 With a green lawn and plantings in the suburban area especially well laid garden paths. Of the gate or the gate to the house, they are usually short and wide enough to be able to separate the two: about 1.5 m And to the garden and the places of the paths can be narrow and picturesque squirm on the site, decorating it.
With a green lawn and plantings in the suburban area especially well laid garden paths. Of the gate or the gate to the house, they are usually short and wide enough to be able to separate the two: about 1.5 m And to the garden and the places of the paths can be narrow and picturesque squirm on the site, decorating it. Bulk track
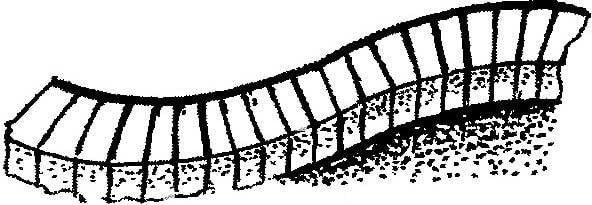
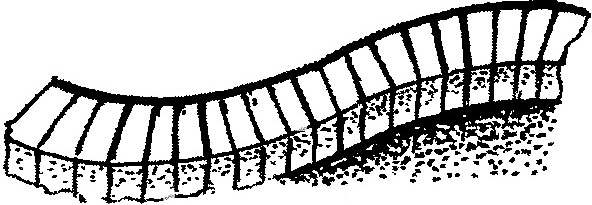
The most simple, at first glance, tracks — of crushed stone or gravel. Usually it is a small crumb of granite or building stone, brick. It can be simply poured into a shallow, dug in the ground a long bed and lightly tamped. However, this track will serve longer, if under this layer will be laid so call cushion is a thick layer of broken bricks or pebbles.
The gravel path looks nice because it turns a color. It does not delay the precipitation, quick-drying after rain and will not be slippery in icy conditions. But its flaws should be attributed to the fact that the smaller factions, especially in the wet state, over time, posted by shoes around the station, trying to get into the house, which is not very desirable.
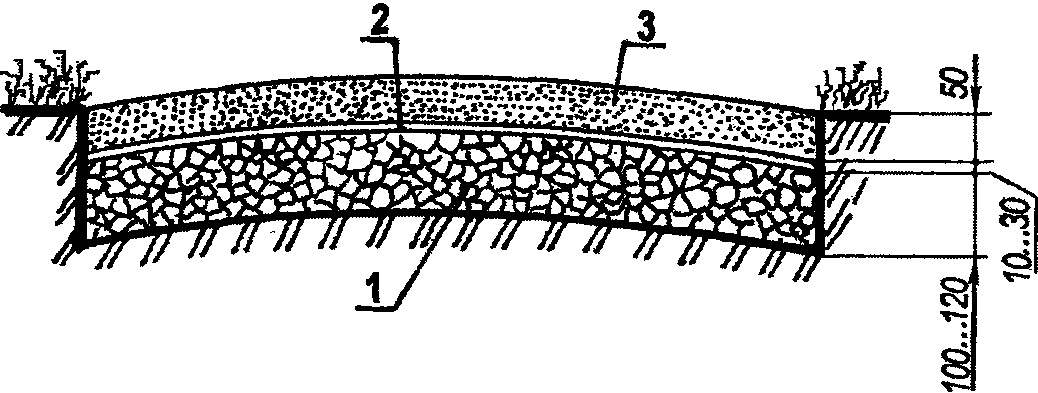
A path of crushed stone or gravel:
1 small broken brick; 2—a layer of fat clay; 3—gravel, gravel.
Track of the plates
It is best suited for walkways paving of the finished plates should have a thickness not less than 6. thus it is necessary to select thoroughly both from aesthetic and practical points of view. The green lawn is best suited finished tiles sand-yellow or ochre; too unpleasantly bright it is blinding in the bright sun.
Natural tile should have a rough rough surface, so that the track does not become slippery in rainy weather or icy conditions.
Because small tiles are difficult to pack tightly enough, it is desirable that their size was not less than 300×300 mm. the Tiles are convenient because they can be laid directly on the sand, and in more lively areas of the garden — cement mortar, laid on a layer of gravel with a thickness of 100 to 200 mm. Each tile needs a little whack with a hammer so that it is securely “sitting” in the sublayer.
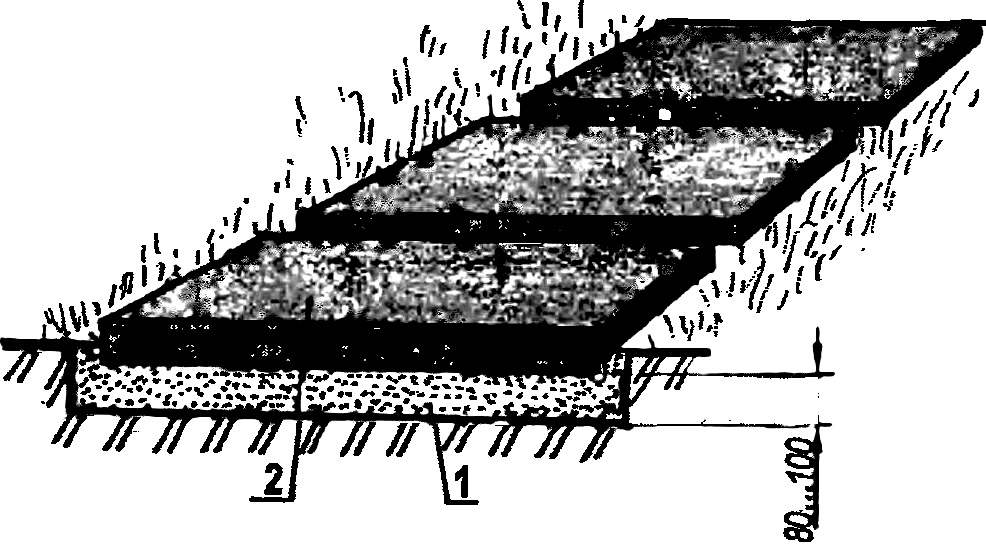
Track of the plates:
1—sand cushion: 2—concrete or ceramic hob.
The cracks between the stone tiles should be done as narrow as possible. If you put tiles of various sizes, their alternation should be the same.
The sides of the road better to use the material larger. With a long Board and level it is necessary during operation, constantly check whether the tiles lie horizontally. The gap between them to pour liquid cement, which optionally can be added and some paint. The surface of such roads should have dvuhgolosyj bias.
Paths of brick
Usually for these purposes, I prefer the so-called peregudy brick, and along with a used and broken, which is used to fill in the gaps or participate in the creation of patterned masonry.
To lay a track of bricks, you must first mark its direction and size, then remove the soil to a depth corresponding to the height of the brick put on the side. The edges with the help of small pegs, the future path is enclosed by wooden boards section 50×150 mm, installed on rib.
The lead track on the planned size, set on the edges of the Board, espereu their remote bars every 1.2 — 1.6 m with one side of the track Board should be somewhat higher, focusing on her brick “masonry” will have a bias the other way, so in the rain is not delayed water. In the longitudinal direction of the track should also have a small bias.
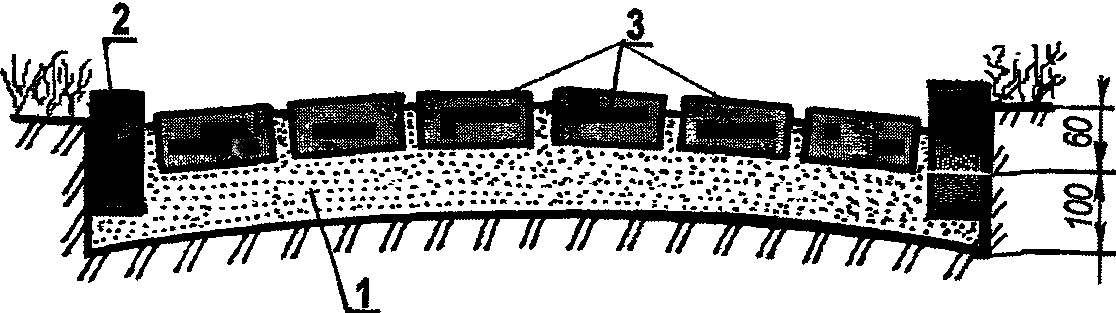
Laying bricks:
1—sand cushion; 2—curb (vertical brick, Board); 3—layer of brick laid flatwise.
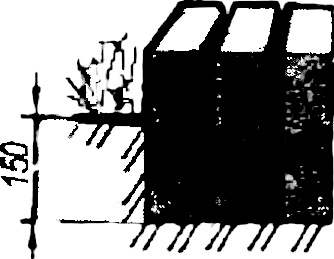
Bricklaying as it is.
The prepared bottom of the trench is filled with gravel or stone chips so that the brick is flush with the edging boards. A layer of gravel is leveled to the desired level with the help of wooden planks floating on remote bars at the correct depth along the side boards.
When the sublayer is completely aligned, you can begin to masonry. Place the bricks can be varied, setting them on either side, but as closely as possible to each other. If it is desirable to leave a gap for grass, then you need to fill them with sand and seal carefully shed water. After laying to prevent displacement of the bricks, gaps in masonry can be filled fine sand.
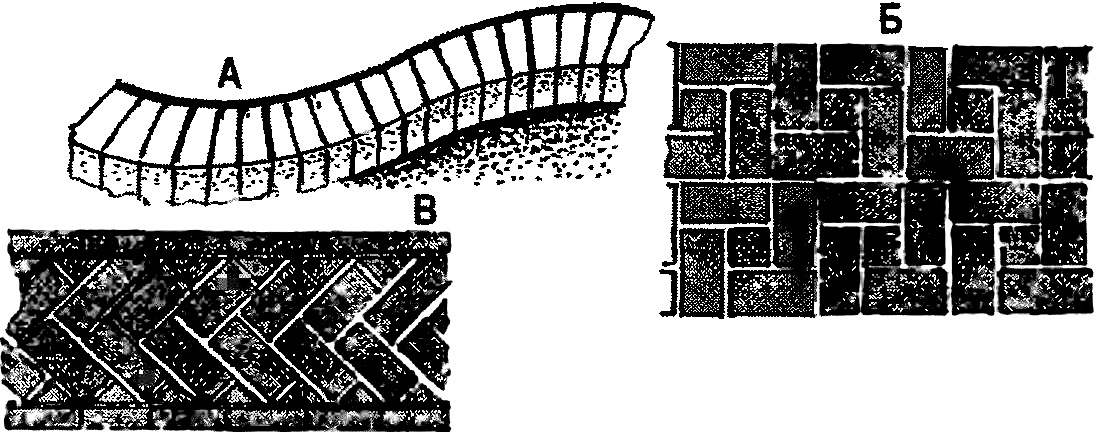
Options patterned paths made of brick:
A — “snake”; — “chess Board”; — “tree”.
Asphalt paths
Lately for laying paths in the garden quite often and started to eat asphalt. For this path you first need to prepare a sufficient basis in the thickness 100 — 250 mm, which should pour filled with asphalt rock dust, in the form of heat it smoothed out and compacted.
The final layer of asphalt needs to be 30 mm thick. you Can use colored asphalt, laying of which is produced in the cold state.
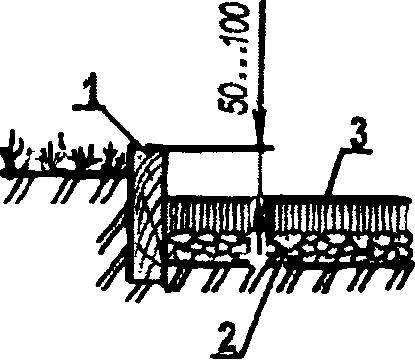
Asphalt track:
1—curb (Board); 2 pebble or gravel pad; 3—layer of asphalt.
A tree
Very beautiful path, paved with wooden bars, but she’s not too good for wet areas. Bars should be at least 200 mm in height. You can use any kind of wood, but hard wood would be more durable.
This track served as long as possible, before placing each brick should be dipped in a special impregnating compound or oil, and then allow it to dry thoroughly. The lower part of the bar can also be dipped in liquid asphalt. To avoid wood rotting, it is placed on a sandy substrate.
You should try to have separate bars below wider and those that are narrower, alternated harmoniously; and then all the walls will look nicer. At the edges it is better to stack the bars larger. The finished coating should be filled up with sand and thoroughly watered so the sand filled all the cracks.