This glider is made of three kinds of materials – foam, fiberglass and epoxy binder, and the design of the wing and tail is a sort of small design masterpiece.
Rib of the wing is made from foam and are covered with thin fiberglass. Toe wing, perceiving torque, is laminated to the foam block filler fiberglass shell. Fuselage beam carved from foam and covered with fiberglass, and the bending moment perceive fiberglass shelves, glued to top and bottom surfaces of the beam. The quality of work – excellent exterior finish – the envy of many DIY. The only “but” to fly the glider refused – as it turned out, in an effort to reduce the weight of the structure, the creators of the glider unnecessarily reduced the wing.
Enthusiasts who passed flight training in gliders initial training, we can recommend more sophisticated apparatus, for example, glider A-10B “eagle”, created by students of the Samara aviation Institute under the direction of V. Miroshnik. Interestingly, the parameters, the glider does not correspond to any sports class and for its size it is less than the standard. While A-10B very clean aerodynamic shape, a simple strut-braced wing is covered with cloth, and the unit itself is made of the most common plastics. A sufficiently large aerodynamic quality of the airframe is able to perform it even long soaring flights. A simple tecnique and allows the beginner to cope with such apparatus. It seems that it is inexpensive and “flying” gliders do not have enough domestic gliding.
A peculiar development of the ideas embodied in the A-10B was the glider “Dream”, created in the Moscow Amateur club under the direction of Vladimir Fedorov. Design, manufacturing technology and the appearance of the “Dream” is a typical modern sports glider, and the specific load on the wing and some other parameters – a typical glider initial training. Flies the “Dream” is quite good, at conventions ULTRALIGHT this glider was sent flying in tow aircraft “Wilga”.
It should be noted that the flights of the gliders with the launch of their with isolator, winch, or small mountains are extremely limited in time and not bring the pilot to adequately meet. Another thing – glider! At the machine with the motor capabilities are severely wider. And even gliders with small motors sometimes exceed the flight data of some light aircraft Amateur-built.
It is, apparently, that the aircraft, usually the wing span is substantially less than that of the glider, and when you reduce the scale of losses in lift are large than the gain in mass. As a result, some aircraft are not able to get off the ground. While training gliders with a rough aerodynamic shape and low-power motors fly well. The only difference of these aircraft from the aircraft is greater wingspan. I think that is why the training gliders are very popular among fans.
Glider HAI-35M “Enthusiast”:
the power of the engine 36 l,p.; wing area – 11m2; the empty weight of 170 kg; takeoff weight – 260 kg; flight alignment – 28 %; maximum speed – 150 km/h; stall speed of 48 km/h; rate of climb is 2.4 m/s; the maximum aerodynamic quality – 15
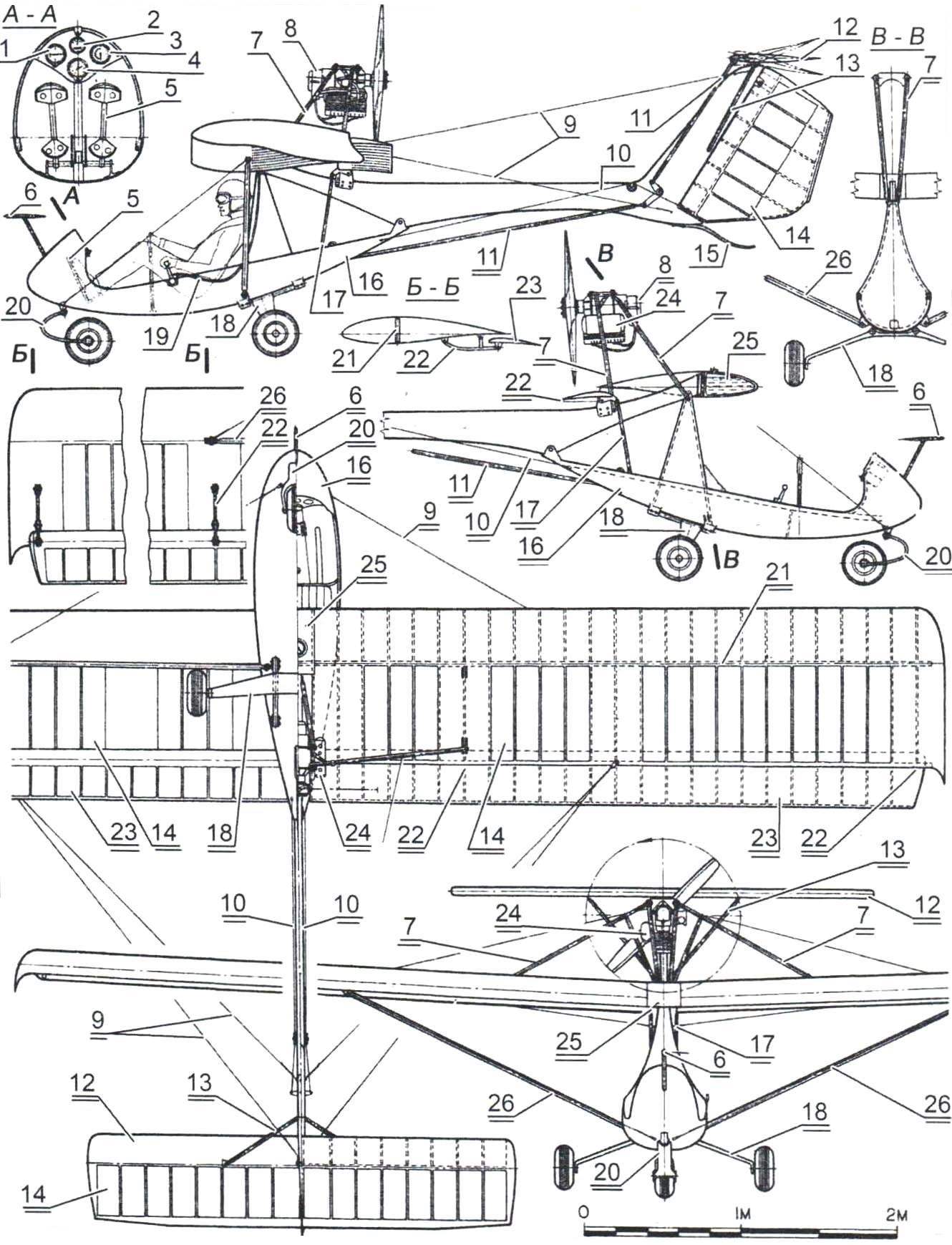
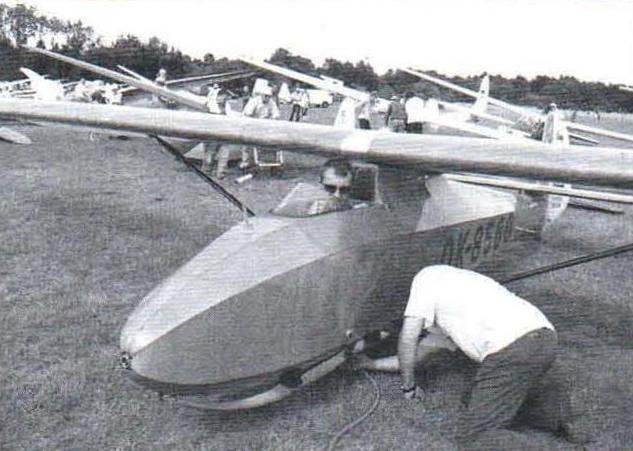
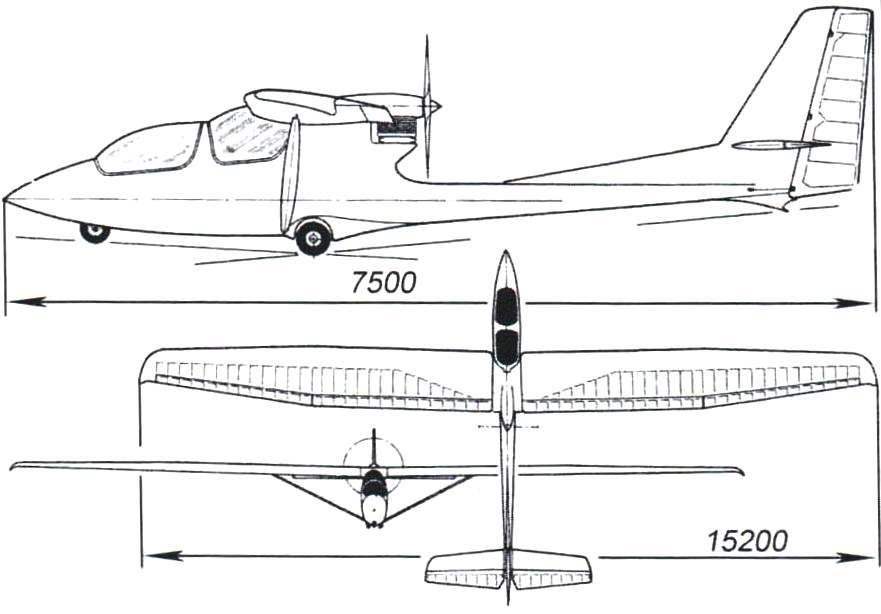
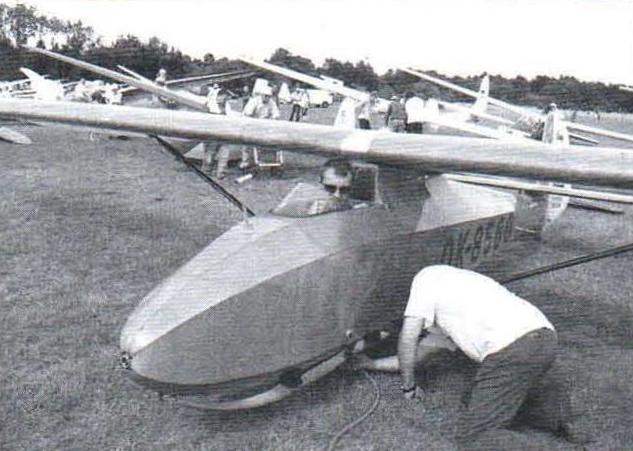
Glider “Garnis” B. Oskinis and H Kishonasa (Kaunas)
the length of the glider -5 m; wingspan -8 m; wing area – 10,6 m2; empty weight – 139 kg; takeoff weight – 215 kg; maximum velocity of -130 km/h; landing speed 40 km/h; rotation frequency of the propeller – 5000 Rev/min.);
1 – variometer; 2 – slip indicator; 3 airspeed indicator; 4 – altimeter; 5 – pedal; 6 – receiver air pressure; 7 – tubular motor; 8 – engine; 9 – cable brace; 10 – control cables, rudder; 11 – pull Elevator control; 12 – all-moving horizontal tail; 13 – tube struts stabilizer; 14 – sections of wing and tail, covered with Mylar film; 15 — tail spring; 16 – fiberglass gondola pilot; 17 – thrust control the ailerons; 18 – spring main chassis; 19 – control wiring engine; 20 – spring fiberglass nose landing gear; 21 — wing spar; 22 – hinge Aileron; 23 – Aileron ( upper casing – fiberglass, bottom – Mylar film); a 24 – silencer; 25 – fuel tank 26 – tubular strut wing
Double glider “Aeroprakt-18” (SKB KuAI):
wing area is 16.3 m2; wing profile modified GAW-1 – 15%; take-off weight of 390 kg; empty weight – 200 kg; maximum velocity of -130 km/h; rate of climb – 2, 3 m/s; the calculated overload from + 10,2 up to -5,1; maximum aerodynamic efficiency -25; the thrust of the propeller – 70 kgs at 5000 rpm
Double motoglider “Baikal” with the power plant of the two coupled 40-horsepower motors “Whirlwind-25” air cooling:
wing area – 18,9 m2; take-off weight – 817 kg; the stall speed of 70 km/h; the maximum speed of horizontal flight-150 km/h
Glider “Solitare” designed by Burt Rutan with a 23-horsepower engine КFМ-107E. located on the folding rack in the forward fuselage:
the wingspan is 12,725 m; the span of the front wing – 4,68 m; the length of the glider -5,86 m; area of the front wing – 1.73 m2; the area of the main wing – 7,79 m2; empty weight – 172 kg; takeoff weight of 281 kg; maximum aerodynamic quality – 32; the maximum speed is 213 km/h, stall speed – 60 km/h; the range of 241 km; range of operating overloads from +7 to -3
Great success in the simplest of such devices is made up students of the Kharkiv aviation Institute, built under the leadership of A. Barannikova glider “Kite-M”, and later under the leadership of N. Laurel was created more perfect “Enthusiast”, had a good aerodynamic shape, a closed cockpit and carefully zakuporivaniya engine.
It should be noted that both of these glider are a further development of the popular in his time of training glider BRO-11 design B. Oskinis. Machines of Kharkov students have a simple design with no claim to originality, but they are very durable, reliable and available to management for novice pilots.
At one of the gatherings SLA H Kishonas from Kaunas showed one of the best-gliders – “Garnis” made entirely of fiberglass. The covering of the wings and tail – transparent Mylar film. The power unit is an outboard motor “Whirlwind M” capacity 25 HP, converted by air cooling. The motor is easily removed from the machine.
The motoglider is equipped with several options readily detachable chassis -tricycle-type aircraft, glider and float balancing.
Motor gliders and gliders on the type of “Kite” and “Garnis” are built in our country by many fans in dozens of instances. I want to draw readers ‘ attention only to one feature such devices, constructed in the image and likeness of BRO-11. As you know, prototype (and its many copies) is fitted with drooping ailerons, kinematically associated with the wheel height. When landing, the pilot takes over the control stick, the ailerons simultaneously deflected down, causing an increase in lift and decrease speed. But, if the pilot accidentally touched the handle, and then correcting the situation, gave the handle away from you – the last movement of the handle causes not only the deflection but also the return of the ailerons in the original position, which is equivalent to cleaning the flaps. Thus the lifting force decreases sharply, and the glider “falls”, which is very dangerous when flying at low altitude, before landing.
The experiments carried out by the glider pilots, flying BRO-11, showed that without hovering ailerons takeoff and landing characteristics of the glider practically does not deteriorate, but to fly a glider is much simpler, which significantly reduces the accident rate. Thus for the wing of the glider-the slug might be a better convexo-concave profile of the “göttingen F-17” – at the time it is used on the glider Phoenix-02, by the engineer of TSAGI S. Popov.
The popularity of the gliders is due, primarily, to start without a special towing devices, and also due to the emergence of simple, easy and powerful enough motors. At conventions SLA was shown a lot of original, spectacular flying machines of this class are created by designers and fans. Beautiful glider A-10A was built by V. Miroshnik on the basis of already familiar to readers AND 10B. Power unit he – engine “Vikhr-25 converted for air cooling; it is located above the fuselage, behind the cockpit. The engine typically is used only for takeoff and climb. After turning it off a special mechanism was folding farm with the installed on it with the engine and cleaned it in the fuselage that significantly reduced aerodynamic drag of the aircraft. If necessary, the engine using the same mechanism could be put forward from a niche and start.
Another aircraft built by students of the Samara aviation Institute, double glider “Aeroprakt-18”. It is compact, lightweight, made entirely of plastic and is equipped with a 30 horsepower engine “Vikhr-30-Aero” air-cooled – this model has the engine in flight is not removed, which allowed to simplify and to facilitate construction.
However, Amateur designers continued to develop the original versions of the arrangements of cleaning of the motors in flight, and one of the most interesting devices was created by a group of Moscow aviation enthusiasts under the direction of A. Fedorov for single twin-engine glider “Istra”. Light engines were fully inscribed in the contours of the wing, not speaking for his theoretical outlines, and the propellers revolved in the cracks behind the rear wing spar. When you stop the engine the screws were fixed in a horizontal position and closed by sliding the shank of the wing.
Another development of the Moscow glider pilots of Amateur – double motoglider “Baikal”, is also equipped with two engines. However, they are placed not on the wing, and V-shaped pylon above the fuselage. In flight, the engines are retracted into the fuselage – just like on “Istra”.
The feature of A. Fedorov-gliders – composite construction, made in accordance with the canons of modern technology.
It is considered that the aerodynamic design of modern gliders and motor-gliders is fully stabilized. In fact, all modern devices of this type differ little from each other, and their geometric proportions are almost identical. However, the design ideas looking for new solutions, other schemes and proportions. The evidence of Swiss aircraft designers and glider Bert Rutan “Solitare”. These original gliders, made by the scheme “duck”, once again demonstrated the advantages of a bearing of the horizontal tail.
 GLIDER OR GLIDER? Unpowered gliding flight has long attracted man. It would seem that what is easier is attached to the back wings, jumped down the mountain and … flew. Alas, many attempts to rise into the air, described in historical Chronicles, has led to success only in the late nineteenth century. The first glider was a German engineer, Otto Lilienthal, glider balance created is very dangerous to fly the aircraft. In the end, the glider of Lilienthal killed its Creator and brought a lot of trouble enthusiasts gliding flight.
GLIDER OR GLIDER? Unpowered gliding flight has long attracted man. It would seem that what is easier is attached to the back wings, jumped down the mountain and … flew. Alas, many attempts to rise into the air, described in historical Chronicles, has led to success only in the late nineteenth century. The first glider was a German engineer, Otto Lilienthal, glider balance created is very dangerous to fly the aircraft. In the end, the glider of Lilienthal killed its Creator and brought a lot of trouble enthusiasts gliding flight.