 There is a whole class of electronic devices that operate in standby mode, “waking up” only for a short time to perform their tasks, such as apartment bell, simple security system, automatic watering installation, houseplants and some other such devices in order to save electricity, it is desirable decrease in voltage when they are “resting.”
There is a whole class of electronic devices that operate in standby mode, “waking up” only for a short time to perform their tasks, such as apartment bell, simple security system, automatic watering installation, houseplants and some other such devices in order to save electricity, it is desirable decrease in voltage when they are “resting.”
Let’s say that ham radio has established a call with stereo sound eight-bit microprocessor, a microcontroller or musical coprocessor that remember the settings and, actually, for working voltage required is constantly Naturally, it is equiped with a transformer power source, which in standby mode consumes a power of 8 W, and while the song is playing at full volume — 13 W (U = 220 V, I = 60 mA) as the period of active work of the call is just a few seconds, followed by a long pause is a step-down transformer with a capacity of 10 watts. And duty 8 watts — a lot or a little?
Yes and no For several years of continuous operation, for example, such a device will consume a lot of energy and a noticeable “catch” the family budget. But not so simple.
First, where do these 8 W if the microprocessor part of the call and the ULF in standby mode consume power less than 1 watt? These additional 7 W is incident as a result of losses in the step-down transformer and voltage stabilizer.
Second, the voltage is not always 220, sometimes, especially at night, it can reach 240…280 V. If most of devices voltage AC 250 V can still be a relatively long time to survive without damage, it is already 280 In for many of them can be fatal. Therefore, if you reduce the voltage in the standby mode, it will not only reduce the idle current of the transformer and the power losses on the linear voltage regulator and increase the reliability of the overall structure when an unauthorized increase in network voltage than the set limit of 220 V.
Energy saving devices for solving such problems are called economizers.
To what value is possible to lower the voltage? In the General case to give a definite answer is virtually impossible, because often for the operation of the apparatus in the standby mode on the primary winding of the step-down transformer enough voltage 150…170 In and occasionally of 120-150 V.
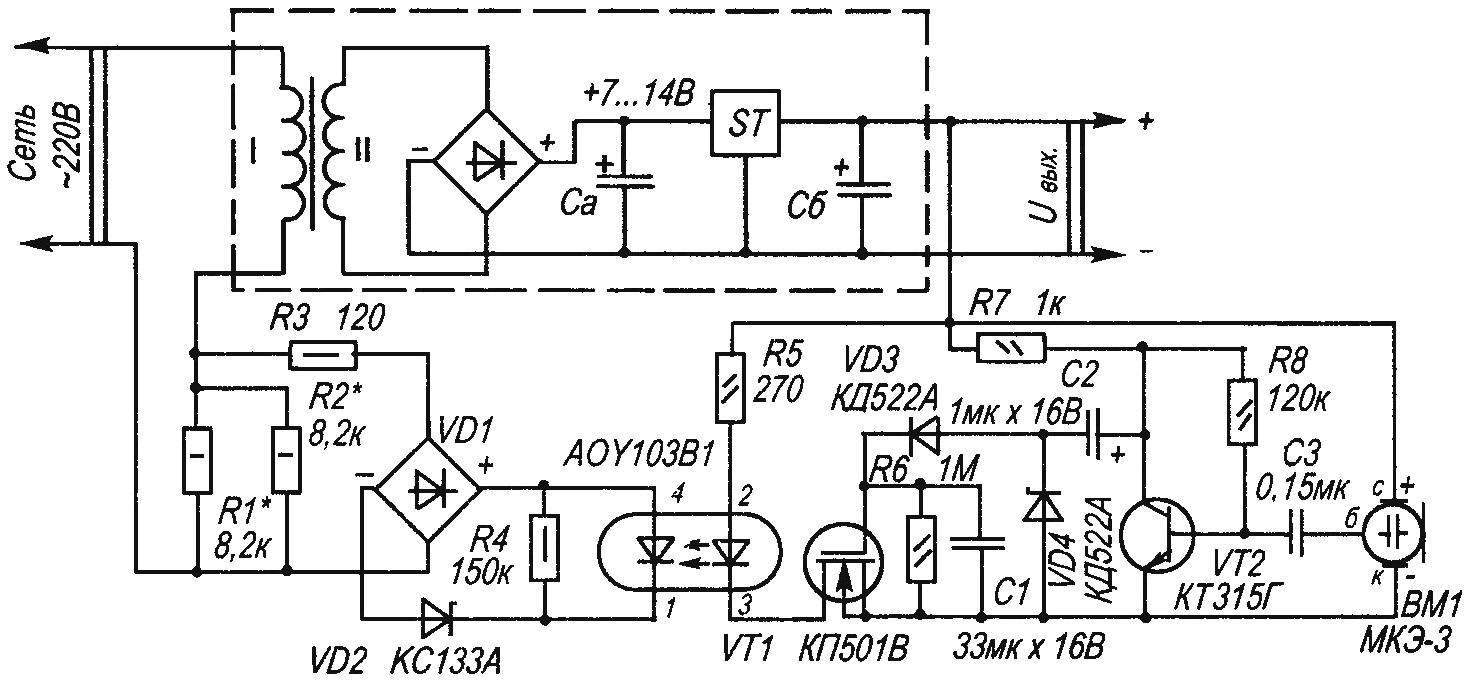
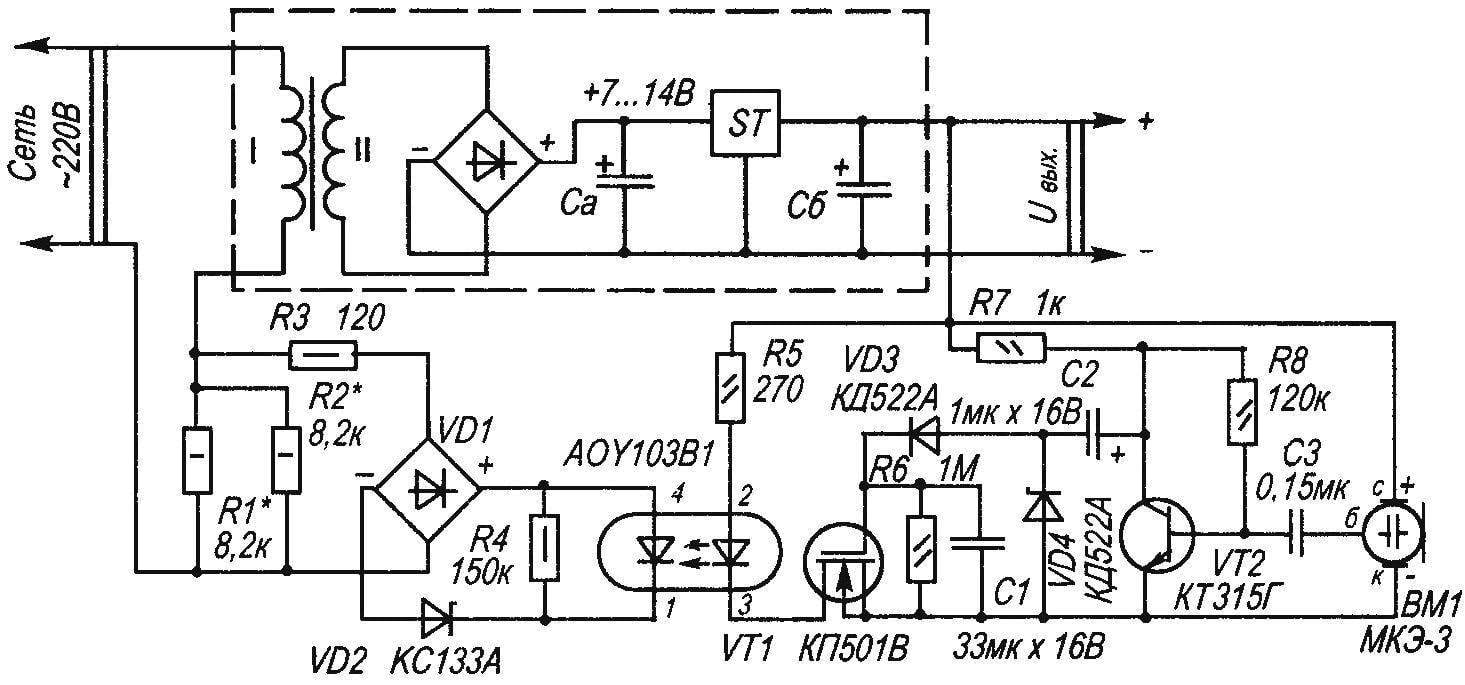
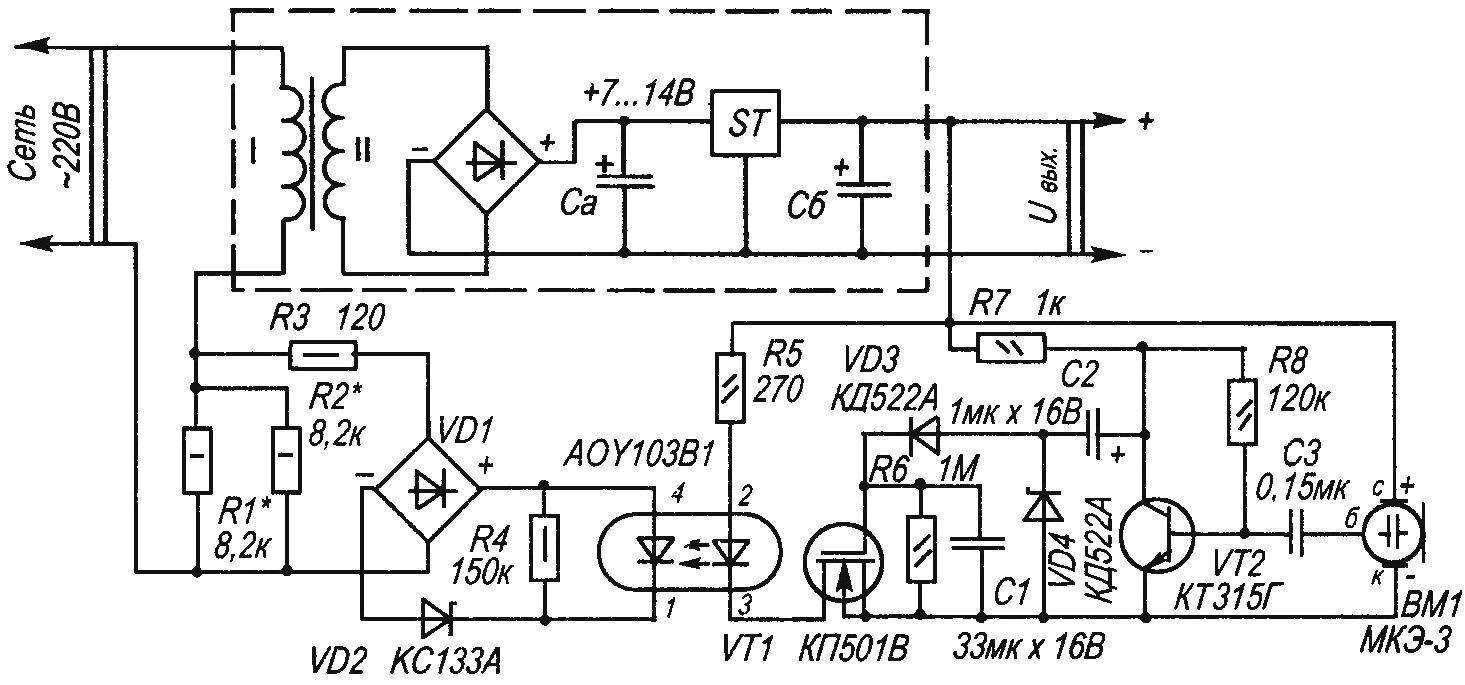
Circuit diagram of automatic economizer
The picture the author presents a schematic circuit diagram of one of possible variants of automatic devices that reduce the power consumption of the network with voltage of 220. The dotted line in the figure circled in the generalized scheme of standard power supply devices is Not necessary that its output voltage was 5 V. If the call (as an example of a device for which you want to save energy) works in standby mode (and so most of the time it is), then the speaker is silent. The amplitude of the AC voltage at the output of the microphone and thus on the collector of transistor VT2 is insufficient to charge capacitor C1 to a voltage greater than the threshold, opening the gate — source field-effect transistor VT1. Transistor VT1 is closed, the current through the led of the optocoupler SCR does not flow, the thyristor of the optocoupler АОУ103В1 is closed, the transformer feeds a low AC voltage through resistors R1, R2. As soon as the dynamic head of the call will issue the first sounds, the capacitor C1 is quickly charged to a voltage 2…3 V, the transistor VT1 opens, hence opens and the thyristor of the optocoupler, to the primary winding of the transformer will be almost full voltage.
The Zener diode VD2 and the resistor R4 is conducive to the full closing of the thyristor of the optocoupler, and the resistor R3 limits the surge current through it. The time during which it continues to flow to the transformer full voltage after the machine in suspend mode depends on the parameters of the chain R6, C1. Generally is about 5…10 seconds.
Details and design
The optocoupler can be replaced by ЗОУ103 index, АОУ103Б or better yet, ЗОУ103Г Diode bridge VD1—КЦ422Г, КЦ402, KTS405 index A—e Transistor /T1 can be replaced by КП501А (or B), ZVN2120, preferably with a threshold voltage of opening not more than 1.5 V. the Transistor VT2 is on any low-power n-p-n, for example, series КТ342, КТ3102, SS9014. VD3, VD4— type KD503, КД103, KD521, IN4148. Zener diode VD2, it is possible to use a series КС139, КС147 Capacitors of the type K50-35, non-polar capacitor—type K10-17, KM-5. The appropriate power resistors type MLT, S2-23, S2-13 In most cases you can do without the microphone, if the right pin of the capacitor C3 connected to the signal output dynamics through a resistor of 10 kω. When the amplitude of the audio voltage at the speaker outputs does not drop below 3 V, it is possible to do without a stage of transistor VT2, and the signal feeding to the right on the diagram, the output capacitor C2. Having dealt with the principle of finalizing the device, you can exclude from the circuit elements R7, C2, VD4, VT2, R8, C3, ВМ1, and to control the transistor VT1 through the diode VD3 is necessary to apply voltage of 2.5 ..10 In the main Board of the device But such simplification is possible and available, so the figure shows the circuit embodiment with a microphone. The node can be mounted on Board dimensions 70×30 mm any convenient form of mounting. The microphone should be placed close to the diffuser to the dynamic head.
Commissioning is reduced to the selection of the resistors R1, R2 to the desired level of reduction of the supply voltage. These resistors are chosen based on the power reserve of not less than 2…2,5 times. It is sometimes convenient to navigate by the voltage on the filter capacitor, labeled Sa.
At the time of switching the device from standby mode to active there was a strong “drawdown” of the rectified stabilized voltage, the capacitance of the capacitor of Sa, SB must be large enough—very reasonable-oxide capacitors 2200 UF. To control the more powerful load, use the appropriate SCR or triac opto-electronic relay.
A. KASHKAROV