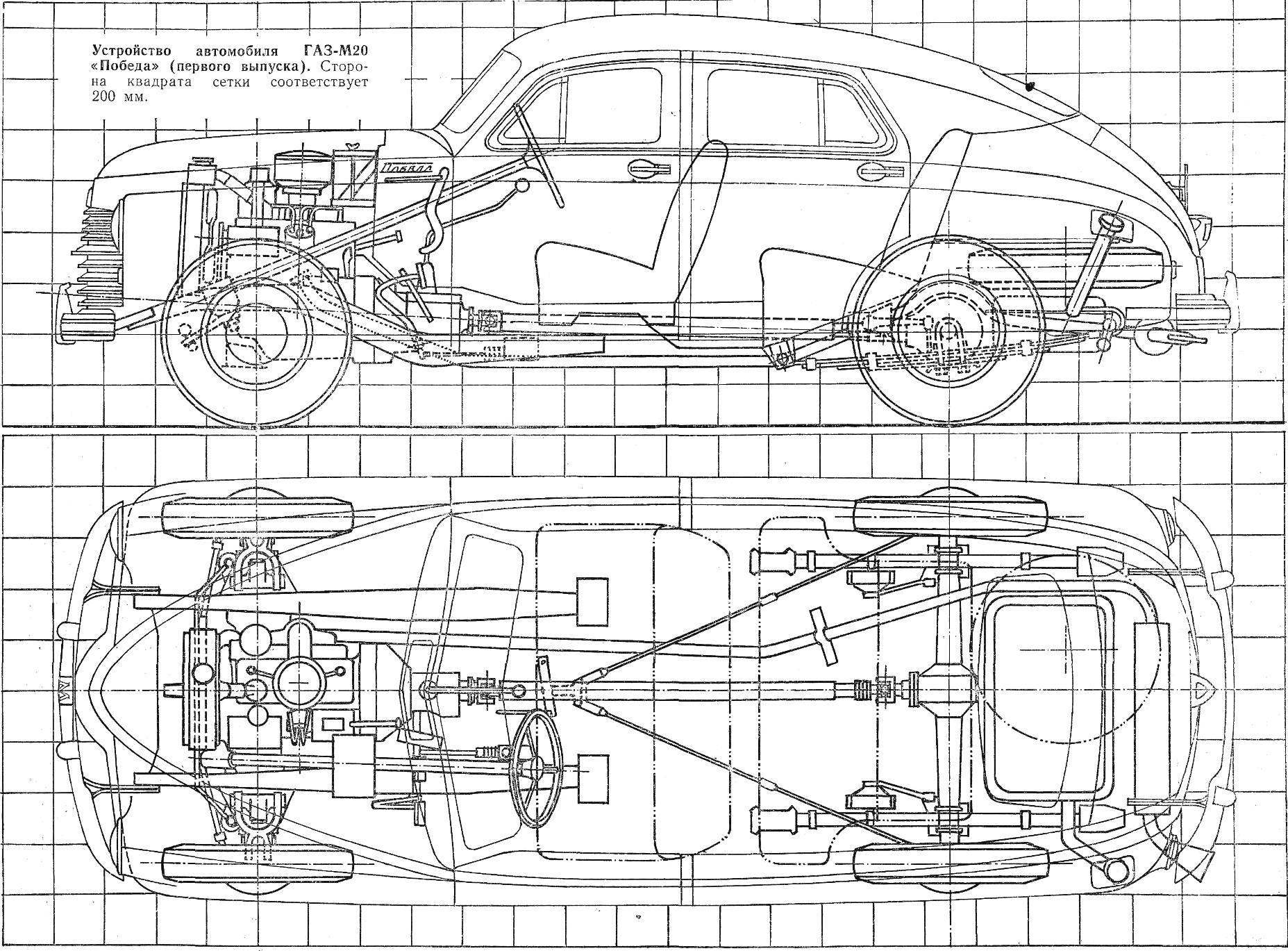
 Still there was the Great Patriotic war, the designers of the Gorky automobile plant began work on a new car that had to produce in peacetime. The design of the machine, which later became known as the GAZ-M20, began in February 1943 and in November 1944 was ready the first prototypes.
Still there was the Great Patriotic war, the designers of the Gorky automobile plant began work on a new car that had to produce in peacetime. The design of the machine, which later became known as the GAZ-M20, began in February 1943 and in November 1944 was ready the first prototypes.
After the war, on June 19, 1945, prototypes of the new Soviet cars had been seen in the Kremlin the leaders of the party and the government, and on 26 August there was a decision of the State Defense Committee “On the restoration and development of the automotive industry”. This document is envisaged to start at the Gorky automobile plant from June 1946 producing a new car.
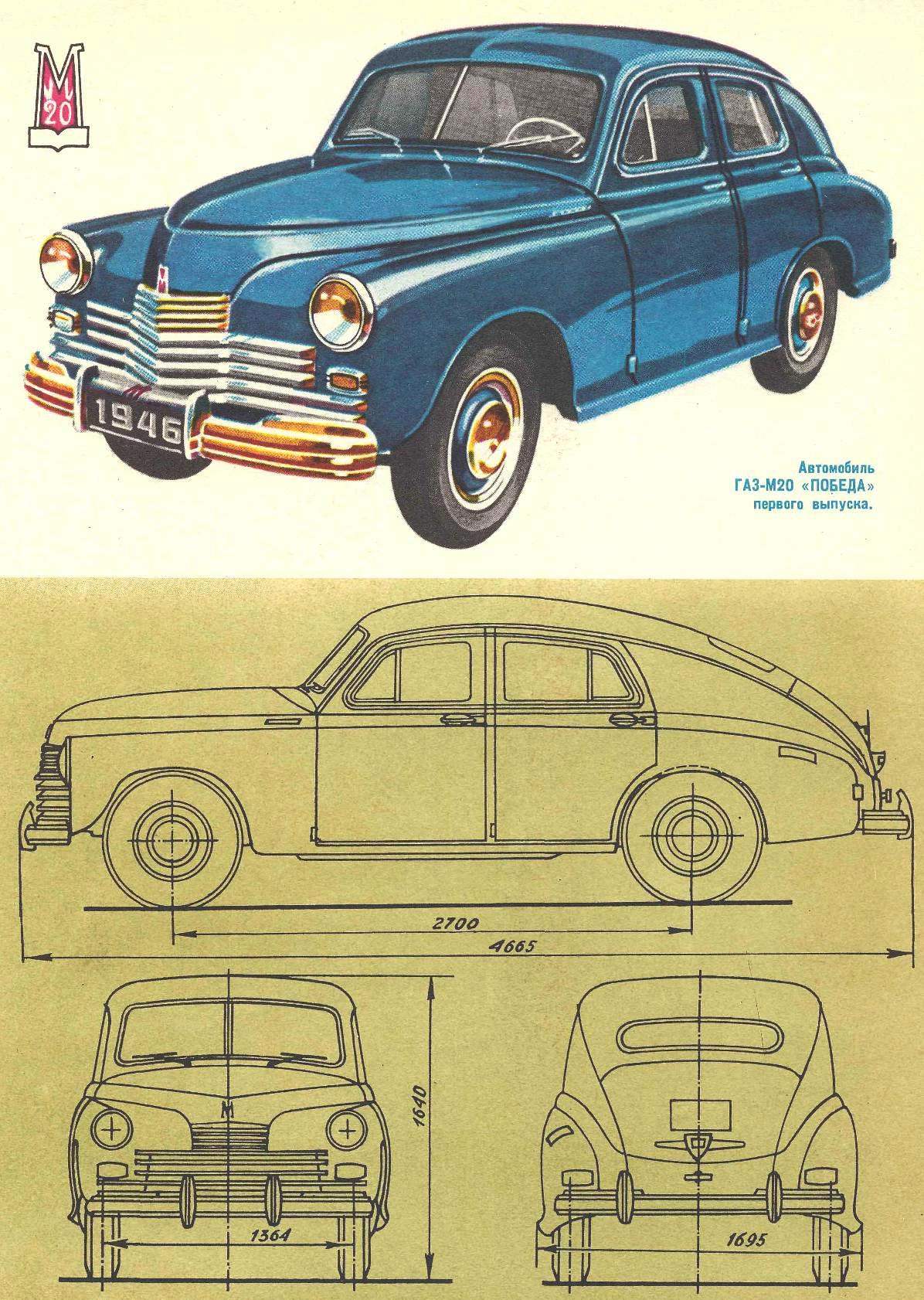
Among our cars she had a special role. She became the founder of the postwar generation Gorky cars, epitomising many significant design innovations. Therefore, it is in the original index system allocated your group numbers — cars GAS with an engine capacity of 3.5 liters and above had index numbers of the first ten (GAS-M1, GAS-M11), and the novelty is equipped with a motor with a volume of 2.12 L., received an index GAZ-M20. The word “Victory” was then on everyone’s lips, and no one doubt that it must be so-called streamlined four-door sedan, production of which began in 1946.
The design of the car “Victory” turned out to be promising. Independent front suspension, monocoque, the engine with a thin-walled liners of the crankshaft, the thermostat in the cooling system, and hydraulic brakes — all this for the first time found a use for the cars. Bearing body of “Victory”, first used in the domestic automotive industry, has established itself as a very solid and durable. Largely thanks to him, the car earned the love and respect of taxi drivers — people, especially people who appreciate good cars.
Speaking of the back of a GAZ-M20, it should be noted and its high aerodynamic quality. The streamlined vehicle is determined by the so-called coefficient of CX (“C-x”). The smaller it is, the more perfect aerodynamic against the body. The “victory” of this coefficient is of 0.34, while the cars that appeared at the same time, it was significantly higher.
From production cars only “Citroen-ДС19” had a more perfect figure — he has a CX of 0,31. But we must not forget that “Citroen” was released 10 years later Soviet car. And even in modern passenger cars with a distinctive sporty character, “Porsche 911” and “Saab-99” — this ratio is of 0.38 and 0.37, respectively.
Radiator shell from 1950 until 1955.

It looked like the radiator after 1955.
Good flow GAS-the M20 is due to the perfect form of his body, which for the first time in the history of world car industry did not have separate wings and running boards — the so-called “pontoon” body shape. It subsequently became widespread: “standard vanguard” of 1948 (England), “tatraplan” 1947 (Czechoslovakia).
First, the “Victory” was scheduled to build in two versions — with four – and six-cylinder engine. First, with a working volume of 2.12 l (82X100), developed power of 50 HP, and the second, with a volume of 2.85 l (82X90),-62 HP the maximum speed was, respectively, 105 and 120 km/h. preference is given to the four-cylinder version and a six-cylinder engine they decided to use the more spacious car, which later received index GAZ-12.
“Victory”, designed for 5 people, was at that time quite comfortable. Despite the fact that it was designed primarily for use in the city, “Win” was a good cross and won the recognition of rural drivers.
The new car is not only superior to their predecessors (GAZ-M1, GAZ-11-73) for strength, reliability, fuel efficiency and comfort, but was at the level of the best foreign cars in its class. For the creation of “Victory” and the development of its production by group of engineers of the Gorky automobile plant, headed by its chief designer Andrey Lipgart Alexandrovich was awarded the State prize.
“Victory” was in production from 1946 to 1958. Early modification of the GAZ-M20 is different from the external cladding of the front end. She was a “three story”: three short at the top “mustache”, then three longer ones and, finally, below are two of the longest, goes under the spotlight.
In 1949 was upgraded machines: larger gear ratio of the rear axle, changed the location of the muffler, lowered to 50mm rear seat cushion, improved carburetor, clutch, rear springs, installed the heater body at the same time change facing front end — it became a “two story”, while maintaining the total number of horizontal bars. Since the 1950s, the car found a new gear box. Replace the old with the shift lever on the floor, gears and shafts, borrowed from the pre-war “emka”, new box, also three stage, but are on the wheel, the gear shift lever and synchronizers on second and third, as they said, “speeds”.
The second major modernisation was carried out in 1955. She brought a power increase from 50 to 52 HP, improved carburetor, thermostat, water pump, front wheel bearings, steering gear. Simultaneously, the increased diameter wheel brake cylinders, and the other was the design of the instrument panel, the car has received a more beautiful steering wheel ring horn button and radio as standard equipment. And to streamline the “Victory” (she was given the index GAZ-20V) can be easily recognized by its appearance, the place is two story facing the front of the body took the grille completely different shape, with a massive “inflated” with decorative moldings. Simultaneously with the front bumper gone was the jumper wire that connected his “fangs”, and the front wing has gained a sanitised form. Thus, in 12 years, “Victory” was twice modernized.
Along with the five-seater four-door sedan, factory produced with
1949 to 1953 modification of the car with a body “convertible”. Because “Victory” has been applied to the bearing body, that is, simultaneously performing the functions of the frame and all bearing assemblies of the machine, one of its main power elements is the roof and sides. Therefore, the creation of open modifications on the basis of a passenger car with a monocoque body presents certain difficulties.
That’s why “Victory” with a body “convertible” saved stiff sidewall, covering the doorways. The lack of a rigid roof compensated by adding different kinds of amplifiers. As a result of “convertible” was on of 35 kg heavier than a sedan, due to the presence of the canvas top has somewhat deteriorated the flow and, consequently, decreased (from 105 to 100 km/h) maximum speed increased (from 11.0 to 11.5 l / 100 km) average fuel consumption.
In addition to the serial versions of “Victory”, there were numerous varieties of this wonderful machine. In 1948 born prototypes of the GAZ-M20 with a modified appearance: a different design of the front part of the body, the other wings, well-defined trunk instead of the sloping “back”, the wide rear window. Around the same time in the US (automotive Research Institute) for “Victory” designed and built experimental models of the automatic hydromechanical transmission of the US-D2. Specialists of the Institute in 1952 and has developed the option of a more powerful engine for “Victory.”

Racing car GAZ 1951, built on the basis of units of “Victory”.
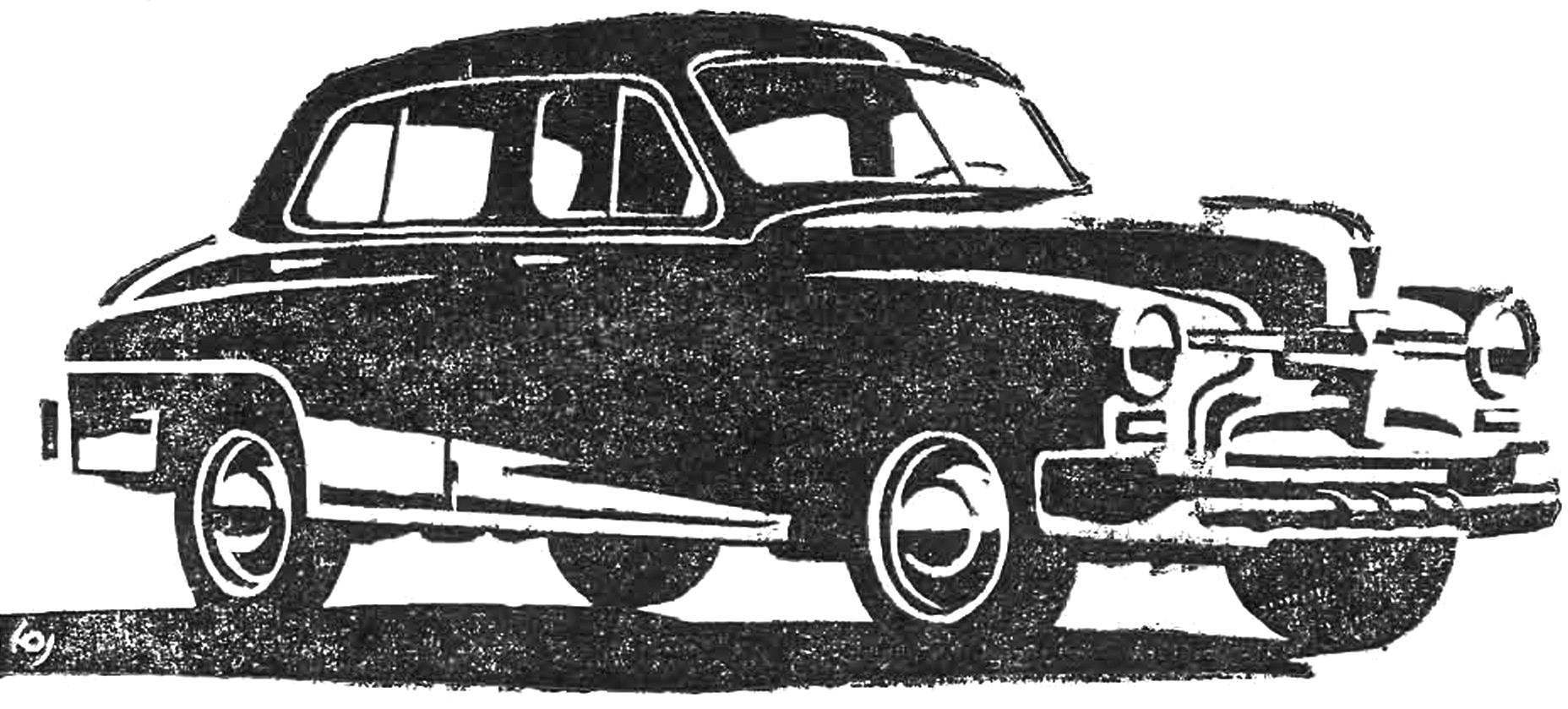
Upgrade option “Wins” (1948).
As you know, the car was Nizhnekamsky engine. The transition to the position of the valves in the cylinder head promised a gain in power, but required a major overhaul of the whole engine. Therefore, the US experienced motor in the head was located only inlet valves and the outlet remained in the same place. This engine with displacement increased to 2.5 liters and two carburetors developed capacity of 91 HP and was installed on the car prepared for racing.
And if we are talking about races, not to mention two cars, built on the basis of the “victory” of Gorky automobile plant. First built in
1950 year, differed from the production model closed double a streamlined body. The machine, named “Pobeda-Sport”, equipped with uprated to power 70 HP engine, weighed 1,200 kg (that is 260 kg lighter than the standard) and developed a speed of 160 km/h On it, the factory test drivers M. Metelev and V. Rodionov became the first Champions of the USSR in Motorsport.
For the competition of 1951, the GAS prepared a new machine with more perfect in form cigar-shaped body and tested units of “Victory”. Engine GAZ-M20 had increased to 2.49 l working volume, and a combustible mixture is supplied to its cylinders via a supercharger. As a result, the power increased to 105 HP, and “GAS-torpedo” (the name of this car weighing 1100 kg) achieved a speed of 191 km/h .
The experience gained in racing, not in vain. When in 1956 the plant began production of the “Volga”, the first of its kind, GAS-М21Б and GAS-М21Г was “paradowski” Nizhnekamsky motor with a displacement increased to 2.42 l (88X100), and a power of 65 HP Generally speaking, the engine of “Victory” have a long life. It was used on light truck UAZ-450, “jeep” GAZ-69.
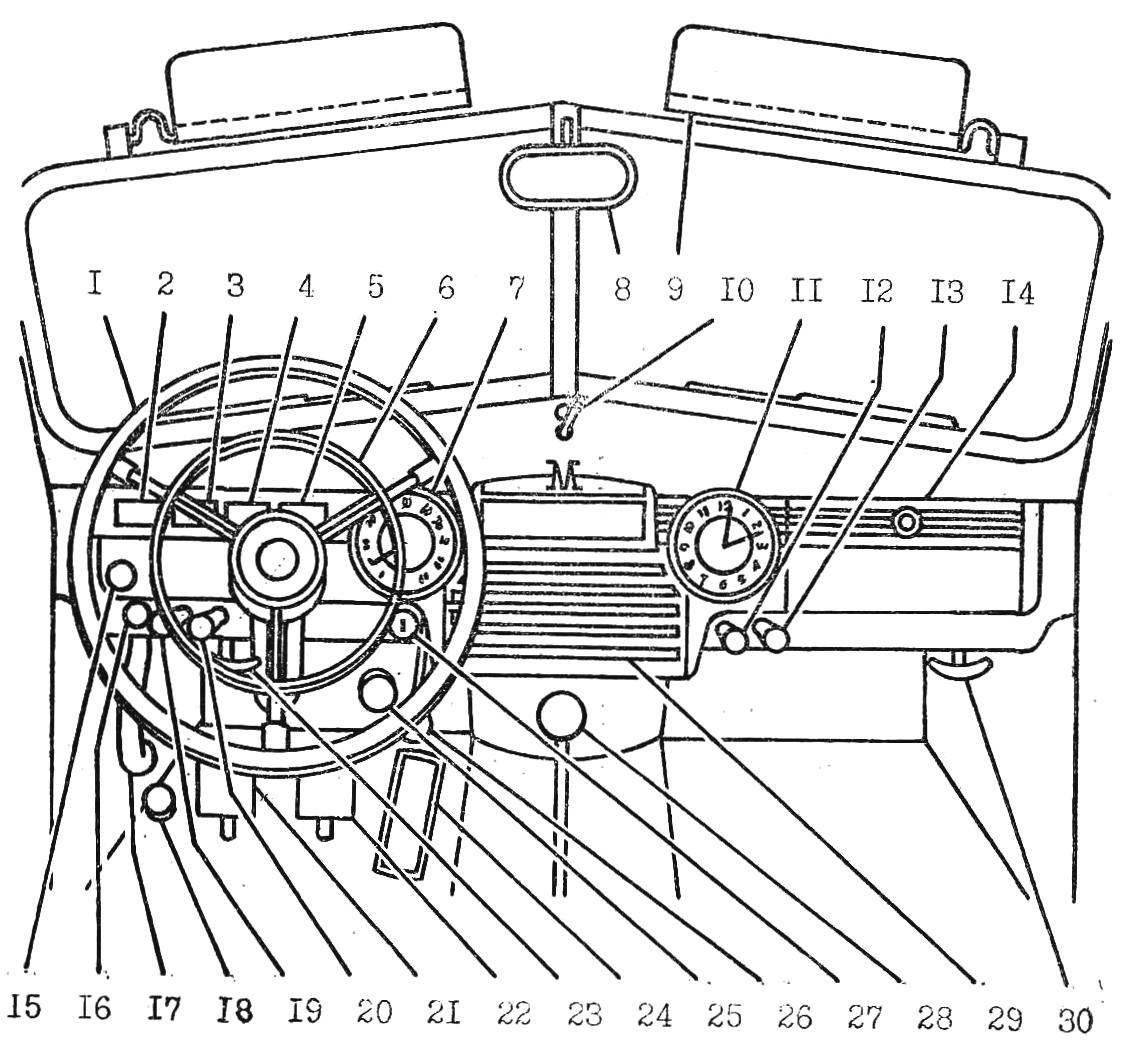
Controls and instruments car GAZ-M20 “Pobeda” (the first issue):
1 — steering wheel 2 — ammeter, 3 — level indicator fuel tank, 4 — temperature gauge-water, 5 — oil pressure indicator, 6 — ring of the audio signal, 7 — speedometer and odometer, 8 — mirror, 9 — sun visor, 10 — signal switch turn, followed by a switch of a wiper 11 clock, 12 — button choke control carb (“choke”), 13 — electrostatically, 14 — glove box, 15 — control lamp of a manual brake, 16 — regulator of heating, 17 •— the Parking brake lever, 18 — foot light switch, 19 — Central light switch, 20 — button control the throttle (“gas constant”), 21 — clutch pedal 22 is a brake pedal 23 — arm grille, 24 — accelerator (gas pedal), 25 — crank vent valve, 26 is the starter switch on, 27 ignition switch, 28 — shift lever (for later releases located on the steering column), 29 — place the radio (on vehicles the first release was not installed), 30 — the handle of the hood lock.
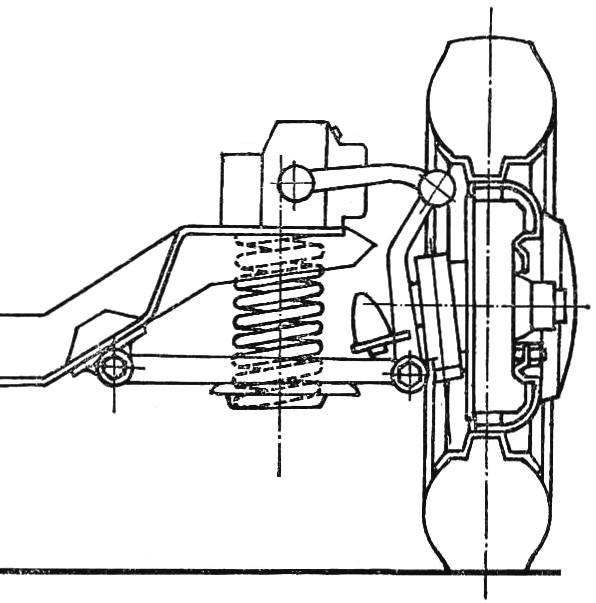
Front view of front axle and suspension, partial section of the wheel (circuit).
And indeed the “Victory” live long. And not only in the form of cars-veterans, surviving thanks to the efforts and care of their owners. Since 1951, it began to produce in the Polish people’s Republic on the FSO plant in Warsaw. Gave her the name “Warsaw”.
“Warsaw” has received over time more modern overhead valve engine with 70 HP., changed the shape of the front and rear parts of the body, decreased from 16 to 15 inch diameter rims, but the car is still (until the end of production in 1973) has retained inherited from the GAZ-M20 strength, endurance, durability.
“Victory” has received appreciation not only in Poland. Thousands of machines of this brand have successfully worked in Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria, Romania, Czechoslovakia and other countries. The British magazine “the Motor” in 1952 noted that “the car exclusively Russian…”, “designed primarily for reliable performance…” and that the Soviet machine is a fun and practical car.
When you will undertake the preparation of the model of “Victory”, it is necessary to keep in mind that cars 40-ies and 50-ies had body panels which were attached to a significant curvature. Therefore, when modeling it is very important to repeat the nature of the curvature of the surface on a particular area of the body. If models of cars 20-30-ies of paramount importance for the accurate transfer of small parts and details, then “Victory” and its contemporaries to the forefront the need to reproduce the shape of the body.
This task in relation to the car GAZ-M20 is facilitated by the fact that the streets more often “victory”of the veterans, and there is always the opportunity to “spy” and sometimes need to photograph detail. Remember, however, that the owners of these vehicles often use different “alien” details to how they seem to make my car different. Radiator shell: bumpers, tires, wheels and their hubcaps, headlights and taillights, different decorations are the most frequently encountered foreign elements.
The “Victories” at the bottom of the front wing, both doors and in front of the rear wing along the sill was a few blurred the shape of the edge, as if a scar from a bygone history of the footrest body. This edge is characteristic of the machine, and it is necessary to carefully and accurately complete. Since we are talking about the front and rear wings, we advise you to pay attention to the fact that their lower edge has a very small radius of curvature; from a distance it even seems that both the front and rear fenders underneath, just cut on the line.
Contact details of external appearance of the body. Shiny (chrome) parts were relatively few: bumpers, trims the radiator grill, bezels, headlights, sidelights and tail lights, door handles, lid locks on the left and right front doors, the inscription “Victory” on the side of the hood and decorative frame, covering both Windows on the side wall of the body. No windshield, no rear nor side Windows had their own brilliant decorative frames. Housing licence plate light painted in body color. Of course, the wheel covers were chrome.
Interesting feature. On machines manufactured before 1950, on the front and rear bumpers were in their grooves applied red stripes. Later they began to do. By the way, on the bumper. Front until 1955 had a jumper wire between the “fangs”. She disappeared with the advent of new veneer the front of the body.
Now, focus on a few small but important in the manufacture of the model details. On the upper rear of the left wing provided the removable cover over the tube of the fuel tank. Front windshield is sliding ventilation hatch. And in the front and rear door mounted rotary air vents. All these details you can perform opening.
“Victory” as it is known, was the last domestic passenger car exterior hinged doors. She is left nesaratnam inside the bottom loop that it would be good to show on the model. If you take a car model first edition, keep in mind that the flat tip of the exhaust pipe was located at the left end of the rear bumper, and the muffler was placed between the gas tank and rear bumper. On machines later releases muffler placed under the body, closer to the front right door, and the tip of the exhaust pipe moved to the right end of the rear bumper.
The license plate on the “Victories” was located vertically above the lamp, lit it, and protrude above the surface of the body.
For production of a model it is important that the color. Serial “Victory” was painted in blue-green, dark beige, cherry color. At the taxi along the waist line from the front was a strip of black-and-white checkered, which ended roughly above the end opening to the rear wheels. Moscow taxi “Victory” had a two-tone color: engine hood and roof — milky color, and the rest of the body is dark gray. Since 1949, in the upper corner of the windscreen has a green flashlight.
L. SHUGUROV



