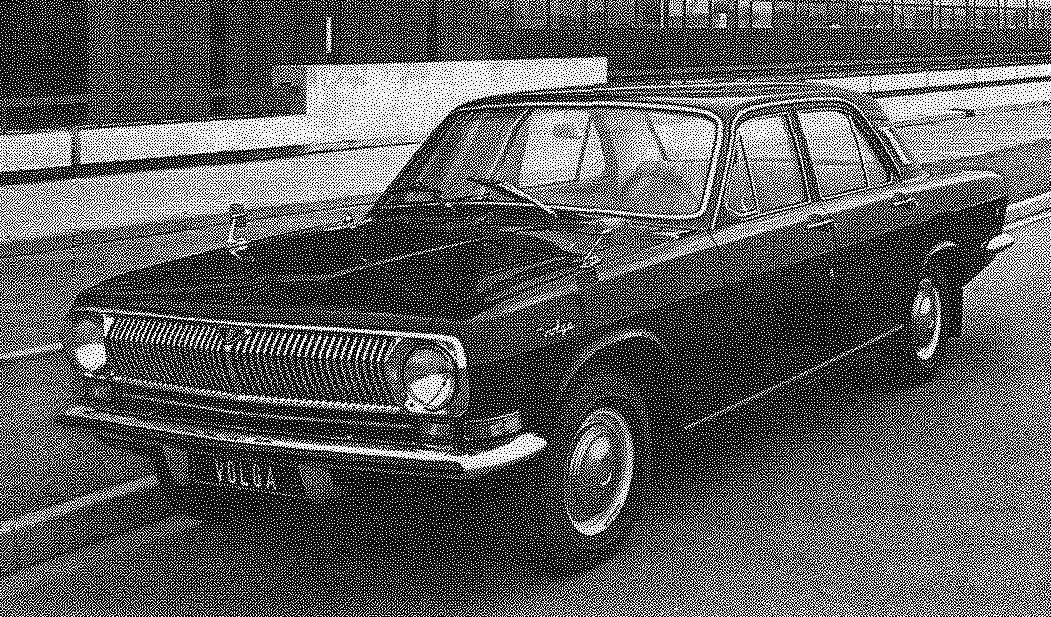
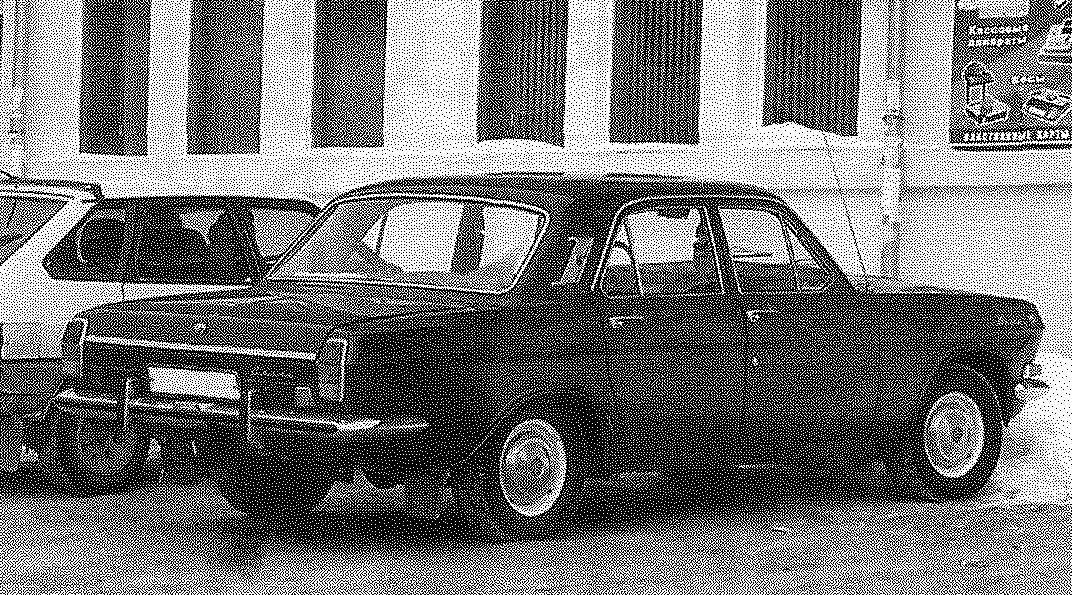


Car of the Gorky automobile plant GAZ-24 Volga. The picture shows the “front three quarter” — “Volga” the first model years with the rear view mirrors on the front fenders and bumper without the “fangs”; the picture “rear three quarters” — the car in later model years with the rear view mirror on the driver’s door and bumpers with the “fangs”.
The first experimental series of 32 vehicles were assembled in 1968 by-pass technology in 1969 so did another 215 machines, and in January launched the main conveyor. About six months lasted the simultaneous release of the 21st and 24th models, and on 15 July 1970 issue of the GAZ-21 was discontinued. Without stopping the production on it began to collect a new car — GAZ-24.
“Twenty fourth,” the scheme did not differ from the “twenty-first” — the same rear-wheel drive with front engine. The base of the car was larger than its predecessor by 100 mm, allowing to lower the rear seat cushion and out of the rear wheel arches. This contributed to a more free accommodation. The increase in wheelbase has led to more smooth running machine.
The body of the car — suspension, with welded thereto under engine frame. The rear fenders are fastened by welding, front — screw. The layout of the body has provided it with maximum commonality with the issue of possible variants of the car — sedan, station wagon, carriage, ambulance, taxi, etc.
It should be noted that the body GAZ-24 was different from the body GAZ-21 not only design, but also its design concept, which incorporates everything new that appeared in the industry during the period from 1955 to 1965. The design of the power elements of the body GAZ-24 was stronger than the GAZ-21.
The hood of the engine compartment — with front hinges, which was a system of levers; the hood was held down coil springs. Open trunk lid took almost vertical position and held therein with transverse torsion bars. By the way, by today’s standards, the trunk of the GAZ-24 was not ease of use. With his giant (0,7 m3!) the amount of use it was not too convenient to reach the front wall was almost impossible, but if you consider that “tilt wheel”, is mounted directly in the trunk took up a large proportion of its volume, and put in the trunk of something bulky was not possible.
The main difference of the body GAZ-24 GAZ-21 was the height of the old car was 130 mm higher. Accordingly, the new was lower centre of gravity (this increased its stability and control) and reduced millevoi section. The last parameter helped to reduce drag coefficient, making it possible to increase speed and reduce fuel consumption.
It is worth noting that with decreasing height, the designers have gone for a violation of GOST — the fact that the value neobosnovano driver zone ahead of the car was not supposed to exceed 8 m, and the GAZ-24, it stood at 9.5 m.
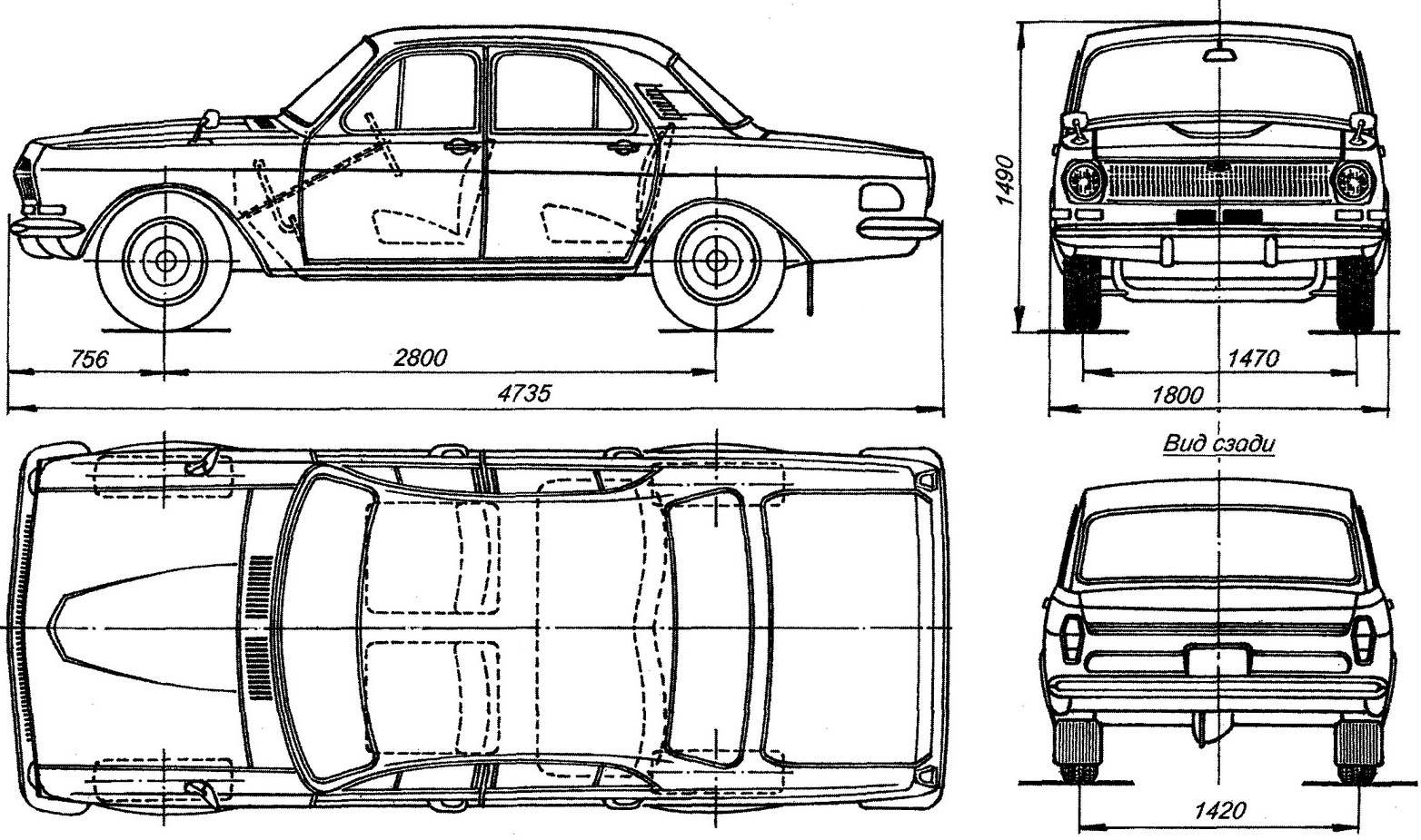
The geometric scheme of the car GAZ-24 “Volga”.
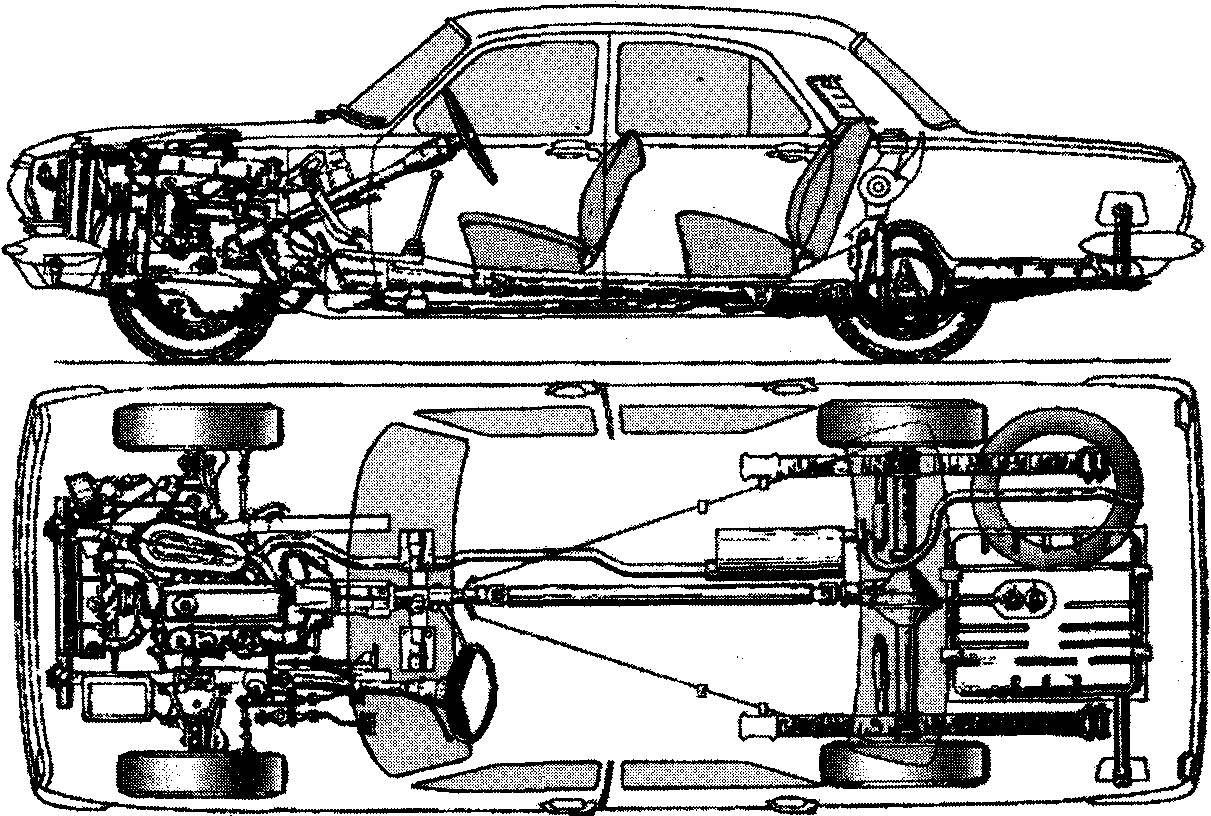
The layout of GAZ-24.
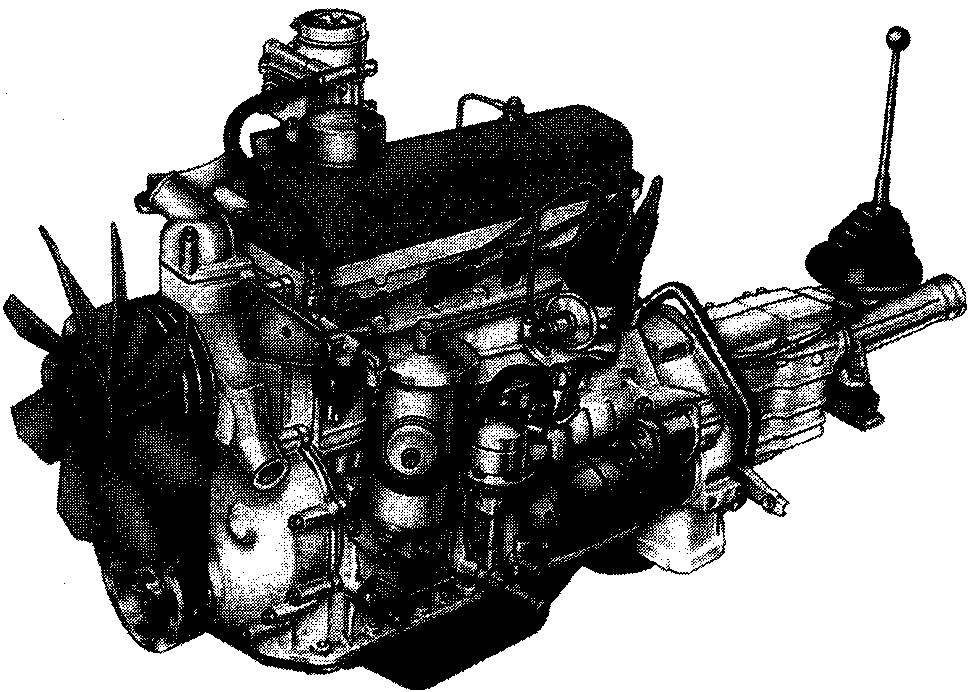
The engine GAZ-24 is an upgraded 2.4-liter engine from the “twenty-first” “Volga” with a capacity of 95 HP (taxi — 85 HP).
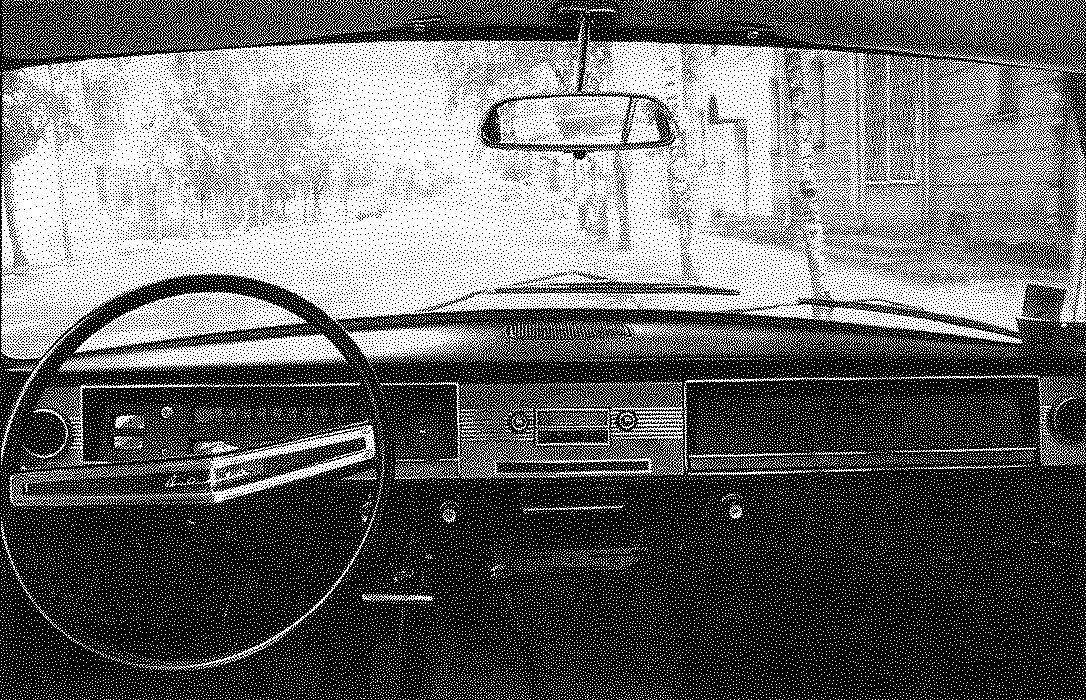

The driver’s workplace.
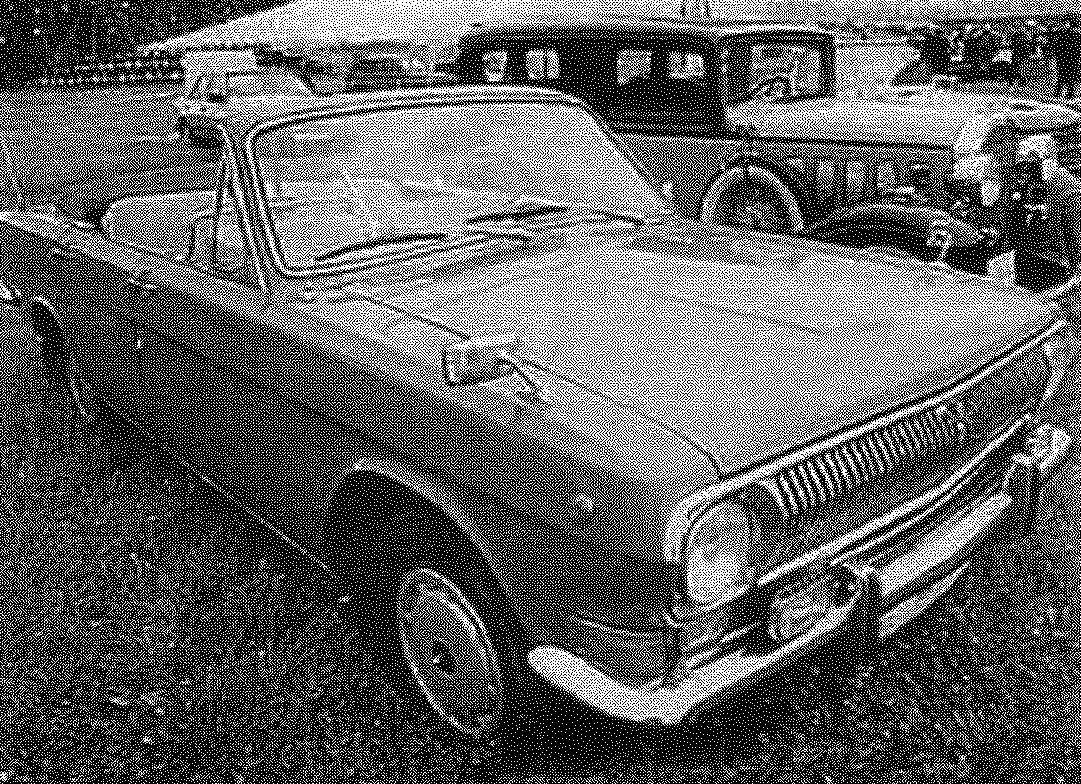

Convertible GAZ-24 was produced in small series for leaders of Russian military districts and the Warsaw Pact countries to receive military parades.
Despite the large wheelbase, “twenty fourth” “Volga” was 75 mm shorter in conjunction with increased rotation angles of the front wheels is slightly improved maneuverability.
GAZ-24 the first model years front mounted triple sofa, the back of which hides a comfortable armrest for the driver’s right hand. The speedometer on the cars produced before 1975, had a tape scale, while increasing speed at scale from left to right crawled the red bar. In addition to the machines until 1978 rear were separate from the tail lights of the reflectors, which later migrated to the tail lamps.
Among the important innovations, which “twenty-four” differed from its predecessor include a fully synchronized gearbox (the “twenty-first” first gear had no synchromesh), full-flow oil filter, the separate drive of front and rear brakes, servo brake system, samopodoben brake cylinders, telescopic shocks and a Parking brake with rear-wheel drive (the “twenty-first” “hammer” was the transmission). To all, although the number of points of regular injection was reduced three times (from 30 to 10), the front pivot suspension, leading its origin from the pre-war Opel Kapitan release 1936, still required regular lubrication.
It should be noted that the new “Volga” gearshift lever in accordance with the new trends was located on the top cover of the box.
Driveline consisted of a shaft with a pair of hinges, a sliding spline connection on the output shaft of the transaxle in the extension cord. This design ensures that vibrations and thus increased durability of the connection.
Rear axle — hypoid, lightweight, with detachable crankcase.
Rear suspension — leaf spring, with telescopic shock absorbers. Spring — asymmetrical, elongated, with the increased width of the leaves and reduced their number — this provides the best performance suspension and good lateral stability. On the back of the spring secured by means of conical rubber bushings.
Steering gear — rear-located steering rods. Joints track rod fitted with plastic liners, is not required in the operation of the lubricant. The steering mechanism is a globoid worm in a pair of dvuhgrivnevka roller, which are located in the aluminum crankcase. Steering wheel dvuhsvetnoe, with a deep wheel hub.
Brakes — drum, drum, with automatic adjustment of clearance between Shoe and drum. Brakes — hydraulic, separate for front and rear wheels.
Wheel — disc, stamped with a tire size of 7.00 — 14”.
The period of production “twenty-fourth” can be divided into three stages in accordance with the basic upgrades of the car.
So, the first generation cars (produced 1968 — 1977) the release process is continuously improved. The first few years of production left to fix various minor bugs — in particular, the rear view mirrors mounted on front fenders of the first production machines were inconvenient to use, so the right mirror was removed, and the left has moved to the driver’s door, installed new, more secure trunk lock, spring with a new profile sheets, the ignition unified with VAZ and ribbon replaced the traditional speedometer dial, as the testimony of the first was difficult to read due to fluctuations of the tape; on the rear roof rack installed Parking lights, switched at the exit of passengers etc.
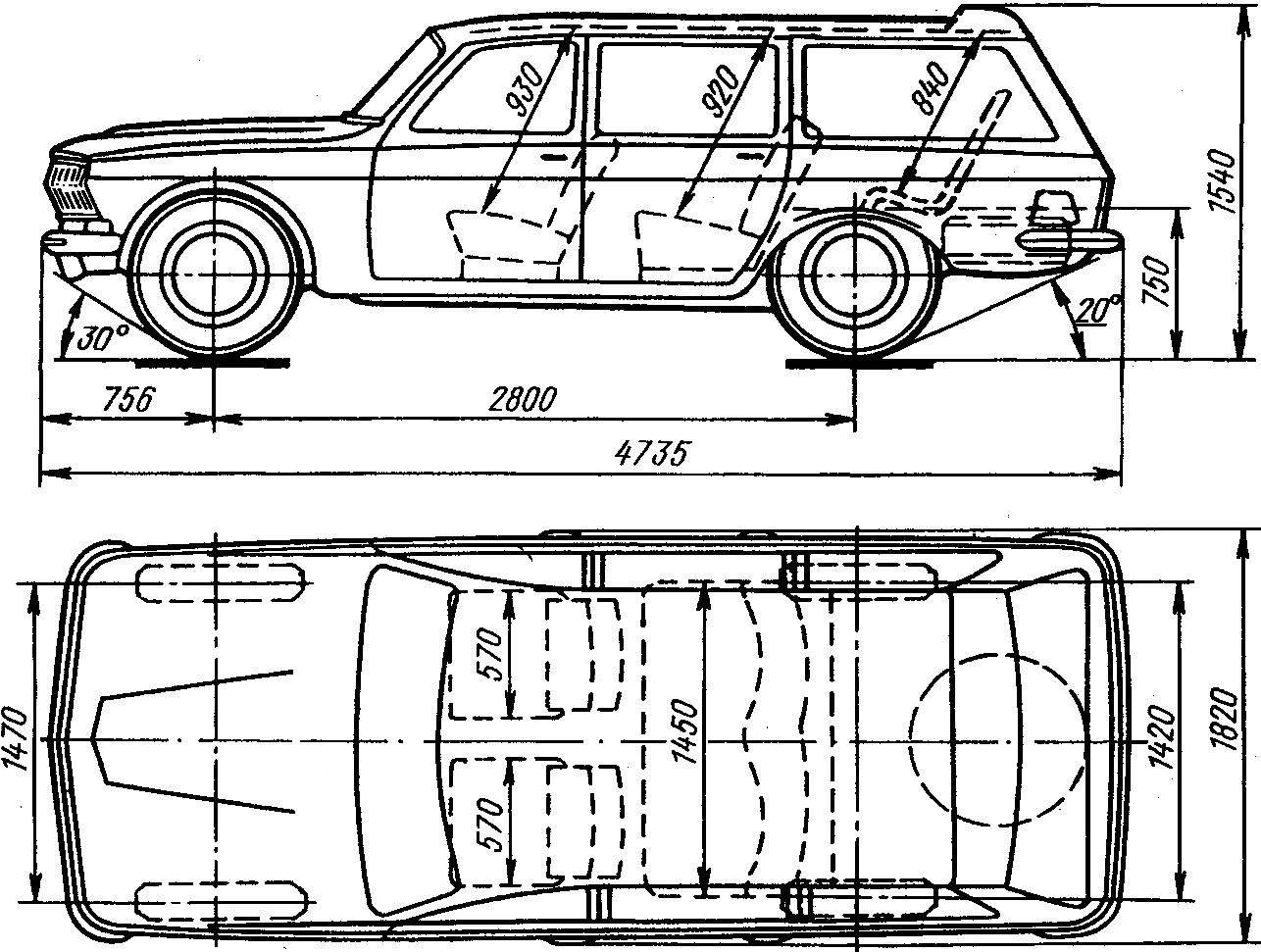
The principal dimensions of the car wagon GAZ-24-02 “Volga”.
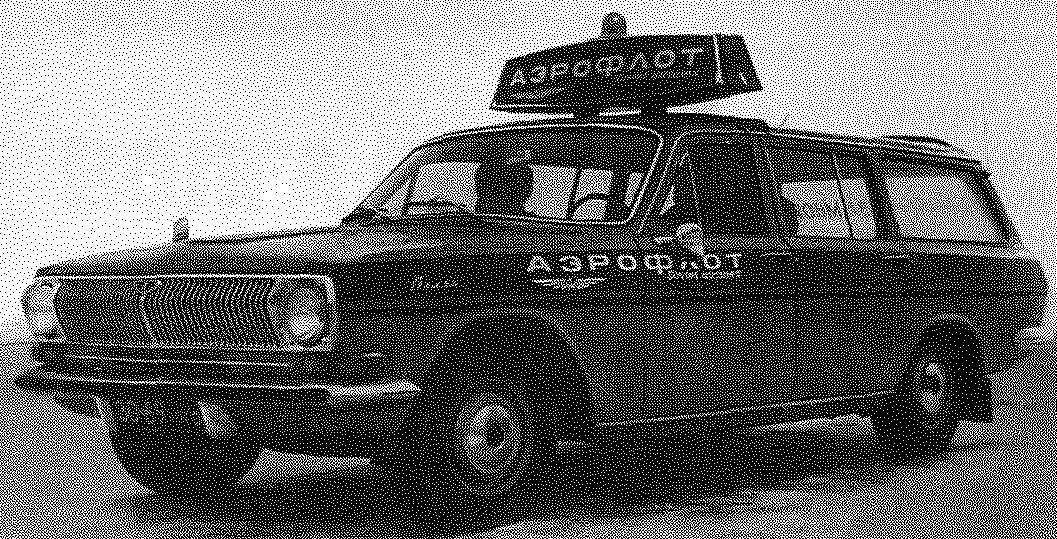

Universal GAS-24-02 — option to work at airports.
In 1977-1978 he was made the first serious modernization, the world saw the second generation of the GAZ-24. Car has got fangs on the bumpers, seat belts, fog lights, an updated instrument panel with new, fully black handles.
In this form the car was produced until 1985 when it was again modernized, this time more radical, which resulted in the GAZ-2410, which can be called the third generation of GAZ-24. In the same period, in 1982, the series launched the GAZ-3102 to the service of state institutions — the car was used the modified body, engine, transmission and suspension from GAZ-24. By the way, that GAZ-3102 became the ancestor of a family of vehicles produced by the plant.
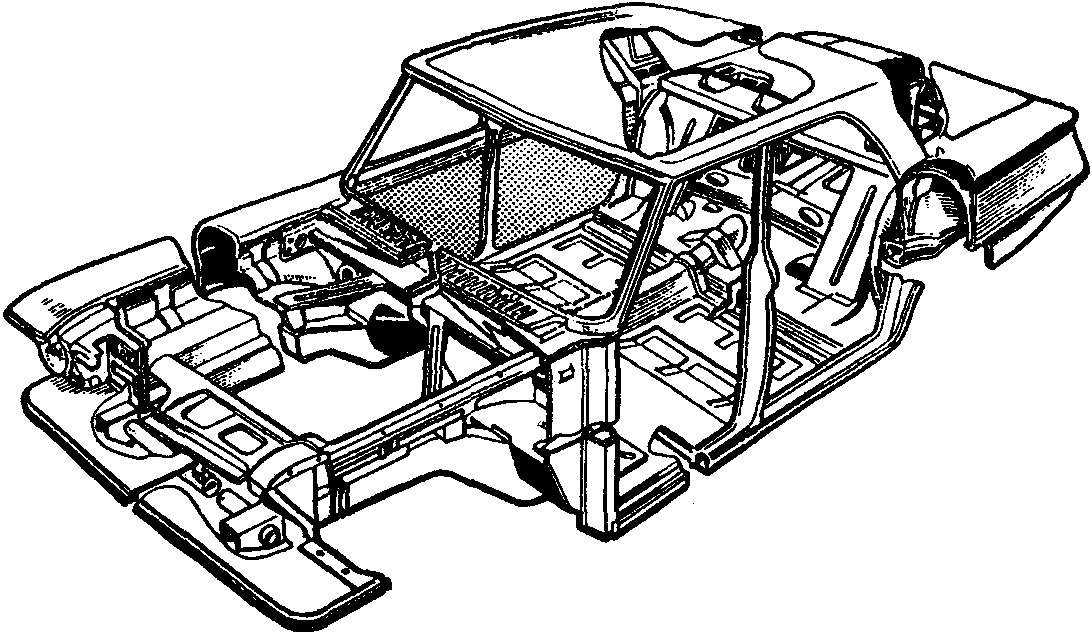
The frame body.
Despite a very sleek design, “Volga” GAZ-24 produces a very favorable impression. At the time of starting the serial production of the look of this car does not look outdated American counterparts of the same class and year were produced until the late 1970-ies. Quite harmonious proportions of a sedan with the flowing to the feed line side and gave it a dynamic and elegant appearance. In the car unexpectedly and quite successfully merged design delights with quite simple, angular lines and requirements of stamping production — almost all body panels were quite technologically advanced. The same combination of technology and design was observed during the mining of shape windshield and rear window — they have a minimum bending corresponding to the automotive fashion of the time, who were equally comfortable in their manufacture. By the way, for the first time in the domestic automobile industry a slight bend and had glass doors.
Brand differences in the new “Volga” became the swage line on the bonnet in the inlet and a stiffening rib on the trunk lid. The grille was almost the same as GAZ-21 — picture “whalebone”. Front turn signal and marker lamps made in accordance with European standards. European (in contrast to the “Volga” GAZ-21, where lighting was done in the us) looked and taillights with red brake lights, orange turn signals and white reverse lights. The machines first stage of a release the lights were three-piece with a separately mounted reflectors, but the reflectors moved to the rear lights. After 1977, on the front fenders were installed repeaters round shape.

In 1968, the Gorky automobile plant has mastered production of the GAZ-24 – Volga car of the second generation, which became the basis of all subsequent modifications of the automobile with the brand of GAS.
The door handles were shaped like a stirrup with a circular button of the lock — it opened when you press the button with your thumb. More on the new “Volga” appeared though safe, but not too easy grip handles, recessed flush with the door surface. Until 1978 the bumpers of the cars had a simple form with a rubber strip in the middle with light collision it has prevented damage to the chrome coating. On the bumpers of all cars manufactured after 1978, there was a rubber lining, but in 1985 they were removed due to frequent injuries of pedestrians.
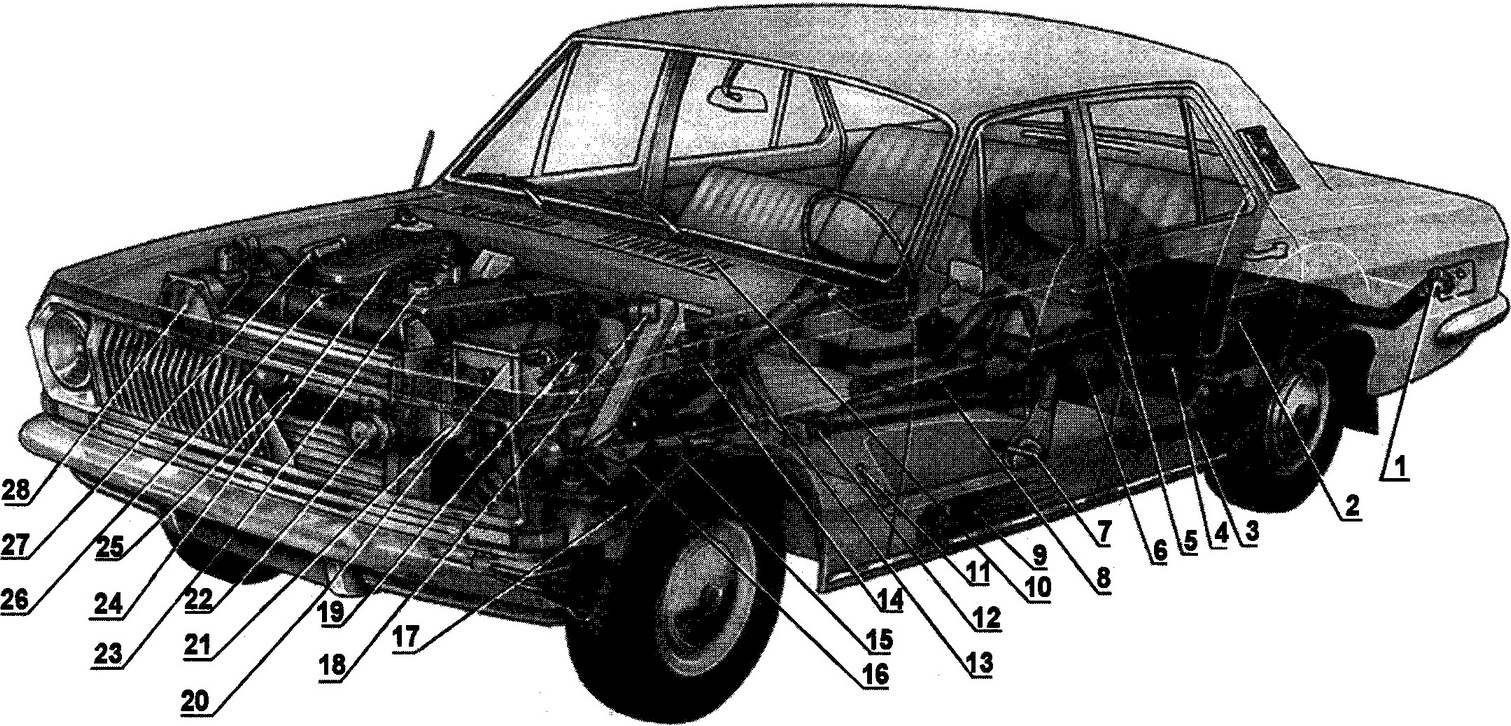
The main units of the GAZ-24:
1 —filler neck fuel tank; 2—fuel tank 3—spring rear suspension; 4—rear shock absorber; 5—spare wheel; 6—the back bridge; 7—the handle of adjustment of inclination of the backrest of the front seats; 8—damper; 9—spar body; 10, the air intake heater and blower; 11 —the lever of adjustment of the seat length of the cabin; 12—propeller shaft; 13—the master cylinder of the clutch mechanism; 14—brake master cylinder; 15—transmission; 16—steering mechanism; 17—spring front suspension; 18—the ignition coil; 19—the ignition distributor (distributor); 20—battery 21 —oil filter; 22—a sound signal; 23—oil filler cap; 24—air filter; 25—oil cooler; 26—a radiator of system of heating of salon; 27—voltage regulator; 28—hydrovac brake booster.
Car in the basic configuration, equipped with interior and external rear view mirrors (on cars of early releases — two on the wings, on cars of later release — one on the driver’s door) and electric antenna in the right front fender.
In addition to known modifications at the Gorky automobile plant in small batches to produce cars to order. In particular, at the request of the Committee of state security and the special purpose Garage, the factory designed the car GAZ-24-24 for work in tuples VIPs. The car had a body with a more powerful front spars, which were installed 8-cylinder V-engine from the “Seagull” GAZ-13. Maximum speed reached 200 km/h, and “hundreds” it accelerates for 12 seconds.
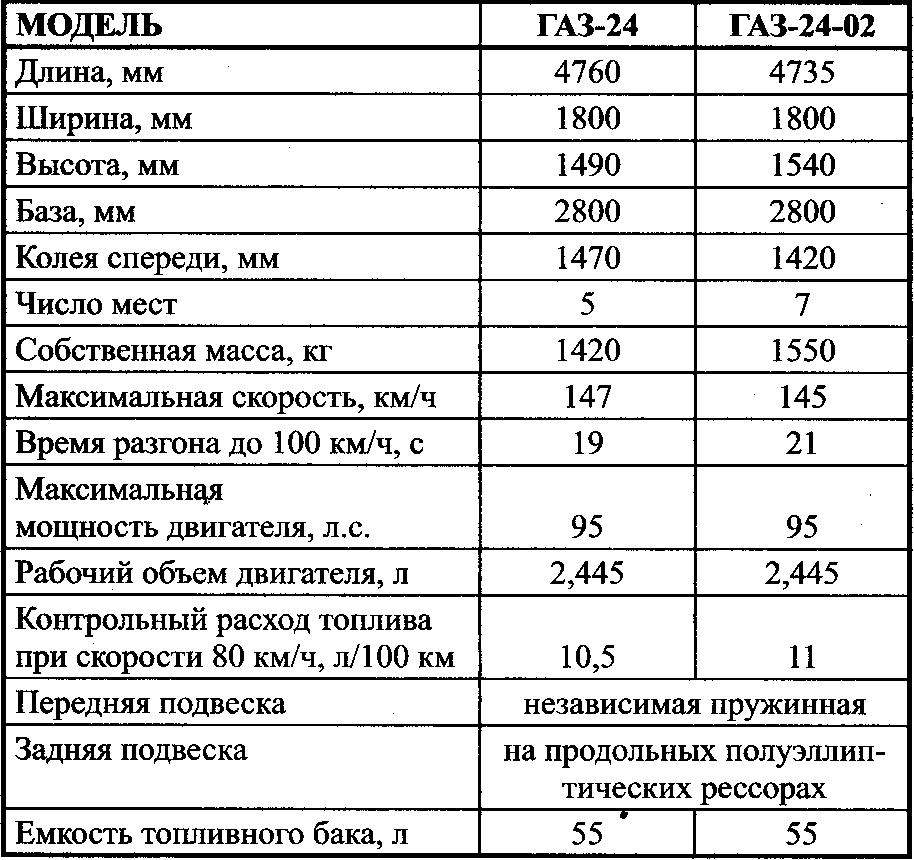
Technical characteristics of the car GAZ-24 and GAZ-24-02 “Volga”
Another little-known modification of the “twenty-fourth”, developed in the winter of 1973/1974, became the GAZ-24-95, a design which combined the comfortable body of “Volga” and all-wheel drive chassis of an army jeep UAZ-469. I wonder what the designers when it was created managed to do without a frame — with her all-terrain vehicle would have been much higher. We collected five specimens of this car, one of them came to hunting in Zavidovo, where he carried the main hunter of the country Leonid Brezhnev.
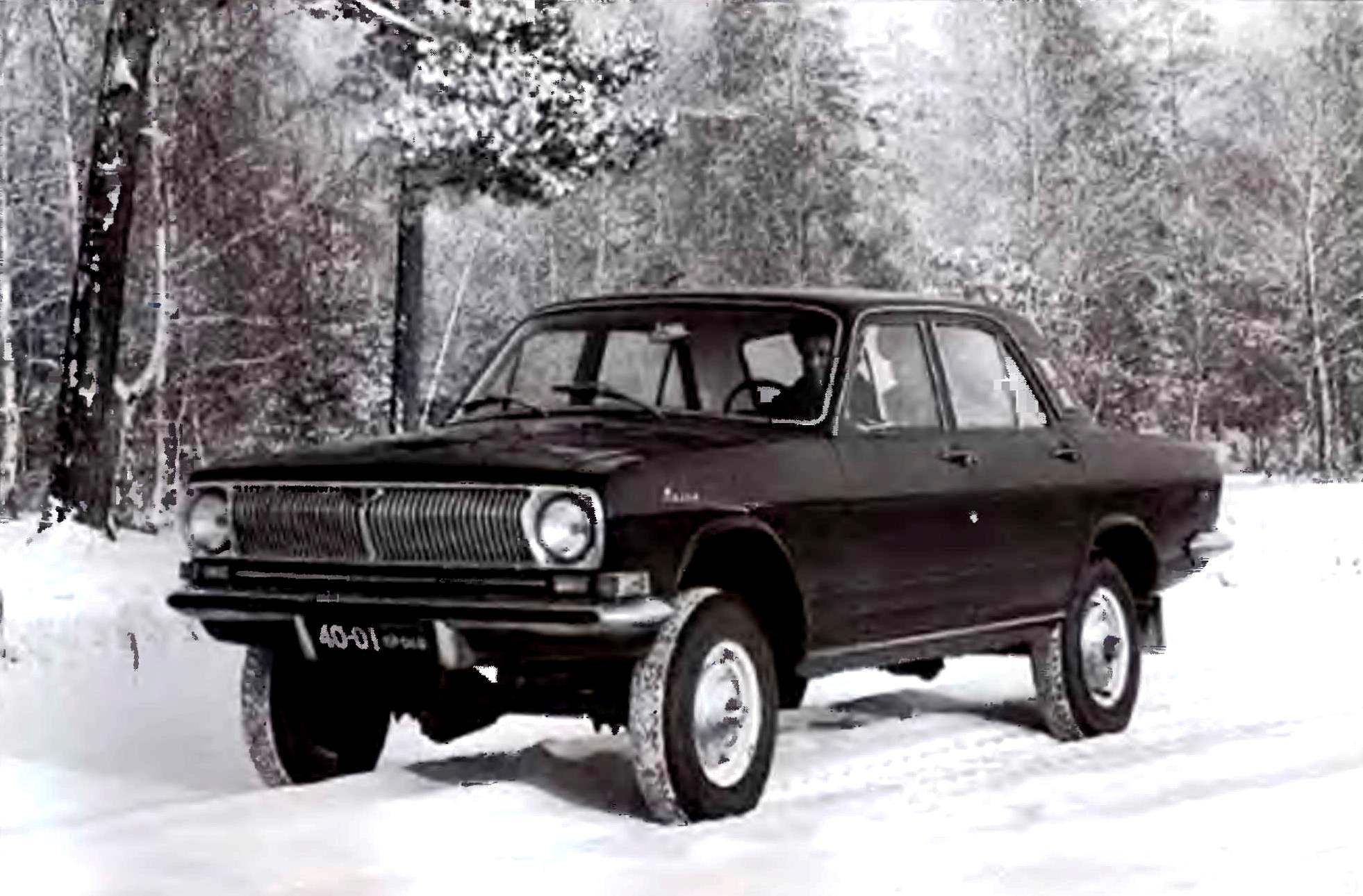

Comfortable frameless SUV GAZ-24-96 “Volga”, created using components and assemblies of the army’s all-wheel drive vehicle UAZ-469, was released ultra-small series of five cars specifically for “Headhunter country” by L. I. Brezhnev.
I. EVSTRATOV