 Not to everyone’s strengths and capabilities to manufacture selenoproteome, laminated fiberglass surfer. Beginner athlete we recommend you to make a windsurfer with a simple Board on the classical technology— frame construction with sheathing of plywood.
Not to everyone’s strengths and capabilities to manufacture selenoproteome, laminated fiberglass surfer. Beginner athlete we recommend you to make a windsurfer with a simple Board on the classical technology— frame construction with sheathing of plywood.
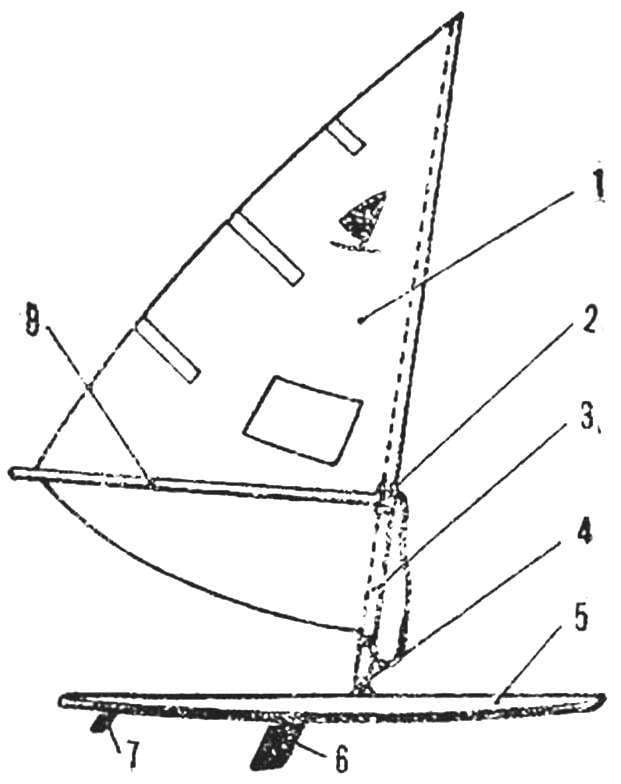
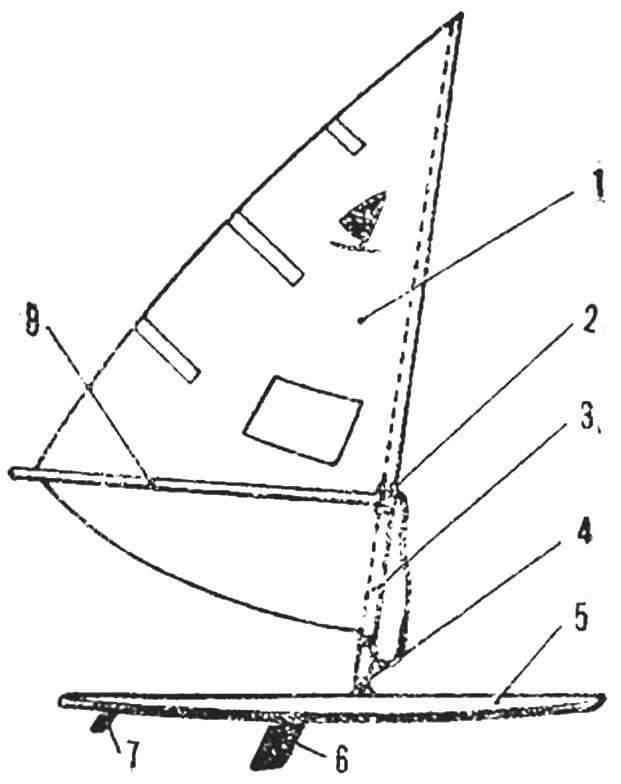
Board-housing. The work begins with the manufacture of the longitudinal beams. It consists of four parts, held together by a tubular copper rivets and waterproof glue, such as epoxy resin. These parts are cut from pine boards with a thickness of 25-30 mm. the Two holes in the middle part of the longitudinal beam — deaf with a length of 100 mm through a length of 350 mm designed for the key steps and retractable centerboard.
Cross set case — four frame (pine boards with a thickness of 20 mm), I. transom bow Board; longitudinal four Reiki stringer (pine 20X20 mm). Sheathing housing can be waterproof plywood thickness of 3 mm. Deck in the area of movement of the athlete must be covered with a thicker plywood or reinforced with another layer of cellular. The lining is attached to the frame using epoxy glue or casein, and small (preferably copper) nails. Nails hammered with a step of 30-50 mm.
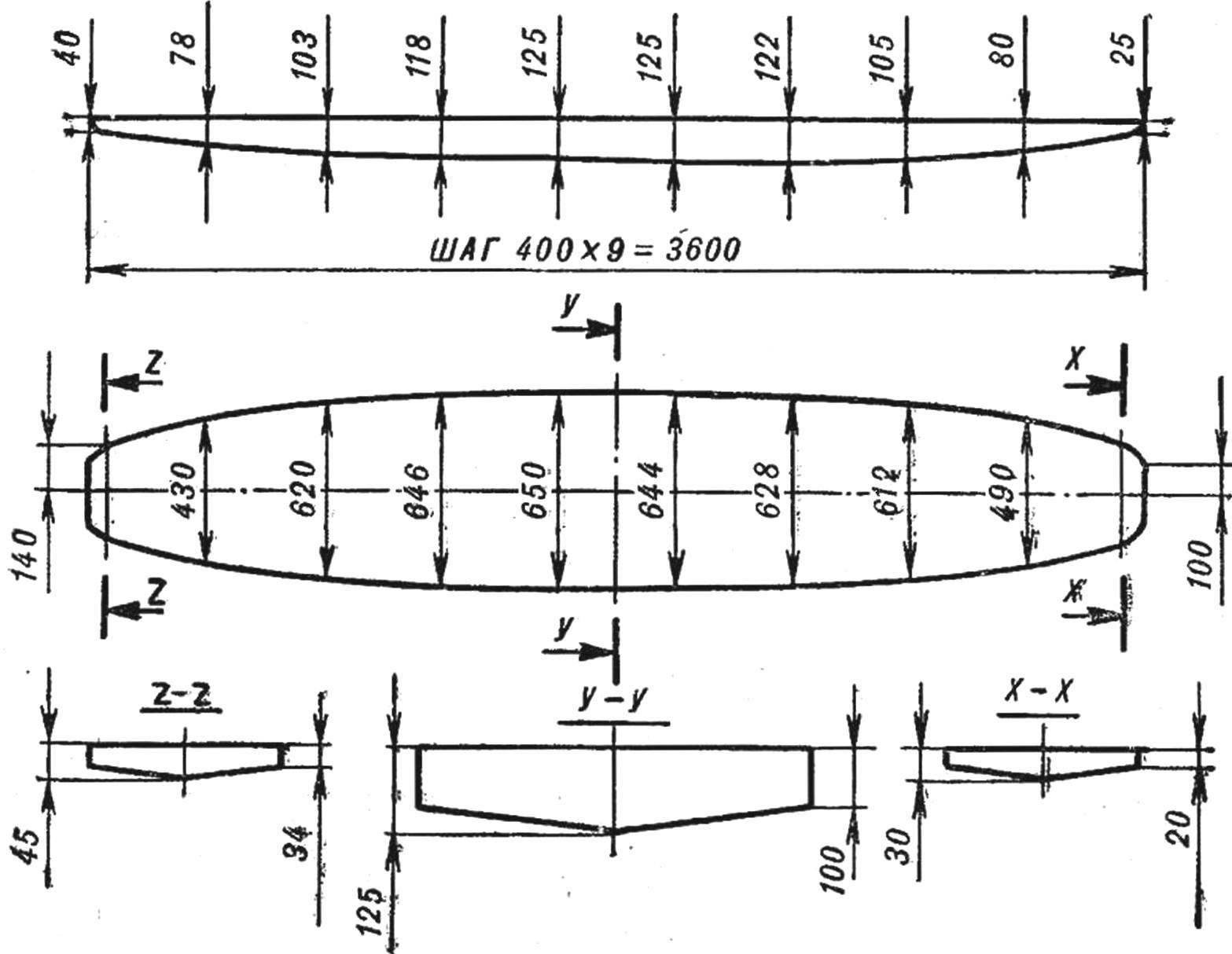
Fig. 1. The theoretical drawing Board-hull
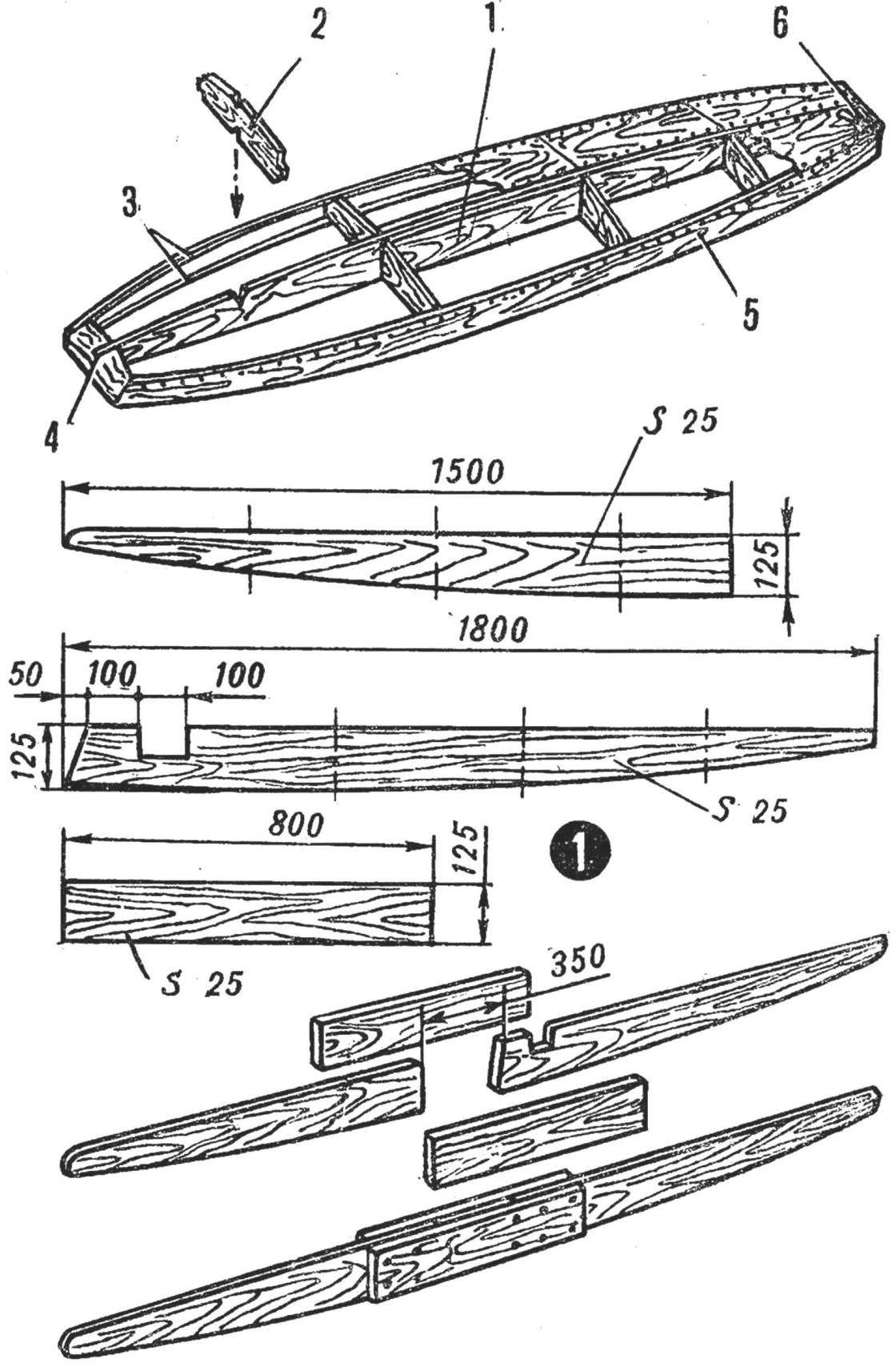
Fig. 2. Board construction corps:
1 — longitudinal beams 2 — frame, 3 — stringers, 4 — bow-Board, 5 — casing, 6 — transom Board.
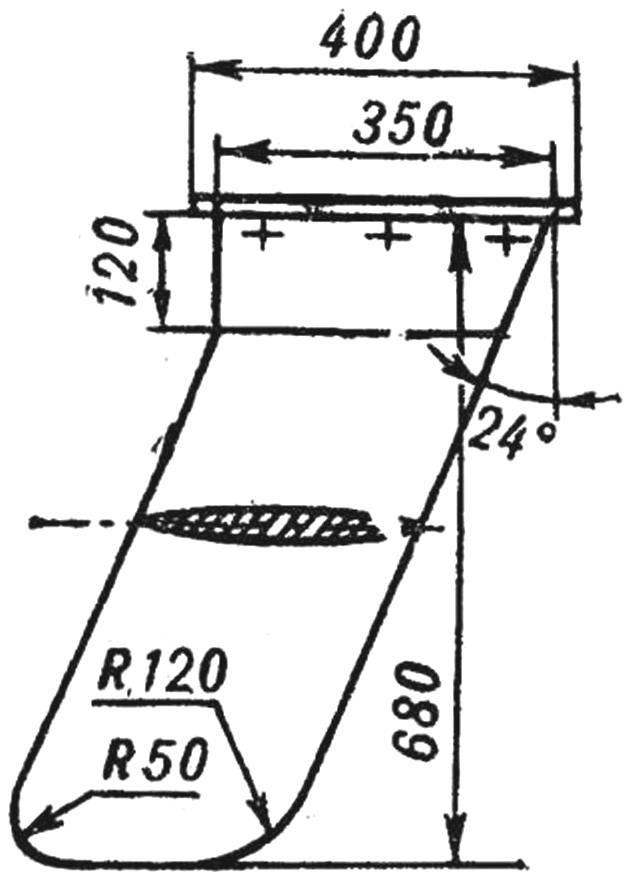
Fig. 3. Retractable centerboard rider.
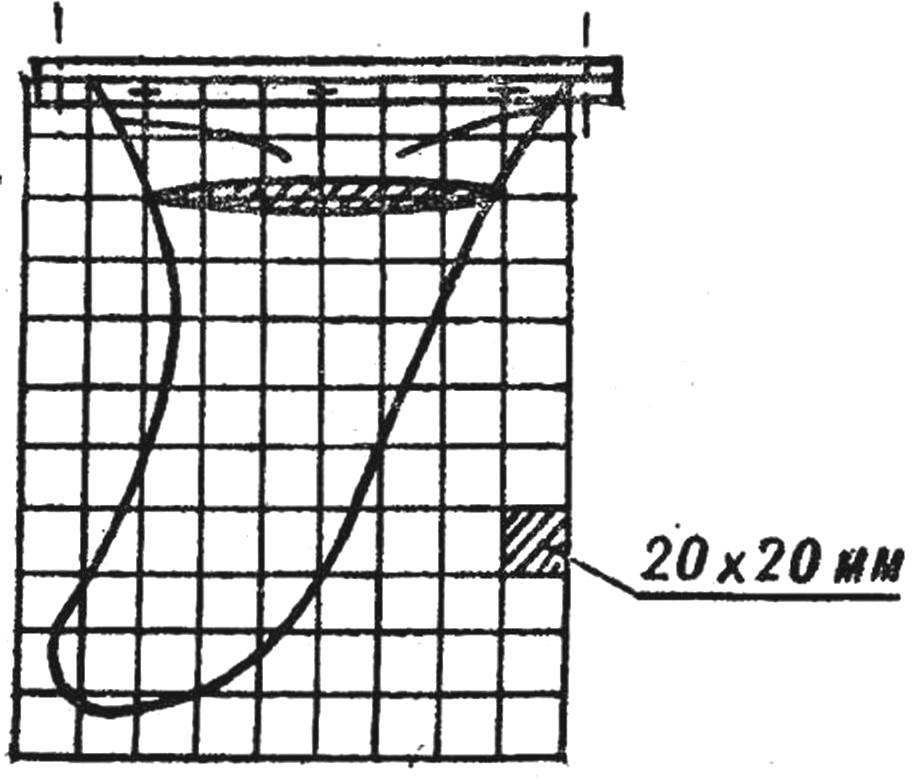
Fig. 4. Fin.
Ready housing is a good idea to paste one layer of fiberglass epoxy resin, if this is not possible, it must be thoroughly soaked several times with hot linseed oil with intermediate intermediate drying, proshpaklevat and painted with bright oil or glyptal paint. The deck in the area of the movement the athlete is required to do saragosti, for which it is sprinkled with fine sand or sawdust layer of freshly applied paint.
The centerboard is cut out of plywood 20 mm thick to the dimensions given in figure 3. Pick up a sheet of this thickness is not easy, but it can be glued together from several smaller thickness.
The profile of the centerboard — concave, symmetric. The surface is first processed by the planer, and then a rasp and glass paper. Then the centerboard puttied and painted two or three coats of paint. To the upper part by several screws and glue docked limiter — oak or beech plank section 15X50 and a length of 400 mm.
The fin is cut from dural or cellular plates, or of waterproof plywood thickness 8 — 10 mm. it is Attached to the Board-the body with aluminum profile t-section if the metal fin or two beech slats with glue and screws.
The hinge is an important design element. It allows the mast of a windsurfer to carry out any bending and twisting that is needed to control the Board. There are many different joints, they all work about the same. The device one of them is depicted in figure 7.
The mast can be made of duralumin tubes with a diameter 35 — 40 mm. a Good mast will jump from dural pole —they are sold in sports shops. But the wooden mast from the straight grained wood is no worse than metal. After final processing, it should soak two or three times with hot linseed oil and covered with oil varnish.
Hicokwith which the athlete controls the sail, and consequently, the windsurfer may be made of dural tube 22X1,5 mm, a length of about 6 m. If the tubes are of such length to pick up is not possible, make hicok of the two pipes, docked them in the middle of the bougie.
Hicok is mounted on the mast of beech two pads and two metal clamps.
The sail should be sew from lightweight and durable material. This will require 7 metres of percale width 100-130 cm to Sew some of the cloth between a better double seam or seam “zigzag”. At the level of the head of the athlete in the sail is sewn a transparent window made of Mylar film. The mast is inserted into a special pocket on the sail* cut from a thicker And more durable fabric than the material of the sail.
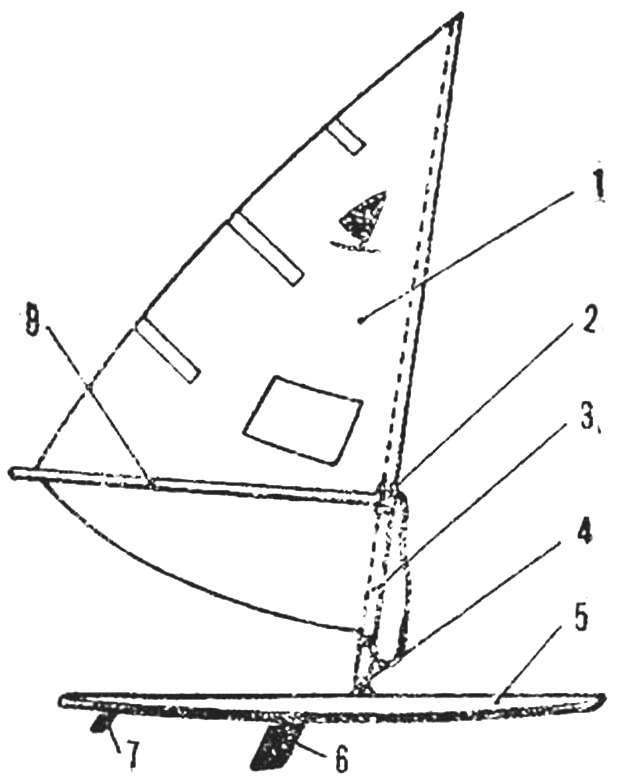
Fig. 5. Diagram of a windsurfer
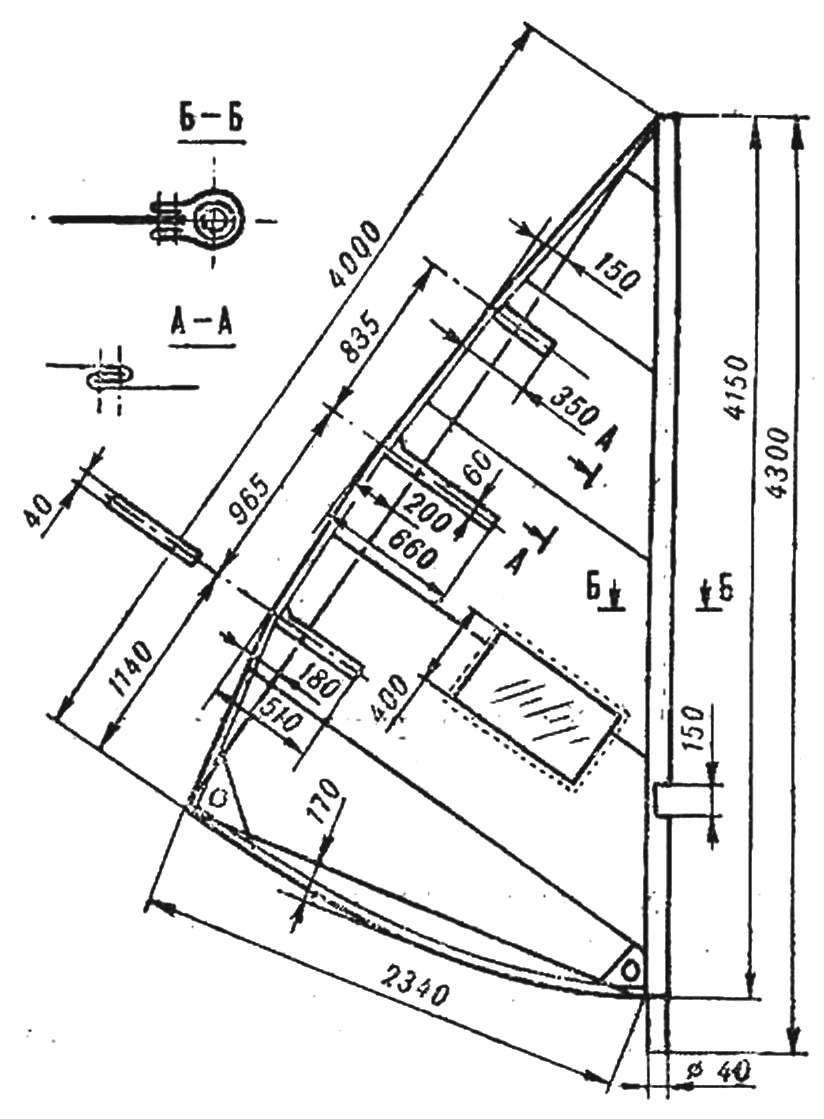
Fig. 6. The sail of the windsurfer.
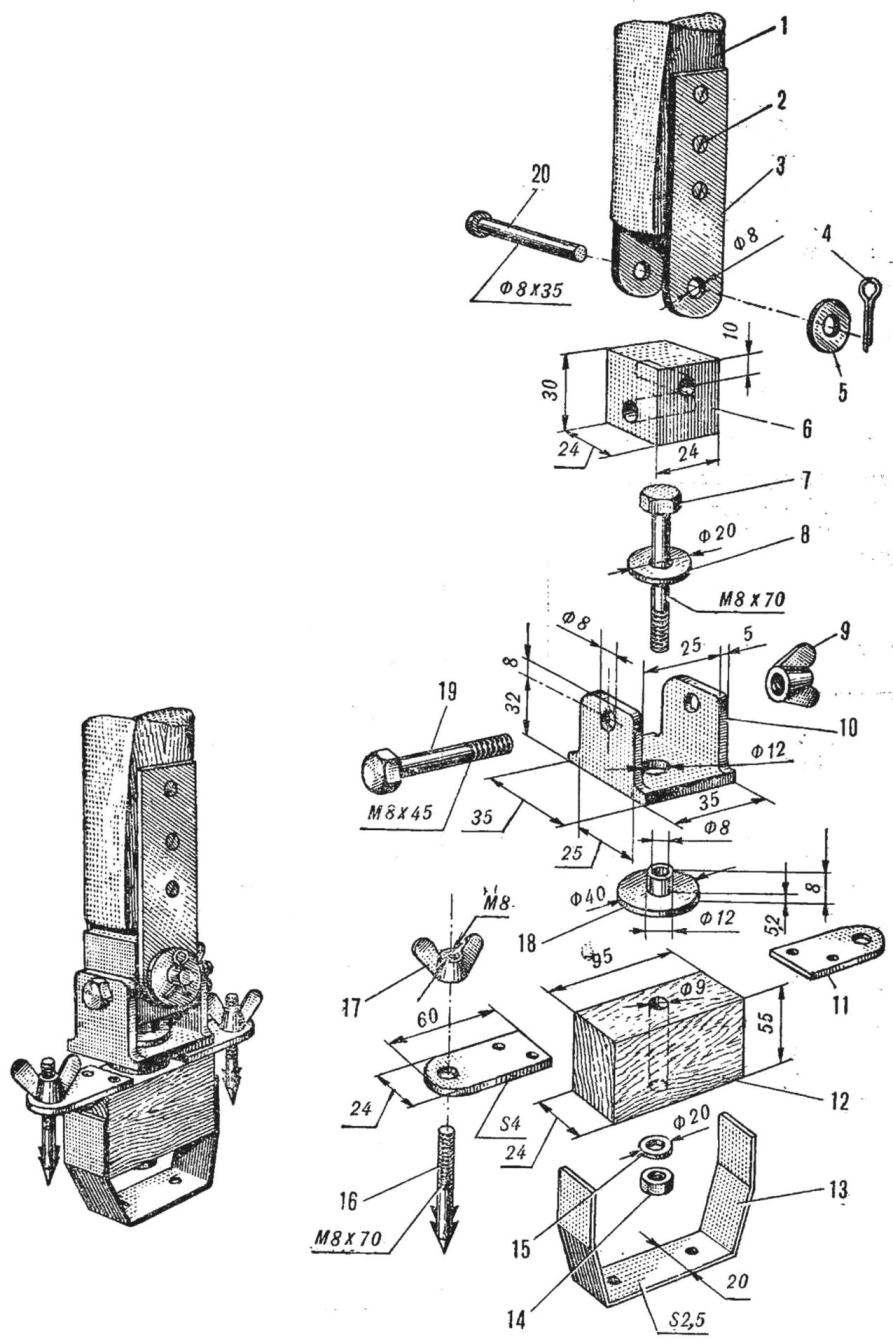
Fig. 7. Hinge design
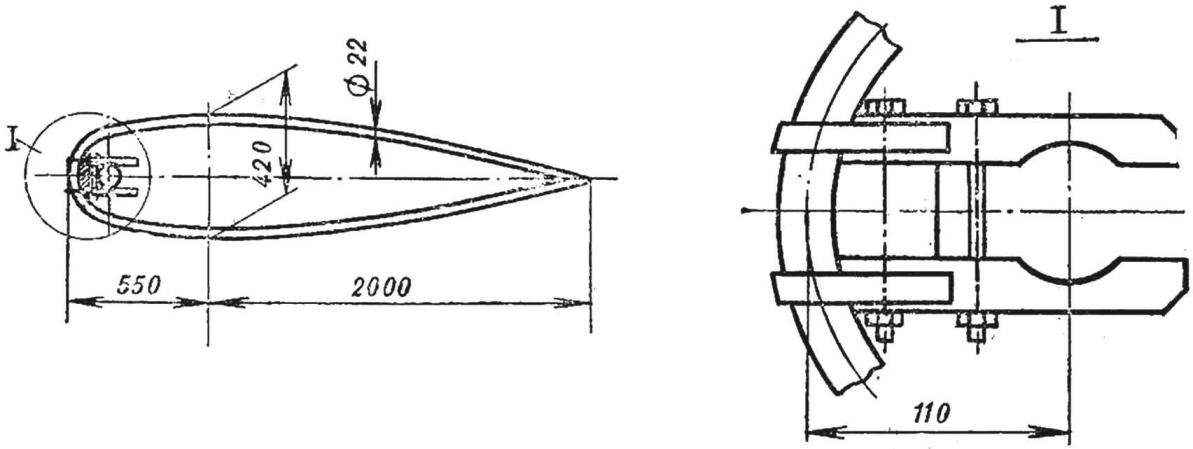
Fig. 8. Hicok and mount it to the mast.
The battens for the sails are made of laminated plastic with a thickness of 1,5—2 mm. They are placed in lat-pockets, sewn from the same fabric as the sail. In the corners of the sail cloth sewed scarves, cut from fabric from the pocket for the mast; the bottom two corners — galbavy and Shkotovo — insert eyelets — metal thin-walled bulochki with washers that serve for the passage through them of the braces of the sail. Eyelets can be replaced with metal rings sewn into the corners of the nylon thread.
We hope that your labor will be rewarded with the pleasure which will bring you slip on a Board under sail. Do not worry, if you stay on Board you will initially be difficult. We are confident that a few days training tame “temper” your windsurfer.