 In the late 1940’s-early 1950-ies in the Soviet Union developed several aircraft guided missile of class “air—air”. The actual results achieved by the designers who created the missile RS-1-U. Their work culminated in the adoption of the interceptor MiG-17ПФУ, armed with brand new weapons. (For more on this rocket in “M-K” No. 4, 2006).
In the late 1940’s-early 1950-ies in the Soviet Union developed several aircraft guided missile of class “air—air”. The actual results achieved by the designers who created the missile RS-1-U. Their work culminated in the adoption of the interceptor MiG-17ПФУ, armed with brand new weapons. (For more on this rocket in “M-K” No. 4, 2006).
Work on the missiles under the open factory codes CMM and SB-32, begun in KB-1 —the parent organization for the development of anti-aircraft missile system s-25, passed organized on 26 November 1953 at the Khimki branch of the Special design Bureau No. 2 of the Ministry of medium machine building of the USSR. Priority OKB-2 was the development of missiles for a new anti-aircraft missile complex s-75. December 10, 1953, the chief designer of OKB-2 was appointed P. D. Grushina, who tried to use scientific and technical groundwork for the transferred missiles to solve the set tasks. In particular, he instructed the Dmitry L. Tomashevich, who led the work on CMM (future RS-1) to CB-1 from the beginning, to prepare a technical report on possible directions of further development and improvement of products of this class. The relevance of this work due to the fact that the product CMM is designed to destroy targets, such as subsonic bombers Tu-4 and Il-28 subsonic fighter-interceptor MiG-17ПФУ and Yak-25K, at the same time in the United States and the Soviet Union began full-scale work on supersonic aircraft.
A few months a detailed report “the Optimal characteristics of the ammunition class “air—air” was ready. The main conclusion of the report was the fact that the main characteristics of CMM correspond fully achieved by the time the level of development of aviation and rocketry. At a meeting held by the chief designer for the consideration of the report D. L. Tomashevich, their opinions about the prospects of the operations sold. Summing up, P. D. Grushin accepted a compromise: the work of CMM in its current form to continue with the implementation of tactical and technical requirements for the missile; at the same time, based on the perspectives of the development of jet aircraft, to start developing a CMM on the basis of a new missile with improved performance, allowing its full use for supersonic fighters. Some time later, D. L. Tomashevich went to work at KB-1, while in the years 1954-1967 he taught at the Moscow aviation Institute, where he produced a generation of aviation professionals for unmanned aerial vehicles. In MAI he defended his doctoral thesis, became Professor, and in 1969 one of his works was awarded the State prize of the USSR.
After a meeting with P. D. Grushina design Department of OKB-2 started development of promising missiles “air—air”, which received over time the industry designation TO-5M, and for CMM preserved—K-5. The chief designer of the missile was assigned I. I. Popov. Initially, the work was carried out in a proactive way: to conduct full-scale development was required to define and justify the main features of the claimed future missiles, to select the subcontractors, estimate the cost of execution of work and all this linked to a planned system of farming in the USSR.
By the fall of 1954, the appearance of advanced missiles K-5M has developed. The main ideas behind D. L. Tomashevich and tested during the flight tests of the K-5 survived. Remained unchanged the principle of guidance—the”three points” ravesignal lines formed by the conical scanning airborne radar fighter-interceptor and aerodynamic scheme”duck”. At the same time, with a slight increase starting weight and dimensions, given the new conditions for the use of the upgraded missile, managed to improve key tactical flight characteristics of the product. The effectiveness of combat units (CU) increased by increasing its mass and the amount of explosives, be adjusted to the contours of the compartment of military equipment; reduced the opening angle of the fragments; in the end, the radius increased by half. To increase maneuverability and maximum height of application of the increased wing area and size of the rudder, as a result the maximum available load has increased in two times—up to 18 units. Most potjazhelevshie launch range of the missile was provided by the increased weight of solid fuel, capacity of the cylinder of pneumatic system and on-Board power supply.
At the end of 1954 in the Soviet Union, it became known that in the United States put into service the missile of class “air—air” AIM-4 “Falcon”. This contributed to the fact that similar works by the country’s leadership began to receive more attention, and New year’s eve of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR adopted a joint resolution on the development of several missiles “air—air”; K-5 K-6 was created by the cooperation among enterprises, headed by OKB-2, K-7, OKB-134 (chief designer I. I. Toropov)-8—OKB-4 (chief designer M. R. Bisnovatyi)-9—OKB-155 (chief designer A. I. Mikoyan) and KB-1 (responsible Manager A. I. Savin).
Simultaneously, the decree provided for the armament of the new missiles, advanced fighter aircraft. In OKB A. I. Mikoyan, who created the MiG-17ПФУ, was already under consideration of the possible use of CMM products in the armament of the supersonic fighter-interceptor SM-7A (article 60) based on the MiG-19. After the decree the scope of work on rocket armed interceptors in OKB A. I. Mikoyan expanded: K-6 intended for-3 with radar “Almaz-3”, and K-9 for heavy machinery E-152. Technical requirements to the second instance of the fighter-interceptor T-3 OKB P. O. Sukhoi was provided weapons guided missiles K-7. Product K-8 was supposed to equip promising fighter A. C. Yakovlev Yak-123 (Yak-27).
Work on the rocket K-5M moved very quickly, and in March 1955 the OKB-2 was charged to the customer preliminary design. In the spring of 1956 began testing Autonomous missile launches sound lab based on the MiG-19, SM—2M (serial number 59210108) with two launchers AAP-4. At the first start in a few seconds after liftoff, the rocket lost control and writing a few bends, went to the ground. The initial study of the fragments of the fallen missiles failed to identify obvious causes of the accident. The cause of the incident is found in a few days. The rear part of the fourth compartment, in which is located the pneumatic actuator of the ailerons, together with a fifth apparatus compartment formed sealed cavity. The removal of exhaust air pneumatic actuator from the cavity occurs through the bleed valve closed until the launch of a membrane of aluminum foil. After the launch of pre-configured valve provide constant pressure between the cavity and the environment. When the pressurization cavity circuit Board in the housing of the fifth compartment is deformed, and there is a short circuit one of them to the body. After a suspicious charge has deployed such cases was no more.
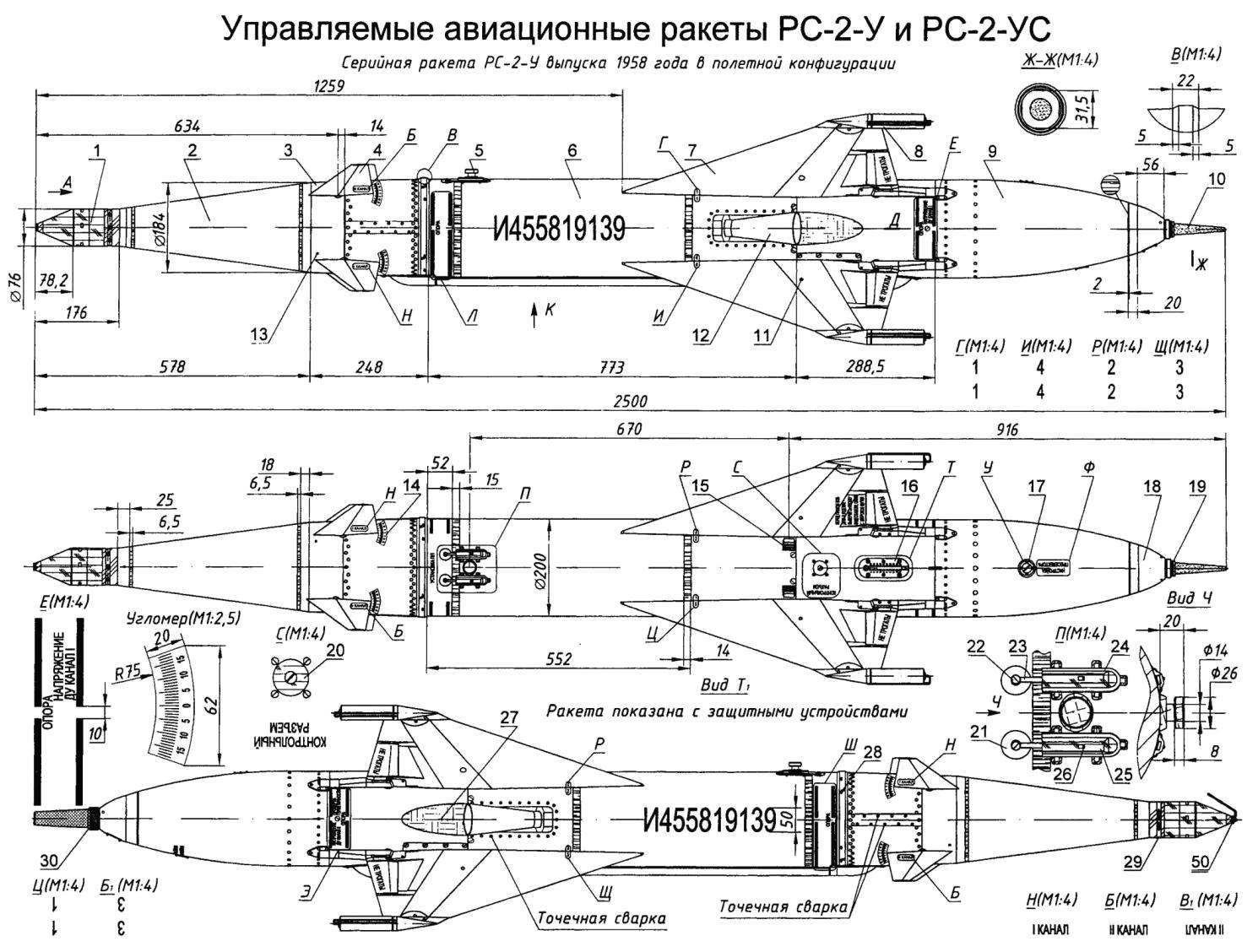
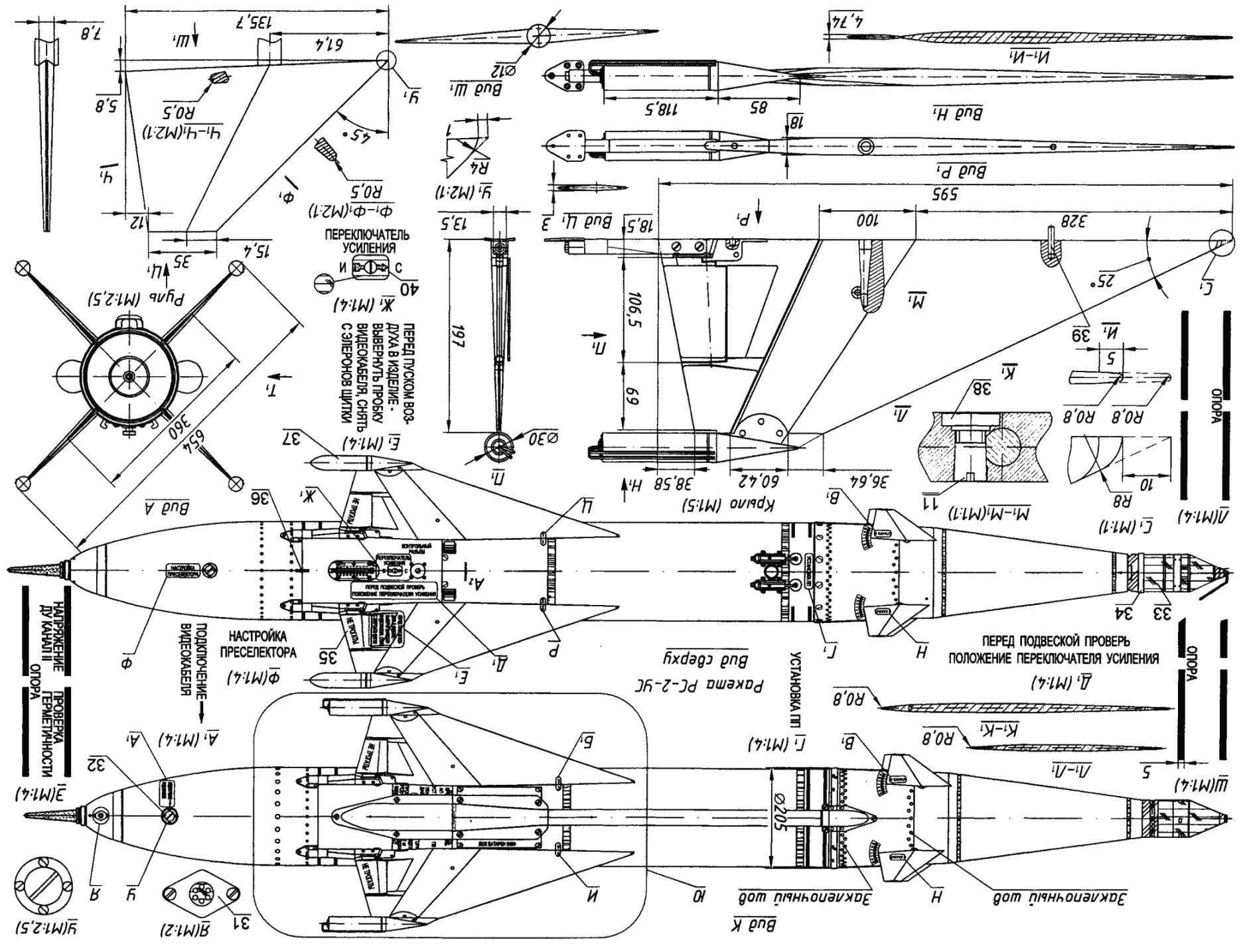
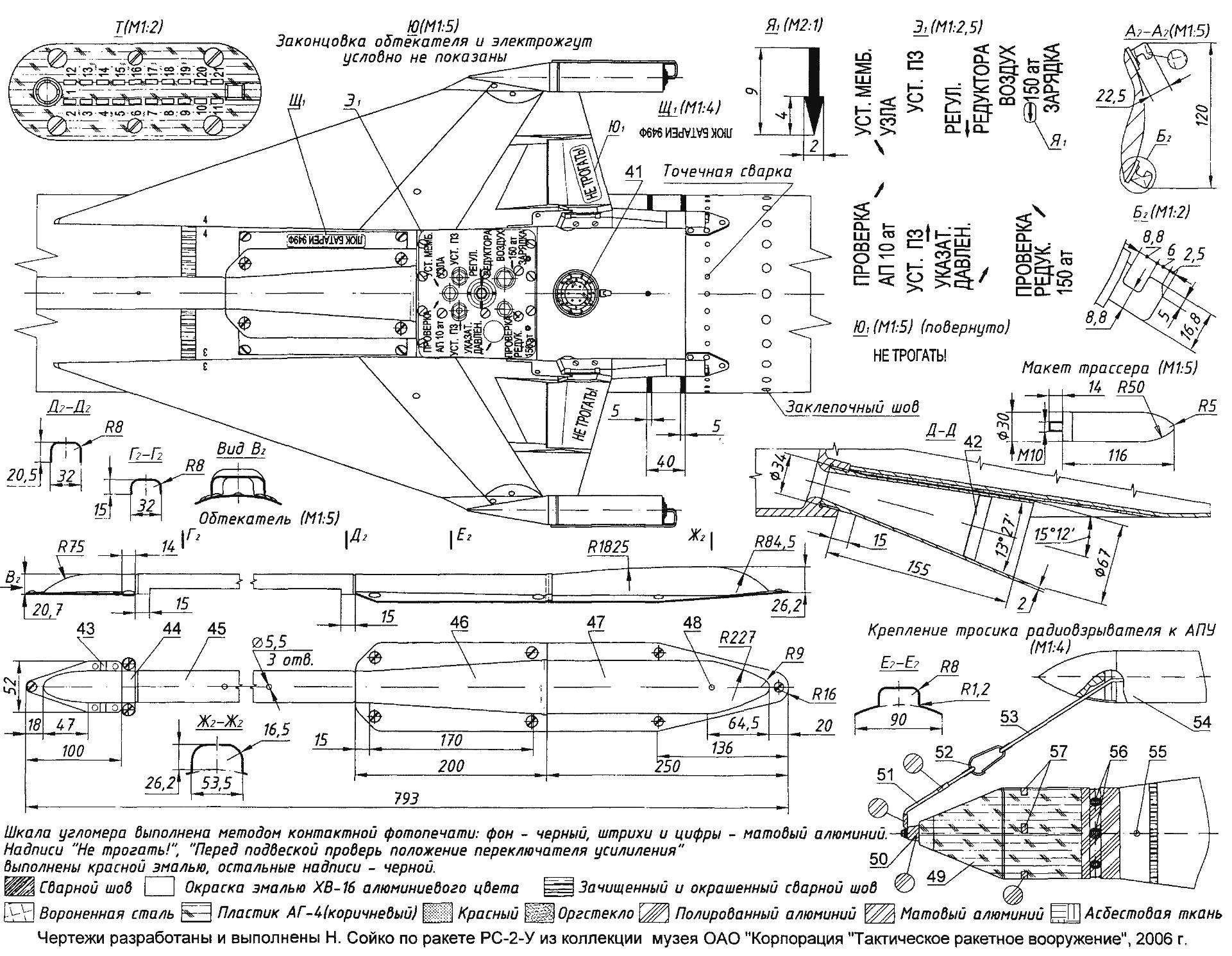
Managed aircraft missiles RS-2 and RS-2-US:
1 — single wavelength non-contact radio controlled fuses PB-2-U; 2 — warhead; 3 — steering compartment; 4 — aerodynamic wheel; 5 — front yoke; 6 — solid-propellant motor; 7 — wing; 8 — tracer OTI-30-1; 9 — compartment radio; 10 — antenna radio equipment; 11 —retaining bolt of the wing; 12 — nozzle of the engine; 13 — locking screw of the warhead; 14 — protractor; 15 — rear support bracket; 16 — socket side of the connector to the GS-4; 17 — the access hatch for the settings of the preselector; 18 — tail fairing; 19 — nut; 20 — pad control connector; 21 — prozator; 22 — screw; 23 — wire; 24 — the case of the contact; 25: clip; 26 — copper contact; 27 — thermal protection from asbestos cloth; 28 —wire pin; 29 — tape protective device of radio controlled fuses; 30 — protecting cap; 31 — bleed valve; 32 — mains connection of the video cable; 33 — dwuhosnovny radio controlled fuses RV-9 (used only with models of tracers); 34 — a protective rubber ring; 35 — Aileron; 36 — control band; 37 layout of the tracer; 38 — nut; 39 — anterior pin; 40 — block of the gain switch; 41 —lead; 42 — plug nozzle: 43 — fairing; 44 — clamp; 45 — middle part of the fairing; 46 — rear part of the fairing; 47 — ending; 48 — drain hole; 49 — single radio controlled fuses PB-2-USM; 50 — protective cap of the turbine; 51 — connecting cable; a 52 — carbine; 53 — cable APU; 54 — rod APU; 55 — locking screw attack; 56 — the outlets of the turbine generator; a 57 — lobes of the antenna ring
One of the defects in the control system of the missile, discovered during flight tests, there were failures in the autopilot, causing uncontrolled rotation of the roll. During the search for the causes of this phenomenon failed to establish that it generate acoustic oscillations that occurred when working gunpowder engine, and caused the disruption of gyros.
To accelerate test and development of missiles with a base carrier in 1956, at the Gorky aircraft plant number 21 on the drawings OKB A. I. Mikoyan, two MiG-19P modified in the variant of SM-7M, aircraft mounted radar sight RP-2-and four pylons for the installation of starting devices the DLC-4. In GosNII-6 machine fly tail number 03 and 04. Subsequently, after adopting this modification of the fighter-interceptor received the designation MiG-19PM.
In September 1956 the rocket K-5M was transferred to the state joint tests (ICG), during which launches were carried out at altitudes of up to 15.5 miles, according to their results, the developers have offered to conduct appropriate revision of the elements of the weapon system, and then to the end of the year to conduct control tests. At the stage of the ICG test team was headed by the head of Department, state research Institute-6 F. L. Antonov, assistant chief engineer appointed I. V. Zabigailo. The flight program has completed test pilots GosNII-6 M. I. Bobrovitskiy, L. N. Peterin, S. A. Devochkin, A. E. Chernyaev and LII — Bychkovsky and A. I. Pronin. The brigade included lead engineer for the autopilot Karpachev M., assistant chief engineer for the autopilot Y. O. Nivert, lead engineer for combat units (CU) and air suspension units (APU) I. Saltan, assistant chief engineer at the CU and APU A. Taraskin, preparation of products for pyrotechnic positions were V. Maletsky.
If the first launches were conducted at medium altitudes and the problems arose, the developers of the rocket, the first launch at an altitude of about ten kilometers they came from the developers of the engine fighter. After the withdrawal of missiles from the guides the aircraft stalled both TRD. At high altitude because of the greater pressure difference at the nozzle exit propellant engine the expansion of the jet after the expiration significantly increased and the gases got into the air intake of a fighter. The pilot had to save the prototype machine and run engines in the air.
This phenomenon OKB Mikoyan faced not for the first time, studied this problem at NII-2 (now GosNII as) and the Central Institute of aviation motors. Engines RD-9B is equipped with a system COP automatically reduces the fuel supply to the engine and transfers it to lower revs when you press the button combat pilot. In 1957, the plant number 21 was built five aircraft MiG-19PM, armed with guided missiles K-5M. In July—August 1957, the three of them spent the factory flight test firing of the system COP. A similar system is further equipped with engine AL-7F-1, when tested fighter-interceptor su-9 with missile weapons.
State control testing of weapons systems, consisting of fighter-interceptor MiG-19PM and missiles K-5M, conducted in August—October 1957.
Rocket K-5M surprises the testers not only in the air but on the ground. One day while preparing to fly the MiG-19PM test pilot GosNII-6 Colonel Arkady Chernyaev had a spontaneous launch of two missiles K-5M. Flying 20 meters, they hit the ground and collapsed. The warhead burrowed into the ground, and working porohovye continued movement of the remnants of rockets at the airfield. Fortunately, no one was hurt. About the incident reported to the leadership of the Institute, and was soon on the scene came the Deputy head of the Institute-6 research work Colonel L. I. Moose who caught one of the engineers of the Institute for the digging of the warhead. Elk ordered to immediately stop this dangerous and called sappers to undermine the warhead.
Actively participated in testing missiles K-5M workers OKB-2, but also the company who manufactured prototypes of the missiles. Head No. 455 for the production of K-5M has become a factory in the Moscow suburb of Kaliningrad. By the mid-1950s, the plant mastered the production of aircraft turrets. In April 1954 the company, thanks largely to the experience and energy of the Director of plant No. 455 M. P. arzhakova, mobilizing domestic resources, the beginning of the development of fundamentally new techniques and processes, led the cooperation of subcontractors, with no less difficulty mastering the production of components. In early 1956, the plant started serial production of missiles K-5. In this case the plant substantial assistance was provided by specialists of the plant number 134, OKB-2 and KB-1. And if the first software K-5 missiles produced pilot production of NII-88, then
1956 year of manufacture, control of missiles K-5 and then K-5M, production control and test equipment and ground equipment have mastered the specialists of the plant No. 455.
Joint decree of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers No. 1343-619сс from 28.11.57 G. rocket K-5M in the composition of the armament system-2-adopted for the supply of the air force. Until the end of the year, OKB-2 and KB-455, organized in June 1956 on the basis of a serial design Department of plant No. 455, together with subcontractors has removed the deficiencies identified in the control tests K-5M, and modified design documentation. After adopting rocket K-5M has received the designation of RS-2, open documents used designation—product I.
Developing the principles underlying the design of the missiles K-5M, the OKB-2 in March, 1956 released the preliminary design of the modified product TO-5C with a launch mass, twice more than the original machine, designed for use with heavy fighter-interceptor. For lesions scoring aerial target took four missiles K-5M, and two — TO-5S. However, due to the heavy workload of OKB-2 main theme—anti-aircraft guided missiles further work on the rockets of class “air—air” in Khimki turned, and scientific and technical groundwork to improve missiles K-5M, including a version with thermal homing head, gave KB-455. In the further modification of missiles K-5M and the creation of unmanned aerial vehicles for other purposes were carried out in KB-455 under the leadership of N. T.Picota.
In December 1957, the plant number 455 has released the first production RS-2-U. In three years the plant has produced 12 400 missiles (1957 — 3000,1958—7000,1959 — 3730 products). A small number of RS-2-in 1959, released plants — carpet-sky № 575 and Izhevsk No. 622. Plant No. 455 provided them with technical assistance in establishing a mass production.
In 1958, KB-455, fulfilling the government resolution and order of the Chairman GKAT, released in November
1957 year, proceeded to the modification of the K-5M for use with the advanced once again MiG-19 — fighter-interceptor SM-12ПМ and with the p re-hatchie su-9, T—43, developed in the above-mentioned policy documents. The main task of future work remained to ensure the maximum altitude of interception of air targets by fighters with more high flying-tactical characteristics.
When retrofitting, the rockets introduced a two-position switch (preselector) “And”, allows to apply shell composed of interceptors, T-43, CM-12ПМ and MiG-19PM. The position of the switch changes the gain of the radio control unit (produced altitude correction effort attributable to the management bodies of the projectile, depending on the type of aircraft carrier). Reinforced yoke and their attachment to the motor housing. Autonomous non-contact radio controlled fuses AR-45M replaced by new AR-45M2, continued to be used more reliable PB-2-US, RV-2-USM and RV-9. Established new tracers OTI-ZO-1; when picking the rocket fuse RV-9-instead of the tracers on the wings fastened to the layout of the tracers. The layout of the product TO-5MS had no significant differences from the base case, however, the flight characteristics have improved and the height of combat use brought up to 20.5 km.
The weapons system of the fighter-interceptor C-9 missiles K-5MS assigned a code number C-51. For missile guidance in the s-51 was used odnoimennaya radar TSD-30T, successfully located in the Central cone of the inlet of the T-43. TSD-30T developed at KB-1 under the leadership of A. A. Kolosova. In April 1958 came another decree of the government on which fighter-interceptor T-43 and the ground system guidance and control “Air-1” includes the constituent elements of the complex air intercept T-3-51. To work with this system on the T-43 placed side part of the guidance equipment “Lazur”. The work on creation of the complex interception was a constant concern of the government.
In the first half of 1958, the OKB P. O. Sukhoi to test modified two standard su-9—T-43-2 and T-43-6 in the media space-5MS, three more cars were built in Novosibirsk factory # 153: T-43-3 — in may, T-43-4 and T-43-5—in August. To the factory flight tests of the T-43-2 began in may, in June, the program connected to the T-43-3, and in July,—T-43-6. In late August 1958, the prototypes of machines presented to the customer. However, once the joint tests of the complex to start failed, since the acceptance of the customer required to eliminate defects of machines and engines.
According to the memoirs of the participant of tests of the missile weapons of the fighters of Colonel-engineer A. P. Kostikova, the results of GosNII-6 were always in sight of air force leadership: most visited Institute Deputy armament commander of the air force A. P. Losyukov, and his successor Colonel-General A. I. Ponomarev, and commander-in-chief K. A. Vershinin and his deputies.
September 2, 1958 on the ground in Akhtubinsk came the First Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee and Chairman of the Council of Ministers N.With.Khrushchev. The preparation for this visit was conducted thoroughly—written papers, and decorated the stands with the main data of combat use of aircraft and missiles. Worked out showing the destruction of aircraft target the Il-28 in the air with missiles RS-2-the MiG-19PM. It in the presence of guests have successfully completed a test pilot of the Institute M. I. Bobrovitskiy.
Other missiles of class “air—air” K-6, K-7, K-8 only passed factory flight tests and to be shown in the air wasn’t ready. Ground the screening was carried out on a special Parking aircraft. Speakers on missiles “air—surface” and “air—air” awaited the guests at the booth with the main data of the aircraft and missiles installed near the aircraft with suspended missiles and rockets on trucks. About the rocket RS-2-US.GN With.Khrushchev and his entourage told the head of the testing team F. L. antonivs.
State tests of the missile TO-5MS in the complex intercept T-3-51 was conducted in two stages: first— the General designer—occupied the period from December 1958 to may 1959, the second — state joint tests—from October 1959 to April 1960. Led test team in the state trials of the aviation complex of interception V. P. Bladedance. Flights under the program of state tests performed test pilots OKB: Ilyushin, A. A. Koznov, L. G. Kaliman, E. S. Solovyov and N. M.Wings and GK NII VVS: G. T. Shore, N.And.Korovushkin, L. N. Fadeev, B. M. Adrianov, V. G. hoarder, S. A. Mikoyan, V. I. Petrov and A. S. Devochkin.
Within 1959 performed 93 test start-5MS, with a total positive result. Certificate of completion of state tests of the complex T-3-51 was approved on 23 April 1960. By government decree, released in mid-October, aviation complex interception adopted by the fighter aviation of the air defense Forces of the country.
The complex was adopted under the designation su-9-51. After that, the rocket K-5MS has received the designation of RS-2-US and P-51.
At the time when flight tests of rocket technology was used as a “safety net”. It was the fact that the interception of aircraft target was prepared several interceptors; in the case that the first intercept is for some reason unsuccessful, the target is supposed to “finish” the second interceptor. The reason is that expensive radio-controlled target on the basis of the Il-28 was not able to return to their base, so it was necessary to shoot down in any case.
According to the memoirs of the participant of tests of V. Lebedev: “On the launch pad ready “number one” were a number of fighter-interceptor, armed with missiles K-13 and RS-2-US. The intercept of the plane target the Il-28 first went fighter with missiles K-13, who hit the target failed. Immediately took off the second fighter-intercept-chick, this time armed with missiles RS-2-US, piloted by a future pilot-cosmonaut G. T. Beregovoy. First they fired a missile RS-2-US a direct hit struck the Il-28. After landing, G. T. Beregovoy in jest threw in the chief designer missiles K-13 I. I. Toropova the phrase: “you owe me, and then added: — We have such missiles during the great Patriotic war.” Present at the starting positions of Deputy Minister of aviation industry V. B. Kupriyanov thanked all the participants and our team has signed the order on encouragement”.
As air targets were used, and other aircraft. January 9, 1959, test pilot
Sa Mikoyan imitated the su-9 interception of bombers Tu-16. Simulated interceptions of high-altitude air targets, in which were the Yak-25RV, the su-9-51 was performed by test pilot LII A. A. Shcherbakov. High-altitude flights with real rockets TO-5MS in high-altitude targets that simulated high-altitude balloon, was carried out by G. T. Beregovoy.
Missile RS-2-under the wing of the MiG-19PM
During testing, the K-5MS revealed a flaw in the design, such as insufficient strength of the joint of the second and third compartment. The missile RS-2-in the second and third compartments were joined telescopically and are held together by four pins made of wire 3 mm in diameter inserted in a special annular groove. After one flight the pilot A. S. Devochkin with two missiles K-5MS on the suspension of the su-9 was rolled out with a concrete runway on the ground. When moving a fighter on the ground on one of the missiles was the destruction of the junction of the second and third compartments;
The warhead fell to earth and rolled, creating a real threat to nearby people and equipment. Senior engineer I. N. The Sultan, who watched the landing, picked up the warhead and took her in his arms at 50 m away from the runway. The warhead blew up the bomb squad.
After this incident, KB-455 changed the design of the interface: products issued in subsequent years, distinguished by increased thickness of the plating of the second chamber, and the number and diameter of screws in the joint. At first the compartments were connected by a telescopic joint with nine screws with a diameter of 5 mm, then the number of screws increased to twelve, and their diameter up to 6 mm.
Simultaneously with the preparations for the trials of the aviation complex of interception of the su-9-51 KB-455 was prepared to work with the interceptor and in OKB Mikoyan. The first flight SM-12ПМ with missiles on APU-4 under production tests began in may 1958. Factory flight-test firing of elements of the complex, including missiles, aircraft SM-12ПМ were held in September—October 1958 at the site of the research Institute-6. They made thirteen flights of seven launches of missiles K-5MS.
The positive results of the factory tests allowed in December 1958 to transfer complex intercept CM-12-51 on state tests. Their implementation began in early 1959, with the implementation of a real interception of air targets, however, the accident airplane SM-12ПМ in April, caused by a defect engine RZ-26, resulted in the suspension first, and then by order of the Chairman GKAT of July 18, 1959, of all the program testing and debugging complex CM-12-51 stopped.
In 1959, the serial production of missile RS-2-US has mastered multiple plants. Plant No. 455 moved from the production of K-5M K-5MS in the second half of 1959 and produced 2400, in 1960 — 3170, 1961—540 products. In addition, the plant No. 455 made training-active and training-split missile RS-2-US and pre-training missiles PPP-51.
At the Moscow plant № 43 the first batch was handed over to the customer on 20 August 1959, and only in 1959 he produced a 1000 missiles, 1960-m—2278, 1961—3500. Missile production at the plant continued until 1964. Kiev factory of No. 485 to them.Artem in 1959 and produced 1500 RS-2-US, in 1960 — 2500, in 1961—3500 products. Production of RS-2-US in
1959 year have mastered the Kovrov plant № 575, 830 manufactured missiles, and in 1960, the 500 missiles K-5MS released the Izhevsk factory number 622.
One of the points of the order of the Chairman GKAT, released in August 1958, provided for testing in the next year to two MiG-21F system jet armament with the installation of the TSD-30 radar (RP-21) and two missiles “air—air”. OKB Mikoyan began development of a future E-7 in full compliance with this order. The placement of the antenna unit of the station TSD-30 in the Central body, OVC (instead of DME) caused a change in the geometry of the air intake: increase in the size of movable cone and shell, which led to an increase of drag, which is compensated for by increasing engine thrust. At the same time to reduce the weight of aircraft structure is dismantled gun, altimeter RV-and replaced the sight ASP-5НД to a simple collimator CRPS.
The first prototype of the E-7/1 manned equipment “Lazur” for guidance of the interceptor from the earth system “Air-1”. The fighter was developed under two types of missiles:-5MS and 13. Missiles K-13 was suspended on the actuator devices APU-13, fastened to the pylon, and the K-5MS—APU-7. First flight on the E-7/1 complied with test pilot I. N. Kravtsov in the fall of 1958. State tests of the missile RS-2-took place in September 1963, and she was recommended for inclusion in the armament of the fighter-interceptor MiG-21 PF, which was one of the options E-7. Missile RS-2-appeared on the MiG-21PF with a 15-second car 16-series.
In 1962 on the orders of the Chairman GKAT P. V. Dementyev modified MiG-21PF (serial No. 76210101), staffed his jamming station TSD-30ТП and launchers APU-7 for the use of missiles RS-2-US. In March
1962 began a joint state tests of the new station as part of the aircraft, and from mid-1962 and 1963 year and the system of missile armament. The tests confirmed the possibility of combat use of missile weapons at low altitudes of about 2 km instead of 4 km with a TSD-30T. Lapping radar continued for several years. System K-51 adopted by the air force in 1965 in the composition of the MiG-21 PFM.
In the tests of the missile RS-2-MiG-19PM in the test team, many of whose members participated in the great Patriotic war, and the conferences held in GosNII-6, there was a question about the rational use of missiles. Repeatedly, citing the experience of the last war, the participants of the discussions expressed opinion about whether the destruction of tactical aviation of the enemy on the ground. After some time, these desires took shape in the task set by one of the participants tests. In 1959 the head of the Department R. J. Filyaev mandated lead engineer I. N. Saltan as a specialist in air arms, well knowing the sight ASP-5 NM, to write a program of works for firing missiles with the MiG-19PM at ground targets. For work identified nine missiles RS-2-U. as a target on the ground drew a circle, divided by a cross on the sector. In the work took part the test pilots E. N. Knyazev, M. I. Bobrovitskiy and L. A. Peterin. The start was made in a dive from a height of 5-7 km at the minimum speed at the angle of 25-35° to the ground. The duration of the dive is 14-15 m. To analyze the results of shooting at ground targets on the part of the approach was recorded by three photographers: two at sides and one back.
Two missiles flew at 10 km and exploded. One of the rockets exploded at 500 m from the CP. During one of the launches, the pilot began to come out of the dive before the rocket was found with the goal. K-5M, located in ravesignal area started to perform the slide and self-destructed after a specified time.
Analyzing the results, found that the attack was triggered at altitude 9 m. -11 Point meetings with the purpose behind the cross. Now began to take the aiming point when firing at ground targets in 5 yards in front of goal.
After reviewing the leadership of the air force with the results of the start, and the decision was made to conduct a full research in 1959-1960. This allocated about 50 missiles RS-2-U. as targets used the Tu-4 and Il-28, vehicles and anti-aircraft missiles “Comet”. The tests involved test pilots GosNII-6 L. A. Peterin, Bobrovitskiy, I. M., Popov, Gaumont and two pilots from the Lipetsk center of combat training of the air force. Work carried out at the test site in Kapustin Yar, which had a target field, equipped kinetheodolite. After the results were made report, which confirmed the possibility of aimed fire guided missiles class “air— air” for ground targets, it was noted that to increase the combat effectiveness of the launches at ground targets need a more powerful warhead. According to the materials of the report N. And.Sultan wrote an article for the departmental magazine, in which the front pilots were given recommendations on the combat use of missiles RS-2-U.
In October 1959, the engineers of plant No. 455, G. A. Kagan and V. N. Morozov, as well as experts from the Moscow factory № 663 and Novosibirsk radio works sent to assist in the development of the aviation industry of China production of missile RS-2-U. Assembly of missiles produced at the plant, 200 km North of Beijing, with the participation of G. A. Kagan, coordinator of the group of Soviet specialists. The rest of the group worked in a factory in the province of Tien-Ching, having mastered the manufacture of equipment of radio control, radio controlled fuses and KPA. Together with Soviet specialists worked with Chinese engineers, graduates of the MAI, held an internship in 1957-1958 at plant No. 455. The first batch of missiles to Chinese Assembly PL-1 in the summer
1960 year, we prepared for the trials that have documented the failure of radio controlled fuses. Running in the same conditions the Chinese pilot rockets manufactured in the Soviet Union, worked reliably. Chinese experts engaged in the search for the causes of failure, and our experts by order of the government in September, 1960, returned Home.
Missile RS-2-US was in service until the early 1980-ies. She has contributed to the establishment and development of guided missile weapons of fighter aircraft in the domestic aviation industry, as well as the acquisition of operating experience in this class of weapons combatant units of the air force and air defense.
The basic data of the missile RS-2-US
Curb weight of a rocket, kg…………………………………………………..83
Warhead weight, kg………………………………………………………………13
The altitude range of combat use, km………………………….0,5…20,5
Controlled flight……………………………………………………12
The minimum allowable velocity of the carriers at the time of launch, km/h:
at the height of 5 km……………………………………………………………………….800
at an altitude of 20 km……………………………………………………………………1700
The maximum launch range in rear hemisphere aerial target, km:
the MiG-19PM………………………………………………………………………….3,5
the MiG-21ПФМ and su-9 (N – 15 km)………………………………………5,0
Minimum launch range in rear hemisphere
air targets, km…………………………………………………………………….2
N. JAY
The author expresses sincere gratitude to the veterans: GosNII-6 and GK NII VVS I. N. Saltan, A. P. Kostikova, gnpts “Zvezda-Strela” V. V. Lebedev, S. M. Vinogradov; the worker of JSC “MKB “Fakel” V. N. Korovin, the employee of JSC “Corporation “Tactical missiles” A. I. Filatov, the worker rgae HP Queen for help in the preparation of this article.