The Messerschmitt factories from July to September presented the four project (or rather two in two versions) single fighter R. R. 1103 and 1104, with the engine Walter НWК 109-501A-1. “Arado” proposed project fighter E. 381 with a pulsating jet engine Argus 109-014 that in the area of finding goals brought the aircraft carrier. “Heinkel” – two very close draft R. 1068 “Julia” and p. 1077 “Romeo”. Firm “Junkers” -the prototype EF 127 “valley”.
Participated in the competition and the project engineer Erich Bahema. He Based was a person, of course, outstanding.
His career he, like many other well-known figures of the German air force, started as glider pilot at the gliding station Rani. In the future, Based proved to be not only a good pilot, but a talented technician and later as a capable organizer and Manager. Working in aviation industry-Based rose to the position of technical Director of factory “Fieseler”. But it was not an accomplishment for an ambitious engineer he dreamed of his own production and wanted to prove himself as a designer.
He managed to create a small firm carrying out the role of a subcontractor at aviation giants, in his hometown bad Waldsee. As you might expect, one day over the factory appeared Armada of American bombers, which turned him into a pile of rubble. It made a big impression on Bahema, and from that moment all his thoughts were focused only on one thing — to create an aircraft capable of repelling massive air raids.
Project-Based BP 20, he created a small group of like-minded people, was submitted to the contest in August 1944, He in concept dramatically different from the proposals put by competitors. In fact, it was a disposable plane.
Of all the proposals of the technical management chose project-R. 1068, “Julia”, the rest rejected. In particular, BP 20 was rejected because the experts seemed foolish to lose it every time.
However, the Bahema was not going to retreat. He was able to motivate his idea of the inspector General of fighter aircraft of Adolf Galland, who gave positive feedback. Designer then has an audience with Heinrich Himmler and was able to convince him of the usefulness of the proposal. The all-powerful chief of the SS called the RLМ and technical management immediately changed his mind. Within 24 hours BP 20 project adopted for implementation: it released the necessary funds (as a loan from the funds of the SS), and he received the highest priority. The aircraft was assigned the designation BA 349 “natter” (“Adder”).
The prototype of the M8, designed for experienced planning. Well seen chassis, borrowed from the aircraft Klemm KI 35. For the wing bottom – open the parachute hatch. Himself of the parachute container with lid rests on the stabilizer
Wooden technological layout “Nutter”. The layout allowed us to work out the design served as a model for production control and was indispensable when serving different bosses
Bahema the project involved the construction of a simple, cheap, disposable rocket fighter, to start a which does not require the airfield. “Nutter” had to take off from a launcher (fixed or mobile) with a height of about 25 m.
After takeoff with the help of powder accelerators interceptor with a working sustainer engine had to quickly gain altitude and get closer to the goal. Further, the pilot gave a volley of unguided rockets, and then using the stock speed, the “Nutter” was to gain some excess over the target and attack it as a ramming attack. Just before ramming the pilot ejected. Simultaneously, with the help of explosive bolts separated the rear part of the fuselage with the engine. It had landed by parachute for reuse. Thus, it saved the pilot and the engine, and the front and middle part of the fuselage rammed the enemy and ceased to exist. The entire flight was to last 3-4 minutes.
It later turned out that the cabin “Nutter” is too small to put in her ejection seat. In addition, the chair itself had yet to create and establish, therefore, from the ramming attack was abandoned, and in the Arsenal of the fighter left only missiles.
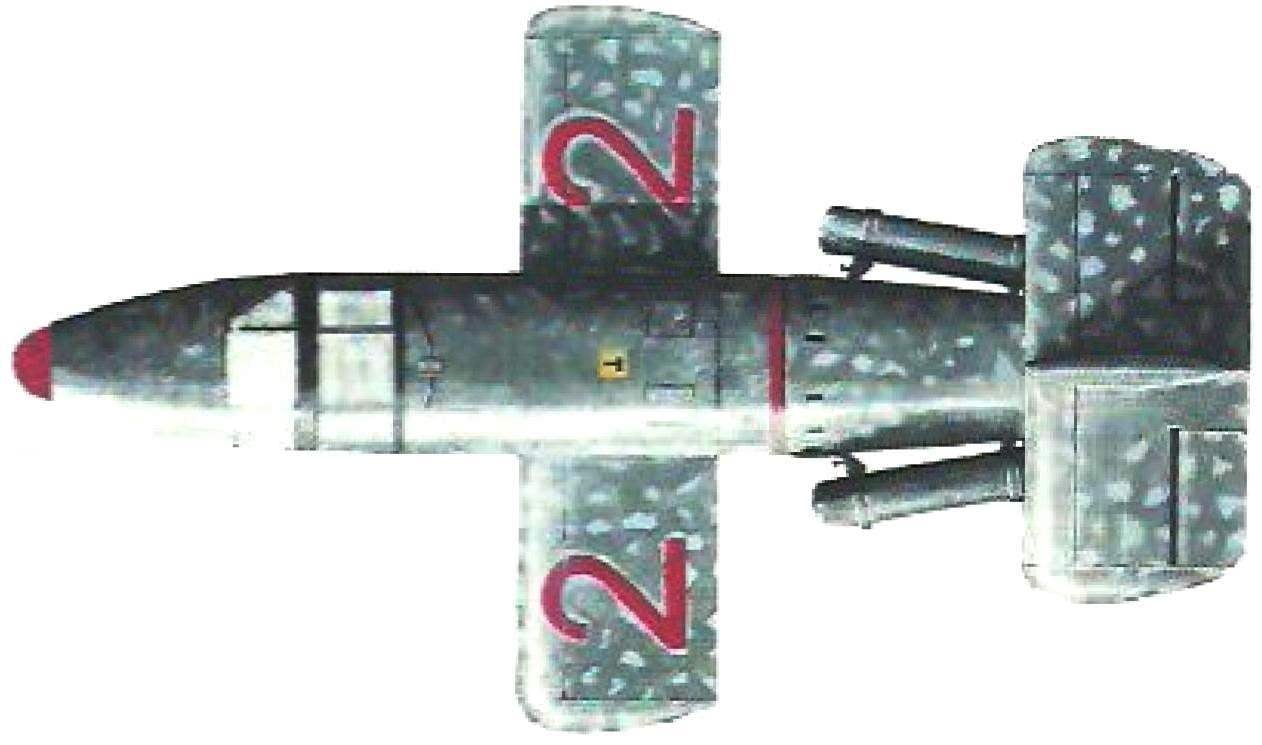
The interceptor BA 349 was a classic all-wood airplane aerodynamic configuration. It had a straight wing with no ailerons. The frame of the wing consisted of the wooden spar and the plywood back wall, which passed through the fuselage. Cross set of each wing consisted of six ribs of the truss Spar were attached to the average power frames of the fuselage on the metal rails. Front and rear edge of the wing was to the side of the fuselage and was a milled contoured beams. Wing tip had a few sub-frames, closed-molded lining. That part of the ending, which was held in the rails of the launcher, further amplified by the overlay of tin. Plywood sheathing was attached to the frame with glue and nails, and then specials and ascariasis.
The fuselage was laminated of plywood and hardwood veneer, and the scheme was a classic monocoque. Cross set consisted of 15 frames, curved two 5-mm slats with plywood walls. Frames passing through the line of the separation was enhanced, and the fixing of various equipment had pads made from plywood or metal. The fuselage was divided into three parts: the front — with battery Nursi and the cockpit, medium – s fuel tanks and wing mounts and rear with the power plant. The front part had plywood sheathing thickness 5 mm, average 3 mm, and the tail is 2 to 3 mm. Plywood and laminated veneer panels were fastened to the frame by glue and 25 mm nails hammered in increments of 25 mm. In serial production was supposed to mold the trim from the special bakelite cardboard with a coating of veneer with a total thickness of 5 mm.
In the nose of the fuselage under a plastic cap, located the armament of the aircraft. Originally it was supposed to equip two cannons MK 108 caliber 30 mm, but for a single transient attack and decided to use rockets. The experts agreed that their volley would be more efficient cannon of the queue. The plane could take nurs 24 N 217 “Fehn” caliber 73 mm or 32 Nursi type R4НL “Orkan” caliber 55 mm, does not exclude also the use of a 46 nurs Rheinmetall R4М.
Before shooting the plastic cap was dropped and missiles launched volley (main mode) or in sections in two or three volleys from the electric fuse. On the rear of the rocket battery was mounted on 15-mm armored plate protecting the pilot. Immediately behind the plate was the apparatus for launching projectiles, which consisted of a battery and simple electrophoretically.
Then followed the cab, which housed the pilot’s seat made from molded plywood, the controls, the simplest autopilot brand “Patin”. Flight equipment was minimal and included the attitude indicator, airspeed indicator, altimeter, variometer, and compass. On the dashboard was also set devices, supplied with the power plant: a guide to the amount of fuel the pointer speed of the turbopump unit, thermometer etc. However, on serial samples of them could not be put. On the right side is attached to a disposable oxygen device. In the cockpit was the place for radio control equipment and radio communications. Control stick and pedals (made of planks) had a classic design. Wiring of the control system was a cable and held in the lower part of the fuselage. And only between the elevon and the last chair was used hard thrust. Behind the cockpit was covered by the second armored plate thickness of 15 mm. from Top to the cockpit was closed the lamp, made of 2 mm steel with slotted rectangular portholes.
The first prototypes of the “Nutter” lantern opened sideways, but then went on to open up – ago, and also established a system reset in flight to ensure the evacuation of the aircraft pilot. Front visor had three bulletproof glass thickness of 60 mm. in Front of the windshield stood a simple framework scope.
In the middle part of the fuselage housed the metal fuel tanks, which were 425 liters of oxidizer (hydrogen peroxide) and 186 liters of fuel (a mixture of hydrazine hydrate, methanol and water). Oxidizer tank (T) was located over the wing spar and fuel tank (S) bottom front spar. The legend for the components of fuel – the C-stoff and T-stoff by the Germans imposed for secrecy, and, indeed, until the end of the war few people knew what is hidden under these names.
Followed by the tail section, which is attached to the middle part of the fuselage by explosive bolts. In the tail section housed the engine, some units of the autopilot and the container with the parachute. The container had a special spring mechanism, which before the division of the plane dropping the cover on the side of the fuselage and through the formed opening pushed the parachute out. The aft compartment housed the combustion chamber and nozzle of the engine, and the outside tail feathers. The keels and stabilizer were also solid wood construction. The keel was carried on the rudder and stabilizer – elevons, which allowed to control the aircraft in pitch and roll. On the sides of the tail section provided the locks for the suspension of boosters.
Sustainer engine served as a rocket engine Walter НWК 109-509А, the last modification which had a throttling range of about 9 and 91 kN (1000 kgf) to 16.9 kN (1700 kgf). The engine had a turbo-pump unit for feeding fuel components into the combustion chamber, the automatic start and control modes, as well as devices, ensuring the safety. For its time it was a masterpiece of engineering. Relevant was the cost, it is not surprising that the engine decided to keep. Along the way, escaped the units of the autopilot, located in the rear fuselage.
Fuel enough for 70 from work on full power. Propellants were aggressive, poisonous liquid, which in contact was snowspeeders. This created great difficulties in the operation of the power plant. The best material for storage of the oxidant was glass, and for fuel – pure aluminium. In practice, applied enameled tank for hydrogen peroxide, the design is similar to the Baku, applied on the rocket fighter Me 163. In the design of the tanks is provided for the inner walls, which exclude fluctuations of the fluid during the flight. Tanks were attached to the frame member with bolts and tie ribbons. To avoid an explosion of “Nutter” at the moment of separation of the tail section on pipelines provided a special separation of the coupling. The original project was supposed to save the entire middle and tail of the glider, but studies have shown that after running out of fuel in the tanks remained a couple of components that, when landing, the moment it hit the ground, could result in explosion and complete destruction of the aircraft. So I decided to save only the tail part of the fuselage with the engine.
At the start, we used four solid booster, Shedding 533 General thrust of 19.8 kN (2000 kgf). After the burn, gunpowder accelerators were dropped at a height of about 1000 – 1200 m. the initial idea was to use two such accelerator (one on each side), and a few prototypes of the interceptor has been tested in this configuration, but then decided that not enough thrust and began to install four solid propellant motors. In the early samples of the front fixing points of the boosters were located on the power frame, which was the separation, but the torches of the engines was damaged the lining of the rear fuselage. Therefore, the boosters pushed back, although this led to more complex structure. Suspension components accelerators had special screws for fine adjustment of the SRB relative to the center of gravity of the aircraft. The start took place under the influence of boosters and liquid rocket engines working at full thrust. Some time after vent boosters LRE was transferred to the low-thrust mode. This way was supposed to limit the starting load size of 2.5 D. In such circumstances, the pilot could not cope with the management, so in the initial part of the trajectory control was carried out automatically using the autopilot “Patin” or by radio from the ground. At an altitude of about 1.2 km congestion decreased, and the pilot took over the controls.
In the future, when mass production was supposed to use the dual-chamber motor HWK 109-509В, which in addition to the main combustion chamber, giving a thrust of 16.9 kN (1700 kgf), had a cruising combustion chamber, giving a thrust of 2.94 kN (300 kgf). During takeoff worked both cameras, and then a big camera was turned off and further flight was at cruising at maximum specific impulse. This scheme promised to improve characteristics of the aircraft in terms of range, overloads during takeoff and maneuverability during the attack. It was supposed to go back to two boosters with a thrust of 9.8 kN (1000 kgf) each.
According to calculations, the cruising speed was to be 800 km/h and a maximum at the moment of attack – 900 -1000 km/h. The application of tactics, it was assumed the following: after the vertical launch the “Nutter” was translated into the climb, at an angle of 60°. Management this was carried out using the autopilot and radio commands from the ground. In the final phase of the pilot took over the controls and guided the interceptor to a selected target. The fire was recommended to open with a distance from 500 to 350 m, as at a closer distance the plane could be damaged in the explosion of the ammunition purpose. The bomber was supposed to hit one volley (basic version), but you could split the ammo in two volleys, and then after the first shot you can repeat the attack from a closer distance, and if the first volley was successful, I was able to transfer the fire to the next target.
After performing the attack, the pilot transferred the plane to decrease, at medium altitudes quenched speed, performing a flying snake, then shot off the nose and put in place the main parachute of the fuselage. As a result, the speed fell, and the pilot easily left the cabin. After that separated the middle part of the fuselage, and the tail was saved.
THE PRODUCTION AND TESTING OF AIRCRAFT “NUTTER”
The first model, “Nutter” for research in the wind tunnel was made in September 1944, He Based foresaw difficulties with the development of this unusual aircraft, so had planned to build a series of 50 specimens intended for testing in different conditions before you perform the first manned space flight. (10 – for flight planning, 10 – for testing a vertical launch, 10 for testing the recovery system of the pilot, 10 — to test the control system with the autopilot and the last is to check all of these systems in the complex). But time was running out, and this program was not implemented. Actually build the 37 samples that have received designation from M1 to M34. M – short for Muster. Some prototypes had dual designations, such as the MGD and MSv and М8а and М8в.
The first prototypes built BP 20 M1 instead of weapons and the power plant had the ballast and was test flown in Neuburg without a pilot, towed behind a bomber is Not 111Н-6. The first takeoff was performed December 22, 1944 (according to other sources, in November 1944) with resettable starter truck. Flight ended successfully – both aircraft landed safely. Gliding performed two test pilot, who worked in the firm “Based in veerka”, – Hans Siebert and Lothar Sieber.
The second sample – M2 – equipped with a fixed landing gear with nose wheel from light training aircraft Klemm KI 35. He in flying were not involved and were used for strength tests. M3 also had tricycle landing gear and was intended for plan tests. At the first landing he cracked one of the landing gear shock absorber, since the vertical velocity at the moment of contact exceeded 1 m/s. Rack was replaced by a reinforced, from the aircraft KI 35V. For planning flights using four other aircraft. They tried resetting the front and the salvation of the fuselage section on a parachute. In General, the flights took place successfully, the main point was that the design of the lantern. Opening in the side of the flashlight when the division was stuck, so starting with the M4, used the lights, leans back.
Diagram combat use interceptor “Nutter”
Until February 1945 did a lot of flying, which allowed us to begin manned tests. At the same time, the model of the “Nutter” was intensively purged in the DVL wind tunnel. 14 Feb 1945 pilot Hans Siebert on M8 for the first time, unhooked the tow at a height of 5500 m and made a free flight planning. According to the plan, at the altitude of 3000 m it has caused a separation of the aircraft and safely landed by parachute. The aircraft showed good stability and handling, though, because significant loads on the wing, flying with great speed. The following sample – M9 also had in tow, and starting with M10 steel to conduct vertical launches on rocket propulsion.
First attempt at a vertical launch was undertaken on 18 February. The sustainer engine was not mounted, so the takeoff was carried out only in the starting boosters. The first pancake came out lumpy – the “natter” was not able to break away from the launcher. Apparently it jammed in the guide. Launcher tower was modified and the second attempt, on 25 February, was a success. Then LRE also not used, and the pilot’s seat was occupied by a mannequin. After takeoff, a normal division of the plane then the manikin and the rear part of the fuselage to the engine without damage safely descended to the ground. In the process of testing fine-tuned also launcher. Well, the M16 took off from an installation height of 17 m and M17 -ramp with a height of 12.5 m. At this stage, not everything went smoothly – the aircraft was often off course due to uneven thrust boosters.
Despite the problems with the start, the leadership of the SS was always looking to start manned flights. I must say that by the time the SS had full control of the project -in addition to financial and political support has been allocated 600 SS, summarized in the “Command N”. Of these, 200 employees were used in the “Bahema the veerka” as workers. The rest – served technique, preparing it for the flight, guarded, etc. In late February, a decision on manned flight was made. First off is carried out on 1 March 1945 Oberleutnant Lothar Sieber on M23. After switching on the ignition interceptor went up (and the acceleration was slightly less than expected), but at an altitude of about 500 meters for some reason he lost his lantern. The aircraft continued to gain height, gradually pulling back till hid in the clouds. Approximately 50-th second of the flight, he in a steep dive fell out of the clouds. The pilot made no attempts to leave the machine or align the flight. The plane at full speed crashed into the ground, burying the pilot. Most likely, the lantern at the Department hit the head of a pilot who lost consciousness, and the deviation of the trajectory from the vertical occurred due to incorrect configuration of the accelerators, or due to the destruction of the gas booster, which did not allow the autopilot to level the machine. Whatever it was, it was the first ever vertical take-off man on a rocket.
The bow of the VA 349А. Seen the main weapon of the interceptor — battery for 24 Hs 217 rockets “Fehn” caliber 73 mm. On sides visible wire system launch. Top front sight and a sighting frame. The frame of the canopy made of 2 mm steel, which is inserted in the bulletproof glass
Experimental BA 349 V installed on the launcher type “steel tower”. This unit worked out under Stari solid-fuel boosters, Shedding 533. Sustainer rocket engine is missing. The cockpit is also missing, and its glazing replaced with plywood
The most expensive unit “Nutter” – liquid rocket motor HWK 109-501A-1. On the left, turbopump Assembly with the fuel equipment. Next, to the right there is a pipe on the end of which is attached to the combustion chamber with the nozzle. The best characteristics of the motor points to max torque is 1700 kgs. Cravings can be Sudoservice to 1000 kgf.
This disaster is not stopped testing. On the same day it was launched, two more “Nutter” (M24 and M25) – but without the people. Starts have passed without significant comment. Until April 1945 executed another 16 flights. All in automatic mode. Continued testing of the vertical launch. So M31 was launched with the installation mounted on the pole, with the length of the guide is only 8 m. M32 had an additional stabilizing surface and was launched from the unit is deflected from the vertical is 22°. The tests were generally successful.
An integral part of the project was the launching pad, which worked in parallel with the plane. They are implemented in the form of a collapsible towers that can be installed on the line of approach of enemy bombers. They had the main guide, made in the form of the letter S, which was wound T-shaped pins mounted on the lower keel and leash on the front of the plane. From the rotation of the “Nutter” kept two guides, which goes into the lower surface of the wing, or a couple other that have got wingtips.
One of the installations was a tower steel structure, assembled from angles, channels and I-beams, connected by steel rivets and bolts. The installation can understand on some parts, convenient for transportation. In addition, this design allows you to easily change the length of the guide – determining minimum required length included in the test program. The stability of the structure gave a special goods, located on the crossbeam. The installation was based on a previously concreted area with the help of screw jacks. In preparation for the launch, the aircraft was brought up by a special truck in a horizontal position. There was his refueling propellants. Then a special cradle was put on the root of the wing, and for them, with a winch, the plane rose into the launcher. The bolt was wound into the guide. After connecting, communication and adjustment of onboard equipment “Nutter” was ready to fly. It took about ten hours.
Another type of launcher had a simplified design. The basis of it was a pillar of a ship pine with a length of 15 – 20 m. it with nails fastened main and two support rails. The post was inserted into the slot previously concreted pads.
Just ordered 50 aircraft for the Luftwaffe and 150 for the Waffen SS, but was built only 50 pieces, of which has only 37 aircraft from M1 to M34, They were a modification 349А VA and VA 349В in different equipment, including eight – for anyone planning a flight with ballast instead of weapons and engine and fixed landing gear, VA 349В had the fuselage lengthened by 300 mm and greater fuel capacity. According to some historians, some of these planes had to carry cannon armament.
Began the construction of the three samples modification VA 349В-1 with a more powerful dual chamber motor НУУК109-509В-1, with a reduced thrust cruising. In addition to these samples, was studied a few projects remain only on paper; designed removable wings for easy transportation “Nutter”; easy to install floodlights for night interceptions and a double training option for the training of pilots.
In April, several aircraft BA 349 was prepared for combat use, but they were not pilots. A quick allied offensive forced the Germans to destroy the interceptors.
In the process of evacuation of the enterprise of Waldsee, where he conducted major works in Kirkham transport “naturama” was fired at aircraft, causing the chaperones and protection left on the road, a few slightly damaged BA 349. Coming up, American troops took them as trophies. A “Nutter” might fall into the hands of the red Army in Thuringia, where going to produce them under license.
Technical data of aircraft BA 349 “natter” and Me 163
Technical documentation for the BA 349 was acquired by the Japanese, who wanted to get their production under license, but those plans went awry.
In General, we can characterize the project Bahema? Compare it with the closest analogue – rocket interceptor Me 163. Moreover, they have the same engine. The estimated speed of both aircraft 800 — 950 km/h At such speeds, the sweep angle is recommended 15 to 20°, this parameter has the Me 163 looked better (the sweep on the leading edge is 27.5°). But this lack of “Nutter” kompensiruet quite a large wing loading: 555,6 kg/m2 is like a modern supersonic fighter! Load 163. – half – 275 kg/m2, which gives better maneuverability at the time of the attack. “Nutter” had a straight keel and stabilizer, which could cause various problems when a high-speed flight (although during testing, due to their small numbers, they are not apparent). There are also comments on the local aerodynamics of the fuselage had a low elongation and a blunt nose, and was also present, standing across the stream of large items – the elements of sight and cutting the leash.
“Nutter” had a more simple design and two times smaller takeoff weight than the Me 163 (2000 kg 4110 kg, respectively), which gave him, in combination with a vertical start, a phenomenal rate of climb: 6,000 m he climbed in 0.6 min, against 2.27 min. 163. In addition, the “Nutter” didn’t need an airfield to which you want to return, so the pilot can freely maneuver in the time of the attack, after all, still have to jump with a parachute, and under you everywhere the native land. And the Me 163 pilot had to remember to get back to their base, and the engine will “shut up”.
In the smoke and roar began the first manned flight in a rocket. According to eyewitnesses, at first the “Nutter” rather slowly rose above the PU. But it was stable, no roll. Then began to fall back and lost the canopy. The flight ended in disaster
Therefore, when almost three times less gas station (VA 349А – 625 l, IU 163 — 2700 liters of fuel) combat radius for both planes was about the same. It should be noted as a progressive innovation – the use of elevons on the stabilizer and the presence of boosters.
Was the “Nutter” significant shortcomings – first and foremost, is the disposability use. After departure it was necessary to find the tail (and how much it will take time unknown), to fix minor damage that is inevitable when landing, and assembling a new aircraft. So prepare for a new mission could be delayed more than ten hours laid down in the project.
The experience with the Me 163 it is known that the rate of convergence with the goal of reaching 150 m/s, which leaves little time for aiming and opening fire. “Nutter” was waiting for the same problems and do not have the means (e.g. air brakes) for their decision.
In conclusion, we can say that mass application of “Nesterov” could make life difficult for the allies, but hardly changed the course of the air war.
Recommend to read RESONATORY CLIMBS Today I want to introduce You to the model class B1, having almost the same set of wings. This force diagram consoles with a transverse set of pine slats is fully justified, since for... FLYING ON THE SIDE Model of a catamaran-class "P" with a sail-wing. Few people remember that the apparatus used for movements the aerodynamic forces, was created more than five thousand years ago. It was a... 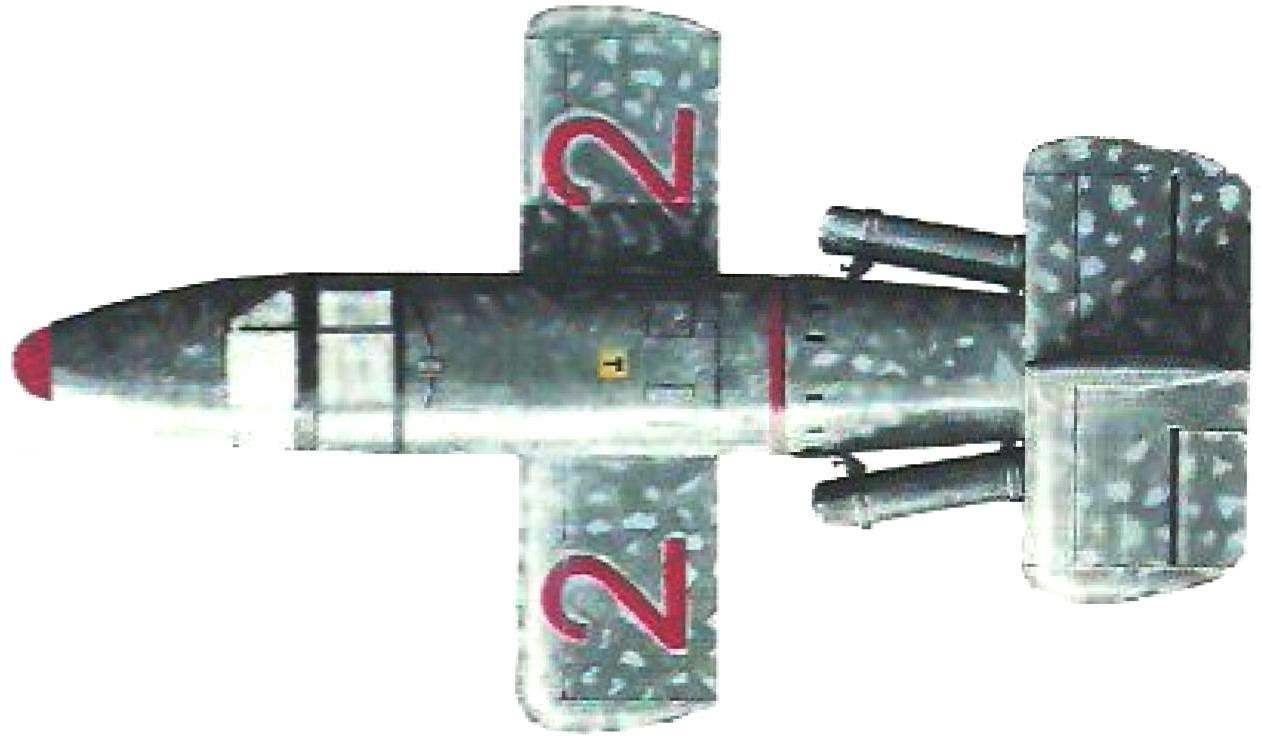 During the Second world war in Germany, there have been many models of aircraft, some of them had a very original design. “Nutter” is definitely one of them, and although he never gained military glory, but in the air up and therefore deserves attention as an unusual and interesting Chapter in the history of aviation.
During the Second world war in Germany, there have been many models of aircraft, some of them had a very original design. “Nutter” is definitely one of them, and although he never gained military glory, but in the air up and therefore deserves attention as an unusual and interesting Chapter in the history of aviation.