 During repair works of structures with steel threaded connections of the work items that have to deal with the complexity of their separation due to corrosion of the thread. These phenomena can be caused by the influence of precipitation, condensation as a result of temperature changes, as well as in cases of operation in different aggressive environments.
During repair works of structures with steel threaded connections of the work items that have to deal with the complexity of their separation due to corrosion of the thread. These phenomena can be caused by the influence of precipitation, condensation as a result of temperature changes, as well as in cases of operation in different aggressive environments.
Use anticorrosive and the same effect of resources does not always lead to the desired results. In these cases we often replace the entire parse node, i.e. re-joined to produce detail drawings, and even model. This complicates and significantly increases the cost of operation and increases timeliness. The latter circumstance is compounded when working in low temperatures. To avoid this phenomena it would be possible to make nodes (and mating parts) of corrosion-proof metals, non-ferrous metals, e.g. bronze. However, this will increase the cost of goods and, in addition, such a decision may not be valid in terms of strength or other performance.
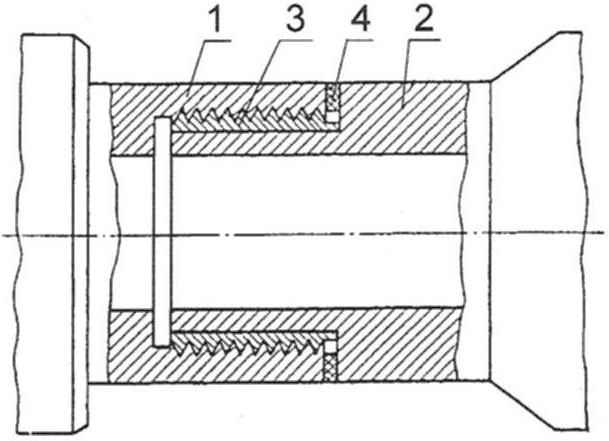
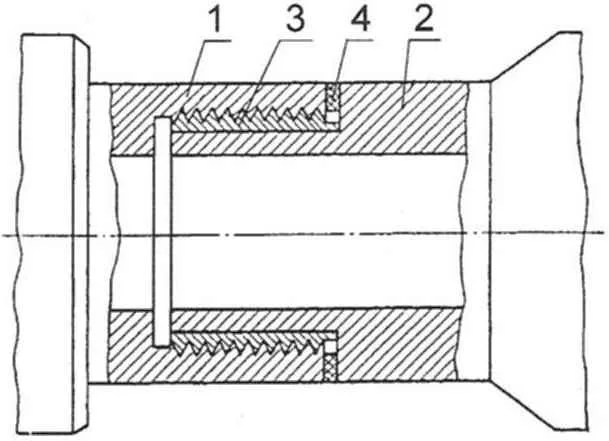
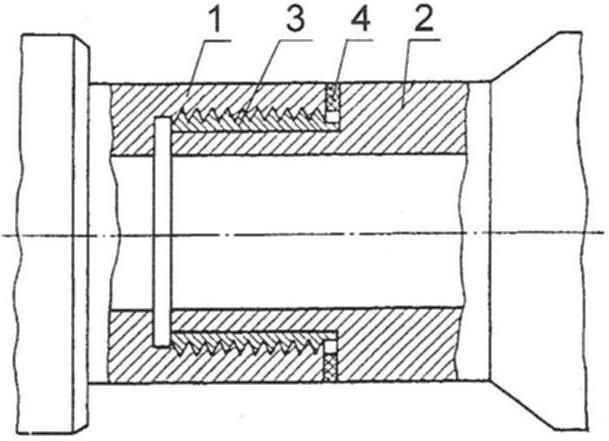
The threaded connection of the pipes:
1 – steel tube with internal thread;
2 – a steel pipe with a smooth end surface;
3 – intermediate bronze bushing with external thread, installed with an interference fit on the pipe 2;
4 – strip
Therefore, the most appropriate in stainless steel threaded connections, low-volume intermediate the threaded elements of the same ferrous metal, e.g., bushings that are installed with an interference fit on bolts or on one of the abutting nozzles (see figure). This decision will allow “a little blood” to solve a number of problems:
– eliminate corrosion in steel threaded connections, resulting in disrepair the entire node;
– to facilitate, cheapen, and expedite maintenance and repair work;
– eliminate the need to manufacture new components and parts to replace the failed one.
S. CHERENKOV, Saint-Petersburg