The wing and tail feathers borrowed from the modification of the FB.5, and the fuselage is designed again. In a double cab side-by-side housed the pilot (left) and radar operator (right). In the bow was RLS A. I. X (similar to us SCR-720B), and additional navigation equipment. Cannons were no changes. The glider gained 122 kg, therefore, as the power plant decided to use the more powerful “Goblin” 3.
The company has built three prototypes of the interceptor, the test of the first of them began on 28 August 1949 (test pilot Geoffrey pike). It turned out that the new machine flies faster than PB.5, but falls short in speed to the “Meteor”. The climb rate was also lower than that of a competitor. In addition, identified problems with stability, causing the tail Assembly had to be refined. The keels have usilili front edge, and the area of the stabilizer is increased due to the additional surfaces, installed with the outer sides of the fins.
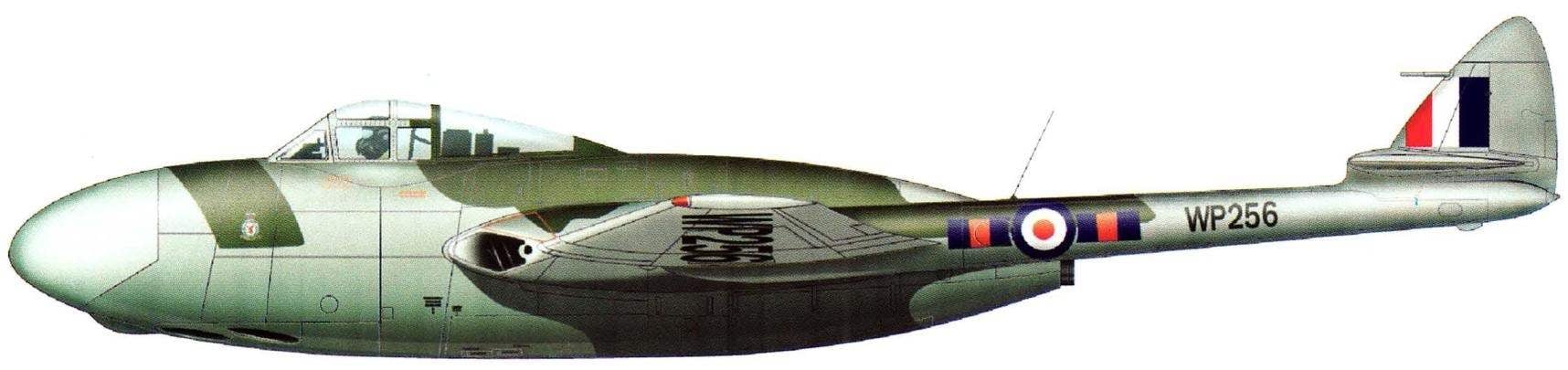
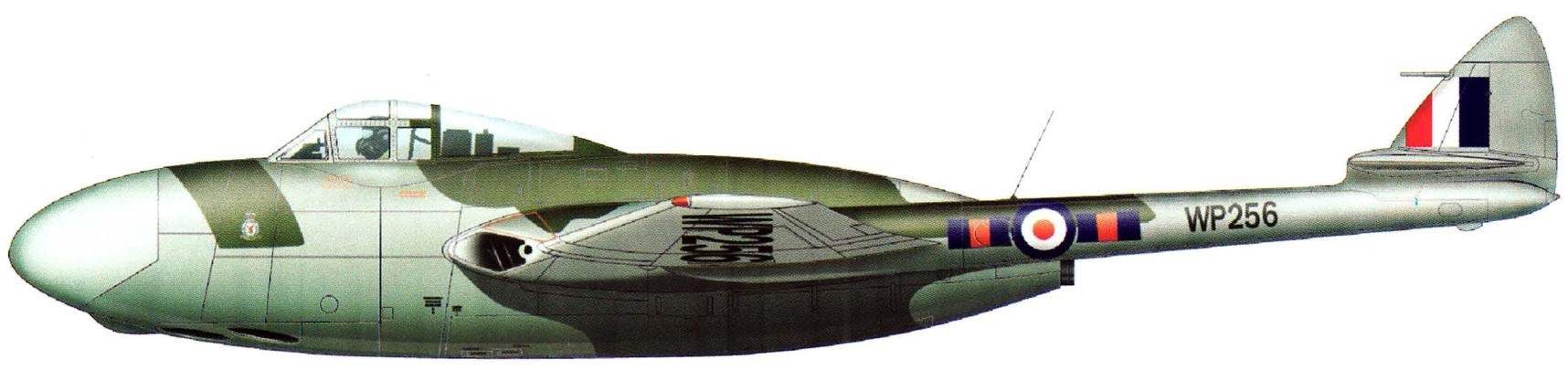
Royal air force new not interested. It was decided that the car is better to promote exports. Interest in it showed the military out of Egypt, and soon signed the first contract for 12 aircraft with an option for another few dozen. And would serve as interceptors in the Country of the pyramids, but another aggravation of the military-political situation in the region forced the British government to impose an embargo on military supplies to Egypt. The order was transferred to the Royal air force, who in the spring of 1951, took the interceptor into service under the designation NF.10. It was assumed that the aircraft will be used before enrolling later a “Meteor” and the new “venom”.
78 was built (according to other sources — 95) within this option. After the termination of their use as a night interceptor in 1954, 36 aircraft were converted for training navigators. Radar dismantled, instead of it installed navigational equipment — station “G. 3”, “Rebecca 3” and ballast. The aircraft were operated until 1959.
SE.535 “Mistral” of the French air force. Visible wider air intakes and the aerodynamic ridges on the wing
Cabin F. 3 canadian air force, who later was in service with Mexican air force
The flight of the second prototype of the prototype of the “sea Vampire” from the deck of the aircraft carrier “Ocean” 3 Dec 1945
Much greater success was expecting a double training aircraft DH.115. Developed it-based interceptor in 1950, November 15 was the first flight of this machine. The Royal air force became interested in the new “spark” like a good addition to the “Meteor” T. 7. In air force aircraft received the designation T 11, “Vampire”, aviation — Etc 22 “sea Vampire.” For the Royal air force built a 526 (other sources — 534) machines, widely used until 1962. some aircraft continued to be used in the auxiliary purposes until 1967.
T. 11 built on the basis of NF.10. The main initial difference was the extended cab with dual controls and more convex lantern. The lack of radar in the bow provided a good operational approaches to systems located here. To the delight of the technical staff, the nose had a huge hatch-type hood of the car. The plane was equipped with turbojet engines “Goblin” 3. Gun armament consisted of two guns.
The main disadvantages manifested with the start of operation was unsatisfactory review (lantern borrowed from the NF.10) and close the cockpit. And if for a night interceptor visibility from the cab is not represented by the most important feature, for “Sparky” it was critical.
Starting with the 144th machine these disadvantages are eliminated. Pilots have at their disposal, and ejection seats MK.THIS company “Martin-Baker”. Due to the increase of size of the lantern worsened directional stability, which required some form of change and the area of the tail. All previously built aircraft eventually modified to this standard.
“Vampires” in the ranks
The vampire F. 1 entered service with the Royal air force in April 1946, with the beginning of re-247, 54th and 130th squadrons (air wing Odiham). First I replaced your “Tempesta” for new fighter 247 squadron, actively involved in the transfer and accumulation of operating experience. “Sparky” was not, and the pilots were beginning to fly jet technology after a theoretical study and explore the cockpit. Fortunately, that “Vampire” was easier to handle than most piston fighters. However, chassis with nose wheel and the increased landing speed demanded more attention on landing.
8 June saw the public debut of the new aircraft during an air parade over London in honor of the anniversary of the victory in world war II. And the fall jet technology have received and two other squadron aircraft, based in Odiham.
“Vampires” became the first British jet aircraft for parts, serving in the Royal air force in Germany when in April 1948 began the re-equipping 3 squadron in Wunstorf. The first “vampires” rearming and auxiliary of the Royal air force (605-I, 501-I, 502-I squadron), who used them until the end of 1951 , After the completion of flight operations the aircraft was transferred to technical units, and in the mid-1950s, most of the machines disposed of.
The transition modification F. 3 RAF began in late 1947 with the re-wings in Odiham (54-I 247-I and ex-130-I and by this time — the 72nd squadron). It was the pilots of 54 squadron demonstrated the increased capabilities of the fighter during a transatlantic flight in July 1948 by the “Troika” armed squadron auxiliary air force — 601, 604, 608 and 614, where they operated until 1952, In February 1948 the same jets and Central flying school.
In the autumn of 1948, the F. 3 was operated at air bases of the Royal air force outside the metropolis. The first new technique was a 73 squadron at TA Kali (Malta), in may 1949- 32-I in Nicosia (Cyprus).
With the advent of FB.5 in 1949 began the re this modification squadrons of the wing in Odiham. In September, units of the wing took part in the annual large-scale air defense exercises “Bulldog”, where together with a couple of French “vampires” from the base of the Dijon and aircraft F. 1 of 605 squadron simulated a RAID on Albion. In the following year on the basis of 54 squadron formed the chief flight team of the Royal air force, consisting of five FB.5. His demonstration performances of pilots of the group caused constant delight of visitors and Farnborough exhibitions in Hindon. In 1952, all three squadrons of Odiham rearmed on the meteor F. 8, and “vampires” left “first line” of fighter command Royal air force.
In Europe, the “vampires” of the Royal air force was removed from the first line rather quickly. At the end of 1953 , wings in Wunstorf (11-I, 5-I 266-I squadron) began to rearm the new aircraft venom FB.1, and a year later the same thing happened with the wings in Hassberge (14-I-98-I and 118-I squadron). By mid-1954, after the re wing in Celle (16-I, 94-I 145-I squadron), “vampires” in Germany is almost gone.
In the middle East were based, a total of six squadrons fives, two had served in Southeast Asia. The first FB.5 received in October, 1949 6 squadron, based in Deversoir (Egypt). In the subsequent two years, the division has rarely been seen at the airfield because of the frequent “visits of courtesy” in Iran, Jordan and Cyprus. In June 1951, part transferred to Iraq (airbase Washers), and in November — in Habbania (ibid.). To the great delight of the pilots, the following year, the squadron re-equipped on FB.9.
“Fives” was also rearmed with 32 squadron in Nicosia (Cyprus, January 1951), 73-I 185-I — in TA Cali (Malta, 1951), and 249-I — there in 1952. 8 squadron, normally stationed in Aden in April 1954 , he participated in the suppression of the uprising, the tribe May May in Kenya. For a 10-day period of hostilities the pilots brought down on the heads of the rebels more than 5 tons of bombs and 12,000 cannon shells.
Based in Singapore, 60 squadron received “five” in December 1950, and at the beginning of the following year they were used against guerrillas in Malaya. 28 squadron from Kai tak (Hong Kong) rearmed with the type in January 1951 But soon, in 1952, these squadrons replaced their materiel in rain FB.9, and operated them for four years until replaced “vampire” did not come more perfect “venom”.
“Nine” has replaced the “fives” in the Mediterranean in late 1952 G. Three years later, most of the “vampires” FB.9 was forwarded to the metropolis, where they are still served for several years in support of the air force and training units, and then (1956 — 1957) was decommissioned and disposed of. The same fate, and at the same time, suffered a “five”. But not all. Some of them continued to operate as training in almost all flight schools, air force and training centers. Last Vampire 5 was used extensively to improve flight training, at least until 1961
Indian vampires also gained combat experience during the second indopakistani war of 1965, however, not very successful.
Used “vampires” and the Egyptian air force during the Suez crisis of 1956.
Various versions of “Vampire” were armed with military aviation 27 States. Mostly combat modifications was in service at the end of the 1950s, “Sparky” — much longer — until the early 1970s. the Most long-lived steel Swiss machines, officially decommissioned only in 1990, Over the years, series (including license) production was built around 4850 aircraft of all modifications (3453 1127 single and double).
 This project began with specification E6/41, dated November 1941 In her Ministry of aviation industry of great Britain has offered the firm “de Havilland air craft company” to explore the issues of creating a jet fighter and engine for it. By that time, the company proactively developed an experimental twin-boom DH’s car.99. It was a single-engine monoplane of all-metal construction with a tricycle landing gear with nose wheel. The development of the engine in April 1941 did the firm “Halford”, headed by Frank Halford, simplifying the design of the turbojet engine with centrifugal compressor and through the location of the combustion chamber between the compressor and the turbine.
This project began with specification E6/41, dated November 1941 In her Ministry of aviation industry of great Britain has offered the firm “de Havilland air craft company” to explore the issues of creating a jet fighter and engine for it. By that time, the company proactively developed an experimental twin-boom DH’s car.99. It was a single-engine monoplane of all-metal construction with a tricycle landing gear with nose wheel. The development of the engine in April 1941 did the firm “Halford”, headed by Frank Halford, simplifying the design of the turbojet engine with centrifugal compressor and through the location of the combustion chamber between the compressor and the turbine.