One of the most important tasks of fighter aircraft is to protect important areas, districts and objects on the territory of the country from air strikes. After the Second world war, the development of tactical flight characteristics of aircraft of a potential enemy greatly complicated the task of defense of the air borders of our country Location of U.S. military bases and their allies near the borders of the Soviet Union put the leadership of our country before the problem of protection from the threat of nuclear strikes on industrial sites and administrative centers, which until recently was considered a deep rear that the enemy at the most critical development of the fighting, It demanded significant expansion of the capabilities of the air defense Forces of the country increase their number to cover all important industrial regions, technical re-equipment of principally new types of weapons and military equipment.
One of the most important tasks of fighter aircraft is to protect important areas, districts and objects on the territory of the country from air strikes. After the Second world war, the development of tactical flight characteristics of aircraft of a potential enemy greatly complicated the task of defense of the air borders of our country Location of U.S. military bases and their allies near the borders of the Soviet Union put the leadership of our country before the problem of protection from the threat of nuclear strikes on industrial sites and administrative centers, which until recently was considered a deep rear that the enemy at the most critical development of the fighting, It demanded significant expansion of the capabilities of the air defense Forces of the country increase their number to cover all important industrial regions, technical re-equipment of principally new types of weapons and military equipment.
From air defense fighters required to ensure that all interception of air targets by day and night, in VFR and IFR weather conditions was needed For this more advanced aircraft than their predecessors of times the recently ended Second world war.
The lineup of aircraft at a great distance them from mid war steel complete system “— another’s” fly at night and in adverse weather conditions, the fighters began to be equipped with radio compasses and blind landing system, allowing the aircraft to return after the assignment, at the aerodrome at night and in poor visibility conditions To improve the efficiency of search and attack air targets, detected ground radar, fighters were required to on-Board radar station (radar).
Work on the creation of radar was started in our country before the great Patriotic war in 1940 the head of Department NII-20 of the electrical industry A B Slepushkin proposed to develop a radio-location equipment of centimeter range with a pulsed mode and an estimated mass of about 500 kg dimensions of the equipment is also allowed to place her on modified PE-2, which was originally conceived as a high altitude interceptor in the Winter of 1941 at the NII-20 made a working model of radio-location equipment, called “Gneiss-1”.
Early in the war due to the evacuation of enterprises to the East and the lack of the necessary components of the work was temporarily stopped At a new place in Sverdlovsk in the winter of 1941/42 g in the Institute of radio station gathered on a serial generating lamps meter range with a radiation power of 10 kW version of the station called “Gneiss-2” has Headed this work In Tikhomirov the target Indicator on the basis of electron beam tube constructed And Used Slepushkin and RS Budanov the Work was carried out on the instructions of people’s Commissariat of defense, and oversaw its military engineer, air force Institute E Stein.
In early 1942 the equipment was mounted on PE-2 part of the units mounted in the cockpit the radio operator, controls and indicator — in the Navigator, and his place was taken by the operator of radio-location stations of the cross Testing of the new aircraft were carried out from the airfield Koltsovo, where during the war, housed the research Institute of the air force Plane piloted by major A N Dobrolovsky as radar operators flew engineers In To Tikhomirov E Stein.
In the result of hard work of the investigators, air force research Institute and specialists of the Institute of radio industry to address the identified shortcomings of the equipment, by July 1942 managed to bring it up to current acceptable condition and complete the state tests.
Work, taking into account the importance, was constantly on the control of the aviation Department of the Central Committee of the CPSU(b) before the completion of state tests in the research Institute of radio industry began production of the first 15 sets of equipment, which at the end of 1942, manned interceptors PE-2 and PE-3 of the Moscow air defense army trials PE-2 equipped with the station “Gneiss-2”, took place in February — may 1943, the 24th GIAP of the 2nd guards air corps of air defense, defending the Leningrad sky.
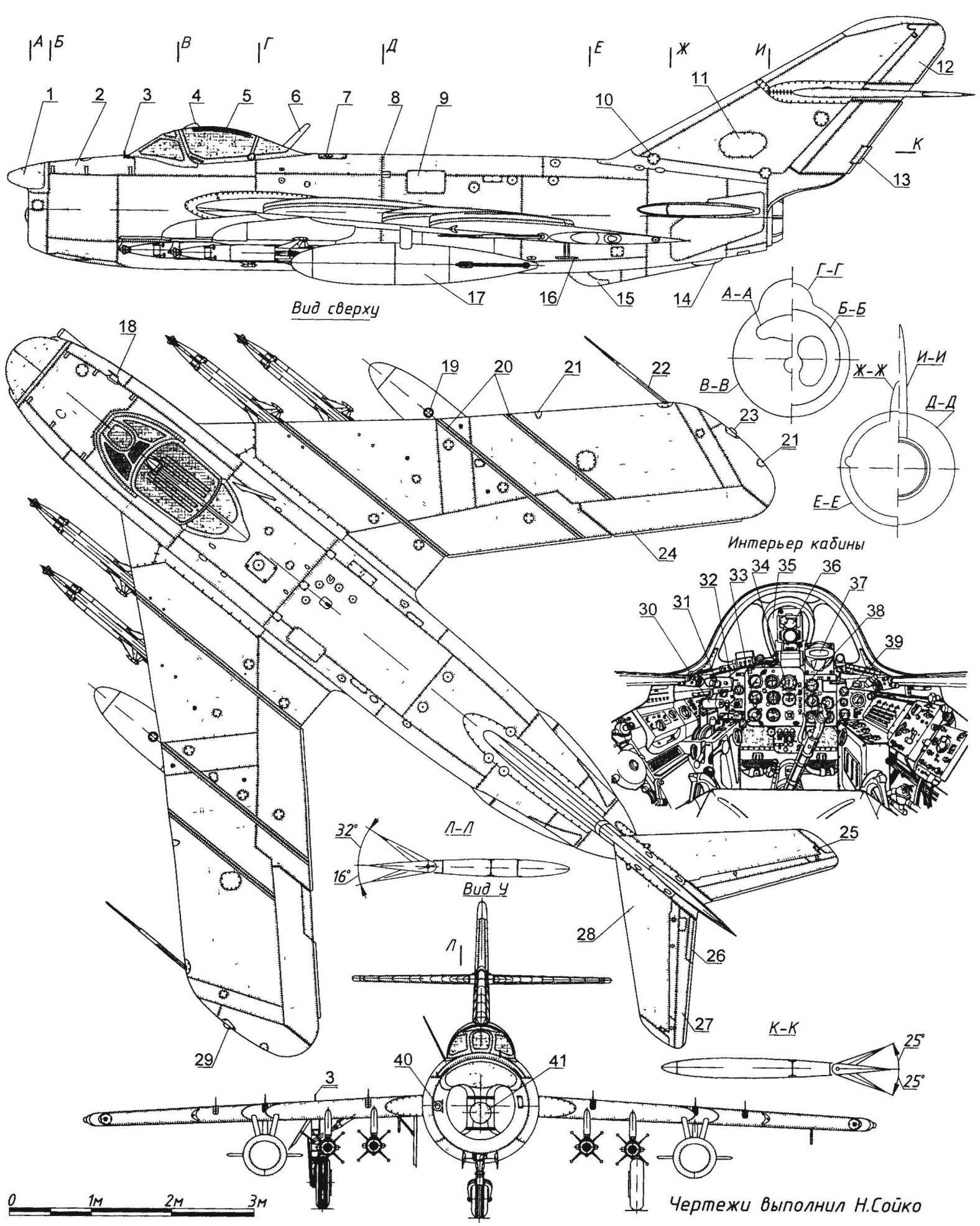
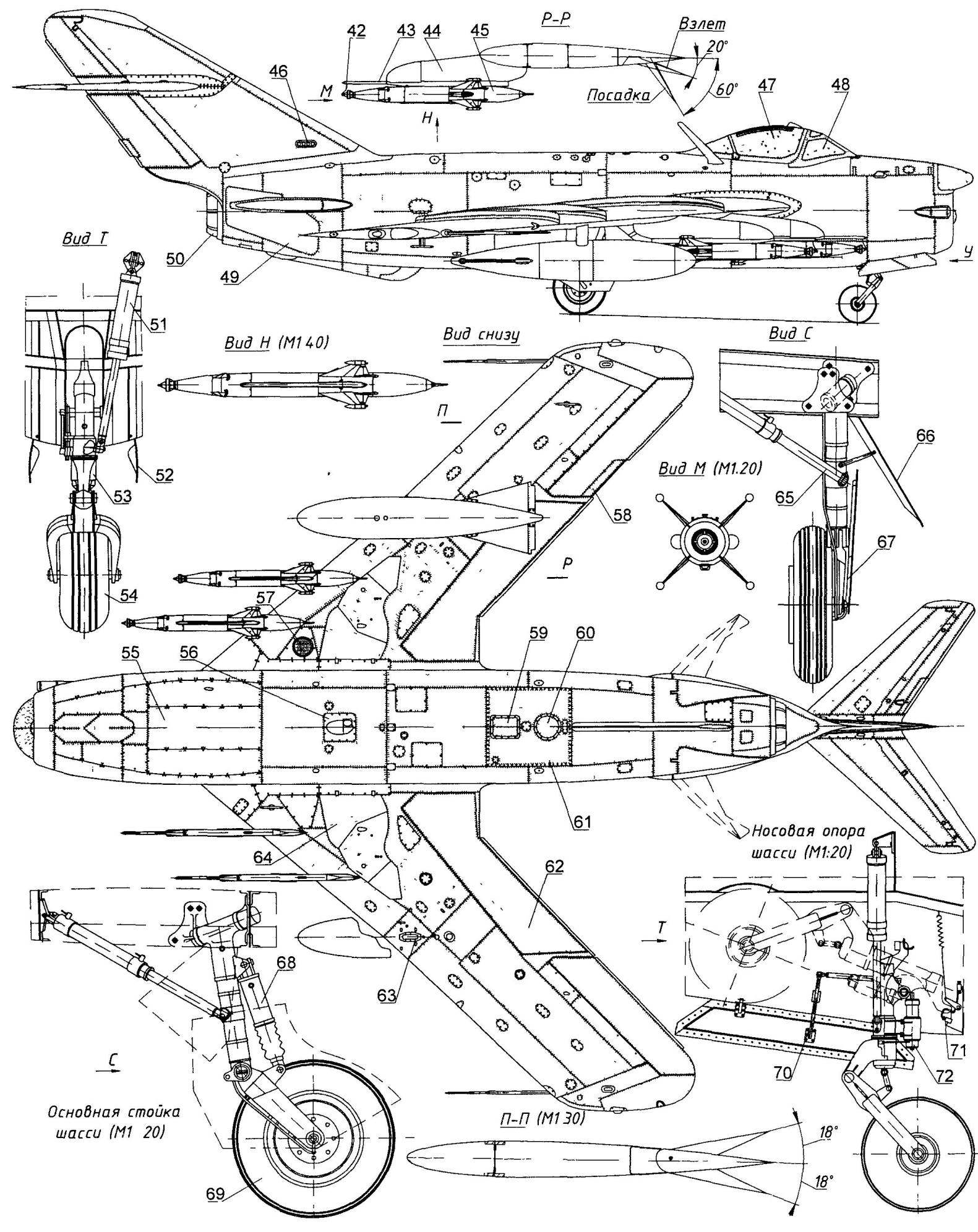
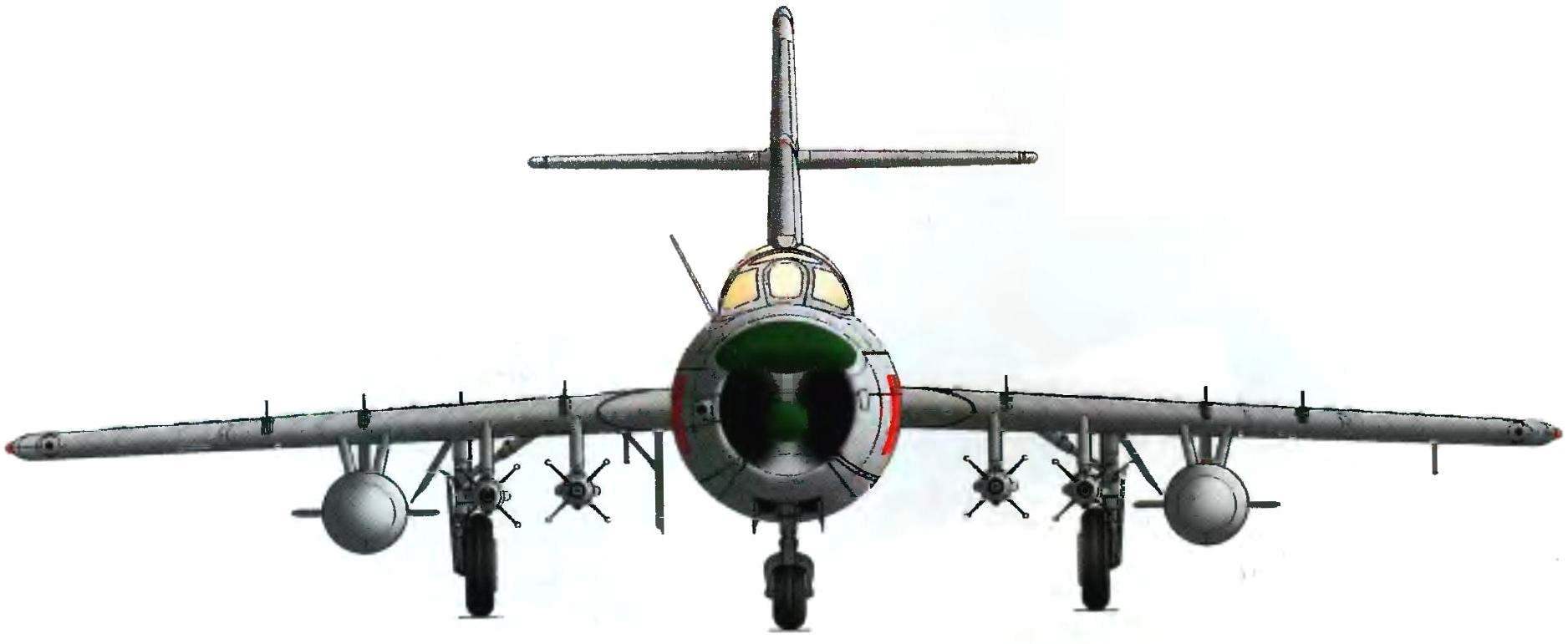
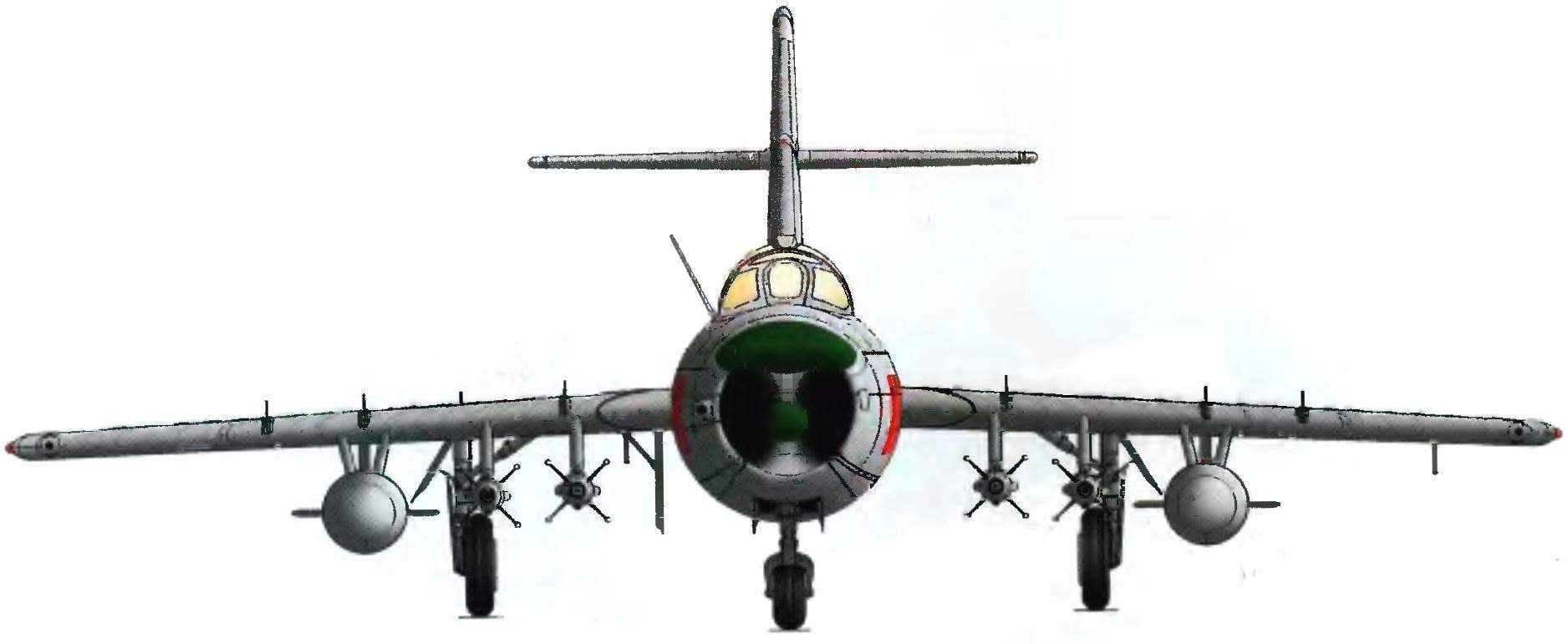
Fighter-interceptor MiG-17ПФУ:
1 — fairing antenna target detection radar gun, 2 — compartment cover electricity and electronics 3 — mechanical position indicator landing gear, 4 — periscope GS 27, 5 — Omni-directional antenna of the radio compass ark-5, 6 — antenna VHF-radio, 7 — filler neck primary fuel tank, 8 — the junction of the nose and tail parts of the fuselage, 9 — operational sunroof power plant 10 is operating the flap control wiring, 11 — cover block heroinusing compass TEAK-1, 12 — rudder 13 — rudder trimmer, 14 — tail wheel, 15 — ventral ridge, the 16 — antenna radio altimeter RV-2, 17 — 400-liter drop tank, 18 — emergency PVD H-156, 19 — tube reference neck, 20 — aerodynamic partitions, 21 — antenna, IFF systems, 22 — LDPE, 23 — right navigation light (green), 24 — Aileron, 25 — anti-flatter the load of the Elevator, a 26 — Aileron rudder, 27 — Elevator 28 — stabilizer, 29 — left navigation light (red), 30 — lever engine control 31 — lighting lamp of a cabin, 32 — valve gear, 33 — a radio compass indicator, 34 — attitude indicator, 35 — BPG, 36 — sight as P-4НМ, 37 — tube radar gun, a 38 — turn-and-slide, 39 — aircraft control stick, a 40 — window kinofotodokumentov C-13, 41 — fairing antenna tracking radar gun, a 42 — check, 43 — aviation starting device ANA-3, 44 — pole, 45 — rocket class “air-air” RS-1-46 — tape signal flares 47 — movable part of the lamp, 48 — visor lamp, 49 — brake, 50 — fold adjustable nozzle TRDC-1F, 51 and 65 cylinders retract landing gear, 52,64,66 and 67 — fold of niches nose landing gear, 53 and 68 hydropneumatic shock absorbers of the chassis, 54 — a non-braking wheel 480×200 mm, 55 maintenance hatch electroradioautomatica, 56 — technological hatch of the fuel system, 57 — landing-taxiway light, 58 — trimmer Aileron, 59 — radio panel antenna marker radio МРН48, 60 — bar radio loop antenna radio compass ark-5, 61 — the technology panel of the second fuel tank, 62 — flap-flap, 63 —universal lock D4-50, 69 — brake wheel 660×160 mm, 70 — pull landing gear doors, 71 — limit switch retracted position of the front support, 72 — damper shimmy
On 16 June 1943 the station “Gneiss-2” was adopted, and the research Institute of radio industry commissioned the production of a large batch of the station “Gneiss-2” to equip their air defense fighter aircraft during state testing PE-2 with the instrument of radio-location “Gneiss-2” has revealed a number of shortcomings of the aircraft, which reduced its value as a night interceptor, lack of range, lack of the Navigator, the “stringency” of control on landing In this respect differed from the PE-2 comes to our country under lend-lease, American multi-purpose aircraft A-20 of the company “Douglas”, proteininteractions equipped with modern equipment and means of radio communication, the Crew settled down in comfort in the spacious cabin, and a safe landing was ensured tricycle landing gear with nose wheel Therefore, in parallel with military testing PE-2 on the Leningrad front in NII VVS tested American cars equipped with the station “Gneiss-2” Flying on a modified car performed test pilot major Sugars.
In the summer of 1943 aircraft A-20 part of long-range Aircraft formed the 56th aviation division long-range fighters dwuhpuchkova composition after graduating in may 1944 embarked on the mission of the 173rd aviation regiment special purpose (upon), and in August — the 56th upon this division.
The first victory was won by the division in March 1945, participating in the blocking of the air large groups of German troops at Breslau, the Crew of Lieutenant Lesnjak of the 173-th, West was hit by two German glider landing two months in the area of Breslau, the pilots of a division performed 246 sorties the crews of the A-20 has spent 13 air battles, shooting down two bombers Not-111 (captain Casnav) and the amphibious glider (Lieutenant Shesterikov).
Simultaneously with the accumulation of experience of combat use of night-fighter with radar was the improvement of the station Until December 1944 radio industry has produced 231 set radar “Gneiss-2” and “Gneiss-2M” — option for the mine and torpedo aircraft of the Navy, “Gneiss-2M” could be used to detect not only aircraft but also surface targets.
The next step in the creation of airborne radar was the development of the NII-20 of the station “Gneiss-5” meter range Station was intended to double fighter, had two main indicator in the cockpit of the Navigator-operator, additional — in the cockpit, the radiation Power stations 30 kW and the total weight with electroplaits — 95 kg, the Development of radar was carried out during 1944, and to December 1 prepared for installation on the aircraft 24 stations.
Since the second half of 1945 under the designation radar “Gneiss-5s”, adopted and put into mass production during the great Patriotic war in the collective, headed by A N Tupolev, was used to develop different variants of heavy fighters on the basis of modifications of the front-line bomber Tu-2, the work continued after the war On prototypes of the fighter was mounted a battery of air guns of caliber from 23 to 45 mm, airborne radar and navigation equipment, allowing to carry out flights at night and in adverse weather conditions.
In 1946 one of serial Tu-2 was equipped with radar “Gneiss-5s” for testing and flight tests, After their successful completion in 1947, Tu-2, equipped with radar “Gneiss-5s” rearmed 56th division.
The rapid development of jet technology put an end to further work on piston fighter-interceptors Therefore, creating in 1948 one of the first domestic jet bombers — plane “82”, Tupolev provided a modification of the variant heavy interceptor “82П” with radar and powerful missile-gun armament But this initiative has not found support among the leadership of the defense.
In July 1947 decision of the government to develop a new radar “Thorium” in the centimeter range was entrusted to the chief designer of NII-17 And B Slepushkin This radar was expected to feature a jet fighter-interceptors.
In the spring of 1947 OKB Sukhoi P About the task force started working on placing the radar on a jet frontline fighter jet su-9, which by March 1948 he was incarnated in the preliminary design of the fighter-interceptor su-13 (factory code TC) with two engines RD-500 the project was Officially to protect was not until April 1948 continued study of this machine, known as factory codes MK and M.
In March 1947 the decree of the government simultaneously with the su-13, the OKB was designed and a single all-weather fighter-interceptor su-15 (factory code P) with radar and two engines RD-500, armed with two 37-mm cannons N-37 Work on the draft design and layout of the su-15 completed by the end of the year, and their defense took place in February 1948, the su-15 — the first aircraft design Bureau P O Sukhoi swept wing (35 degrees on line tricks) and radar “Tory” was built at the end of October 1948, a Characteristic feature of the interceptor was ridanna layout of the power plant consisting of two engines RD-45F engine was behind the cockpit, the second in the rear fuselage 11 January next year, the test pilot of the GM Shiyanov lifted him into the air In the thirty-ninth flight, on 3 June 1949 test pilot s N Anokhin left the plane after shaking of the pedals resulted in a shaking of the whole machine, corresponding to the maximum velocity head Despite the successful prior to this event tests further work on the interceptor has been discontinued.
In June 1948 came the decision of the government on the development of the double jet all-weather fighter-interceptor with two engines RD-45F or one TR-3, equipped with radar “Thorium” Fighter with a range of at least 1,500 km (with external fuel tanks — 2000 km) were armed with 37-mm guns.
And OKB Mikoyan, who was at that time on the rise, offered double (crew placed shoulder to shoulder) fighter-interceptor And a-320 (R-1) General structural diagram of the repeated proposed the year before P On a Dry Swept wing (35° to the front edge) worked for another MiG-15 In the wing housed the main landing gear compared with the “fifteenth” the size of the machine increased by almost half the Normal takeoff weight was Ute Armed with two 37 mm cannon N-37Д, placed on the sides of the forward fuselage.
In April 1949 to the factory flight tests produced the first instance of the interceptor 16 APR test pilots LII map I Vernikov and Amet-Khan for the first time lifted the car into the air In the factory tests was also attended by test pilots A N Chernoburov, And T Ivashchenko, N. Anokhin and ml gallay
In November 1949, realizing that for elimination of the revealed during the tests faults (transverse instabilities with M = 0,89 — 0,90 and valeski when air speed 840 — 930 km/h) require substantial improvements, flight tests of the factory was interrupted, and passed NII-17 for finishing and state testing radar “Tory” During the tests the radar performed 14 flights, of which nine were conducted testing the release to air targets Tu-2, Li-2, Tu-4 and b-17.
By this time, the test was prepared by the alternate-320 (R-2), which eliminated the identified deficiencies and took into account the wishes of the customer At the backup set of more powerful engines VC-1, improved visibility from the cab, mounted anti-icing system of wing and stabilizer, electrical heating of the inlet air ducts of the power plant, the Number of guns increased to three During the factory test from December 1949 until September 1950, performed 100 flights during the tests the aircraft was fitted with a radar “Kite” (the chief designer And In Slepushkin) To improve the stability of the channel Bank halved the angle of the transverse V-wing, mounted the third partition of the aerodynamic wing, increased the length of the spoilers on the lower wing surface.
In the first flight of the modified interceptor 31 March 1950 revealed a deterioration in longitudinal stability To improve mounted ventral ridge and introduced a mechanical link of spoilers with ailerons 20 September the aircraft was transferred to the state tests, and in 10 days after 24 flights, the aircraft was removed from the tests due to poor lateral stability.
The OKB simultaneously with the I-320 was developed under the factory code SP-1 modification of the successful MiG-15bis with the same radar “Thorium”, automatic radio compass ark-5, marker receiver MRP-48, a new optical sight, armed with one 37 mm cannon N-37 For placement of additional equipment the nose of the aircraft extended by 120 mm, changed the contours of the lamp, improving the visibility from the cockpit increased the size of brake flaps, their shape, the position of the axis of rotation of the Nose support gear shifted forward by 80 mm.
SP-1 did not comply fully with the issued technical requirements for an all-weather interceptor, but allowed to obtain the necessary information on the use of a fighter with the same equipment At the end of November 1949 on the SP-1 set the current radar “Thorium-A” and has started fine-tuning In December, pilots A N Chernoburov and GA Sedov spent the factory tests, and in the end of Jan next year the car passed the state tests held before may 20, 1950, but their car could not stand the test Pilots the air force Institute A P Suprun, Yu M Kalachev, V G Ivanov, D G Pikulenko, And the Annunciation, Yu And Antipov, M Dzyuba noted in the report, insufficient lateral stability, the inability to simultaneously track the target and radar to pilot the car, as well as the low reliability of the on-Board locator.
OKB Lavochkin And presented in February 1949, the layout of the fighter La-200 from mid-sagittal (40°) wing, which in the cockpit shoulder to shoulder, sat the pilot and the operator radar Armament consisted of three 37-mm cannons N-37 radar “Thorium” was located in the Central air intake of the aircraft One of the engines RD-45F was set at an angle of 10° to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft before the cockpit and cut his nozzle was located under the fuselage at the rear edge of the wing without the Express redan, like the su-15 the other RD-45F was placed in the tail part along the axis of the fuselage, Both engines had a common entrance of the air intake, divided by partitions into inlet channels to each motor Main landing gear with dual wheels retracted into the fuselage niche Normal takeoff weight of the fighter was 9910 kg After thorough ground testing of La-200 was transferred to the factory flight tests on September 16 1949 the pilots and f Mashkovsky and A f Kosarev raised the car up in the air For two and a half months was able to identify the main flight data and to identify the weaknesses of the aircraft a top speed of 1,090 km/h at an altitude of 3500 m climb 10 km of 5.85 minutes, service ceiling — 15 200 m At the same time, the testers noted a great effort on the aircraft control stick and pedals, the tendency to wingheaviness on the right wing To correct the deficiencies identified machine 1 Dec 1949 returned to the plant After completion and installation of the radar “Thorium A,” January 13, 1950 flight tests were continued In February, began flight testing of the improved version of radar “Thorium-A”, using as target the Li-2 aircraft, which carried out six visits with a distance of 7 km In the opinion of the crew, visibility of purpose and the land was good, 10 February the car was transferred to the state tests.
The first flight under the program of state tests was made on 12 April, the Car was evaluated by test pilots, air force research Institute And M Dzyuba, V G Ivanov, V P Trofimov by throttling back the engine to low speed, and full gas on the front dash speed of over 650 km/h is found shaking a tail part of the fuselage, and at speeds in excess of 820 km/h the plane careened to the left there were comments on the work of the two-wheeled landing gear, messenger radio RSIU-3 Program was interrupted on may 3, 1950, after the 31st flight.
OKB Lavochkin And managed to eliminate the disadvantages of the interceptor With shaking was done by installing an automatic sash bypass air before entering the rear of the engine and improved seal his flame tube and changing the shape of the fairing between the fuselage and the keel Cause kuenenia left was the suction of a landing flap of the left wing Is paired wheels mounted single larger Cause abnormal operation of a connected radio station, was exceeding the maximum temperature in the equipment compartment.
In late July, the plane was again transferred to the state tests For a month and a half was performed 57 flights of Major deficiencies identified during the tests, was lack of range at high altitude — 1025 km, instead of the stipulated technical requirements of 1,500 km, failure of hydraulic controls for negative g, the shaking of the aircraft when flying with drop tanks But these flaws did not prevent the machine to obtain an overall satisfactory evaluation on the results of state tests left Open the question of the reliability of radar “Tory” only in three cases out of 19 the station was provided the job.
During testing, all developers are usually faced with two kinds of problems first, the traditional stability and control, the shortfall of performance specified by the client, the second associated with the work of the new radar and electronic equipment If the solution to the first is not engaged in one year and how to resolve them, in General, were known, then the solution of the second started relatively recently In the country felt an acute shortage of specialists in the field of electronics, production of elemental base of high quality on an industrial scale only was adjusted, and the electronic equipment needed and aviation, and air defense, and the Navy So the answers to the questions on the second issue, the experts on radio equipment aviation companies looking for in close contact with the developers of the new electronic equipment.
By this time in TSKB-17 developed two new similar-size aircraft radar odnoimennaya “Kite” chief designer And Slepushkina and two-antenna Izumrud — V V Tikhomirov design Bureau And the Lavochkin gave preference to “Kite” In the refinement of the La-200 under the new radar moved the Radome radar to the top of the entrance to the intake, changed the location of the radio equipment, modified inlet channels of the power plant, which allowed to remove the bypass doors and to increase the capacity of the fuel system wing-mounted spoilers Tested in NII VVS in the first half of 1951 have confirmed the effectiveness of the improvements carried out of the interceptor, the maximum speed increased up to 1090 km/h, flight range at high altitude was 1170 km the Aircraft was recommended to serial production the Future of the machine depended on the results of state testing radar “Kite”.
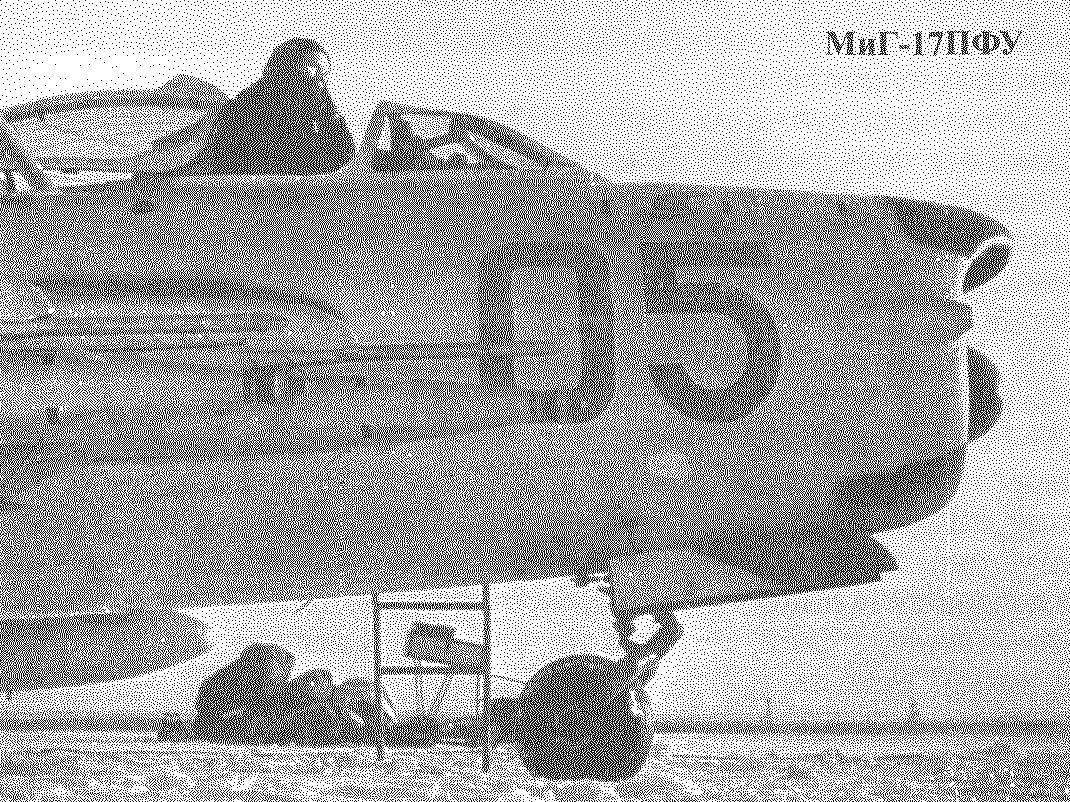
In June radar “Kite” has not passed state tests on a light interceptor, the Yak-50 August 5, 1951 a meeting was held with Stalin, which took the decision on the construction of fighter planes with turbojet a A Mikulin AM-5, With the OKB And Yakovlev was commissioned to build a twin-engine interceptor loitering with a range of 3,000 km and radar “Falcon”, and And And OKB Mikoyan — long-range escort fighter This decision was left of the fighter aviation of air defense for a few years without all-weather interceptor Despite the support of Lavochkin aircraft by the air defense command and noticeable progress in the development of radar “Emerald” In Tikhomirov, La-250 was in “limbo” state In the future, in the summer of 1952 for testing the on-Board locator is used substantially modified OKB Lavochkin And under the radar “Falcon” La-200Б, and on a lighter Yak-120 was carried out flight tests of the radar “Emerald”.
Radar “Emerald” successfully passed state tests in the first quarter of 1952 to the single MiG-15Пбис (SP-5) Search antenna was located on the upper lip of the air intake, and reception — in the center of the inlet In contrast to sight “Tory” and “Kite” the capture and target tracking was carried out “Emerald” automatically, which simplifies the use of weapons And the aim to work more reliably with the Aircraft series is not built, but the results of this work used to create the interceptor based on the MiG-17 and MiG-19.
In 1950 one of the MiG-15bis modified for the installation of a radar “Kite”, using the nose of the fuselage due to the delay of fine-tuning the radar in the NII-17 fighter-interceptor SP-2 in accordance with the order of Minaviaprom of August 11, 1951, was converted into a wing with a sweep angle of 45°, changed the contours of the visor light, and increased the volume of rear fuel tanks from 165 to 250 litres, turning it into a MiG-17 (factory code SP-2), which further and tested the station “the Hawk” Armament of the fighter consisted of two guns NR-23 ammunition 90 rounds to one and 100 to another, the Factory tests were conducted by test pilot Mr. Sedov from April 1950 to November 1951 In the state trials, from 28 November to 29 December 1951, was attended by military pilots of the NII VVS and PVO And P Suprun, Yu And Antipov, V G Ivanov, M Dziuba, E I, Savitsky and PH Sereda.
The main disadvantages odnoimennogo sight were considered unreliable automatic tracking and inconvenience associated with determining the position of targets on the screen with a circular sweep, the small area of the air brakes do not provide a fast clearing speed Further work on the car turned.
In the summer of 1952, the plant number 21 was built three interceptor SP-6, which gave the OKB for testing two of the aircraft produced plant № 155 Aircraft SP-6 were the precursors introduced into serial production of the fighter-interceptor MiG-17P.
After SP-2 G Sedov began flight tests of the interceptor SP-6 with the radar sight RP-1 Izumrud, paired with optical sight ASP-TNM two-antenna RP-1 had to detect the target Tu-4 at a distance of 9.5 km and to accompany her on ranges up to 2 km In practice, the maximum detection range does not exceed 8 km.
Externally, the modification of the “P” differed from the MiG-17 the contours of the lamp and the fairing station antenna RP-1, and increased to 0.97 m area of brake flaps Installation RP-1 led to an increase of the flight weight of the aircraft at 220 kg and to the deterioration of the review pilot of the front hemisphere Armament originally consisted of three NR-23, later the aircraft were produced with three, and with two NR-23 ammunition up to 100 rounds per gun.
The development of the MiG-17P was difficult mainly due to the imperfect methods of training pilots to intercept and pretty sophisticated guidance system.
In August 1952 made the first flight of SP-7 — interceptor MiG-17P with uprated engine VK-1F-16 December 1952 g was made 46 flights in the test program of the aircraft, stations and shooting of weapons On state tests of the aircraft were delivered in December 1952, They ended in may 1953 with a positive evaluation of the Aircraft was introduced into production, called the MiG-17ПФ.
Flight performance of aircraft is significantly increased, but, as for the generic version of the MiG-17F, reduced cruising speed and range due to falling 100 kg maximum thrust of the engine at work in the nonafterburning mode, the Arms on the different series of MiG-17ПФ consisted of two or three guns NR-23.
The experience of operating the MiG-17ПФ showed that the power system of the aircraft is overloaded Generator GSK-3000 struggling to cope with the increased load, mainly due to the radar sight RP-1 collected in vacuum tubes and consumed too much power In this regard, the generator was replaced by a more powerful GSK-6000.
In accordance with the government resolution of June 27, 1953 g, and additional requirements air force aircraft SP-7F was installed an upgraded radar RP-1 Izumrud (instead of serial) and changed the location of the equipment of this station for the release of the maintenance approaches carried out works on elimination of the remarks revealed GK NII VVS. In January 1954 the aircraft was submitted for state tests, which ended in April of that year with satisfactory results.
At the end of 1954, built and presented to the factory testing of the MiG-17ПФ (SP-8) with a radar RP-5 “Emerald-5” Station RP-5 was an upgrade of the station RP-1 and had a number of changes that allowed to increase the range of automatic acquisition and tracking of up to 4 km, as well as to protect the station from nonsynchronous impulse interference After successful tests radar “Emerald-5” put into mass production and installed on the MiG-17ПФ (factory № 31 December 1955) and MiG-19P.
In 1953 five of the MiG-17ПФ (SP-6) re-equipped launchers APU-3 under the four guided missiles “air — air” K-5 (RS-1), dismantling two guns HP-23 has Also been enhanced radar “Emerald-1” These aircraft were factory code SP-15 On them in the autumn of 1953 began practicing guided missiles “air — air” K-5 created under the direction of P D Grushin.
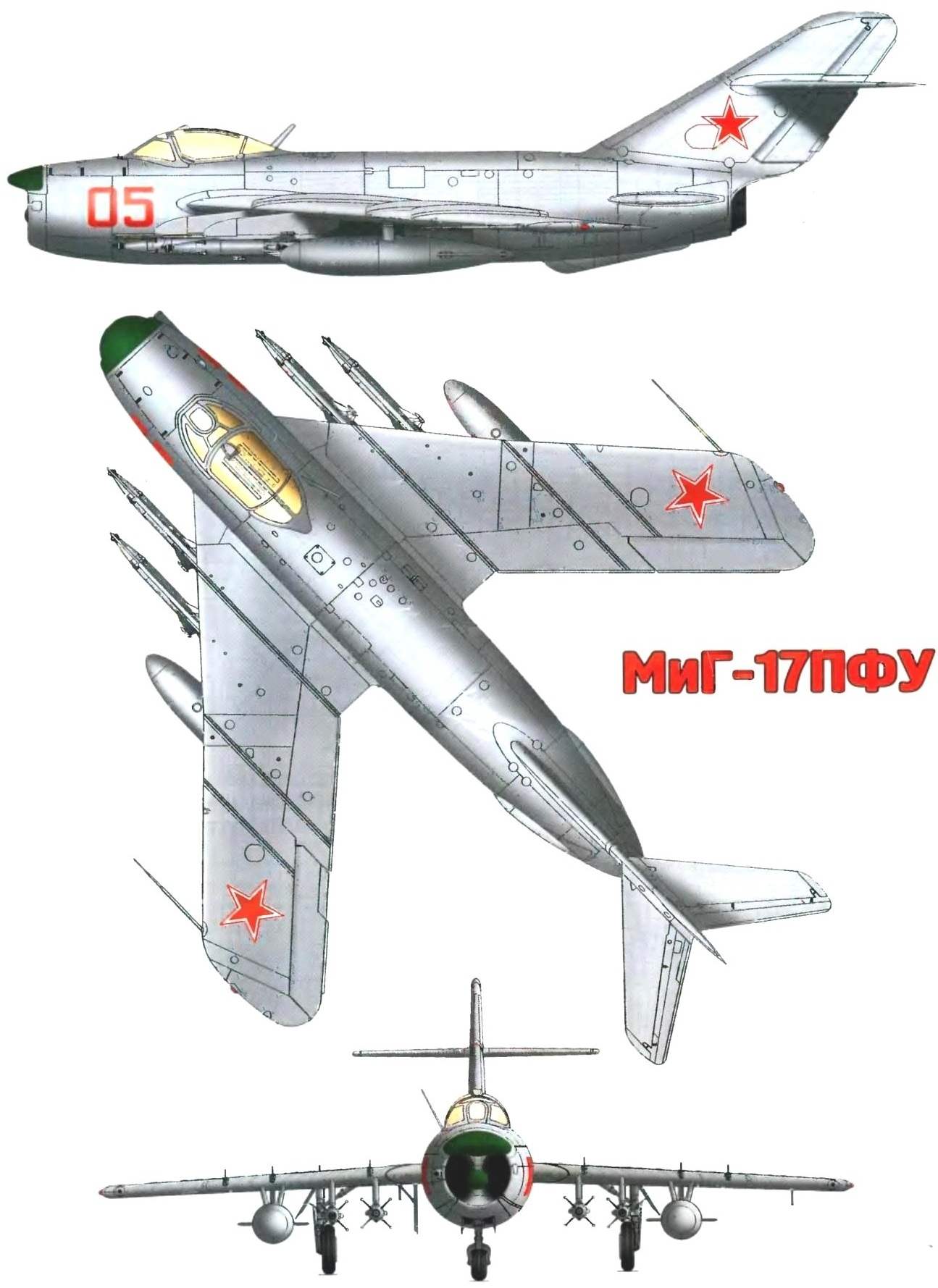
In accordance with the government decree dated December 30, 1954 g after the completion of state tests of the system controlled weapons s-1-forty-MiG-17ПФ adapted for use guided missiles RS-1-U Missiles were directed at the target by the beam radar “Emerald” and was intended to combat the bombers, in simple and adverse weather conditions at distances up to three kilometers Modified interceptor was named the MiG-17ПФУ.
Weapon system p-1 U in 1956, successfully passed the military tests of the MiG-17ПФУ a long time he served in two regiments of the fighter aircraft of Moscow district air defense on airfields near Rzhev and Kotlas.
During state testing missiles K-5M on one of the MiG-17ПФ (factory code SP-16), equipped with radar, BL-60, developed by KB-1 of the defense Ministry, evaluated the possibility of using guided missiles K-5M (RS-2) MiG-21 And OKB Mikoyan And together with the CB-1 MOS was converted two aircraft Factory flight-testing station of the BL-60 ended in October 1957 with positive results.

Fighter-interceptor MiG-17ПФУ, Moscow district PVO, the beginning of 1960-ies
Improvements to the MiG-17ПФ continued after the termination of its serial production In accordance with the decision of the State Committee on aviation technology and the air force from January 21, 1963 in the fourth quarter of 1963 one of the MiG-17ПФ equipped with guided missiles K-13 In 1964, together with the plant № 134 was conducted flight tests that ended with positive results.
The MiG-17 was built on two Soviet aircraft factories, the Gorky aircraft plant number 21 until August 1955 built 225 MiG-17P and MiG 388-17ПФ, Tbilisi aircraft plant No. 31 to January 1958 280 MiG-17ПФ.
In the future, more than 400 MiG-17ПФ put our allies 129 — Algeria, 96 — people’s Republic of China, 42 Socialist Republic of Vietnam, on 24 — Korean people’s Democratic Republic and Czechoslovakia, 18 — Syria, 16 in Afghanistan and Iraq, 12 — Bulgaria, Cuba and Romania of the cars in the 1960-ies devouroil K13 missiles in addition to Soviet MiG-17ПФ license is made under the notation LIM-5P— Poland, S-104 in Czechoslovakia and J-5A— in China.
The main performance characteristics of the MiG-17ПФУ
Engine……………………………………………………..TRDC-1F
Thrust, kgf
at maximum capacity………………………………2600
in afterburner…………………………………..3380
Wing span, m…………………………………………….9,628
Length, m……………………………………………………….11,68
Height, m……………………………………………………..3,8
Wing area, m2……………………………………….22,6
Weight of empty aircraft, kg……………………………4065
The aircraft’s takeoff mass, kg…………………………5723
Maximum takeoff weight, kg………………….6665
Maximum speed at altitude 3 km, km/h…1123
Time to 5 km altitude, min.
on the maximum mode of engine operation….3,3
in the afterburning mode of engine operation………2,0
A climb of 10 km, min.
at the maximum operating mode of the engine is 7.9…
in the afterburning mode of engine operation……..4,8
Service ceiling, km……………………………..16