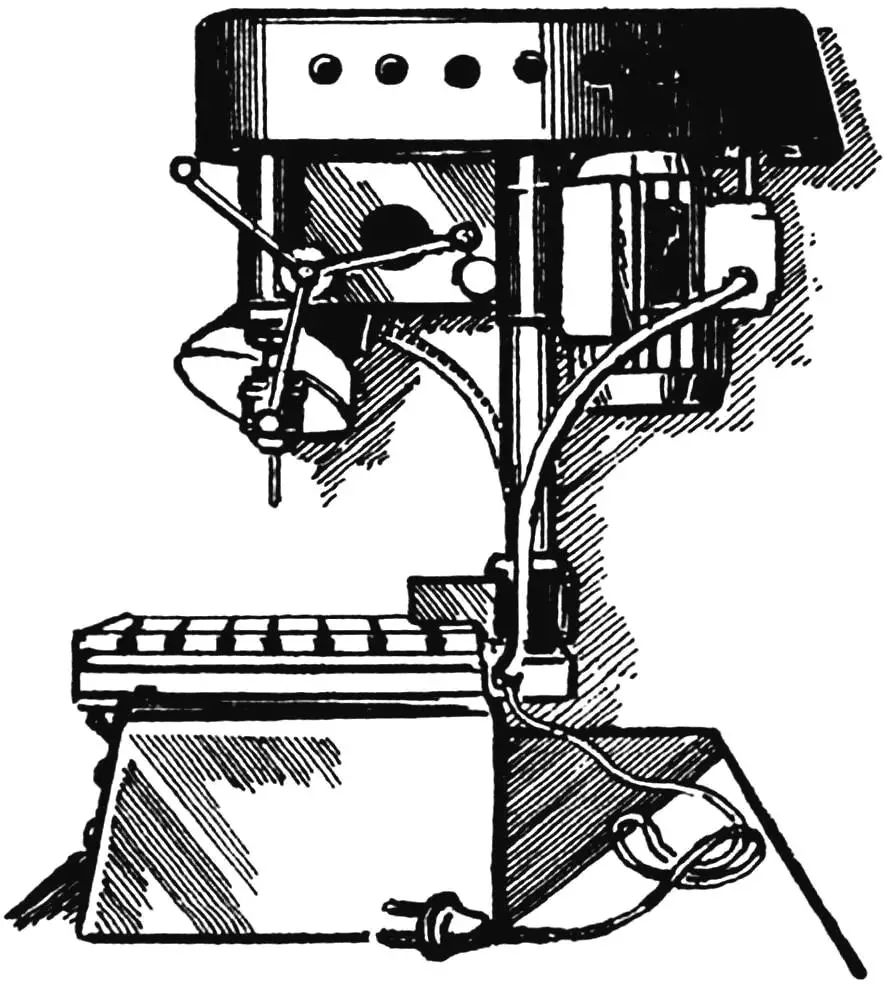
This machine, operating from a single-phase AC network at 220 V, was manufactured in a technical creativity club at a lyceum. It turned out to be compact and convenient, meeting safety requirements. In addition to drilling holes and countersinking, the machine can also perform simple grinding and milling work using various attachments.
The machine has a welded frame with a stand and a movable carriage that is fixed on the stand in any intermediate position. The carriage houses a quill with a spindle, a quill gear drive with three rotary feed handles on one shaft, and an electric motor with a V-belt drive.
The power of the drive electric motor was selected based on the maximum expected drill diameter used when working on the machine. Here, an asynchronous three-phase electric motor type AIR-50V4 with a power of 90 W and a rotation speed of 1340 rpm is used, powered from a single-phase network through a phase-shifting capacitor.
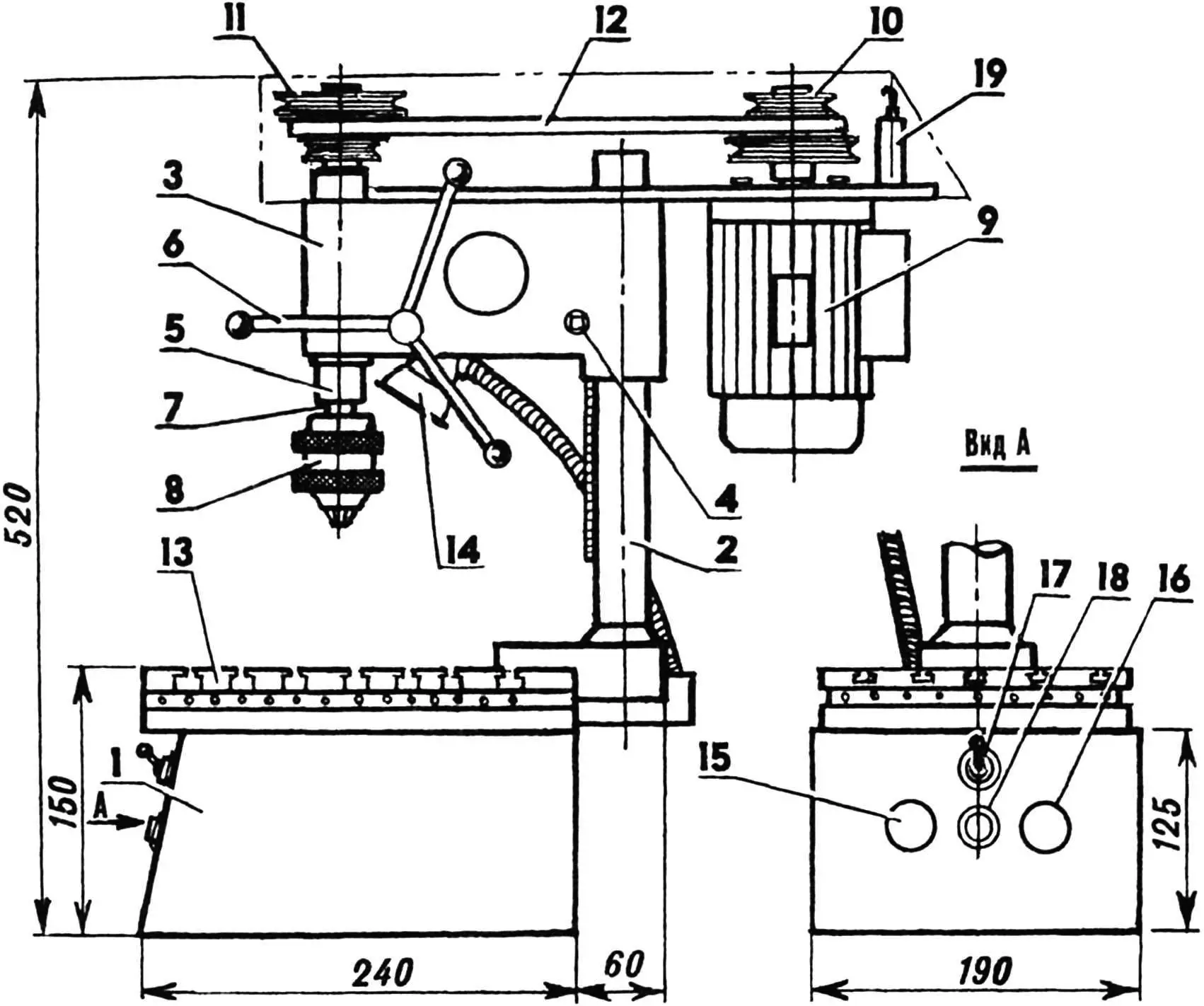
1 — housing; 2 — stand; 3 — carriage; 4 — carriage movement mechanism; 5 — quill; 6 — feed handles; 7 — spindle; 8 — chuck; 9 — electric motor; 10 — drive pulley; 11 — driven pulley; 12 — V-belt; 13 — plate; 14 — lamp; 15 — START button; 16 — STOP button; 17 — REVERSE toggle switch; 18 — indicator lamp; 19 — interlock switch
A three-groove V-belt drive pulley is mounted on the electric motor shaft, and exactly the same pulley is on the spindle. By shifting the V-belt to one of the pairs of opposite grooves (with the machine turned off!), you can get 400, 1340, and 2500 rpm on the spindle.
The entire V-belt drive is covered by a housing. The housing is attached to the carriage using a hinge, and when it is raised, the limit switch interacting with it blocks the machine from turning on.
The machine housing contains electrical equipment: two magnetic starters type PML and a step-down transformer type TBS-250 A (220/24 V), which powers the control circuit, local lighting lamp, indicator lamp, and rectifier bridge that provides dynamic braking mode. Protection against overloads and short circuits is provided — fuses.
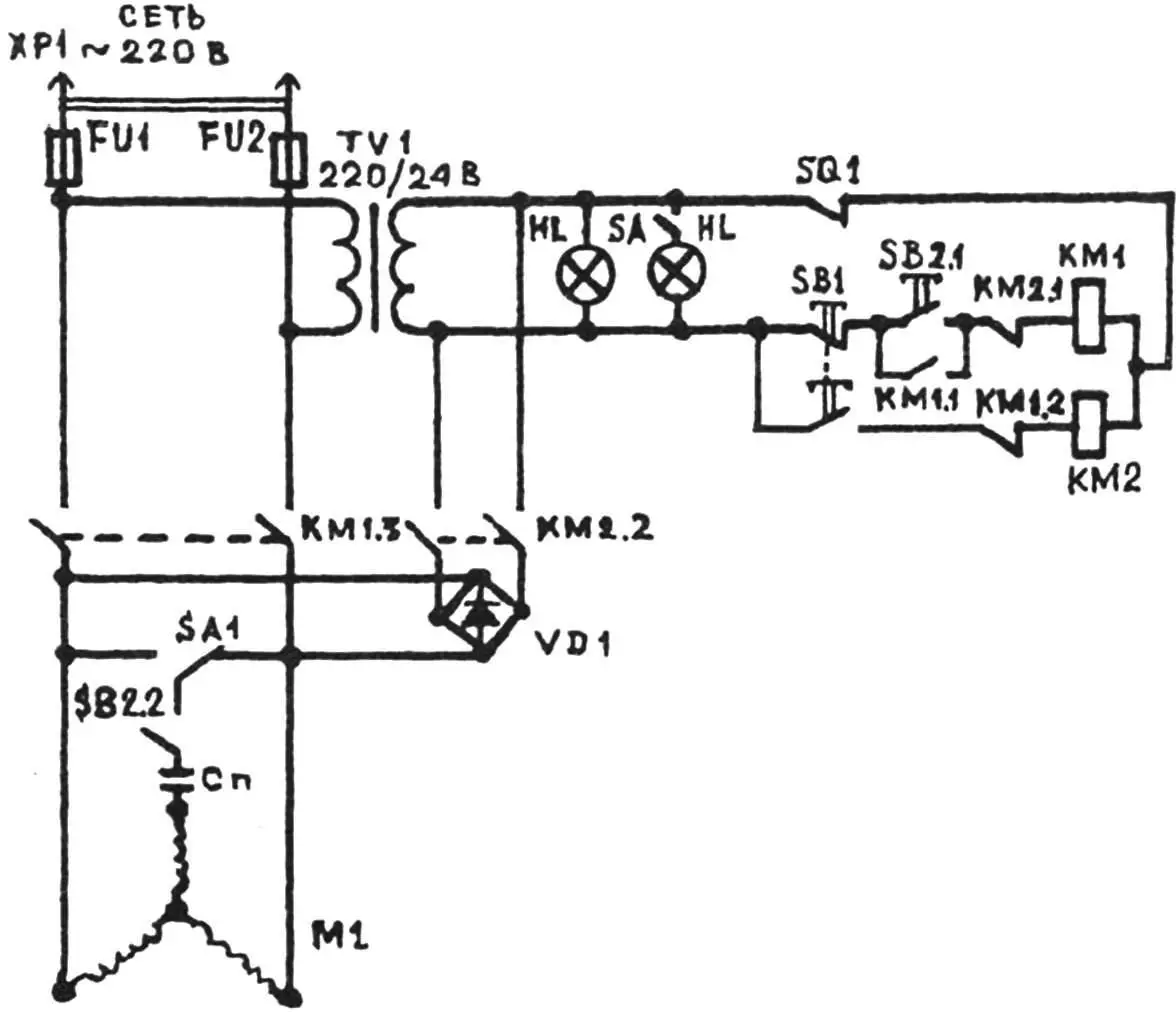
In the electrical circuit, protective “grounding” of non-current-carrying parts (special plug) is provided in case of electrical insulation breakdown, and the machine housing also has a grounding screw. The circuit includes a protective interlock that prevents simultaneous activation of both magnetic starters.
A local lighting lamp type HKC is located on the left side of the housing, switched on by a separate toggle switch.
A workbench plate is installed on top of the housing on four screws, on which various attachments and workpieces to be processed are secured.
Before starting work, it is necessary to bring the workplace into proper condition, check the reliability of fastening of individual machine units, drill, and workpiece, make sure there is no drill runout and that grounding is present.
Work is performed as follows. The plug is inserted into the socket — the indicator lamp lights up on the machine’s front panel. By pressing the START button, the first magnetic starter is activated — the electric motor starts. If necessary, the STOP button (with red push button) activates the second magnetic starter — dynamic braking of the electric motor begins.
The drill should be pressed smoothly, and before it exits the through hole, reduce the force. During work, chips should be removed with a brush or special hook. It is recommended to stop the machine after the drill is removed from the hole.
E. GAYNEEV, M. TOKUNOV