 Serious modeling starts with a small design. Noteworthy experience in the construction of the simplest models of gliders have gained members in the House of pioneers and school students of the Frunze district of Leningrad. In the first stage they do developed in the circle training model, then the glider “Junior” class A-1 and only then start making the model A-2, which ends the program of training of young modelers-athlete. Today the leader of the group V. Bashtannik acquaints readers with the first two gliders of Leningrad.
Serious modeling starts with a small design. Noteworthy experience in the construction of the simplest models of gliders have gained members in the House of pioneers and school students of the Frunze district of Leningrad. In the first stage they do developed in the circle training model, then the glider “Junior” class A-1 and only then start making the model A-2, which ends the program of training of young modelers-athlete. Today the leader of the group V. Bashtannik acquaints readers with the first two gliders of Leningrad.
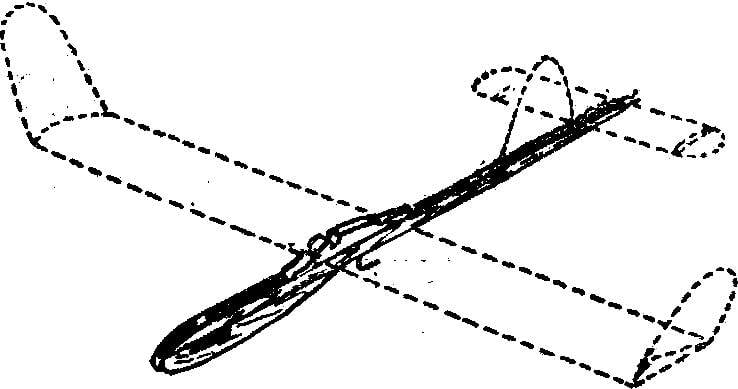
It is applied to the volumetric profile of the wing and stabilizer. By replacing the cargo in the fore part of the fuselage, and because of this, and change the installation angle of the wing to demonstrate how the shifting centre of gravity affects the quality of the flight.
Practice has shown that the location of the wing at the distance indicated in the drawing, the most profitable. Therefore, you should load the bow part of the model so that the wing has been established in this place.
Increased the size of zakonnost wing made of aluminum wire, provide an opportunity to change the cross “V” wing, to correct the distortions. Kiel also made of aluminum wire, has no steering, and therefore to achieve good results when tightened on the guard rails need to bend it in the direction of rotation. Such adjustment is very simple and facilitates rapid training of a young athlete puff model on the guard rails.
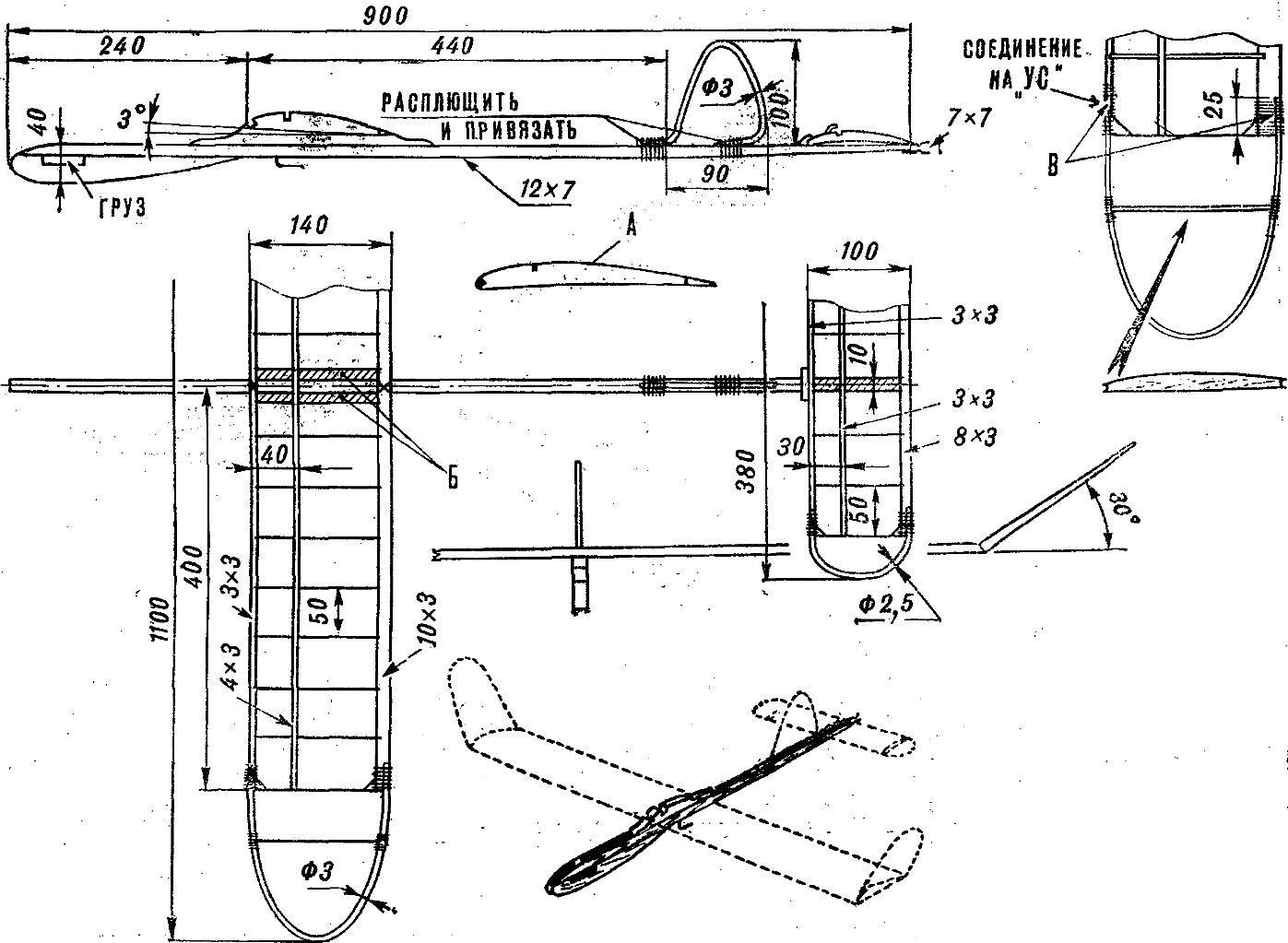
Fig. 1. Training of the model glider:
A — wing profile; B — filling foam; In — circuit connection of the wire of the wing tips and stabilizer.
“Junior” A-1
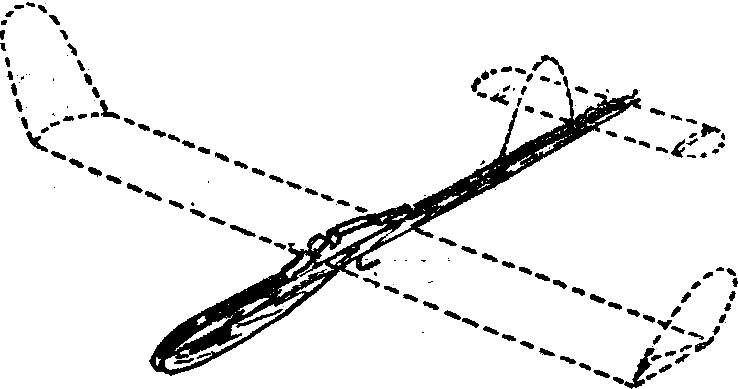
Work on the airframe A-1 is the next step in the improvement of the model athlete. Although the practice of design there is a long way to fixing half of the wing on the pins, in our circle in preference to braces. The keel has the rudder associated with the starting hook on the front of the wing.
When tightened it becomes a situation in which you can raise the model on the guard rails at maximum height, and when the cutaway is automatically rotated in the desired direction and angle required. The mechanism of rotation of such steering is well described, for example, in the book V. S. Rozhkov “model aircraft club”.
And training models, of aluminium wire made by Kiel, increased the size of the wingtip and the stabilizer, but the rigidity of the parts is increased by lengthening the spars and install the ribs.
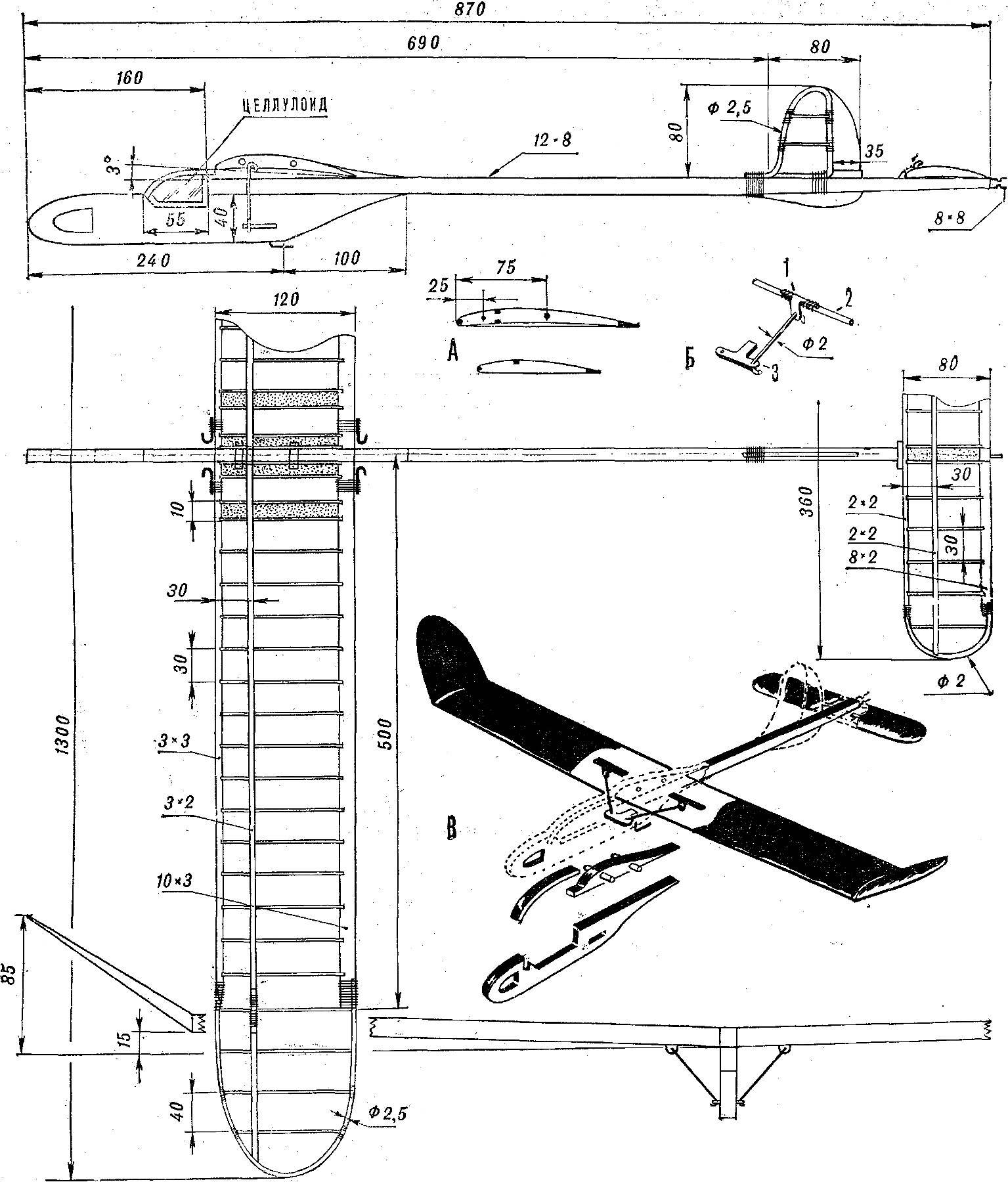
Fig. 2. The model glider “Junior” A-1:
A — the profile of the wing and stabilizer; B — the design of the struts: 1 — the place of soldering, 2 — wire, EIA Ø 2 mm, 3 — rocking chair, made of anodized aluminum 1 — 1.5 mm; In — circuit Assembly.
The glider is designed so that all non-metallic parts can be made from readily available materials. The fuselage is made from pine slats and plates. Ribs I advise you to make from the block of pine, aspen, or basswood, which is then sawn into individual parts of the jigsaw or on electrodance with disc cutter (machine UK-4).
A well-executed model not only looks beautiful but also allows you to be successful with it in competition.