 Few, probably, ever see a modern sailing ship. It is widely believed that in our age of powerful engines and high speeds boat the best place in sports or for training cadets of sea schools.
Few, probably, ever see a modern sailing ship. It is widely believed that in our age of powerful engines and high speeds boat the best place in sports or for training cadets of sea schools.
But this is not true. In many countries again began to build sailing vessels, passenger and other, different tonnage, equipped with the most modern equipment and the most modern equipment. Today sails are made of polyester plastic, and run them remotely through hydraulic and electrical mechanisms.
Now, sailboats are improving I. presumably, will be reborn, if not in the form of cargo ships, in any case, as passenger ships engaged on tourist flights. Their importance, and scope, is likely to grow and expand even in connection with the activities for the protection of our environment.
However, I would like to tell you about sailboats without sails. As you know, sailboats are referred to as the court using motion SIPU wind. And so there had to be a separation of sailfish into two categories: vessels, driven by the wind, and the vessels that use wind energy to drive the propeller, i.e. with wind turbines.
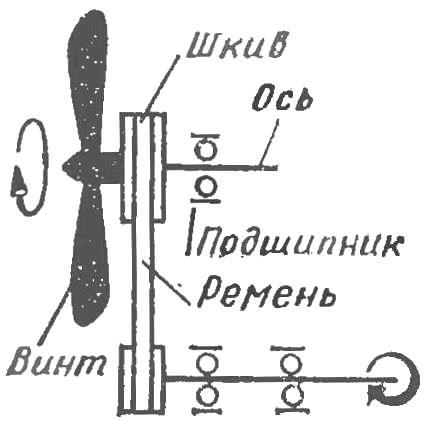
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the wind turbine with transmission from the propeller to the propeller.
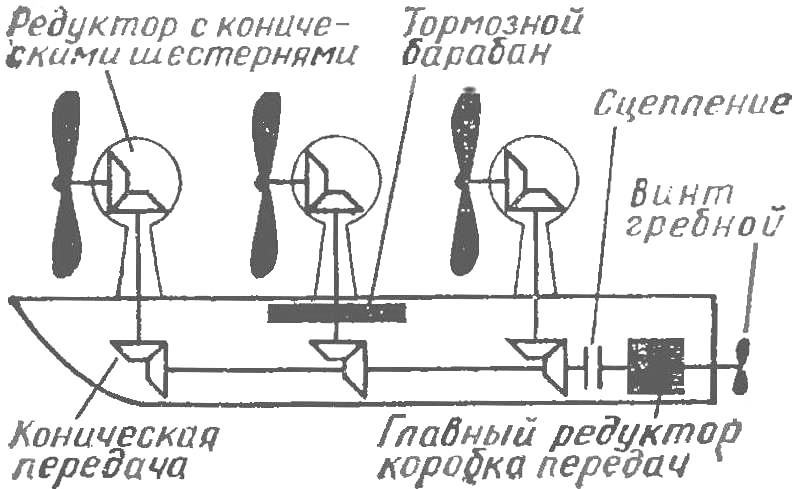
Fig. 2. Diagram of a ship with three wind turbines and a gearbox on the propeller.
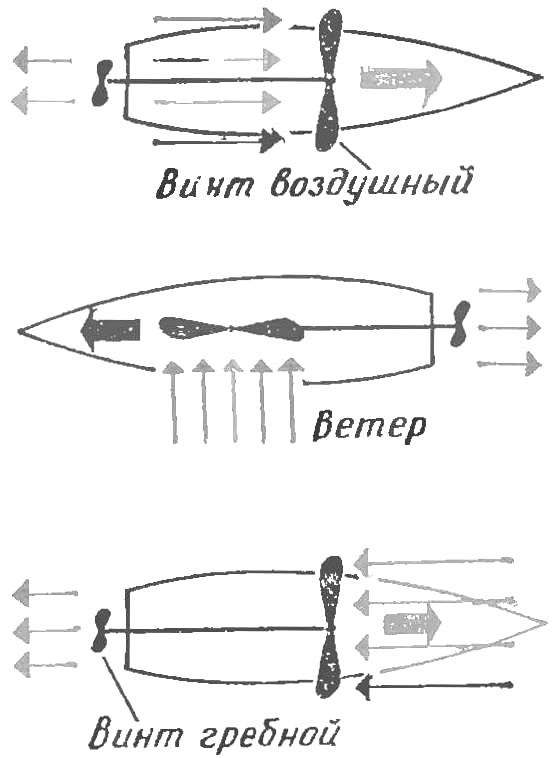
Fig. 3. Diagram of the possible movements of the vessel with the wind turbine at different angles to the wind.
The design of this class of ships engaged a French engineer Constantin. In 1923, he proposed to build payner, the screw which would have been in the movement three wind turbines located on the forty-meter masts. However, no shipbuilding company at that time agreed to carry out the project.
A different path went to the German engineer Flettner, who proposed and built in 1926, the ship is moving under the influence of the wind with the original device. Design feature it is. The reader will remember what is the “Magnus effect”: light coil is wound a strip of paper; if quickly pulling the strip. to the bottom of the coil was moving to meet the oncoming airflow, the coil will go up describe a somersault and fall on the surface of the earth. This is due to the action of lift forces resulting from different speeds of movement under the coil and over it.
Due to braking of air flow under the coil and accelerate it to the top of a pressure difference is produced. The resulting force supports the coil in the air; she moved the ship Flettner. The deck was equipped with three cylindrical columns that were rotated by electric motors of small capacity. The force that occurs by the interaction of wind and circulating rotating columns of air, moving the ship in the right direction. The described engine is called “migrating”. The maximum speed the ship has achieved in a crosswind. It should be noted the high quality agile: the ship can turn on a dime, move sideways, the stern. But we can not say about such disadvantages as the need to tack with the wind and against it, smaller in comparison with a true sailing ships speed.
The next step in the struggle for speed and high maneuverable qualities of sailboats without sails was the invention in the late forties the jib rotary microdigital and followed directly behind him the use of his ka catamaran.
Staxel-rotor wind turbine represents the cross, freely rotating on the axis. At the ends of the cross set of the sail, which the wind rotates, and the rotational motion of the crosses is transmitted to the propeller. This ingenious design allows the ship to go at any angle to the wind, ensures a high maneuverability, but does not increase scope any significant speed.
Another development is vertically positioned rigid rotor that consists of multiple semi-cylindrical surfaces. This type of wind turbine has enough windage and high torque, which allows the ship to go, even with small winds.
I have built a model of the ship with a wind turbine having a rigid vertical rotor. She showed the efficiency and high maneuverability, was able to walk the bow and stern, to turn on a dime. Construction and testing of a large ship, constructed on this principle, — depo sailing enthusiasts.
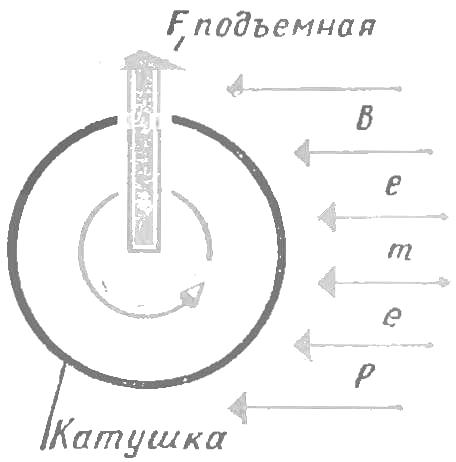
Fig. 4. The emergence of the “Magnus effect” during the rotation of the coil.
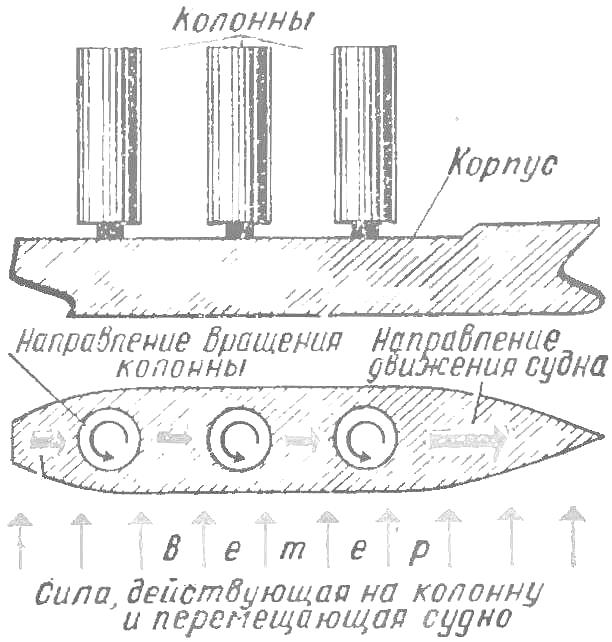
Fig. 5. Scheme wintrading ship Flatner (side view and top).
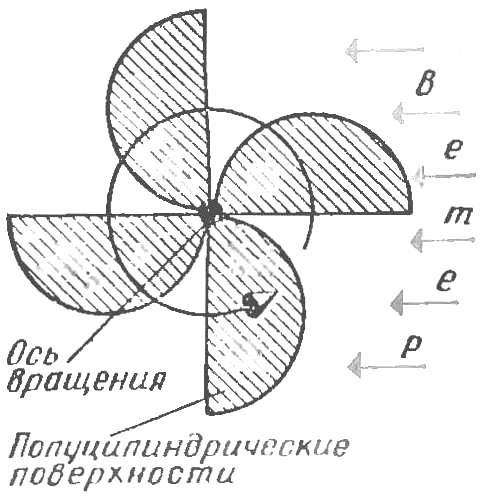
Fig. 6. Rigid vertical rotor (top view).
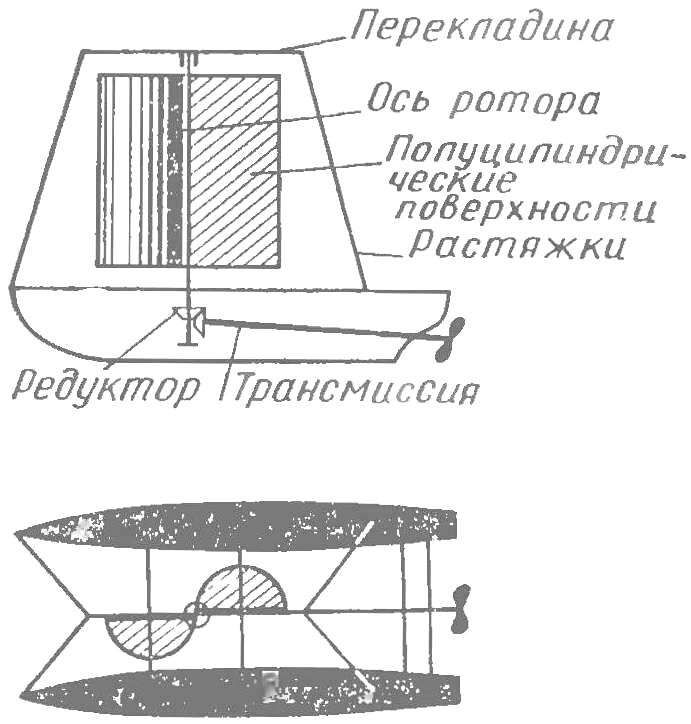
Fig. 7. Model of a catamaran with a rigid vertical rotor (side view to the top).
Of great interest is the wind turbine of a different kind: with the air screw.
The incoming airflow spins the propeller, which when rotating with a high speed serves as a kind of sail. The rotational energy through the transmission is transmitted to a propeller, which also helps to increase the speed of the vessel. I built a model of the ship and the propeller. She was quite efficient, but its speed and maneuvering qualities much inferior to the previous one, because it had a lower rate and could not produce rotation around the vertical axis.
Of course, experiments on models are not able to give comprehensive data about the effectiveness of wind power plants. Checking them should be on the courts commensurate with natural. I hope that among the readers of the journal “modelist-Konstruktor” there are enthusiasts who will undertake the construction and testing of wind turbines, for example, on the type of yacht “Optimist”, “Cadet” and “Ruff”. It is not costly but can give extremely interesting results. Remember the story of the development of rigid aerodynamic sails — all objections skeptics have been refuted by the first test, and now no one doubts the appropriateness of its application.
Of particular interest is the improvement of existing wind turbines, rather, increase their efficiency by using, for example, multi-blade coaxial propellers, rotating in opposite directions. Say no to the first screw thread of the air pressure on the blades of the second screw is almost perpendicular to the working surface of the blades, ensuring the increase of K. L. D. of a wind turbine and increase its power.
CHEREPOV



