Four-wheel drive truck GAZ-63. The emergence in the early twentieth century a large number of vehicles and the subsequent rapid development of road transport has required the creation of an extensive road network. However, in many countries, including in our country, road construction clearly lagged behind the production of cars.
Four-wheel drive truck GAZ-63. The emergence in the early twentieth century a large number of vehicles and the subsequent rapid development of road transport has required the creation of an extensive road network. However, in many countries, including in our country, road construction clearly lagged behind the production of cars.
The needs of vehicles still somehow answered the streets in major cities, but the Russian backwoods roads, in the modern sense of the word had. Here are just a few of the figures shown in “Reference book of avtodorovtsy” issue in 1929. According to 1924, there were about 3 million km of country roads, of which only 18 500 km was a gravel highway, 4550 km of cobblestone roads, 10,000 km gravel, and 10,000 km improved earth and 500 km of improved gravel cobbles and the Remaining 2 956 900 km was an ordinary dirt roads become after rainfall and consequently in the fall and spring are absolutely impassable.
Under these conditions a significant help to the national economy and the army could provide off-road vehicles, and the orientation of the domestic automotive industry on such cars — primarily freight — would be quite rational. However, the first vehicles began to appear in the USSR only in the 1930-ies. During this period, the number of domestic plants have been designed and put into production triaxial modification of trucks. Of course, this was not the SUVs, and only all terrain vehicles, but they are allowed in the offseason to pass on the Russian primers, However, a significant proportion of these machines was designed for the needs of the red Army — permeability for army vehicles was the most important quality!
The first in the history of domestic autostructure serial three-axle truck terrain became YAG-10 with the wheel formula 6×4, established in the Yaroslavl automobile plant on the basis of five-ton vehicle I-5. Serial production of this machine began in 1932. The machine is equipped with engine capacity of 93 or 103 l with the American company “Hercules” in transmission was used to timid two-speed transfer case and brake system with a mechanical actuator had a vacuum booster. In the first year it made 37 trucks, just as was done only a few hundred machines. The reason for such a small issue was the lack of suitable engines, and the weakness of the productive base.
The first domestic three-axle truck terrain YAG 10th edition 1932
ZiS-6 — three-axle truck terrain wheel formula 6×4 issue 1934
ZiS-32 edition 1941 two-axle all-wheel-drive car based on the “three-ton” ZIS-5
GAZ-AAA three-axle version of “lorry” GAZ of issue, 1934
Four-wheel drive army jeep GAZ-67B sample 1944
GAZ-51 — truck mass car production in 1946
Four-wheel drive truck GAZ-63 sample 1948
In 1934 in Moscow began mass production of another three-axis machine — ZIS-6, created on the basis of “three-ton” ZIS-5. These vehicles later became the basis of the first rocket launchers BM-13, better known by the name of “Katyusha” On the basis of ZIS-6 was also created heavy armored car BA-11.
In the same year the production of three-axle car, called the GAZ-AAA. started in the Gorky automobile plant It is based on a serial “polutorka” GAZ-AA. From the base model GAZ-AAA was different wheel formula (6×4), increased capacity (2 tons), a more powerful engine (50 HP), and other constructions transmission and suspension. The new machine was equipped with a four-speed transmission, intermediate two-step gear —shift stage, the gimbal and the main transmission, intermediate and rear axles. The main transmission was a worm gearboxes with overhead worm drive shaft Brakes on the GAZ-AAA was a drum, mechanical. Machine, and decided not to cross, formed the basis of average three-axle armored cars BA-6, BA-10, PB-7 and BA-22.
I must say that three-axle vehicles with the wheel formula 6×4 still could not be a real SUV — a relatively large mass of design, small clearance and lack of front-wheel drive significantly reduces permeability. To solve this problem only by using the two-track four-wheel drive vehicles with high clearance. One of the first attempts of creating such a car was made in 1940 by the designers of the NATA, designed on the basis of a serial “three-ton” ZIS-5 two-axle four-wheel drive truck NACHI 2 TO Serial production of this car has received the name of the ZIS-32, was deployed at the Moscow automobile plant named after Stalin in 1941. Unfortunately, in connection with the evacuation of the plant the production of these cars was discontinued in late 1941.
Working out the concept of all-wheel drive two-axle vehicle started at the Gorky automobile plant in 1941, with the serial production of passenger AWD SUV upgraded on the basis of “emka” GAZ-11-73 of the sample of 1940. The first Soviet passenger all-terrain vehicle meant primarily for the high command of the red Army
Machine, received the name GAZ-61, was equipped with a 6-cylinder engine capacity of 85 HP enabling it on the highway with a full load to reach the speed of 107,5 km/h, and the permeability of it was such that in our days she would be quite able to compete on the roads even with modern jeep mi Serial production of GAZ-61 continued until August 1941. Many of these machines have been through the war; the GAZ-61 was visited by such prominent Soviet generals like Zhukov, Konev and Rokossovsky.
Geometry all-wheel drive car GAZ-63
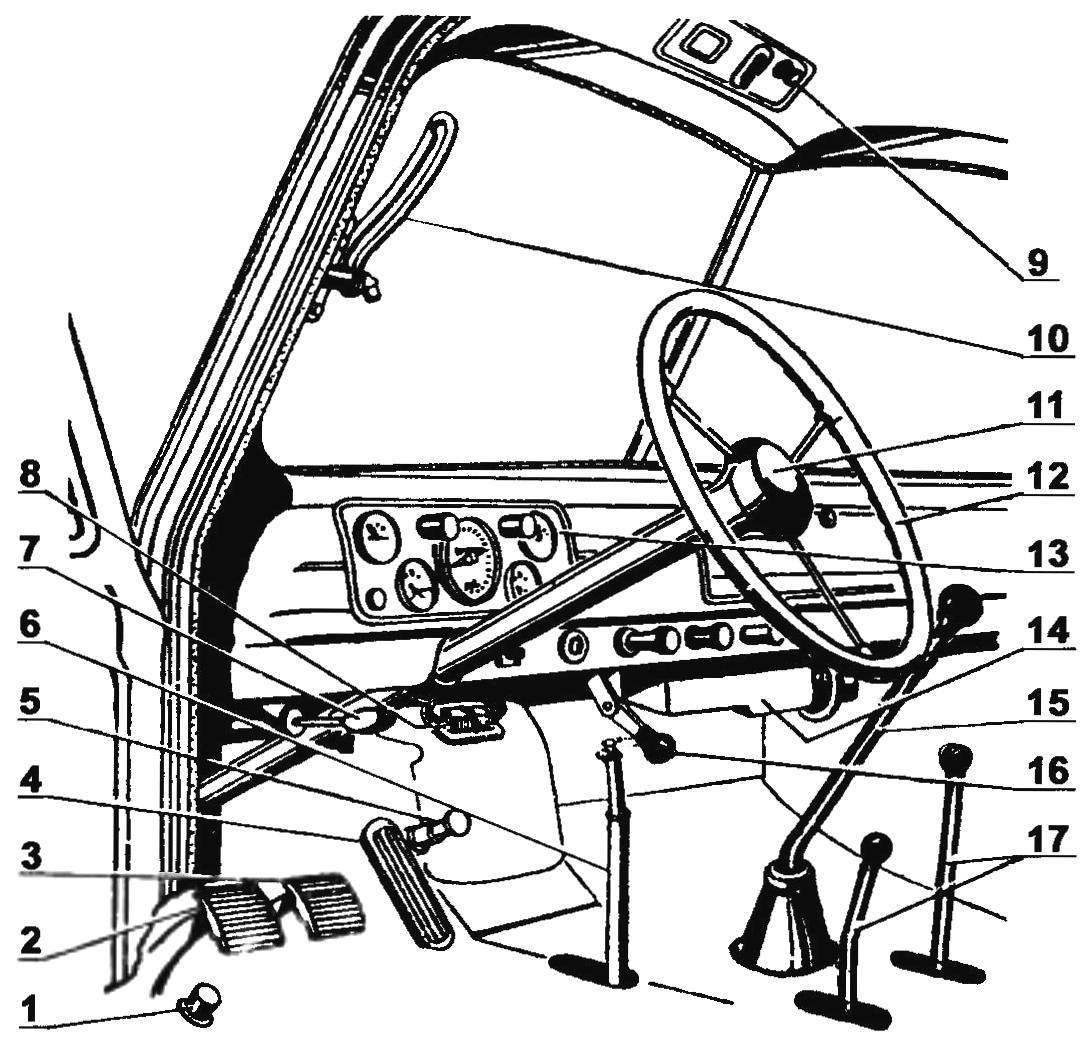
The driver and the combination of instrumentation of the GAZ-63
The layout of the GAZ-63
The location of the car control:
1 — the foot switch of light of headlights; 2 — clutch; 3 — the brake pedal; 4 — throttle; 5 — pedal starter; 6 — Parking brake lever; 7 — control handle grille; 8 — fuse block; 9 — toggle switch wiper switch; 10 — the yoke of a windscreen; 11 — audio signal; 12 — steering wheel; 13 — unit control devices; 14 — cabin heater; 15 — lever control transmission; 16 — the lever of the sliding roof heating and ventilation of the cab; 17 — lever control dual
Successful scheme was the basis for the establishment of the army passenger AWD SUV with simplified bodies of the open type — GAZ-64, GAZ-67 and GAZ-67B. These machines were used by the red Army for reconnaissance, liaison, escort and transport light guns. Last modification — GAZ 67B — were a fairly well-developed design which was widely used the main aggregates of the production cars of the Gorky automobile plant. On the basis of this machine produced a light armored car BA-64 with a 7.62 mm machine gun in a rotating turret. Serial production of the army jeep lasted until 1953.
In the mid 1930-ies it became clear that of the old woman — “lorry” GAZ-AA care of almost everything, and no amount of modernization will not be able to make it a modern car. In front of the Gorky automobile plant was tasked with creating a completely new mass of the truck.
The design of this car, called the GAZ-51 began in 1937. The team of engineers headed by chief designer A. Gas Sephardim. had to create a simple and reliable universal truck, compiled from the most reliable units, worked by the practice of the world car industry. Already in may 1939, we began testing the new car ended in July 1941.
The war interrupted the work on promising car, it was only in 1943. Of course, for two military years, automotive engineering has gone far ahead, and lead designer A. Prosvirina had to assemble the car almost from scratch the Truck got hydraulic brakes, new all-metal cabin and tires are oversized. The capacity of the machine was increased to 2.5 tons of Accumulated experience in the creation and serial production of military jeeps GAZ-61, GAZ-64, the GAZ-67 and GAZ-67B allowed the designers to quickly design and all-wheel drive version of the truck. The cars were drawn almost simultaneously, on adjacent building panels. Truck-SUV dubbed the GAZ-63, in contrast to the basic model had two drive axles and single wheels with tires increased section and powerful cleats.
Four-wheel drive truck turned out very successful; and the army and the civilian drivers he enjoyed the deserved respect
GAZ-63 was equipped with 6-cylinder carburetor engine GAZ-11 liquid-cooled with a capacity of 70 liters. equipped with a triggering device that allows you to heat it with a blowtorch. Fuel for the engine served low-octane gasoline A-66; two fuel tanks had a total capacity of 195 liters Reserve fuel was 650 km away.
The electrical system was performed via one-wire schematic and designed for a voltage of 12 V. In contrast to modern machines, with the body was connected to the positive terminal of the battery.
As sources of electrical energy used DC generator type Г108 power of 250 watts and battery 6ST-68. Starting the engine is made by electric starter ST8 with a capacity of 0.96 kW, or crank.

The drivetrain consisted of policetrainer single-plate dry friction clutch, gearbox, transfer case-auxiliary gearbox, driveline and axles. Transmission was mechanical, three-way, four-speed. Transfer box has had increasing downshift of the transmission. Main gears of driving axles were a tapered reducers.
Suspension front and rear consisted of longitudinally extending semi-elliptic leaf springs with hydraulic shock absorbers and lever-type two way action. Rear axle had additional podreczniki. Suspension provides the possibility of movement on unpaved roads at speeds up to 30 km/h to Improve patency of the car contributed to the use of axles with single wheels with almost the same gauge and use a tire size of 10.00-18.00 powerful grouser type “oblique tree”.
The service brake system had a hydraulic actuator and the Shoe mechanisms, fitted to all wheels. The handbrake worked on the transmission.
The steering mechanism consisted of a globoid worm and dvuhgorbogo roller.
Part of the GAZ-63 was equipped with a winch, located at the front of the frame directly behind the bumper. The drive was through a cardan shaft from the power takeoff mounted on the transmission. Winch developed a force of 3,500 kgs; working rope length was 65 m.
The car had a steel double cabin, and a wooden platform of 2 ton capacity with high lattice sides and opening tailgate.
GAZ-63 was able to overcome a Ford with a hard soil to a depth of 0.8 m, up to 30 degrees and move the slope with the roll up to 15 degrees. In the Soviet Army four-wheel drive truck was used as an artillery tractor; the loading platform housed the gun crew and ammunition.
The car was produced by Gorky automobile plant from 1948 to 1968. In 1964 GAZ began serial production of the more committed all-wheel drive truck-terrain vehicle GAZ-66 cab with the cabover design. Well workaholic the GAZ-63 was destined for many more years to overcome the Russian roads. A lot of machines have survived to XXI century, and today the “jeep”out-of-the road in good condition still come across on country roads.
I. EVSTRATOV
Recommend to read
 IF YOU NEED A TRUCK
IF YOU NEED A TRUCK
A “car” in combination with a cargo trailer is an extremely convenient vehicle. However, it is not without its shortcomings, which sometimes negate all its advantages. In particular, the...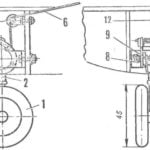 GEAR UP!
GEAR UP!
Ask any kid, building the first schematic model of what he wants Almost certainly he will answer — about copy. And it is clear. It's no wonder it is believed that the replica model is...
 Four-wheel drive truck GAZ-63. The emergence in the early twentieth century a large number of vehicles and the subsequent rapid development of road transport has required the creation of an extensive road network. However, in many countries, including in our country, road construction clearly lagged behind the production of cars.
Four-wheel drive truck GAZ-63. The emergence in the early twentieth century a large number of vehicles and the subsequent rapid development of road transport has required the creation of an extensive road network. However, in many countries, including in our country, road construction clearly lagged behind the production of cars.