A jigsaw is a common tool. However, when working with it, one often runs into certain difficulties: the blade breaks, slips out of the clamps, and when cutting along a curved contour it often twists, which makes it hard to keep the desired direction.
It is much more convenient to use an electrothermal (hot-wire) jigsaw, which allows cutting parts of any shape from plywood (wood), organic glass, ebonite, and other combustible or meltable materials. This improves both comfort and quality of work.
The general view and main dimensions of the electrothermal jigsaw are shown in the figure; they depend on the size of the parts being made.
The jigsaw consists of a tubular bow, handle, electric switch, nichrome wire, screws with wing nuts, insulating spacer, lug, and power lead. The bow is made from a duralumin tube Ø 12 mm. It can also be made from laminated plywood. This part should be light and strong. The handle is made of 10 mm textolite. It has a cylindrical shank whose diameter matches the tube bore of the bow. A groove for the power lead is cut in the shank; the lead runs inside the tubular bow.
The lug—made of 1 mm sheet copper—is fixed to the bow with two screws. The end of the nichrome wire (heating element) is attached to it with a screw and wing nut. On the handle, between two cheeks made of 0.8 mm sheet duralumin, the electric switch is mounted.
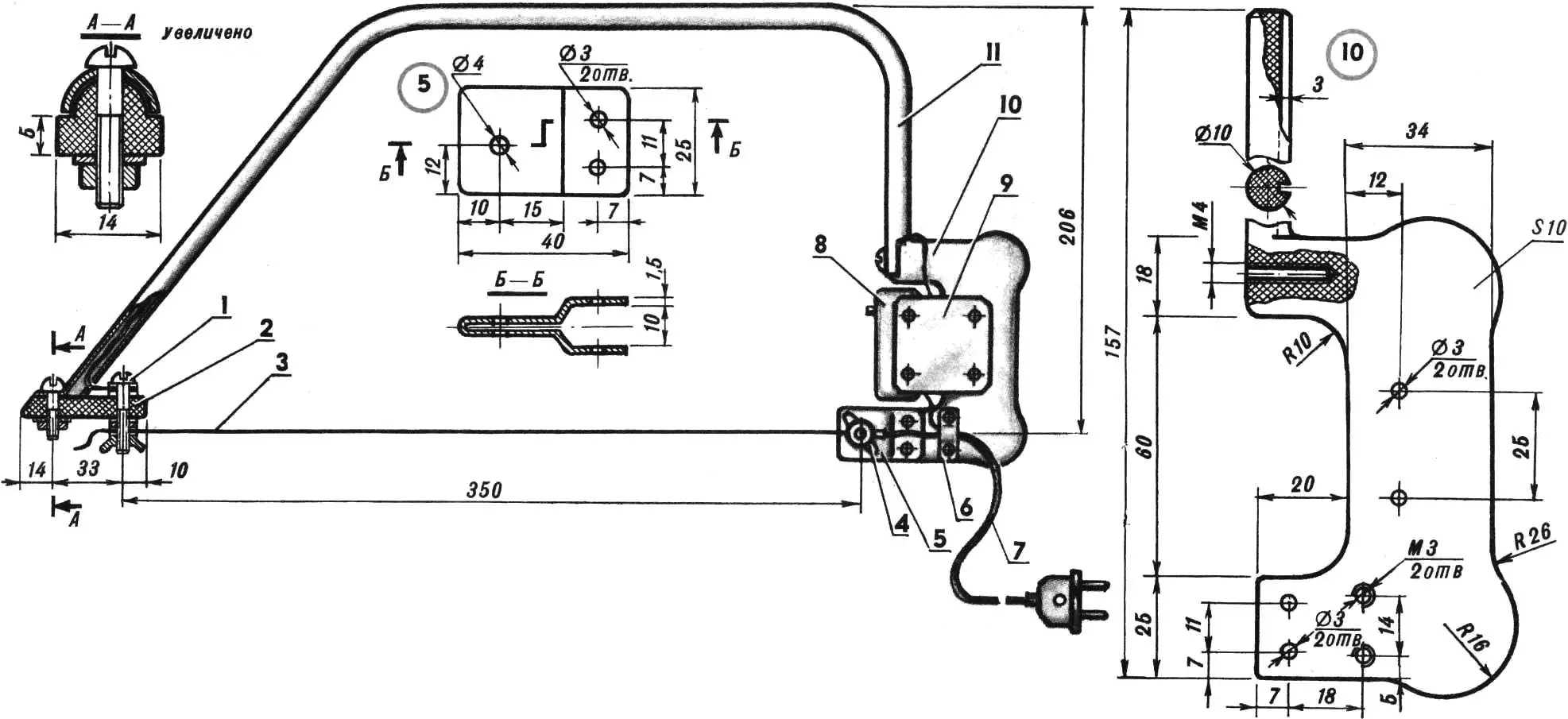
1 — M4 screw, 2 — spacer, 3 — nichrome wire, 4 — M4 wing nut, 5 — lug, 6 — bracket, 7 — power cord, 8 — switch, 9 — plate, 10 — handle, 11 — tubular bow.
The heating element is the spiral from an electric iron; the most suitable is Ø 0.5 mm. The wire length depends on the length of the tubular bow. The nichrome wire is fastened with some tension.
The electrothermal jigsaw is powered at 12–14 V; a rheostat is advisable when cutting. The current draw depends on the material being cut and on the length and thickness of the nichrome wire. For the bow dimensions shown in the figure and 0.5 mm nichrome wire, the current for different materials is 3–5 A.
Before starting, set the required current with the rheostat according to the material. Note that at high current (hot wire) plywood can ignite, while with insufficient heat organic glass only softens and does not cut.
The electrothermal jigsaw is simple in design, convenient to use, and allows cutting (burning) parts of any shape.
The only drawback is that cutting produces smoke with an unpleasant smell from the material.
When using the electrothermal jigsaw, safety rules must be followed: protect hands from burns, keep flammable items away from the work area, and ensure the room is well ventilated.
«M-K» 3’89, P. KAPITONOV