As a result of mass repressions of 1937 -1938. considerably thinned the ranks of skilled workers, research institutions, including creating new military equipment. With the acute shortage of professional personnel in the USSR in the ongoing struggle “enemies of the people” the country could be without leading experts. In September 1938 at the suggestion of people’s Commissar of internal Affairs USSR L. P. Beria in the NKVD Division was established special design Bureau, renamed in 1939 to the Special technical Bureau of the NKVD of the USSR From July 1941 until its dissolution in may 1953 it was called the 4th special Department of the NKVD (since 1946 — MGB) of the USSR. The main objectives of 4-th special Department were: the use of inmates specialists to perform research and design works on creation of new types of military aircraft, aircraft engines and engines of naval vessels, artillery and ammunition, chemical means of attack and defence, and the procurement of radio communications.
As a result of mass repressions of 1937 -1938. considerably thinned the ranks of skilled workers, research institutions, including creating new military equipment. With the acute shortage of professional personnel in the USSR in the ongoing struggle “enemies of the people” the country could be without leading experts. In September 1938 at the suggestion of people’s Commissar of internal Affairs USSR L. P. Beria in the NKVD Division was established special design Bureau, renamed in 1939 to the Special technical Bureau of the NKVD of the USSR From July 1941 until its dissolution in may 1953 it was called the 4th special Department of the NKVD (since 1946 — MGB) of the USSR. The main objectives of 4-th special Department were: the use of inmates specialists to perform research and design works on creation of new types of military aircraft, aircraft engines and engines of naval vessels, artillery and ammunition, chemical means of attack and defence, and the procurement of radio communications.
Where has this idea personally practical Lavrentiy or anyone else, is unknown, but the proposal received support at the highest level.
Actually, the idea was not new: in the late 1920-ies in the OGPU had already created a similar organization after the trial of the “Prompartia”. Many well-known technical experts, convicted on charges of sabotage, got in closed the design Bureau, engaged in the development of new technology. In particular, the rudder of the prototype of one of the most popular pre-war fighter-5 was decorated with the abbreviation W — inside the prison, entered in a five-pointed star. Aircraft built at the plant № 39 named after V. R. Menzhinsky in the spring of 1930, designed in the Butyrka prison “pests” under the direction of N. N. Polikarpov and D. P. Grigorovich, convicted under the 58th article of the criminal code of the USSR One of the “black” humorists called the history And-5 the first example of “brainstorming” in the USSR.
In the autumn of 1938 of highly qualified specialists were brought from prisons and camps in a securely fenced Barack farms of the NKVD in the village of Kurakino, near the Moscow station Bolshevo. Here you can meet famous designers of aircraft, artillery and ships, managers and leading technical workers of large defense enterprises and research institutes. From here they were taken to a meeting with the leadership of the NKVD in Moscow, where he determined the fate of each.
Among marine specialists included in this barracks, was a talented engineer and shipbuilder, chief engineer of the Amur shipyard Paul Gustavovich (Paul Henry) Hoinkis. A graduate of the Kronstadt Naval engineering school, he became widely known among ship engineers, when in 1916 in Arkhangelsk for one night developed drawings of the caisson and nine days to replace the damaged blades of the propeller on the icebreaker “Canada” that, to perform this operation, proposed to send for repair in foreign Doc. For this unique work, the Society of naval architects awarded to Paul Gustavovich special prize.
After graduating from the Naval Academy in 1918 Hoinkis on the recommendation of I. G. Bubnov is appointed by the Dean of the naval architecture Department of Marine engineering school. For 10 years he teaches ship theory, first in school, and from 1920 — at the Naval Academy. The teaching combines with the work the chief engineer of the ship at the Baltic shipyard. Under his leadership, the plant on the instructions of the Northern sea route in a short time designed and built lighters with the capacity of 2500 tons and a diesel tug. At the suggestion of P. G. Hoinkes final Assembly of the lighter of the ready-made body parts, delivered by rail, was held in Tyumen, where it constructed a shipyard. At the Baltic shipyard with the active participation of Hoinkis built a few dozen commercial vessels. Paul Gustavovich organized at the plant pilot production of welded beams and extensive testing. The positive results of the studies led in 1931 to introduce into the production of the first welded bulkheads for submarines, which was the beginning of the widespread introduction of electric welding in domestic shipbuilding. At the end of 1929, P. G. Hoinkes appointed technical Director of the Leningrad Admiralty shipyard built vessels-reefers, tugs and the first Russian torpedo boats, and in 1932 the decision of the government, he is appointed Deputy Governor for technical Affairs Enterprises of the far Eastern shipyards “Vostokskuter”. Before the Association was set the task of revival of the Pacific fleet. For this purpose in 1932 in Leningrad, laid the first seven of the 12 submarines “Pike” V series. Paul Gustavovich, given the weakness of the far Eastern enterprises and the timing of construction, as in 1924 during the construction of the lighters, proposed to build at the Leningrad plant sections of the hulls of submarines and transport them for final Assembly in the far East. Section maximally staffed with the necessary equipment and fittings. Hoinkis personally supervised the technological process of preparation of sections for transport. In the far Eastern factories in the specially equipped berths of the body Assembly was carried out for several days. In the composition of the government Commission Paul Gustavovich participated in industrial site selection for shipbuilding plant in Komsomolsk-on-Amur. For the successful execution of the task for the construction of ships for the Pacific fleet P. G. Hoinkes in 1934 was awarded the order of red banner of Labor.
In the next few years, Hoinkis is a technical Director and chief engineer at Dalzavod, chief engineer of Glamorama, and since July 1936 chief engineer and Deputy Director of the Amur shipyard. At this time on the slipway of the factory was built the leader of the destroyers, which later received the name “Baku”. Sections of the leader were made shipyard No. 198 in Nikolaev by rail and then by water transport delivered to the place of final Assembly. To accelerate the timing of construction of the ship P. G. Hoinkes proposed to install turbines and shafting directly on horizontal building berths, and not after the descent ship on the water according to the traditional technology. Supporters of the proposal, the new chief engineer was not only the factory but also in the departmental research institutes, where the management of the enterprise asked for the conclusion. Taking full responsibility, the chief engineer exercised his offer. As a result, with some increase of the length of the stacker Assembly stage, could significantly reduce the overall construction time of the ship.
25 Jul 1938 took place the launching of the leader of the destroyers, and two weeks before that, the KGB arrested the chief engineer. It was the second arrest of Paul Gustavovich of Hoinkis, the first time he was arrested on the case “industrial party” in the fall of 1930 and April 1932 he worked in oktb-2 of the OGPU at the Baltic shipyard, doing the technical preparation for railway transportation “pike” in the far East. Perhaps someone did not give rest to his personal data: German, born in Poland in the family of a merchant, an officer in the Royal Navy. The military Collegium of the Supreme court on may 28, 1940, rigged once again the case in absentia condemned P. G. Hoinkes 10 years of imprisonment.
In 1939, when the Leningrad “Crosses” have created a special prison No. 8, which included three engineering offices and a branch at defense enterprises of the town Ship offices, and was designed two light cruisers and two torpedo boats, including the M-400, which was diving. In one of these engineering offices is enclosed Hoinkis worked as the chief designer of the project, a light cruiser. Protection preliminary design was successful, but orders for the development of tekhproekt not received, and Paul Gustavovich came out with a proposal to the leadership of the Department about the development of the project seaworthy torpedo boats long range.
Choice of torpedo boats as the object of design was not accidental: first, it was a relevant topic for the Soviet Navy, and secondly, given the position of specialists-prisoners, he gave hope for a real result in a relatively short period of time and, moreover, the release in case of success.
In the USSR later than in other countries, realized the need to have the fleet of seaworthy torpedo boat that appeared in the second half of the 1930s, first in Britain and then in other countries that have purchased from the British for their fleets ready-made samples, or a license for their production. Before world war II, Tupolev redania torpedo boats G-5 were almost the only member of the worker-Peasant red Fleet. In the USSR in the late 1930s he developed several projects of large torpedo boats D-2, D-3, CM-3, CM-4. The letters in the designation of the project meant: D — wooden case, SM — steel nautical; numbers — the number of engines in the power plant. On these projects for the Russian Navy until 1945 the 73 boats of D-3 and one testing CM-3.
The main advantage of the available rednich G-5 — high speed, this is the boat significantly superior to their foreign counterparts. At the same time, they differed low seakeeping characteristic predannyh of gliders. Testing models of the corps G-5 in hydraulic canals TSAGI, made in 1936, showed that it is possible to enhance the seaworthiness, speed and stability of the boat on the course, changing the contours and proportions of the body by increasing its width. But because of the limitations given the technical requirements of the customer on housing under the terms of rail transportation, it continued to build in the old lines.
Another significant disadvantage of the G-5 was a torpedo stern drop. They are allowed to use only torpedo at full speed, as once they drop the boat needed to leave sharply aside. In addition, open the location of torpedoes has led to them freezing and failures in the autumn-winter period. Created before world war II designer F. V. by Panaevym rope torpedo launchers BS-7 installed on boats like D-3, allowed to drop torpedoes even on the foot, but still open the location of the torpedoes impacted negatively on their reliability.
Combat use during the civil war in Spain four G-5 in the Republican Navy has identified the unsuitability of their defensive armament: one machine gun Degtyarev rifle caliber was not enough to combat aircraft. Therefore, starting from the eleventh series began to install the turret with heavy machine gun DShK, and during the great Patriotic war over torpedo tubes added another small point with the ANC.
The disadvantage, is typical not only for G-5, and most similar ships of the time were high-heat and explosion hazards related to the use as a power plant aviation gasoline engines, which possessed a large specific capacity. Only during the fighting red banner Baltic fleet in 1941 out of service 17 torpedo boats, of which ten had exploded or burned.
The solution was found by Russian specialists. In the early 1930s, the division of oil engines TsIAM under the leadership of A. A. Charskogo was created by a 12-cylinder V-shaped diesel aviation an-1. On the basis of it under the leadership of V. M. Yakovlev, who succeeded A. D. Charskogo repressed, has developed a marine modification of the motor — EN-1M with a capacity of 950 litres .with. In 1939, an-1 the factory test, but at the end of the year the work stopped because the people’s Commissariat of the Navy changed the original specifications. In the same year under the leadership of V. M. Yakovlev began the creation of special marine diesel MN-1. In 1939, he has four times exhibited at state tests, but they failed. However, next year plant them. Marty one of the boats G-5 (serial No. 543) series XI-bis, built with engines of MN-1. After trials in July 1941, the boat was handed over to the Navy. He joined the 1st brigade of torpedo boats of the black sea fleet and participated in the great Patriotic war.
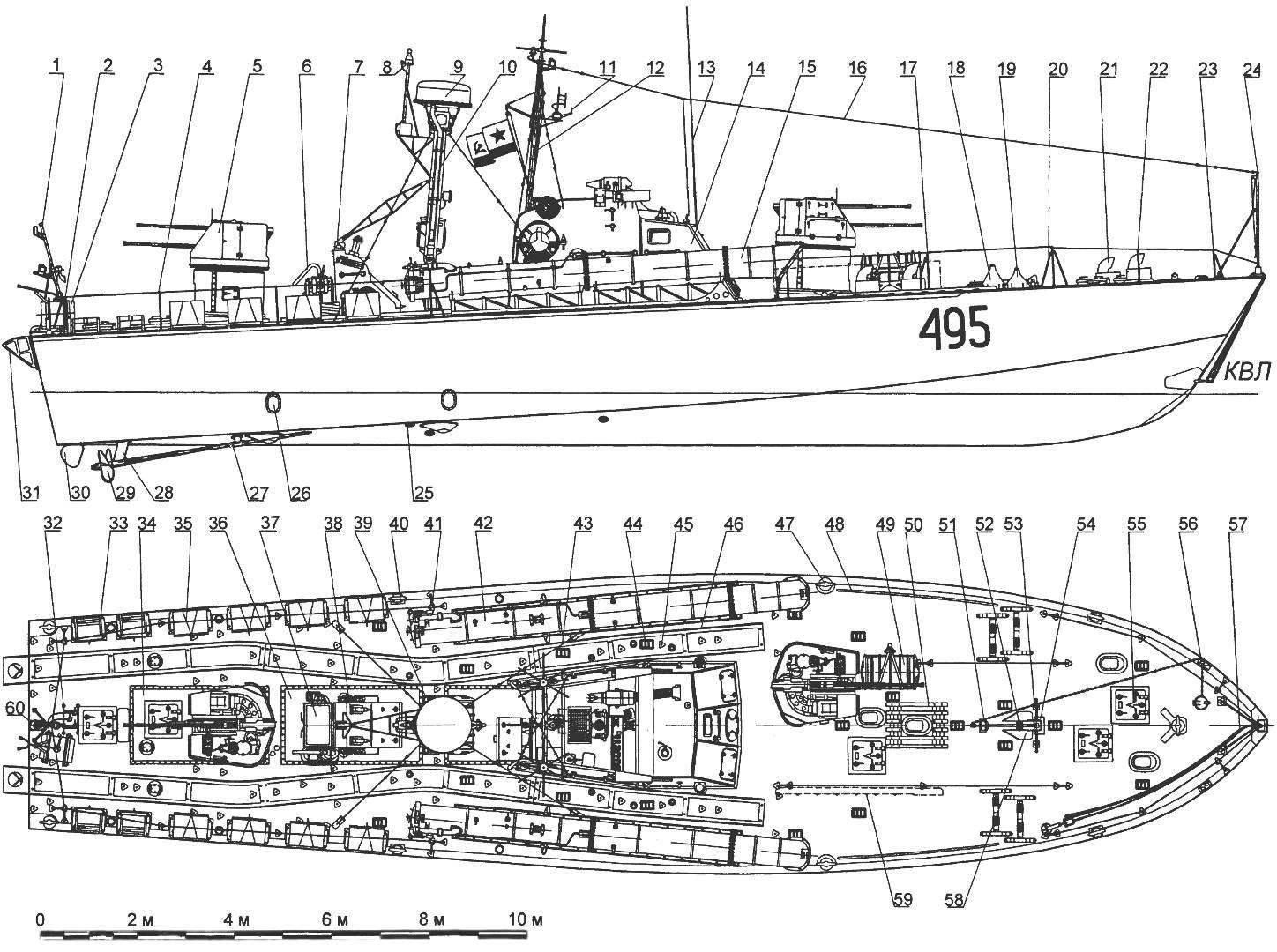
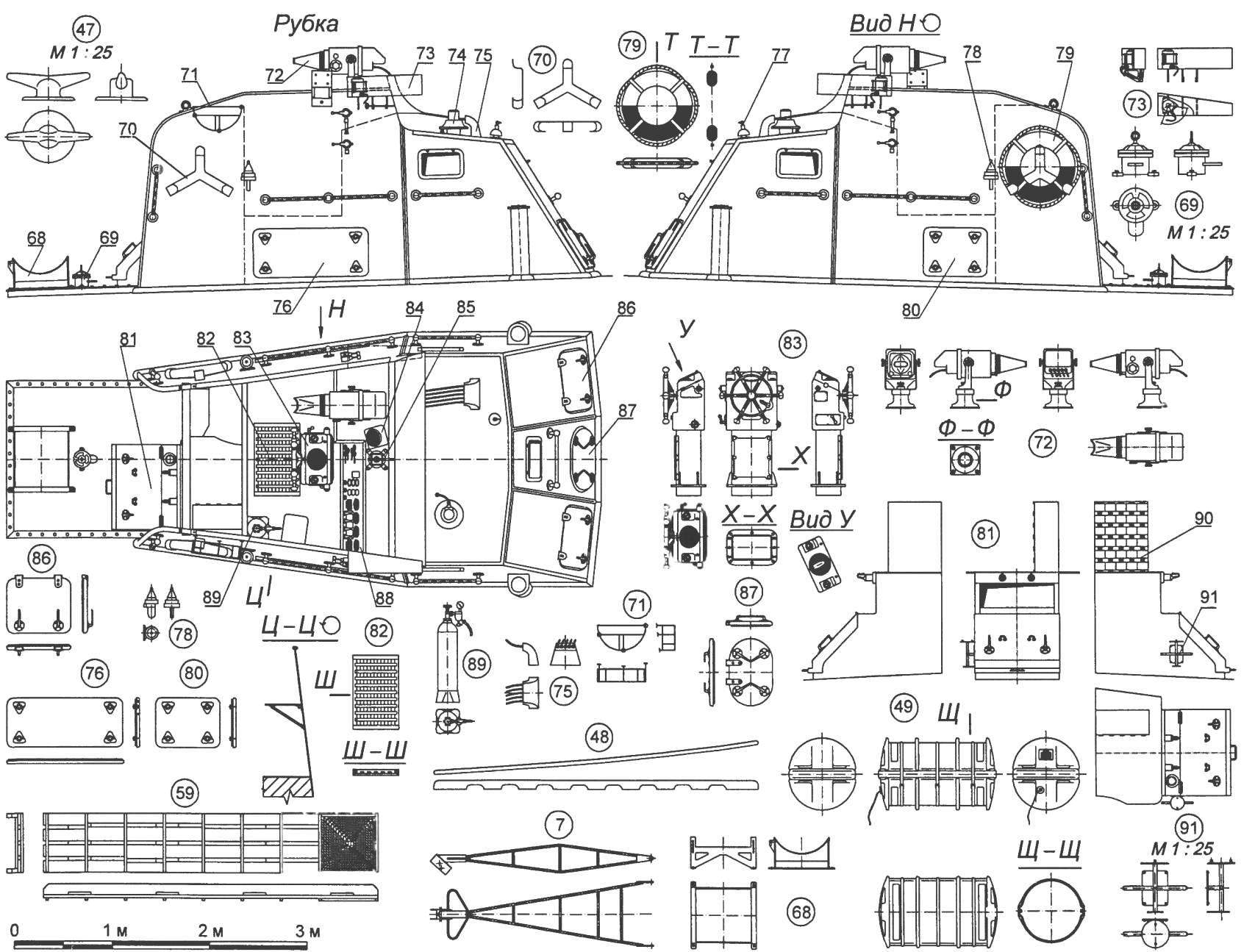
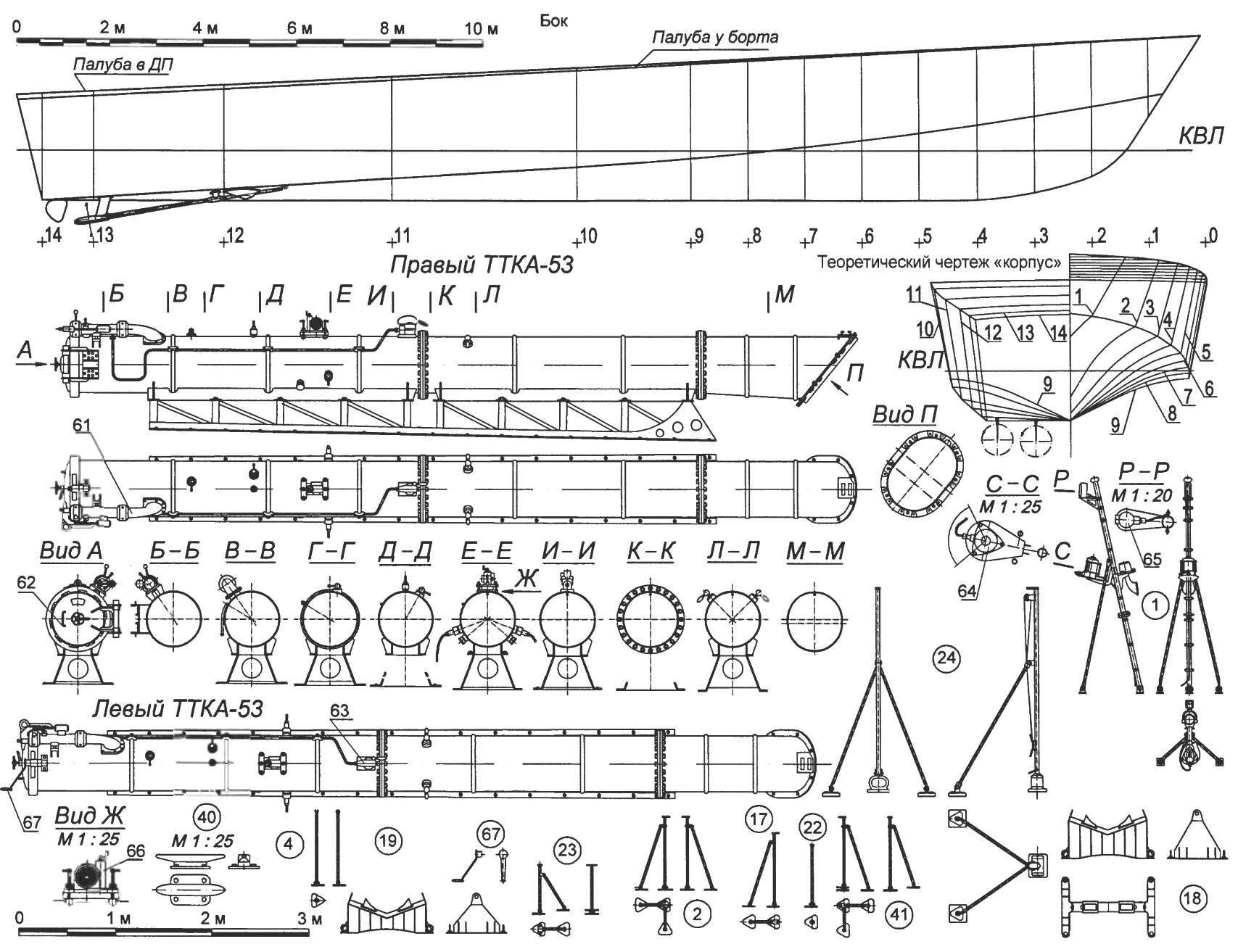
A large torpedo boat of the project 183:
1 —the flagpole; 2,4,17,20,22,23 and 41 relingowe stand; 3 — the instrument is smoke generation; 5 — 25 mm daugavmala turret gun mount 2M-3; 6 — fire pump; 7 — truss brace; 8 — antenna Radiotechnika; 9 — Radome radar “Reya”; 10 mainmast; 11 —antenna; 12 — fore-mast; 13 — antenna VHF-radio; 14 — cockpit; 15 — right torpedo tube TTKA-53; 16 — cable antenna HF radio; 18 and 19 — racks-533-mm torpedoes; 21 — vent; 24 — guessto; 25 — the water cooling system of the engine; 26 — the exhaust of the engine; 27 and 28 with brackets of the prop shaft; 29 — thruster 1ДГ-Ю0; 30 — steering wheel; 31 — Minna scat; 32 — a guard switching boxes; 33 — rack smoke buoy; 34 and 36 cover the technological hatches; 35 — on-Board release gear for depth-bombs; 37 — fender first shots of the installation of the 2M-ZM; 38 and 81 is similar to the vestibule; 39 — the base of the mainmast; 40 and 47 — duck; 42 — left torpedo tube TTKA-53; 43 — guy; 44 — deck porthole with fencing; 45 — fitting; 46 — mine rails; 48 — a pneumatic Board; 49 — liferaft PSN-10M; 50 and 82 the duckboards; 51, 53, 54 anchor pillow; 52 — threaded stopper; 55 — cover entrance hatch; 56 — tilting plate; 57 — mooring line; 58 — Danforth anchor; 59 — a similar ladder; 60 — Proclus; 61 — the powder chamber; the 62 — cap; 63 — the gas valve; 64 — lamp bottom feed lamp; 65 — Wakefield lamp; 66 — the mechanism for setting depth of stroke; 67 key cap torpedo tubes; 68 — rack liferaft; 69 — locking liferaft; 70 — bracket lifebuoy; 71 — basket of fire hoses; 72 — indicator radar; 73 — side a distinctive fire; 74 Serena; 75 — cable gland; 76,80,86 and 87 — manhole covers, 77 — antenna input; 78 — side fire; 79 — a lifeline; 83 — the steering column; 84 — binnacle magnetic compass; 85 — torpedo sight; 88 — dashboard; 89 — high pressure cylinder; 90 — mailbox with signal flags; 91 — bracket
From their gasoline counterparts, he was not only less fire hazard, but also a 40% greater cruising range of economic progress due to less specific fuel consumption diesel engines.
In the process of finishing and crossing power aviation diesel EN-1 a its modifications geared turbo —EN-1РТК, renamed in April 1940, the M-40.
At its base there was created the naval analogue of the M-50, equipped with reversing device and the other mechanism of boost. In late 1940 the M-50 was considered quite driven to run in the series, but the beginning of the great Patriotic war produced only ten of these diesels.
In August 1941 the Department of the Leningrad design Bureau of the NKVD, which worked as P. G. Hoinkes evacuated at shipyard No. 340 in Zelenodolsk. There of the siege of Leningrad sent design documentation for the project is large torpedo boat D-4, which were used by the design Bureau of the NKVD as a prototype. A feature of this project was a power plant, in which for economical progress, we used two auxiliary car engine ZIS-5 with a capacity of 73 HP
In October of the same year, the Office of shipbuilding of the Navy gave the design Bureau of the NKVD order to design seaworthy steel torpedo boat for long range (STKA DD), and in January UK Navy approved technical project, giving room 163. The choice of structural material of the body made on the basis of the production capabilities of Zelenodolsk plant. By December 1942, the plant built a prototype of the STKA DD, which is from may through August 1943 were tested in the Caspian sea near Baku. In the course of them, despite all efforts, failed to achieve the developers calculated the maximum speed 37 knots (obtained amounted to 30 knots). At the same time the boat showed good seaworthiness and cruising range, several times higher than the indicators of other Russian torpedo boats. After completion of the tests STKA DD gave the black sea fleet, where it was used until 1946
Designed in Zelenodolsk project 163 became the world’s first planing torpedo boat with a diesel power plant. After the trials, the staff of the design Bureau of the NKVD in the factory number is 340, taking into account the experience, started in 1944 to develop a series of projects of small ships, hunting for submarines and torpedo boats.
The shortage of seaworthy torpedo boats during the great Patriotic war was partly filled through lend-lease. In April 1943, part of the Northern fleet entered the first two large wooden torpedo boats of the Higgins company, which in the Soviet Navy received the designation A-2 (just as in our country they were delivered 52). From January 1944 it was added to the boat Vosper types 300 and 400, we have received the designation A-1 (90 of them were part of our four fleets). Also this type of vessels supplied by the allies, at the Leningrad plant No. 5 was organized for the construction of components of the American torpedo boat company Elco (60 of them under the designation a-3 became part of the Northern and Baltic fleets at the end of the war).
At the end of 1945, shipbuilding design Bureau of the NKVD returned from Zelenodolsk to Leningrad, and in February 1946, the specialists took part in the construction of torpedo boats Е1со shipyard № 5, where the design Bureau was renamed OKB-5 MGB.
Construction of lend-lease ships continued until 1947 At the conclusion of this work the question arose about creating their worthy replacement. Technical leadership for the development of a large torpedo boats for the project, receiving room 183, instructed by P. G. Hoinkes. Clean up the American counterpart considers it inappropriate, as this would lead to a significant gap in this area. Designed a new boat given the military application of such technology in the Second world war and emerging trends in the global catastrophie. The Foundation for the development of large modern torpedo boats in our country at this time there.
First of all, decided to abandon the “train” overall, as it is not allowed for a given displacement to give the hull optimal shape. In addition, over the past years has significantly increased the capabilities of the shipbuilding industry in the far East that allowed to establish the production of ships on the spot.
As the main construction material used wood. This in no small measure contributed to the fact that the plant No. 5 was the leading domestic company in the field of wooden shipbuilding, and that wood was widely used in foreign shipbuilding firms for combat boats. Wood has high specific strength, allowing us to produce lightweight body with high hydrodynamic characteristics. As the power plant used four engine M-50, the mass production of which in 1947 he mastered the Leningrad plant No. 800, specially organized for this purpose in 1945, Undertaken in the previous period attempts to set up production of diesels M-50 in other plants are not successful.
The boat was armed with two single-tube torpedo tubes TTKA-53. Application 533-mm torpedoes with 400-kg of military equipment significantly improved the efficiency of the primary weapons.
It was also important to improve the defensive armament of light-duty fleet vehicles by increasing caliber anti-aircraft and transition to small-caliber antiaircraft machine guns. Not by accident become one of the latest trends in the work of the team at Special design Bureau No. 43, headed by M. V. Kondakova. During the great Patriotic war the OKB-43 developed ten types of multi-barreled anti-aircraft guns under heavy machine gun Degtyarev, Vladimirov and aircraft automatic gun Volkov and Yartseva. Designers were found a number of original technical solutions, which allowed to significantly improve the combat effectiveness of anti-aircraft installations.
In the winter of 1945 Artillery research experienced the Leningrad Maritime Institute gave industry tactical and technical requirements for 25-mm twin automatic deck installation, intended for the armament of torpedo boats and light vessels. OKB-16 under the leadership of chief designer A. E. Nudelman on the basis of the gun 84-KM has developed a gun 110-PM. The draft project was finished in 1945, after which the OKB-16 design Bureau began production of working drawings and prototyping, bypassing the stage of technical project. In March 1947, the Deputy commander of the Navy has approved a revised specification for the development of 25-mm turret daugavmalas artillery installation 2M-3.
In 1947, the part of the experts at which has expired the term of imprisonment in pre-war sentences, were released, and they continued to work in OKB-5 as freelance professionals. In July 1948 he was released and appointed chief project designer of OKB-5 P. G. Hoinkes.
To build a prototype of a large torpedo boat project 183 graduated in 1948, and by the spring of 1949, he successfully completed sea trials, demonstrating a maximum speed of 40 knots. In April, the boat was transferred to the Baltic to check seaworthiness. Test the boat, despite some of the identified comments was held so successfully that its developers expect to receive for this work, the State prize. In April, some workers of OKB-5, including Deputy chief designer B. P. Sokolov, was arrested again and sent to exile in Siberia.
In November 1949 the first boat 183-year project was commissioned to the fleet, and with some modifications it recommended in a series. In particular, there were comments on the installation of the 2M-3 and machine 110-PM fine-tuned only on the fourth prototype in January 1950
After the meeting in the Ministry of weapons in February 1950, a decision was made to start the installation, 2M-3 in production with the manufacturer this year, 16 pieces. In the course of comprehensive fire tests one of the first production installations 2M-3 has gotten very good accuracy, exceeding the agreed technical specifications in 2 — 2,5 times and achieved on the first prototype in 4 — 5 times.
During the operation of the first boats, their crews are faced with the stop of the diesel engines M-50Ф-1 when reversed. After additional sea trials organized by the specialists of Central research Institute of military shipbuilding on the boat TKA-297, was able to establish the cause of the phenomenon and make recommendations on bench test of a diesel engine, eliminating the defect of operation.
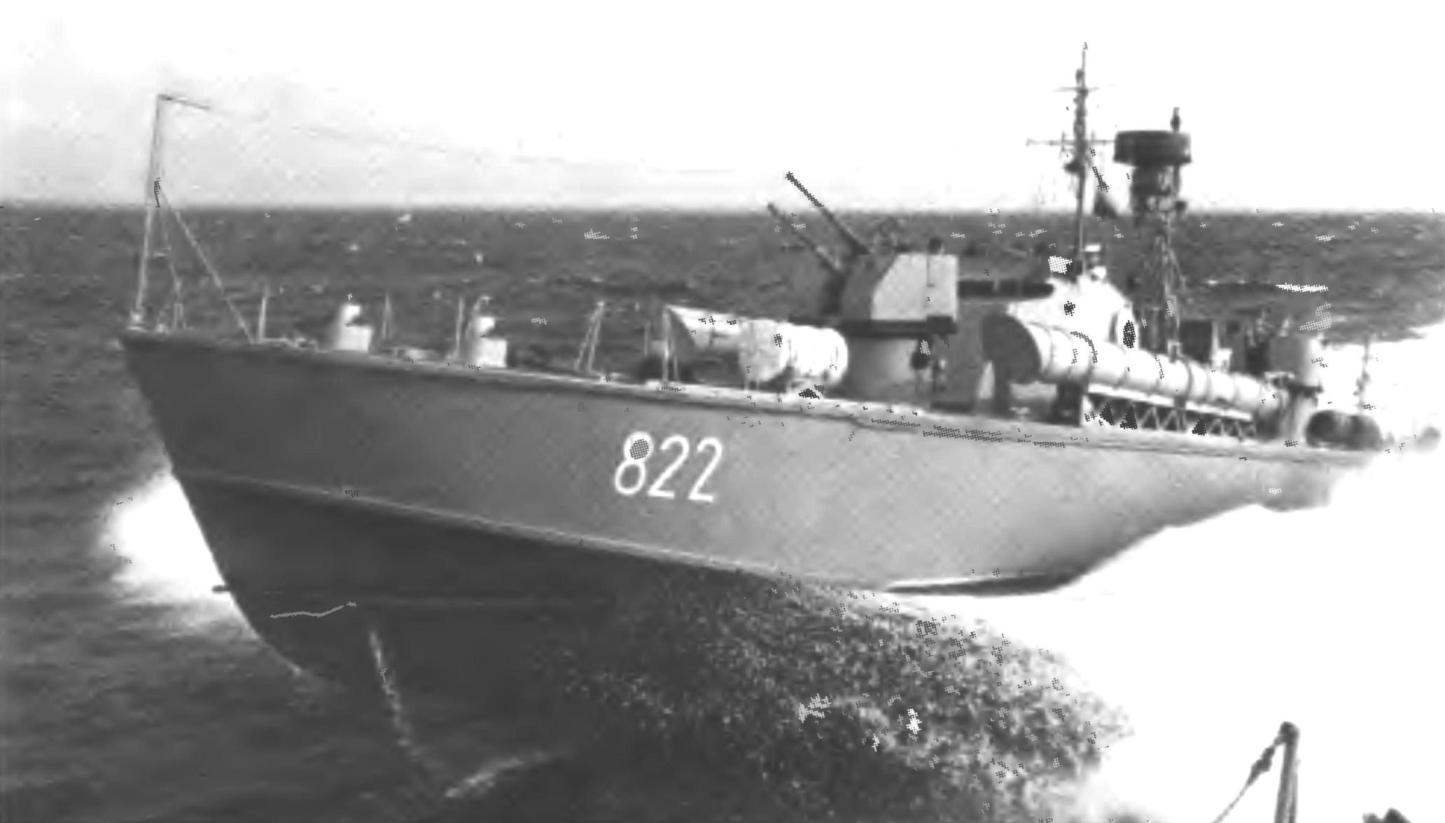
In addition to the Leningrad plant № 5 the building of large torpedo boats was conducted at two plants: No. 602 in Vladivostok and # 640 in the village of Sosnovka in Kirov region. Only in the Soviet Union at the three shipyards built the 674 torpedo boat project 183 various modifications (they were part of the Soviet Navy until the early 1970s). About 80 were built in China by Soviet technical documentation.
In the 1950s and 1960s, more than a hundred torpedo boats of this project in the framework of military-technical cooperation transferred to foreign Navy, including the GDR — 31, Guinea — 4, SAR — 36, Indonesia — 8, Iraq and China 12, Korea — 10, Cuba — 11, Poland — 20, Somalia — 4, South Yemen — 2. Egypt boats 183 used in the Arab-Israeli wars in the mid-twentieth century. From more than three dozen boats, delivered from the Soviet Union in this country, two were killed during the war of 1956, four — during the war in 1967, and four during the “war of attrition”; by 1973, the Egyptian Navy had 26 units in this project.
Torpedo boat project 183 in its class were considered as one of the best in the world. For their creation the chief designer of P. G. Hoinkes the body and head of the Department E. A. Popov in 1951 he was awarded the State prize.
(To be continued)