It has long been noticed: the pilots, even the most beautiful aircraft, whether it’s a huge “Boeing-747” or fast and agile MiG-29, never refuse to fly on UltraLite if they are given the opportunity. Paradox? Not at all. Most likely, only in the cockpit unprepossessing at first glance, the ultralight aircraft they are fully able to experience the feelings that accompany a free flight.
It has long been noticed: the pilots, even the most beautiful aircraft, whether it’s a huge “Boeing-747” or fast and agile MiG-29, never refuse to fly on UltraLite if they are given the opportunity. Paradox? Not at all. Most likely, only in the cockpit unprepossessing at first glance, the ultralight aircraft they are fully able to experience the feelings that accompany a free flight.
However, I like to float on a small slow aircraft not only professional pilots. Worldwide, there is literally booming in microaviation. Thanks wing, Rogallo appeared hang gliders, then trikes and other UltraLite. To them in the 100-500 m no one but the birds did not fly. Now this niche is occupied high-rise.
According to the classification of the International aeronautical Federation (FAI) ultralight (the same SLA, only American terminology) —aircraft with a takeoff weight of not more than 450 kg and a landing speed not exceeding 65 km/h. Such parameters give a lot of advantages even before the machinery of light aviation, and this slug, for example, it is not necessary airfield — you can use more or less suitable for short run or run of site. He is the best suited for initial training of pilots: even if inexperienced rookie and make a hard landing or getting run over on hidden grass tussock, the airplane will “forgive” him the error. Finally, the simplicity and cheapness of construction, as built UltraLite classic flight technology —dural tube frame plus fabric lining. And what are the prospects for ALS in agriculture, for example, chemical treatment of crops!
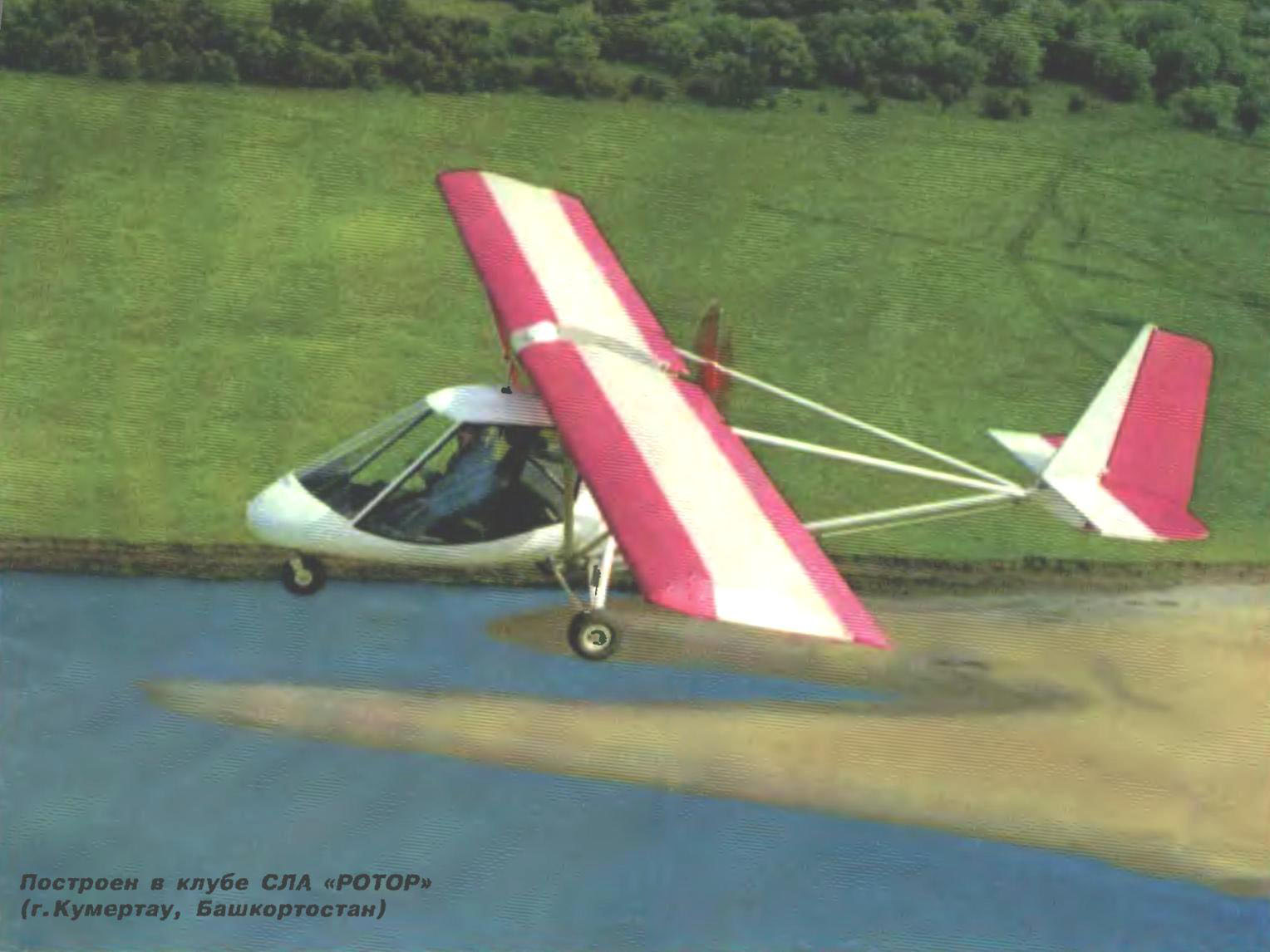
All of these qualities in full measure has an ultra-lightweight two-seater “Chick-2” built by enthusiasts of microaviation of Kumertau in the South of Bashkiria. The name of the city from the Bashkir language is translated as “Coal mountain”. It was there, the airport, the local aviation plant, “Chick-2” first flew in the air.
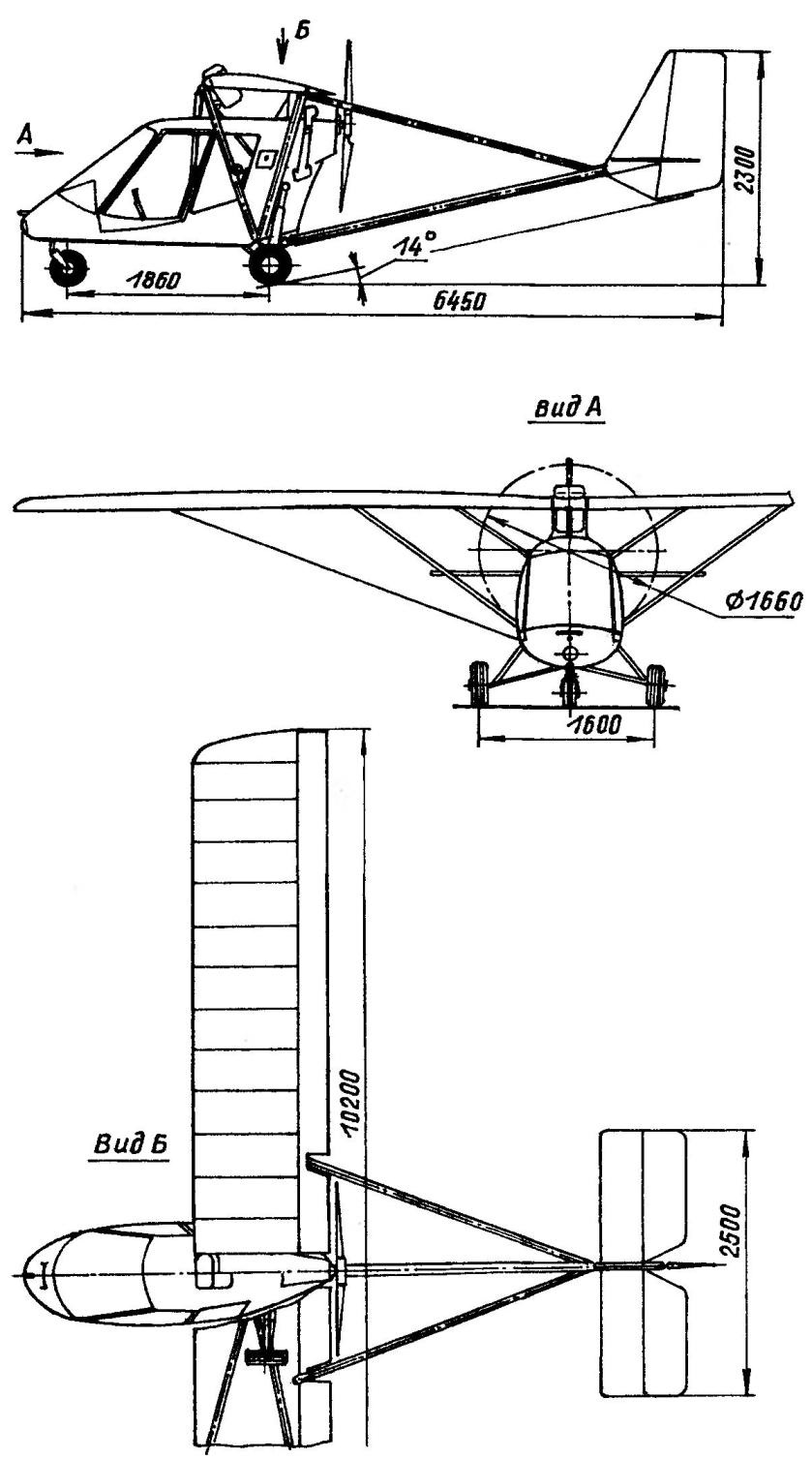
Ultra-lightweight double plane “Chick-2”
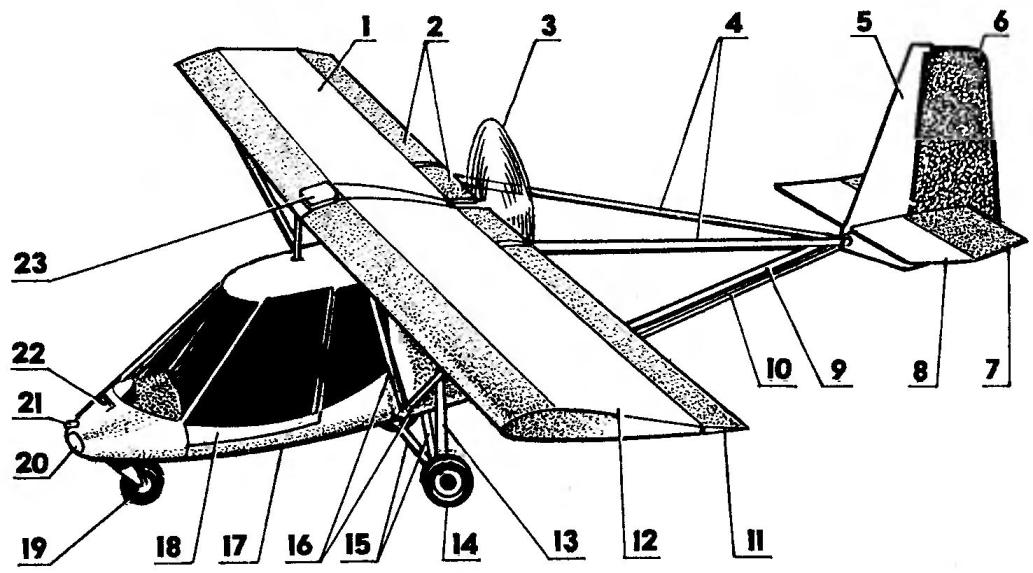
The main components of the airframe:
1,12 — right and left halves of the wing; 2— section of the right flaperon; 3 — the plane of rotation of the propeller; 4 — struts keel; 5 — keel; 6 — rudder; 7 — the left half of the Elevator; 8 — the left half of the stabilizer; 9 — tail boom; 10 — pull rudder; 11 — a large section of the left flap; 13—absorber side fairing landing gear; 14 — wheel side of the landing gear; 15 — lateral struts of the landing gear; 16, the struts of the left half of the wing; 17 — aeromodel; 18 — left the cockpit door; 19 — wheel nose landing gear; 20 —headlamp; 21 receiver air pressure (LDPE); 22 — intake ventilation of the cabin; 23 — container shoots a parachute rescue system
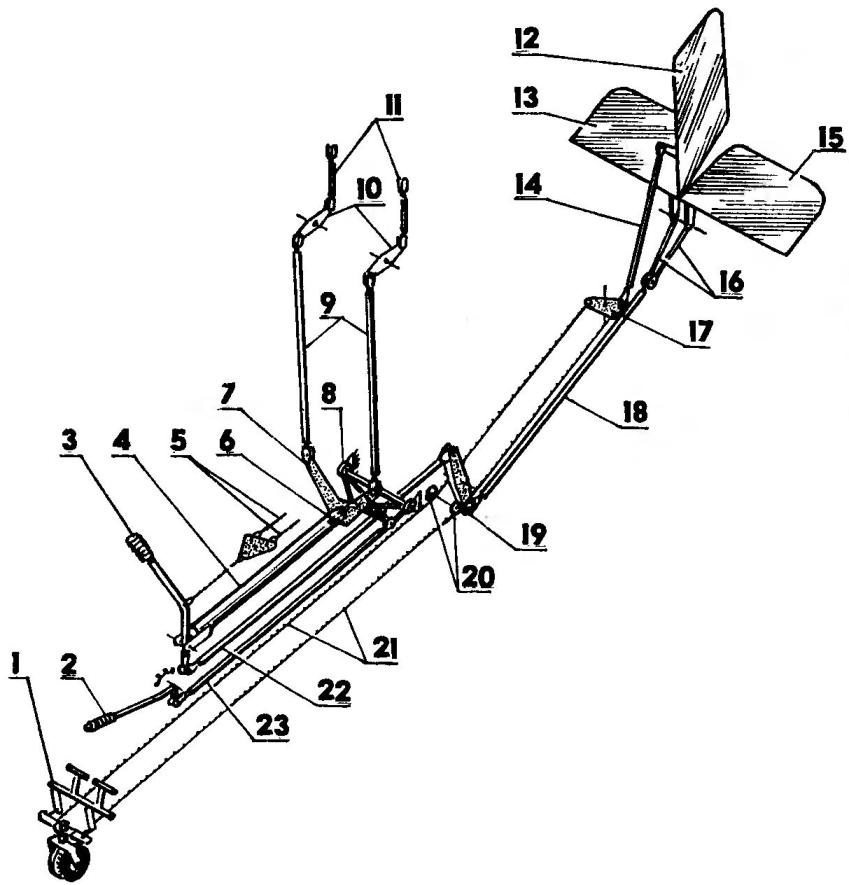
Diagram of the system UPRAVLINNYA plane:
1 — pedal unit; 2 — lever with the sector fixing the installation angle of the flaperons (WWF); 3 — handle; 4 — shaft control flaperons; 5 — brake cables to the side posts of the chassis; 6 — tongue of the locking mechanism for UWF; 7,10 — rocking control flaperons; 8 rocking of the locking mechanism for UWF; 9,11 — traction control flaperons; 12 — the rudder (PH); 13,15 — elevators (PB); 14,17 — pull and rocking of PH; 16,18,22 — pull PB; 19 — rocking the RV on the tail boom; 20 clips cable runs; 21 — control cable PH: 23 — thrust of the locking mechanism for WWF
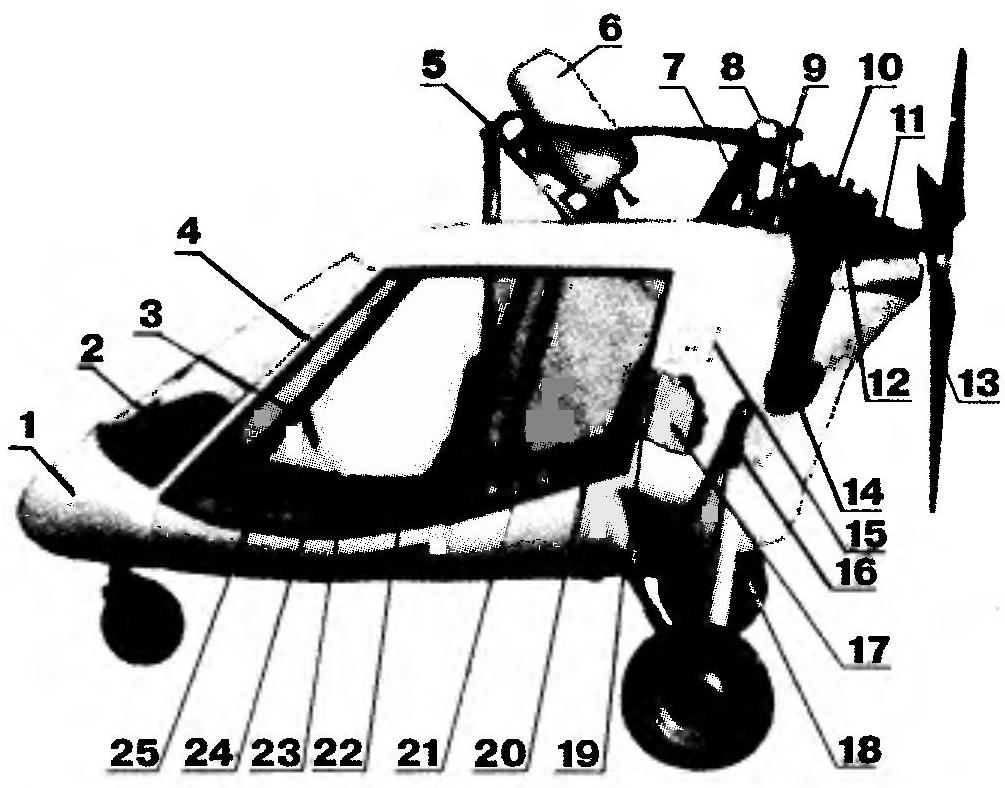
The layout of euromodule:
1 — cabin; 2 — dashboard; 3 — handle control of the aircraft; 4 — piano hinge hinge left door; 5 — pole with front mount wing; 6 — container shoots a parachute rescue system; 7 — radiator cooling system of the engine; 8 — cover-stopper of a radiator; 9 — pylon rear attachment of the wing; 10— engine; 11 — built-in reducer; 12 — pull on the bellcrank control the left flaperon; 13 — rotor; 14 — the silencer; 15 — hatch access to fuel tank and manual kick start engine; 16 — damper left landing gear; 17 — fuel tank 18 — beam frame cabins; 19 — to the outside of sound – insulating partition; 20— seat passenger (to starboard); 21 — the Luggage compartment; 22 — the pilot seat (port side); 23 — side panel control; 24 — lever engine control (ORES); 25 — the lever of the angle of the flaperons
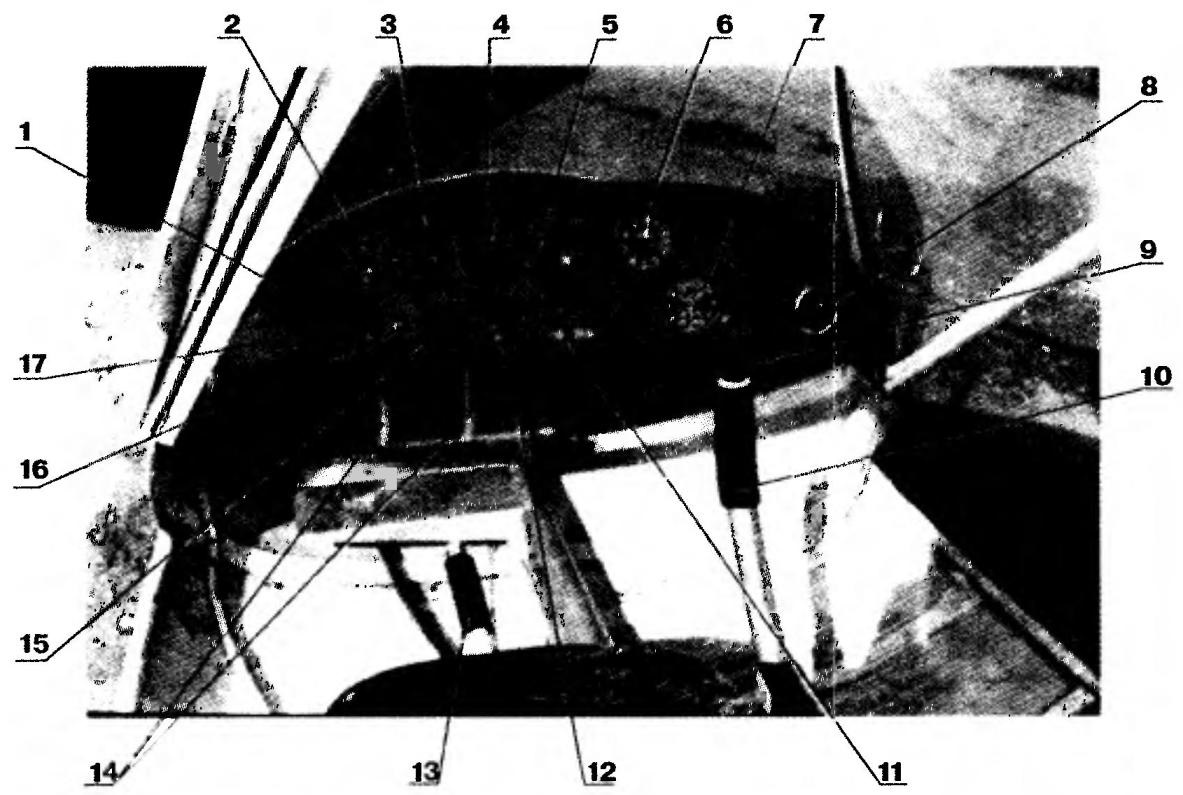
The dashboard and major organs UPRAVLINNYA:
1 — vent airflow compartment: 2 — switch lights; 3 — the Vario VR-10; 4 — speed indicator US-250; 5 — compass-attitude indicator MV-90; 6 — altimeter VD-10,7 — aviation watch; 8 — hour meter; 9 — button of the radio station; 10 — control stick Elevator, flaperons and brakes main landing gear; 11 — gauge slide; 12 — tachometer; 13 — the lever of the angle of the flaperons; 14—pedal control the front of the chassis and the rudder; 15 — the engine temperature gauge; 16 — button starter; 17 — switch on-Board electrical network
Side control panel:
1 — lever engine control (ORES); 2 — the switch of ignition; 3 — the switch check ignition circuits; 4 — the handle opening of the door lock; 5 — door lock
The microplane created for ALS “Rotor” based on years of experience with similar kinds of aircraft — deltalyo and the first “Chick”. Second, retaining the simplicity and ease of design, as well as the high performance characteristics of its predecessor (“Chick-1” at the fourth all-Union review-competition, the SLA-87 in Moscow took the first place in the class of ultralitej) of greater reliability and comfort.
“Chick-2” is designed for the training (possible installation paired control), sports (pilots club — winners of Russian Championships and world Cup winners) and patrol flights.
Additional safety in the air provides launched the parachute recovery system is placed between the outer wing panels. And soundproofing, ventilation and heating of the cabin, coupled with a low noise propeller create the crew is quite comfortable. Wide cockpit glazing provides almost all-round view, allows you to use the microplane for excursion and tourist and entertaining flights. For example, a young family of three people in a day can in full force go on a “Chick” in a nearby town to visit relatives or friends. In fact, besides a passenger seat, which folds out allowing you to rest in the road, the cabin has plenty of room for a child (or Luggage, if travelling without children).
In cases of emergency in the unfolded passenger seat can be transported in the supine position of the patient or injured person.
The microplane can be easily disassembled into four parts, stored in garage and transported outside the city to the start place any vehicle, including the trailer for “Lada”. In addition, the chassis “Chick” can be equipped with floats or skis. Also provides for installation of radio and satellite navigation system GPS.
The first feature-link “Chick” is that its powerplant is equipped with a pusher propeller. The reasons of this choice are two. First, the pilot must be maximum visibility and comfort. Second, the tubular struts of the keel and tail boom surround the rotor, forming a kind of fence is especially necessary outside the airport — Gawker there’s always.
The second feature is that the microplane, as already mentioned, can be disassembled into four units: aeromodel, the two halves of the wing and tail is enough to Unscrew three bolts for each half of the wing and tail. Measuring time two people for this job, do not spend more than an hour.
We intentionally do not use the term “fuselage” and replaced with “aeromodeler” not only because this part of the design of the microplane is a unit of storage in a disassembled state. The fact that aeromodel has an independent function: without wing and tail “Chick” can be used as an aircar, snowmobile or airboat, depending on what he “shod” in the wheels, skis or floats.
The third feature is in the layout of the cabin. As the designers have a seat in a double cab? Different: tandem (one after another) or “duet” (near-road). Each option has its pros and cons. For example, while learning beginner when planting a “duet” two times less than handama —proved world practice. However, the midsection of the fuselage on ultralitej is not determined by the size of the engine and there is no need to make it wide. The same — decreasing the width for the sake of reducing drag— aerodynamics; in this respect, narrow amidships cabin-a winning tandem. But it is long, which limits the review of the second pilot. In addition, require another set of instruments. In short, designers always face a dilemma in tandem or “Duo”?
For “Chick,” the chosen is not yet very common layout of chairs with a bias, or “side by side”. This can be found unless that in modern French “Mirage” or national educational “drying”. On ultralitej, like, is nowhere not found.
So, when the layout of the chairs “side by side” and quite freely accommodate two people the width of the cabin “Chick” a little less than one metre, and the midsection is 1 m2. The layout of the “Duo” would require 1.2 m2, that is twenty percent larger. The same amount would have increased and the drag.
And another feature of the present WEAK— side control knob that allows to drive and pilot, and with the right seat the co — driver or student.
It is useful, I think, to talk about the control system of the microplane as a whole. She is direct action, that is, all its command bodies, handles and pedals used by the pilot directly (without compensating and damping mechanisms) are associated with the Executive bodies: a steering front wheel, brakes, side wheels, chassis and aerodynamic elevators and directions. Control wiring mixed: hard part of it, using tubular rods (towards the steering wheel, flaperons and elevators), partly soft, with cables (for motor, brake side of wheel and wheel direction).
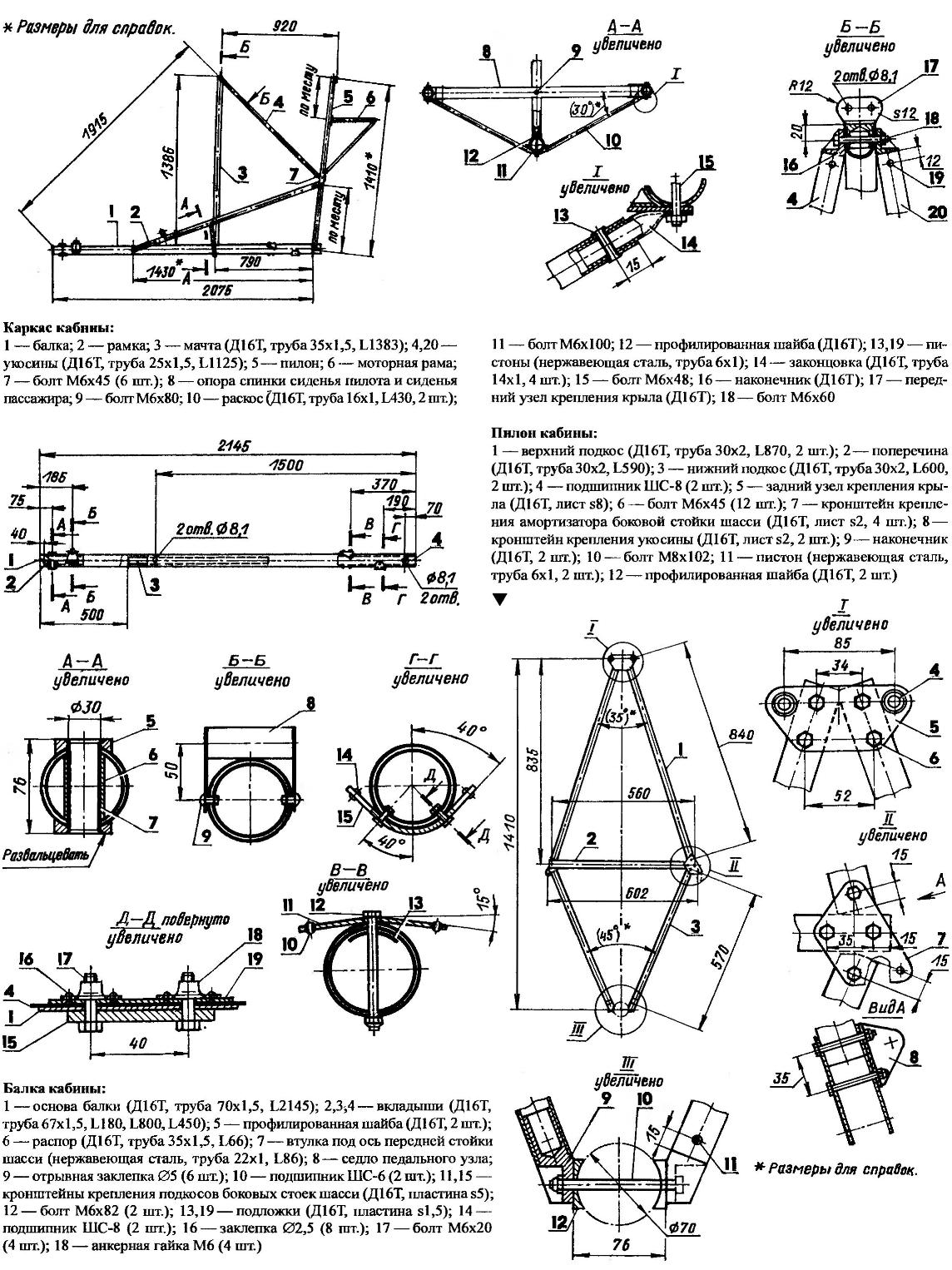
Cabin frame:
1 — pad (D16T, plate s2, 12 PCs); 2,6 — arc (D16T, pipe 35×2, L1650); 3 — the support of the seat back passenger (D16T, pipe 35×1,5, L830); 4 — the support of the passenger seat and seat back of the pilot (D16T, pipe 35×1,5, L870); 5 — support the pilot’s seat (D16T, pipe 35×2, L940); 7 — radius of the barrel (D16T, 2); 8 — bolt М6х95; 9 — bolt М6х48 (6 PCs.); 10,11 —caps (stainless steel pipe 6×1-12 PCs and 2 PCs L45 L40); 12 — tip (D16T, 2); 13 — shaped washer; 14 — a bolt М8х100
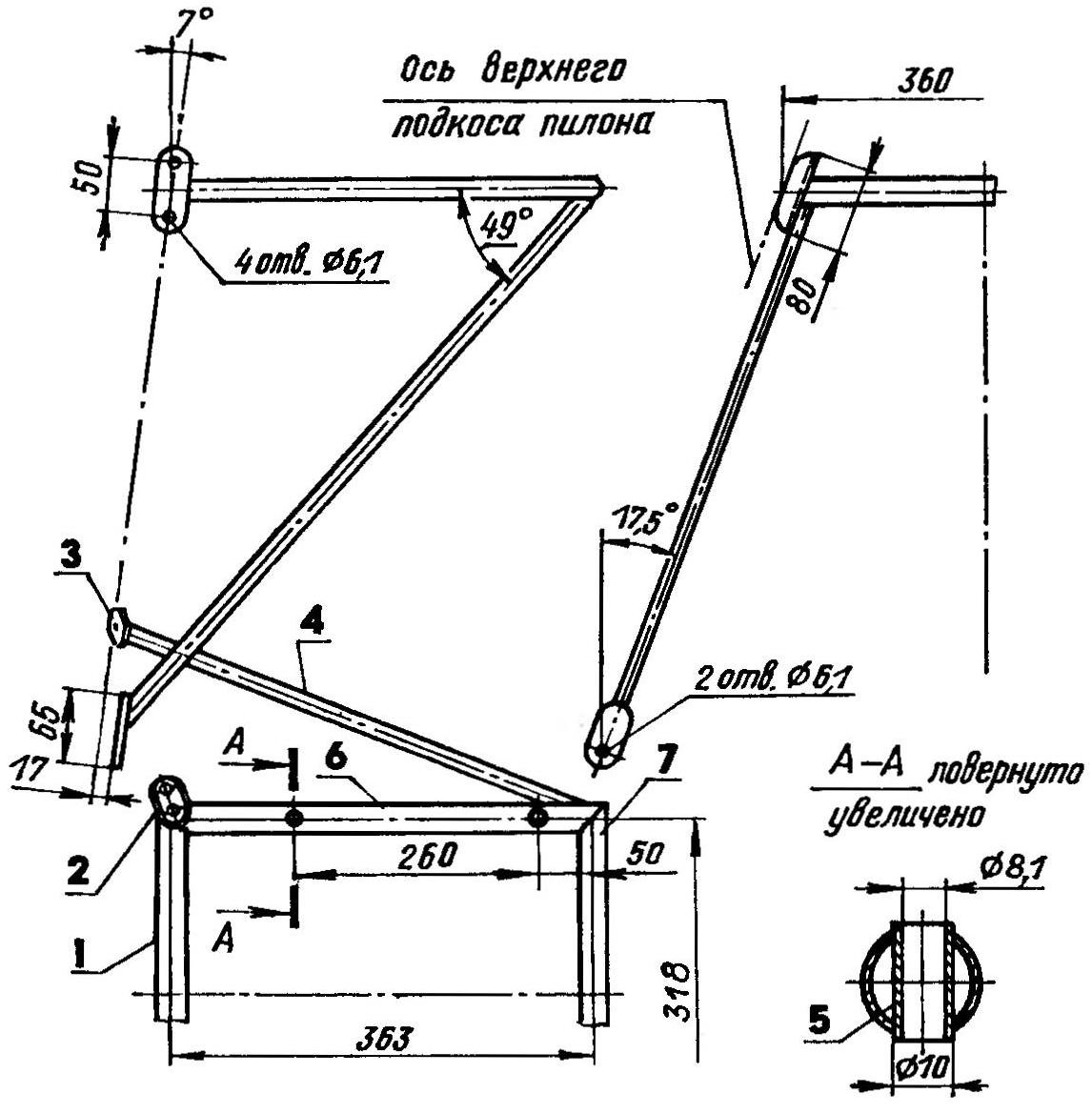
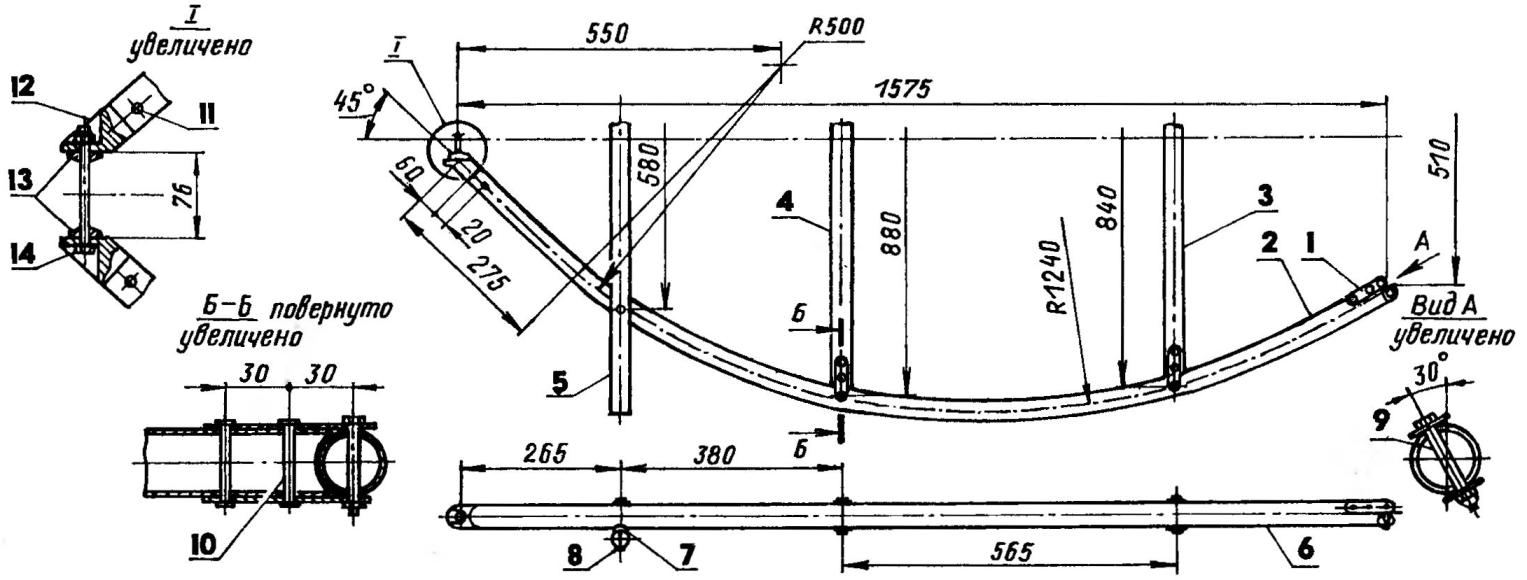
Motor frame:
1 — front cross member (30KHGSA, pipe 25×1,5); 2 — the cradle (30KHGSA, pipe 32×2, 2); 3 — earring (30KHGSA,.strip s3, 2); 4 — brace (30KHGSA, pipe 14×1, 2); 5 — Bush (30KHGSA, pipe 10×1,4-piece); 6 — longitudinal (30KHGSA, pipe 20×1,5,2); 7— front cross member (30KHGSA, pipe 20×1,5)
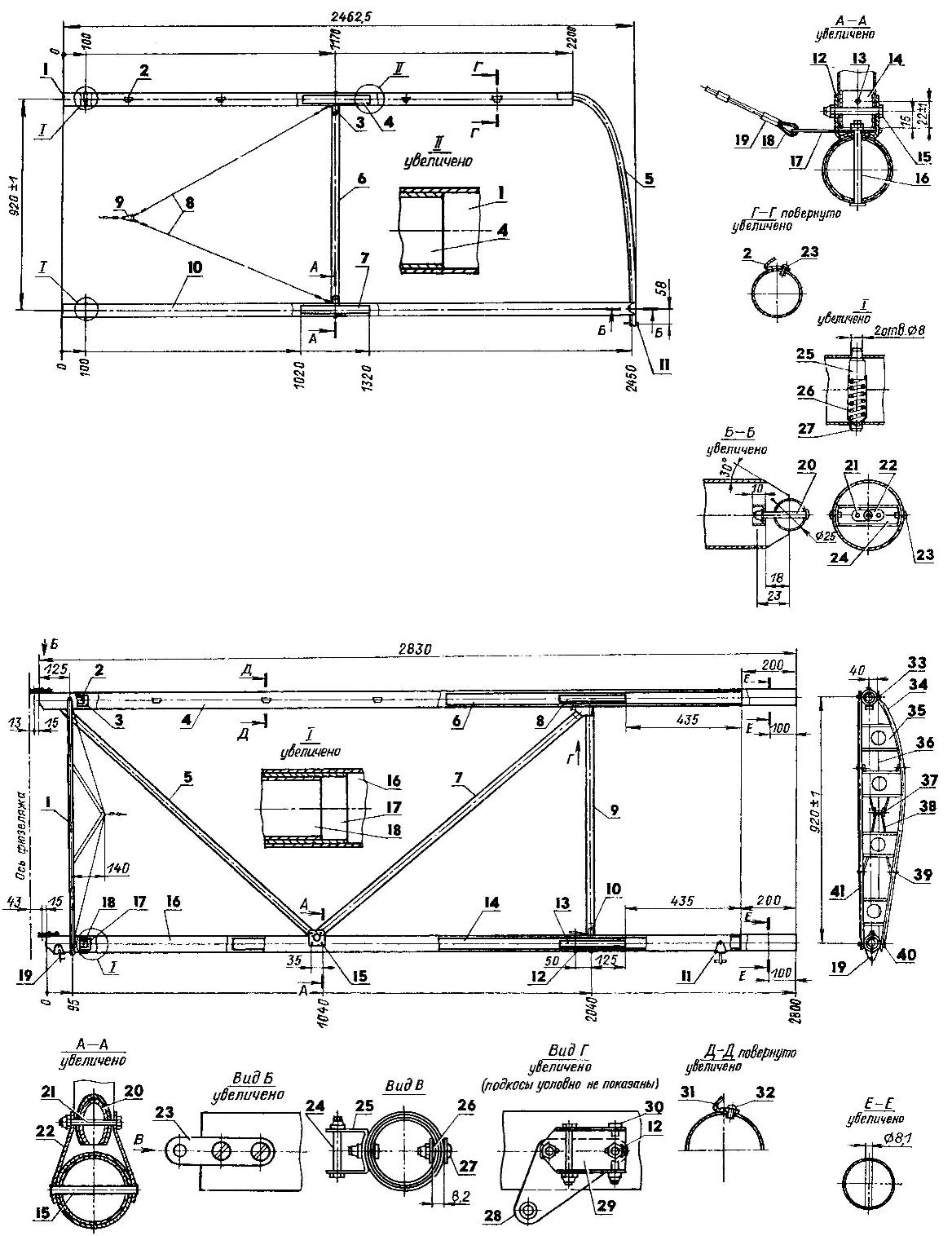
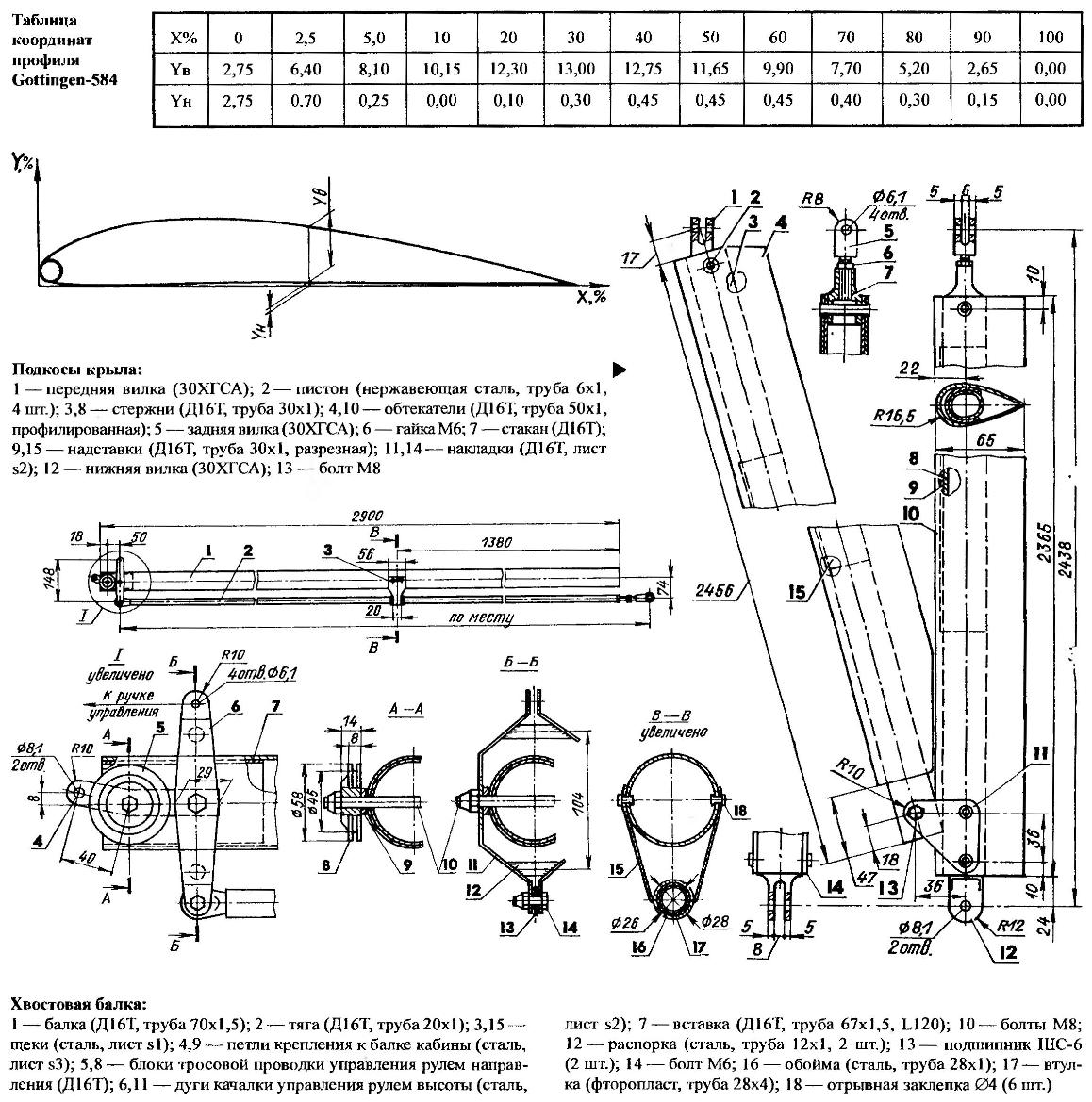
The frame is the root of the wing:
1 — root rib; 2,18 — short amplifiers (D16T, pipe 52×1,5, L150); 3,17 — average amps (D16T, pipe 55×1,5,L170), 4,16 — front and rear spars (D16T, tube 58×1,5, L2830 and L2800); 5,7,9 — struts (D16T, pipe 30×1, L1255, L1295, L850); 6,14 — paste (D16T, pipe 55×1,5, L1100, L1900); 8,13 — long amplifiers (D16T, pipe 52×1, L250); 10,25,29 — bracket (ДІ6Т, sheet s1,5); 11,19— brackets with the axes of the hinge sections of the flaperon (place); 12—bolts М6х70; 15 — the piston (stainless steel, pipe 8×1, L67, 2 pieces); 20 — bugey (D16T, pipe 28×2, L40, 6 PCs); 21,24,30 bolts М6х40 (6 PCs); 22 — Klondike (D16T, sheet s2, 2); 23 — plate (D16T sheet s2, 4 PCs.); 26 — profiled washer (2 PCs); 27 — a bolt М6х20 (5 PCs); 28 — eyelet (D16T, sheet s2, 2); 31 — emphasis (D16T sheet s1,5, 6). a 32 — tear-off rivet Ø3,5 (12 PCs); 33,40 — bolts М6х80; 34,41 —shaped arc (D16T, rough 14×1); 35 — the lining (D16T sheet s1,4 PCs.); 36 — stretching (steel cable Ø2. 5, 2 PCs.); 37 — a bolt М4х28; 38 — brace (D16T, pipe 8×1, 4 items); 39 — М3х25 bolt (4 PCs.). Shows the right half of the frame. The left half is a mirror image
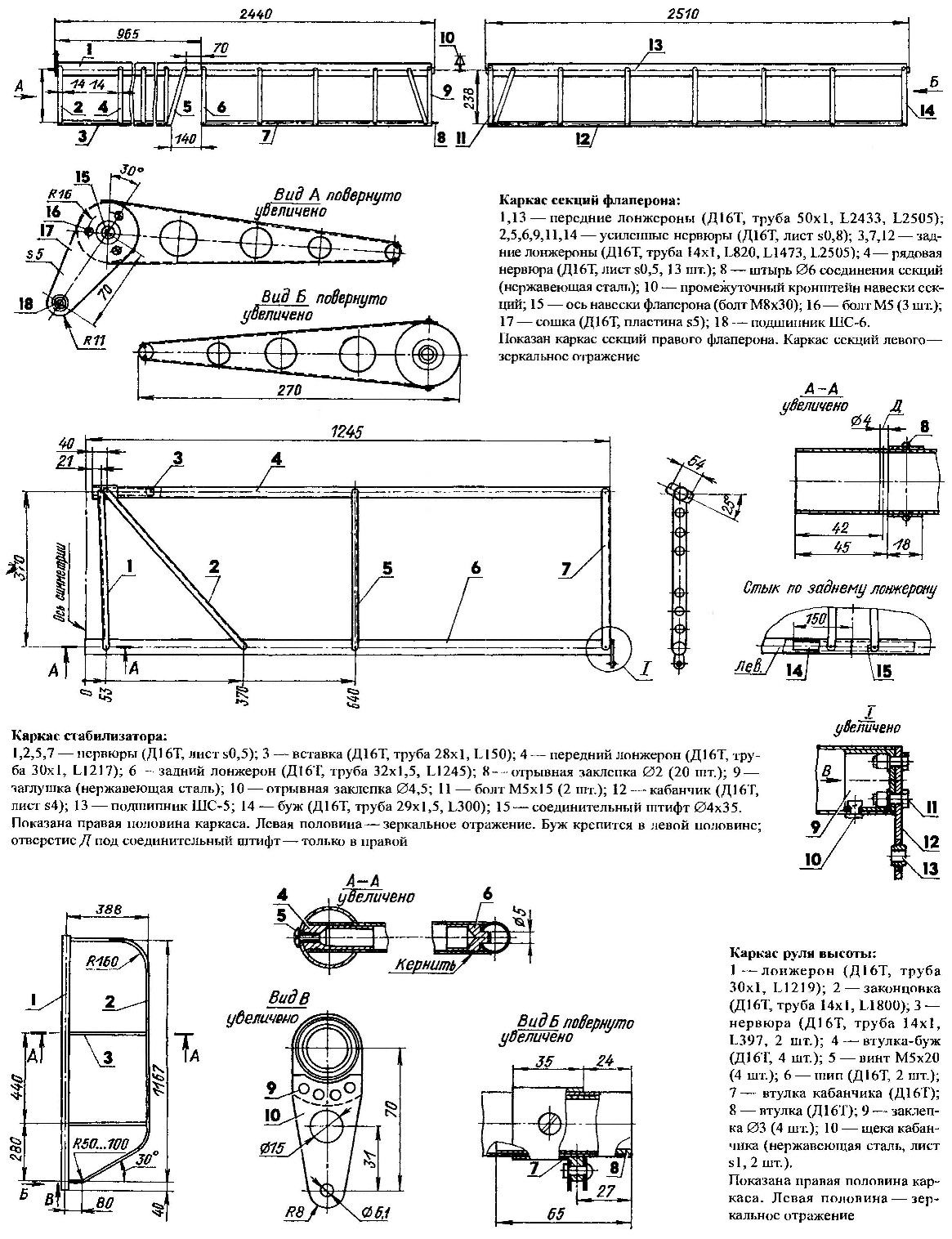
The frame end part of the wing:
1,10 — front and rear spars (D16T, pipe 55×1,5,L2200, L2450); 2—stops (D16T sheet s1,5, 6 items); 3,12 — bracket (D16T sheet s1,5); 4.7 — amp (D16T, pipe 52×1,5,L300); 5 — ending (D16T, pipe 25×1,5, L1180); 6 — brace (D16T, pipe 30×1, L855); 8— stretch (steel cables Ø2,7); 9 tee (stainless steel, sheet s3); 11 — axis attachment section of the flaperon (Ø6 rod with thread and nut M6 at the end); of 13.23 — tear-off rivet Ø3,5; 14—bugey (D16T, pipe 28×2, of 1.35); 15 — bolt М6х42 (2 PCs); 16 — a bolt М6х70 (2); 17 — a petal (stainless steel, sheet s2, 2); 18— thimble (4 PCs); 19 — a sealing wire (stainless steel, sheet s1,5, 8); 20 — болтМ5х40; 21 — rivet Ø2,5; 22 — M5 anchor nut; 24 — jumper (stainless steel, sheet s2); 25 — pin; 26 — a spring; 27 — locking. Shows the right half of the frame. The left half is a mirror image
As for the layout of auromodele, it’s a classic. In the front, in the bow, nestled the receiver is full of air pressure (static pressure sensor displayed on the left side of the cab), vent (from the car “Lada”) and heating equipment (warm air is taken from the engine radiator and the bypass channel is directed to the windshield), and the instrument panel; in the middle of the seat and of the passenger Luggage compartment; rear, sound and heat-insulating baffle — engine compartment with the power plant and the fuel tank. At the top, above the cabin, placed the container fires a parachute rescue system MVEN with squib. With a minimum height of 40 m it saves the plane and crew (total weight up to 400 kg) with a maximum speed of 150 km/h.
Dashboard “Chick-2” and the side control panel (to the left of the pilot seat) contain everything you need for a proper and safe piloting, namely: a set of tools and indicators for air navigation, control parameters of the power plant and fuel system equipment to create a comfortable cabin environment, as well as the engine controls and on-Board electric network.
In addition, there is communication equipment — Japanese VHF radio lcom-22 with the aviation frequency band for communication on the route with air traffic controllers.
Structurally, aeromodel made under the scheme: power frame plus lightweight streamlined shell.
Shell “Juv-2” is not made by the carrier and performs only two tasks: wall cabin space and provides its aerodynamics. (Bearing shell is very complicated and weighted the design.) Composite materials of the cabin, do not take the point loads from the power elements of the wing, tail and landing gear. Be design without a metal frame, it would have to be reinforced, here and there enclosing and podkladyvaya fiberglass. Attacks shell euromodule weighs only 22 lbs!
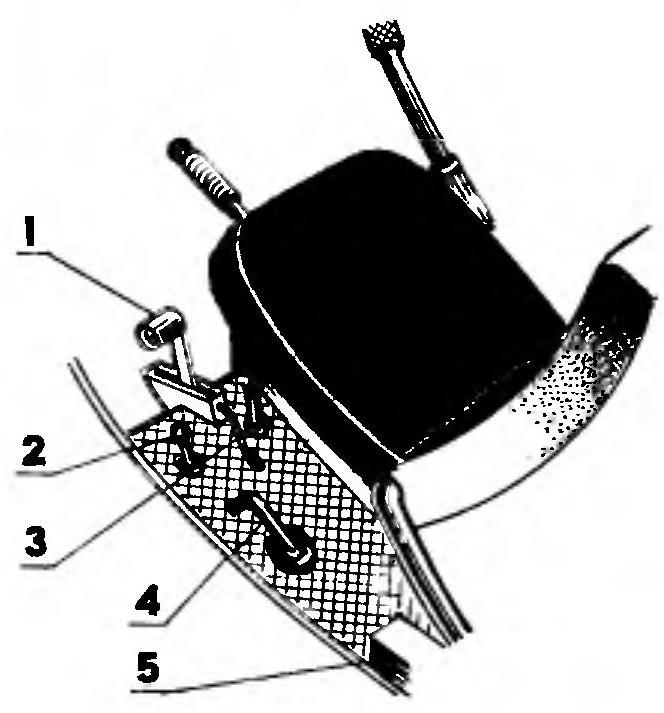
The shell consists of several parts, which are made from either foam-reinforced fiberglass with a thickness of 1-2 mm fabric (nose and tail fairings, roof, bottom and hood), or organic glass with a thickness of 2 mm (frontal and lateral glasses), or from combinations of these materials (door).
The nose cone has two glued the foam “frame” with a cross-section 36×4 mm and cutouts for lights, air intake ventilation of the cockpit and landing gear.
The bottom is reinforced with five, and the roof — four foam “frames”. In addition, the roof is provided with axial “stringer” of the same section — 36×4 mm, dural corners 12x12x2 mm to dock with the hood and banded rubber holes for outlet tubes of the mast and ucoin.
The tail fairing has rubber edged holes and cutouts for spring shock absorbers, muffler, carb and air filter, quick release hatch for fuel tank access and kick starter manually start the engine, and the undercut under the side struts of the landing gear.
The nose and tail fairings, the roof, the bottom and the windshield is single curvature and glued to the duralumin cover, connected with bolts and anchor nuts.
The front section of the bonnet is edged dural tube with a diameter of 10×1 mm and the cutouts for the muffler, carb and air filter — rubber. Inside the hood are covered with sheet polyethylene, at the junction with the tail fairing is reinforced with duralumin corners 30x10x2 mm and equipped with quick-release locks.
Each door frame is glued into the stocks of duralumin tubes of diameter 16×1 mm and dural area 14x14x1 mm—edging the side Windows. Then trim wedged and glued previously elastically deformed glass so that it remains slightly arched. Front tube doors reinforced with riveted thereto dural area 18x18x1,5 mm for connection with two loops combs on the cover of the windshield. In the closed position, door euromodule fixed the door locks from the car “Lada”.
The pilot’s seat has a frame of hromansilevyh diameter pipe 20×1 mm and is designed for 15-fold overload in the forward direction and 10 times backward. The pilot seat and the passenger car is equipped with seat belts.
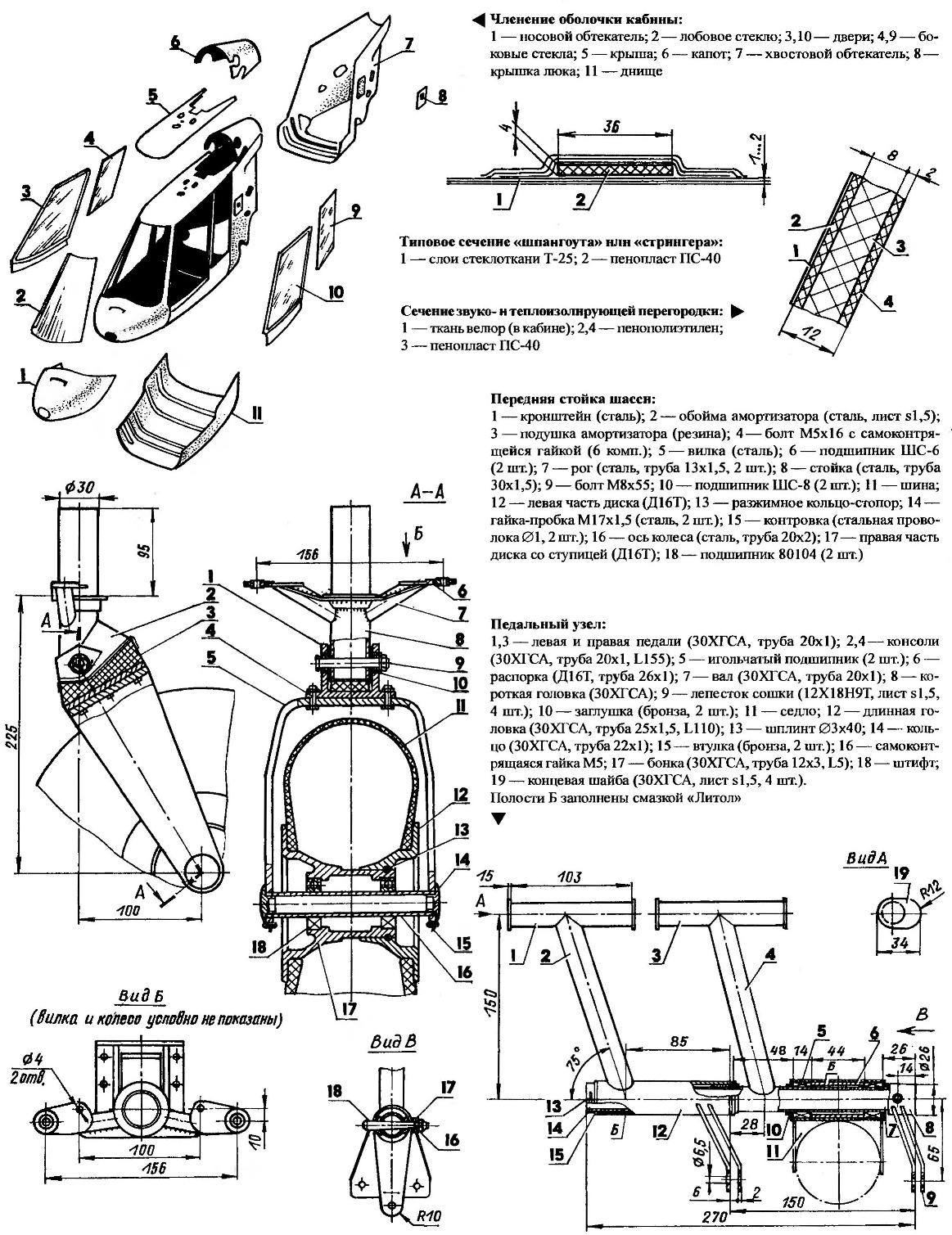
Chassis euromodule classic — front wheel and pyramidal side racks with telescopic spring shock absorbers. Bow front, driven by pedals in conjunction with the rudder, has air pneumatic size 300×125 mm and polyurethane shock absorber (extra turn of the rack according to the console beam of the frame of the cab due to its elasticity). Side wheel with a diameter of 400 mm —mokik equipped with disc brakes.
The fuel tank is welded of alloy AMC and placed for sound and heat-insulating partition. Primer is the syringe used for the initial fuel injection when starting a cold engine, located in the cockpit on the bulkhead (behind the pilot).
The basis of the power plant microplane is a two-stroke 2-cylinder engine Rotax-582 with a capacity of 64 HP with dual ignition (four candles). Fuel — 95 Ron gasoline mixed with oil in the ratio of 1:50.
The engine is mounted inside the tail fairing on the frame from steel (30KHGSA) pipe attached to the pole frame cabin. The radiator of the cooling system (from the car “Oka”) made between the cabin and the wing to the oncoming airflow. The engine and the radiator is covered by a hood.
The propeller-diameter 1660 mm three-bladed fixed pitch. The blades are made from an established club tech fiberglass with sickle-shaped ending and fittings of the leading edge of stainless steel. A seat in the duralumin hub standard: inch centering hole and six M8 bolts on the diameter of 75 mm.
This screw is designed for flight speeds up to 180 km/h with engines ranging from 30 to 60 HP and speed from 2200 to 2900 rpm the Warranty service life of the screw — 300 h
Frame structure of euromodule made by the club and well proven on many trucks deltalyo fernandovalley design, part of pipes which works in tension-compression and some bending.
Wing microplane — the high-wing monoplane-parasol, separated from the fuselage and without harmful interference. This modular arrangement makes technological gain: separately done cabin (aeromodel), separately for the wing. However, it is not without loss — in a head-on resistance. But for a small cruising speeds the increased drag is not too noticeable.
Wing microplane designed according to strut-braced scheme. In conjunction with the V-shaped tubular struts and pretensioned mechanical rope stretch marks, making the Park the wing looks bent down, it has increased strength and rigidity. In turbulence the wing is not spinning. And this is additional comfort and safety!
Structurally, the wing consists of two halves, the frame which, in turn, is divided into the root and end parts. These parts are connected telescopically with the use of internal cable stretch and spring-loaded pin-locks.
The profile of the wing — convex-concave G584 (the Atlas profiles — Gottingen-584). Chosen because, first, among his own kind, he has the maximum lift coefficient and better aerodynamic qualities; secondly, the bottom surface of the soft skin in-flight bend inside the wing and thus takes the position closest to the theoretical. And again, this profile fit well with the tubular side members.
It should be noted that in flight the upper surface of the wing skin doesn’t fit the profile, and the moment it usually turns out great. Therefore, the angle between the wing and stabilizer “Chick” is not a classic 2-3° and 4-5°.
The wing are cut from fabric on the basis of Mylar material (nylon is not good because of the loss of half its stiffness when wet). “Chick” is mostly used German Dacron brand Profill-LL (such as “Mylar” film-coating), although it may be advisable and cheaper Kemerovo fabric “yacht”.

“Chicks” over the surrounding area Kumertau
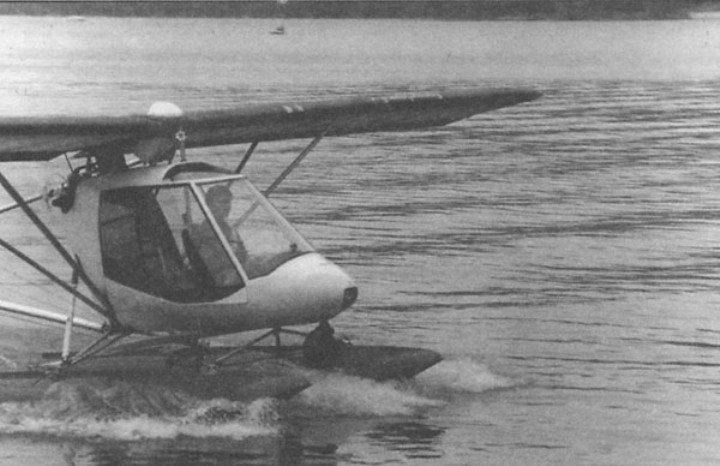

With floats “Chick-2” becomes a seaplane. In the cockpit — pilot Yu Bushuev
The sheathing is longitudinally mounted on the frame of the wing, like a bag, and stretched. It throughout the length of the front edge of the sewn pocket with a width of about 25 percent of the mean aerodynamic chord. In this pocket is a special insert of composite material with a thickness of 0.4 mm, which gives the forehead of the wing rigidity needed to withstand the dynamic pressure of the air.
Then inserted lats, performed by the classical Delta-glider technology of duralumin tubes with a diameter of 10×1 and 12×1 mm. First manually in those pockets are introduced lower LVL 12 (if necessary they can be easily taken out by pulling the drawstrings). Then in a special fixture and with great effort — upper profiled battens. Finally the covering is tensioned lacing in the center of the root rib.
The space between the two halves of the wing, where the container of the parachute rescue system is closed at the top with a sheet of composite material composed of carbon fibers and fiberglass brand SVM.
The two-piece flaperons of the wing. Turn the bearings on the pins embedded in the frame of the wing. In effect are tubular rods extending from the fixation mechanism of the mounting angle of the flaperons in the engine compartment. The mounting angle is set from the cockpit by a special lever, a sector which is fixed in four positions: +5°, 0° and minus 8° and minus 22°. Thus, the flaperons from its neutral position can be deflected up and down respectively at angles up to 17° and 10°.
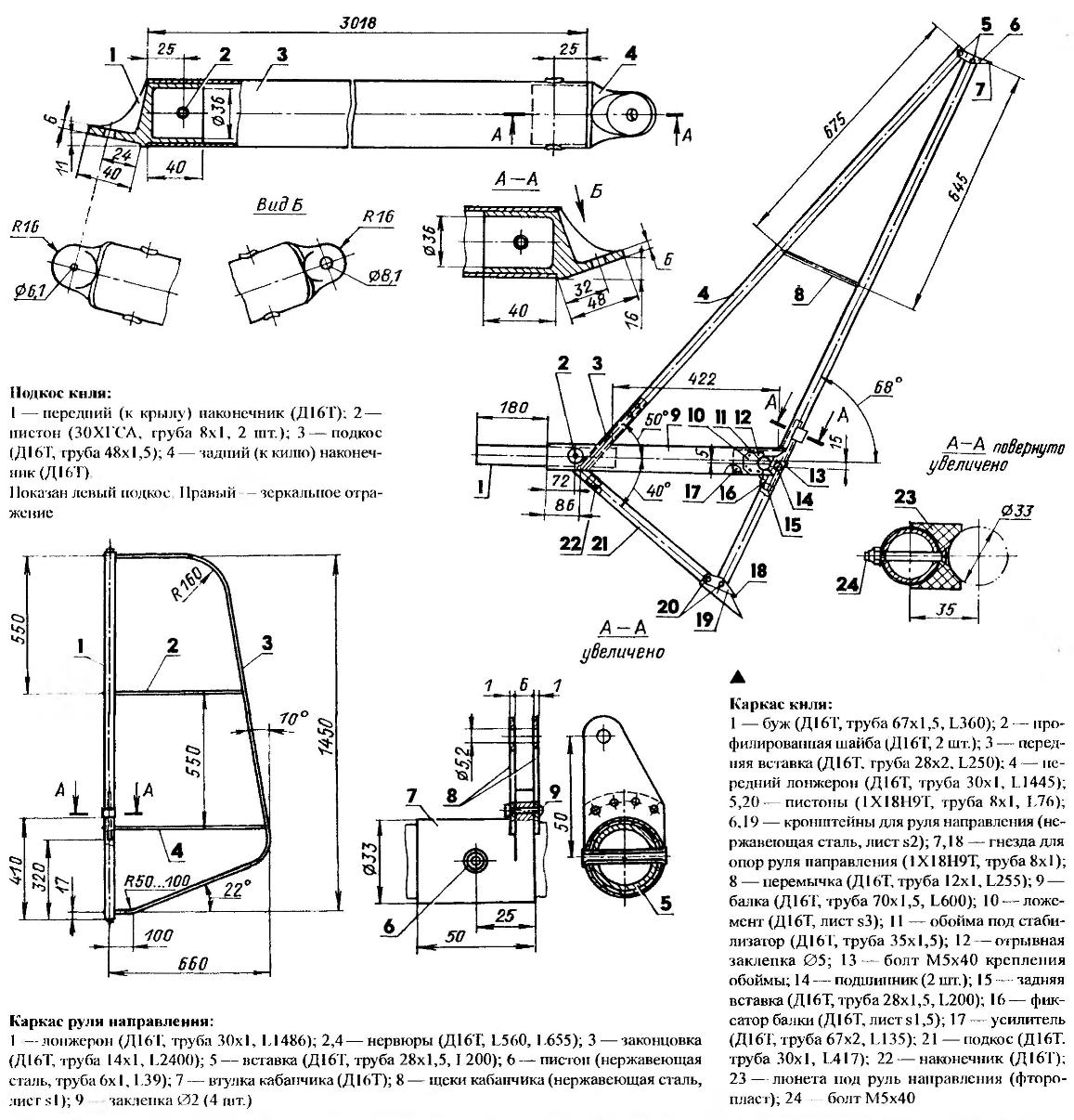
The tail Assembly was decided not to profile. Let the profile remains flat, as most aircraft. It’s easier in technology and easier to use. And no braces with braces. And aerodynamically clean cantilever tail!
The frame of the keel and keel beam telescopically connected tubular bougie and fixed bolts of the struts of the keel. Frame stabilizer consisting of two parts, joined with the keel at two points: at the front (two bolts penetrating the front longitudinal keel) and rear (clip, vkladani in the keel beam).
The skin of the fin and stabilizer are made of Dacron (available from fabric “poliant” or “Mylar”), Other fabric, e.g., nylon, is unacceptable, as is afraid of water, and most of all — the oil spray from the engine exhaust. Oil leave it dirty, slack and even rotting. And with the “Mylar” — like water off a duck!
On the elevators and turn the fabric used “Mylar”. Finally, the sheathing on the elements of the tail is stretched manually by using the lacing.
Such is the brief construction of the “Juv-2”, which the chief pilot of the club master of sports of the international class Yury Bushuev has achieved remarkable results, making the microplane and the club ALS “Rotor” is known all over the world.
A. TIMCHENKO, V. GRIBKOV
Flight data ALS “Chick-2”
Speed km/h:
the maximum allowable……………………………………….170
maximum………………………………………………………..150
cruising…………………………………………………………..120
landing without flaps…………………………………………65
with flap……………………………………………………………60
Lifting speed, m/s…………………………………………….3,2
The rate of descent m/s…………………………………………..2,6
The length of the run, m……………………………………………………..70
Range max, km ………………………………….450
The maximum flight altitude, m……………………………..4500
Range overload n………………………………………….-2…+4
Mass data ALS “Chick-2”
Takeoff weight, kg……………………………………………………420
Weight of structure, kg……………………………………………….230
Including: cab………………………………………………….. 83
power plant……………………………………………………..64
wing…………………………………………………………………………56
tail………………………………………………….17
recovery system ……………………………………………………..10
Mass (volume) of fuel, kg (l)………………………………..40 (50)
Powerplant SLA “Payez-2”
Engine type………………………………………………….Rotax-582
Power, HP…………………………………………………………….64
The diameter of the propeller, mm…………………………………1660
Geometric data ALS “Chick-2”
Length, mm………………………………………………………………6450
Height, m……………………………………………………………….2300
Wingspan, mm…………………………………………………10 200
The average aerodynamic wing chord, mm……………1250
Wheel base, mm……………………………………………………….1860
Wheel track, mm……………………………………………………..1600
Area, m2:
wing……………………………………………………………………12,7
the horizontal tail…………………………………….1,90
the vertical stabilizer……………………………………….1,20
flaperon…………………………………………………………….1,24
Shoulder, mm:
the horizontal tail……………………………………3850
the vertical stabilizer………………………………………3900
Angle, deg.:
cross V…………………………………………………………..1
stabilizer relative to the wing…………………………3,5
Cab height, mm………………………………………………..1200
Cabin width, mm…………………………………………………980
ACHIEVE MICROPLANE “CHICK-2”
First place in the championship of Russia (pilot Yuri Bushuev), July 1995 First place at the VIII open championship of the CIS and Russia on deltalina sport (motor ALS) (in the class of microplane, pilot Yuri Bushuev), July 1996
First place in overall SLA-97 on the route Moscow—Maikop (pilots Yu Bushuev and Ivan Chumachenko), July 1997
Second place in the Cup of Russia on deltalina sport (pilots Yu Bushuev and Ivan Chumachenko), July 1997
Third place and a bronze medal at the world Cup in Hungary (pilot Yuri Bushuev), July 1998
Third place and bronze medal at the world Championships in Hungary (pilot Yuri Bushuev), August 1999
Participant of International aerospace show MAKS-99 in Moscow and a participant of the Festival of ultralight aviation, August 1999, First place in the Cup of Russia on ALS, ALS aviarally, dedicated to the 55th anniversary of Victory (in class single SLA, pilot Yuri Bushuev), may 2000
EDITORIAL:
Special thanks to heads of club ALS “Rotor” for the drawings microplane “Chick-2” and regretted the failure to publish all of them — it is not enough even two issues of the journal. Therefore, we inform the interested readers that the missing drawings to the club.