 This will meet not often. I must say that in my memory this is the first time Both champion’s in one class (S6F) among boys and among adults the same team—Poland. But that’s not all. They— Michal Kumar and Leshik Malaga—student and coach. This creative community can only rejoice.
This will meet not often. I must say that in my memory this is the first time Both champion’s in one class (S6F) among boys and among adults the same team—Poland. But that’s not all. They— Michal Kumar and Leshik Malaga—student and coach. This creative community can only rejoice.
Their model missiles aroused great interest among the participants and specialists of the 16th world championship at Baikonur. At first glance, it seems nothing special. Conventional, traditional design. But it is a fact that, in my opinion, deserves attention. Moreover, this apparatus is “armed” Polish athletes in two categories: Ѕ3А and Ѕ6А.
And in the category of rotochutes (Ѕ9А) base (body) is made in a similar way.
One of the features of the model—a rather long tail section—170 mm.
This can be seen as the desire of the designers a little bit to ease construction material for the hull and stabilizers. Another feature is the original solution ejection recovery system model from the case and a very unusual use of the wad. But more on that below.
The case is made of two layers of fiberglass trehsutochny thickness integrally with a tail part on the mandrel of variable cross section, the maximum diameter of which is 39,9 mm, minimum—
10 mm. In this part of the mandrel is formed of three layers of the cylindrical part of the engine compartment. First the carbon and then two layers of fiberglass. This is done with the aim of improving the thermal stability of the rear of the hull. In the process of rolling is added to the resin and the pigment.
Giving polimerservice the resin, the mandrel with the wound preform is clamped in a lathe and the outer surface is treated, after which a sharp cutter cut to desired length—425 mm, Then the mandrel is heated slightly and removed from her willing body.
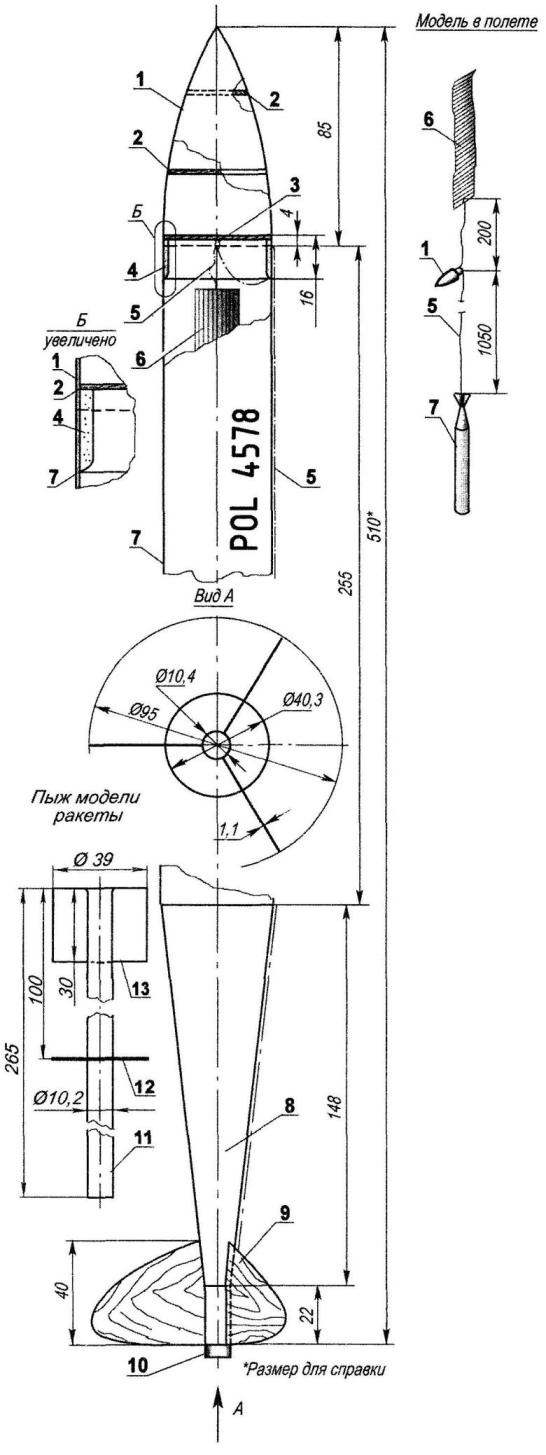
Universal model rocket (Ѕ3А and Ѕ6А):
1 — fairing; 2 frames; 3 — loop suspension; 4—connecting bushing fairing; 5—thread suspension rescue system; 6—system of salvation (parachute or brake band); 7—housing; 8—the tail cone; 9— stabilizer; 10—mrad; 11 —a tube-body; 12— centering disc; 13—cylindrical frame
The same technology mold fairing with a length of 85 mm. Inside of fairing attach three balsa frame (for rigidity), and then from the bottom to a depth of 4 mm, glued to a ring—connecting bushing height of 16 mm, also carved from balsa. In this frame fix hinge for connecting the fairing with the recovery system and to the housing by means of thread suspension.
Stabilizers (three of them) cut from a balsa veneer with a thickness of 1.1 mm, a fighting surface is reinforced with “glass”.
To the body butt glue them. Along the line of attaching one of the stabilizers attach to the thread of the suspension.
Brake band has a size of 1050×97 mm, material: printing polyester with a thickness of 0.02 mm. Styling—accordion with a step of 4-5 mm.
Originally produced at the Polish missile wad. In contrast to similar parts of models of other athletes, this is not a trivial piece of cotton or foam cylinder, and a paper design. The basis of it—a tube of writing paper with a length of 265 mm and a diameter -10,2 mm. At one end of it glued to the paper disc (blank—no holes), on which is planted a cylindrical frame with a diameter of 39 mm, length 30 mm. At a distance of 100 mm from the disc on the tube wearing one centering disc the same diameter as the upper, for durable host the wad on the body.
The advantage of this design is obvious. Lots of wad—1.5 g. It does not allow the recovery system of the model down, in the time of the launch, and in flight. Thereby achieved a stable position of the center of gravity of the model.
Preparing the model for flight takes place in this order. First in the top of the body down a wad before the advent of the lower end of the stern cut of the body. Into the tube of the wad insert the upper part of the engine to a depth of 2-3 mm and fix it to the engine compartment. Then the top stack recovery system (brake band or a parachute), and attach the fairing.
In flight, after firing the lifting charge mrad, an energy pulse (blast wave) is transmitted through the tube (small diameter 10.2 mm) and rests on the disc wad. He moves up and throws out of the housing recovery system (if it can fly itself).