The creation of a reliably operating crossings for heavy equipment engineering has provided the possibility of strengthening our troops, operating in the bridgehead, artillery and tank units of the Reserve of the Supreme command and maneuver along the front to achieve surprise when conducting subsequent offensive operations. For the contribution to the common victory in the Battle of the Dnieper 342 warrior pontoon bridge units were awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union, which accounted for half of the total number of Characters in engineering parts for the war.
The importance of the role of engineering troops to achieve victory over the enemy said decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR, entering in October of 1943 for their commander the title of “Marshal”. It was emphasized that the contribution of engineering troops to the defeat of the gates of no less weight than the aircraft artillery and armored forces.
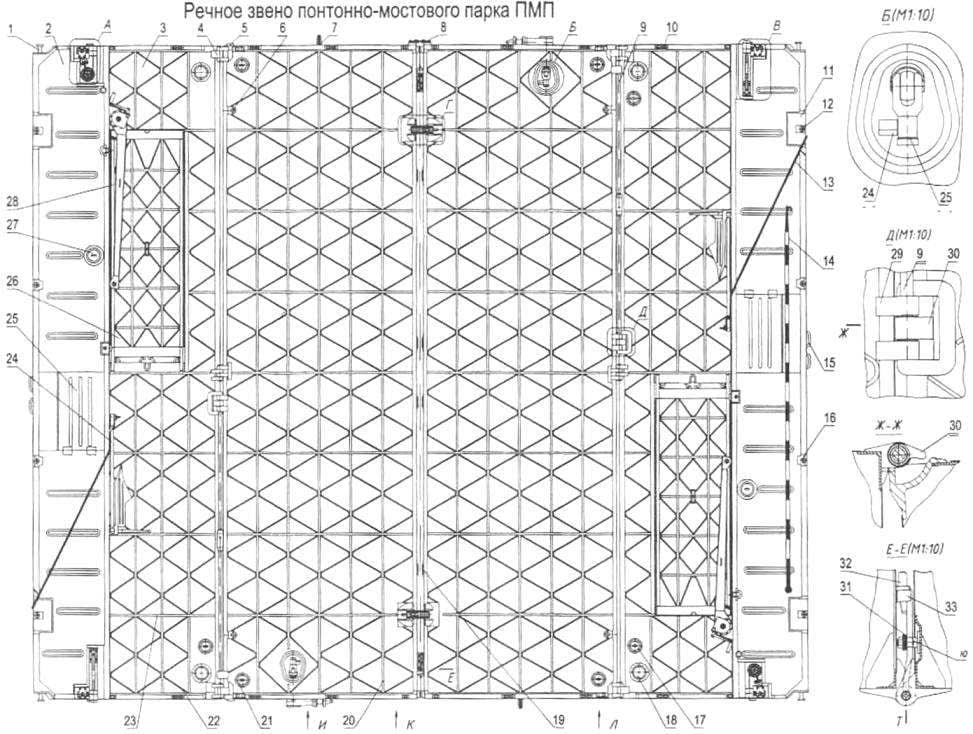
River link pontoon-bridge Park (PMP):
1 — tow-eye; 2 — the extreme deck light pontoon; H — heavy carried below it offers extreme; 4 — deck loop; 5 — upper butt stop; 6 — tube rybnogo Cup to set eye if the suspension link to the helicopter; 7 — a connecting ear; 8 — hinge transitions on the diagram; 9 torsion; 10 — apparel socket; 11 — a niche under an outdoor deck lock; 12 and 16 — glasses for mounting of the pushing device; IZ — anchor rope; 14 — hook; 15 — bracket for outboard installation of the anchor; and 17 21 — sump tube; 18 — glass installation of apparel-beam; 19 — clamp kolesovoy; 20 and 23 of the longitudinal and transverse diarrhea gain pastille; 22 — circle amplification of the deck; 24 — anchor; 25 — niche cover anchor winch; 26 — ramp; 27 — buoy (its socket is also used for installation of apparel-beams; 28 — ramp-beam; 29 — loop; 30 — torsional Cam; Z1 and 49 Belleville spring; 32 — arm bottom loop; 33 —an emphasis of the lever; 34 — the average pontoon; 35 — magpantay stop; 36 — ring for attaching a loop of a rope when folding pontoon; 37 — loading hook; 38 — the emphasis of the loading hook; 39 clip folding link; 40 — loop fastener hinge easy transition to the scheme; 41 — manhole cover; 42 — eye loading hook; 43 — ring retainer; 44 — keystone extreme pontoon; 45 — clip mounting of the reflector; 46 — the lever bottom lock 47 and 50 axle; 48 — thrust; 51 and 64 pin cross pin; 52 and 62 of the transverse pin; 53 — a guide; 54 — flat pin of the joining link; 55 — lanyard loop; 56 — ratchet; 57 — doggy; 58 — arm to pontoon arm; 59 — nest under the pontoon arm; 60 — flat pin; 61 — plate with holes for the tubular arm; a 63 — guide flat and transverse pins; 65 — stir gniewowo lock; 66 — cheek bottom loop; 67 — bottom of the ear loop; 68 — bushing; 69 — lever deck lock; 70 — bracket; 71 — the right middle ear of the pontoon; 72 — top cover deck lock; 73 — earring; 74 — hook bottom lock; 75 — top stop; 76 — extreme pontoon; 77 — a Z-shaped profile kolesovoy; 78 — bracket kolesovoy; 79 — bracket for installation of the pontoon arm; 80 male; 81 — locking pin lower locking device; 82 — a guide; 83 — cycloid shaft; 84 — traverse; 85 shaft; 86 and 88 axle sleeve ivachnova device; 87 — traverse; 89 — head shaft lower coupling; 90 — lower emphasis; 91 loading ring; 92 — locking screw; 93 — lower emphasis; 94 — the transom of the middle pontoon; Yu — locking groove on the flange of the axle; I cut the pointy end of the pontoon arm; A1 — groove for wire rope
When it died down, the Great Patriotic war, in the Royal engineers, as in other branches of the armed forces, compiled and analyzed the obtained combat experience and continued improvement is created and the development of new technologies, including those designed to overcome water obstacles. While great attention was paid to increase their capacity and mobility, reducing the complexity of the guidance floating bridges and ferry crossings, improving their survivability in combat.
One of the main areas was a deep modernization of the existing armed samples, with the aim of improving its performance characteristics taking into account prospects of development of models of military equipment and the changed conditions of warfare with the use of nuclear weapons.
Another important aspect was the creation of special equipment for engineering troops, the search of new technical decisions which would allow new samples efficiently to meet the requirements of his time. In the laboratory of the Department crossing equipment research engineering Institute in the Moscow suburb of Nakhabino Yury Nikolayevich Glazunov in 1950 was formulated constructive ideas pontoon bridge-tape. In the same year he had made a small model that contained the main technical solutions incorporated in the proposed to development of prospective pontoon-bridge Park (PMP). The demonstration model has negative reviews of some experts, including the Military engineering Academy named after Kuibyshev, and the doubts of the advisability of further work in this direction.
Authoritative experts believed that the proposed Glazunov bridge will work as a dam, especially strongly this effect will manifest itself in the shallow fast flowing rivers: under the influence of the incoming water flow bridge sink, a substantial increase of effort in connecting the nodes will lead to the rupture of the structure. It should be noted that the history of the use of the tape bridges the Russian army has a long history Ivan the terrible to provide a workaround in the capture of Riga ordered to restore the log bridge-a ribbon of rafts through the river.
Justice theoretical disputes decided to check in practice. In 1952 – 1953, on Noobinson repair and mechanical plant has manufactured the first four links of PMP, and four more made no one of the enterprises of Riga. For the first variant of the bridge with removable ramps used all terrain vehicle ZIS-151, which imposed restrictions on the size and the load capacity of the crossing means.
In the 1953-1954 biennium, the prototype PMP on the ZIS-151 was tested in the Belorussian military district in which PMP have found a number of shortcomings, including the destruction of the roadway of the bridge after the 38th passage of the tank. General conclusion on the results of the tests were negative.
In the next two years Yu. N. Glazunov with his faithful comrade-in-arms designer M. M. Mikhailov, etc., would eliminate the identified deficiencies PMP and designed new river unit, which had to carry the heavy semitones domestic off-road vehicle of yaz-214.
By this time, the design of the Yaroslavl triaxial all-wheel drive truck with diesel engine, first left the factory floor in 1951, was sufficiently worked out and the car was preparing to start serial production (in 1957).
In the new version of PMP length river even was increased from four to seven meters. In 1958, at the Navashino shipbuilding yard have produced a prototype of a new pontoon Park for yaz-214, which showed on tests.
In this embodiment, as the saying goes, the equipment and the car found each other. The tests were successful and in 1960, a new Park PMP for yaz-214 was flattened by the Soviet Army.
In April 1958 the Yaroslavl automobile plant, the government’s decision has become a leading enterprise on manufacture of diesel engines for the Minsk and Kremenchug automobile plants. The plant of bridge structures and the Ukrainian city of Kremenchug for two years before mastered the production of corn harvesters and road machines, was entrusted with the manufacturing of three-axle diesel trucks. In April of 1959 at the stands of the KrAZ collected two three-axle truck-type “yaz”. most of the components for which put the citizens. In December of 1959 already rolled OFF the first production of the KrAZ-214. Ten years later the factory developed an improved version of triaxial SUV KrAZ-2555.
So the troops of the pontoon-bridge parks do on the KrAZ. Three main characteristics, deployment time, number calculation of the pontoon and the PONTOON number MISHIN in the Park — he much excelled the best at the time in the world Soviet heavy pontoon Park (TPP), developed a few years after the end of the great Patriotic war. Even more impressive was its advantage over foreign М4Т6 Park (USA). In addition, the capacity of our perebrav increased considerably.
In 1963, during the military doctrine of the pontoon of the Soviet Army have demonstrated the First Secretary of the Central Committee of the CPSU N. With.Khrushchev advantages of modern engineering technique, compared with that which was the red Army in 1943 during the battle for the Dnieper. In 17 minutes after launch flares PMP bridge connected both banks, and on it at full speed, “blazing brilliance of steel”, was a tank battalion. Twenty years ago in this place, a floating bridge was brought over the axis night and in the morning it gently, but slowly, moved Soviet tanks.
In 1968.. given the experience of operating the Park PMP upgraded to extreme pontoons river links established hydrodynamic shields, made and Uglich. The prototype of the Park PMP-M underwent tests on the Kura river in 1970, after which CSOs have adopted ingenero of the Soviet Army.
The main differences Park PMP-M from his predecessor was: the above-mentioned hydrodynamic shields, callers to use the Park on the rivers with greater flow velocity (3 m/s to 7 m/s) and higher anxiety (up to three points instead of two) and the availability of lifting equipment to hold the bridge in the fast current;
changed the design of the pavement, which significantly increased its strength;
straight, without inflection deck of the coastal link, which allowed to increase the speed at the entrance of the bridge and the exit from it, and also ruled out the possibility of damage to the deck level impact loads.
increased by four units of the number of boats in the Park.
the addition of the Park sets reconnaissance of water obstacles, traffic control, and curfew;
inclusion in the Park of means of masking radar corner reflectors and lenses of the type “Sphere”, flares and reflectors of laser radiation.
In order to understand the advantages of PMP. compare it with the predecessor of CCI.
To transport the full set tagengo pontoon Park CCI was required 116 cars ZIL-157 or ZIS-151, 96 of them were specially equipped day transportation of the pontoons (they drove 48 48 nasal and middle pontoons and girders), the rest of the car was intended for the transportation of the shore spans. jetties, flooring shields, and accessories. Towing motor boats were part of the TPP, towed on a special trailer (BMK-90) or its suspension (BMK-150) for cars. carrying deck panels and accessories. To build the basic type of bridge with a lifting capacity of 60 tonnes and a total length of 265 m (244 m — floating part) at a rate of flow of the river up to 1.5 m/s calculation of the 48 compartments of the pontoon a total population of 336 people was required in the daytime for 2 hours.
Complete set Park PMP was composed of 32 river link. 4 coastal link 2 pavement 12 tugboats. For the transport link, and liners used 38 specially equipped KrAZ-255В or KrAZ-214 (the first sets of the Park). Boats of a type BMK-90, BMK-130 or BMK-150 was towed on trailers or wheeled chassis of own 12 trucks ZIL-131 (ZIL-157). When picking the Park boats of a type BMK-T last carried 12 cars KrAZ-255B.
To restore floating bridge with a length of 227 meters and a lifting capacity of 60 tons with a wide cross part of the 6.5 m was required for the calculation of the pontoon 102 and 34 VOD naked time: up to 30 minutes a day and up to one hour at night.
Park PMP full set armed with an army or front separate pontoon-bridge battalion (APOMB). The latter consisted of two pontoon companies (16 cars from the river, with two coastal units, six boats and one vystrazny machine in each company), private engineering platoon, equipped with a set of bridge-building funds (IMR) or the installation of bridges (USM). a set of heavy mechanized bridges (TMM) (four cars). Named platoon provided the docking of the floating bridge to the shore by small bridges on supports for lack of pontoons. The composition of the division included the repair and household platoons. The total number of APOMB was about 250 people. As part of the engineering-sapper battalions, tank and motorized infantry divisions had a pontoon company with a PMP terminal, providing guidance floating bridge, half-length or appropriate number of ferries.
The main technical solution to guarantee the success of the pontoon-bridge Park — minimizing the operations to restore the bridge. Structurally, it was provided that the link ferry (Bar and river) constituted after the disclosure of the sections of the pontoon bridge.
River link in the slider open position represented ready part of a 60-ton bridge with a length of 6.75 m carriageway width of 6.53 m. roadway Width a 20-ton bridge 3,39 m.
The link consisted of two middle and two outer pontoons. The middle pontoons were joined together with deck castles and bottom hinges. The actuators of the hinges located on the sides of the pontoons. One extreme pontoon pivotally connected with the middle three hinges, placed on a heavy decks. In the open position of the outer pontoons is closed in the plane of the bottom middle two bottom locks, drive which were on the transoms of the middle pontoons.
Bottom hinges and bottom locks open from the deck level using levers, worn on the shanks of the levers of the actuators.
Deploying polusognuv in-line 20-ton bridge was performed relative to the hinge, installed on the transoms of the middle pontoons.
To connect links with each other used the bottom seam of the device in the plane of the bottom, the top seam stops in the plane of the deck and tightening the device in planes of light decks extreme decks, consisting of pin mechanisms and mechanisms reels.
Pontoon ferry
Skew the location of the butt and obsolescent devices are provided connection units regardless of how the transoms they are facing each other.
To improve the survivability of the average and extreme pontoons were divided transverse bulkheads into two compartments.
River link in the folded position were transported on the pontoon car. Disclosure level after the discharge to water occurred automatically as a result of turn average and extreme pontoons with respect to the axis of the deck and bottom of the loops under the influence of forces of displacement, self-weight of pontoons and torque of the torsion devices.
An important element of the pontoon-Mostovoy Park is vystrazny car intended for arrangement of entrance to the floating bridge. He carries in his body a special metal coating – pavement, which join with the coastal link. Pavement, designed for 1,000 passes of tracked vehicles, protects adjacent to the bridge portion of the soil from significant mechanical damage to the chassis of the transported technique and partly from erosion of surge wave. This makes it possible to increase the throughput floating bridge in two and more times. With the destruction of the pound at the entrance to the coastal link bridge is usually fused for a short distance downstream at 10 to 20 m, where the ground is preserved in its original state.
The river links of the PMP could be used to ferry terminal. In this case, mostly of them collected 40-, 60 – and 80-ton ferries, which use two, three and four even, respectively. Depending on the depth of the river, speed of flow and the velocity of the boats were selected, the number of boats. Boats BMK-130 and BMK-150 had a pusher device, and at the far pontoons special nodes for their fastening. The boat could also tow the ferry its personnel with ropes, fastened to the transoms of the link.
The boats from shore to shore could move the rope or “aircraft”. The rope was pulled through the boat or floating of the conveyor and are pulled from the source Bank car Park or a large artillery tractor (BAT).
The rope, stretched across the river, the ferry is fastened by means of anchor cables given at the running blocks that were removed from the pontoon car. The ferry rope was moved by boat, svetosavska to the middle of the stern of a watercraft a pusher device.
The movement of the “aircraft” used for ferries carrying capacity of 110 tons and above. The vessel with this end turned at an angle of 30 — 45° relative to the direction of flow the Movement of the rope ferry “aircraft” operated by etching of cables with anchor winches.
For loading equipment on the boats of river links were used two ramps from the kit link which is mounted on each transom. For entrance of cars with narrower than the tank, the track is one of aparupa rearranged closer to the other, allowed the presence of the third ramp. Raising, lowering and movement of a ramp in the horizontal plane, hold it in a raised position on a transom of a watercraft, and to perform auxiliary hoisting operations used apparel-beam.
To install machines on the ferry in two rows to hang four ramps or two ramps were installed alternately on each half of the transom of the boat.
The cars were placed on the boats so that it wasn’t a great roll and trim differences. When movement of the latter in the direction across the carriageway the cars were shifted to the stern of 0.5 m from the Central position in the movement of the ferry in the direction along the carriageway (“hook”) of the machine displaced to the rear by 1 — 2 m.
During the operation of the PMP was developed 26 modifications that take into account the interests of various branches of the Armed Forces of the USSR. These options Park provides not only the crossing of water obstacles, but also other activities on the water (including marine areas) and as seaworthy ferries Navy: extended schemes and increased capacity. floating docks, floating cranes, ferries-suppressors-rasprodala, sea and river planatary, runways for aircraft, and areas for highways, rescue funds for emergency situations.
One of the first PMP received a separate pontoon-bridge battalions and pontoon motorized rifle and tank divisions of the Soviet forces in Germany, where the emergence of new models of engineering machinery did not go unnoticed by NATO “colleagues”. And soon in the Bundeswehr there was a tactical pontoon Park FSB-1 — an exact copy of the PMP, with the exception of vehicles for transport. In the future, the German designers have tried to improve the performance characteristics of the pontoon-bridge Park: but and FSB-2, who succeeded FSВ-1, markedly inferior to the domestic counterparts, while maintaining the basic solution of the PMP unchanged. Currently, the Bundeswehr uses a pontoon-bridge Park FSB-2000, which is another German modification of the Soviet tape floating bridge.
The us army uses a similar “seamless” pontoon Park RB and his last modification — IRB. Contrast to domestic ones is to use aluminum alloys for the manufacture of pontoons.
The ideas contained in the pontoon-bridge parks and PMP PMP-M, tried to develop the Polish and Romanian military engineers to improve the operational characteristics of the bridge they have changed the pattern of disclosure of parts of the bridge, but the performance of domestic experts, they failed to beat.
The main characteristics of river link pontoon-bridge Park (PMP)
Mass of unit, kg ……………………………. 6790
Dimensions open, m:
— length………………………………………. 6910
— width……………………………………..8090
— height ……………………………………..1110
Dimensions folded, m:
— length………………………………………. 6910
— width……………………………………..3154
— height………………………………………2277
N. KULESHOV
Recommend to read GLIDER-GYROPLANE “BUMBLEBEE” The design and construction of the "Bumblebee" creative team "Rise" was based on microalloy design V. Barkovsky, V. Vinitsky and Y. Rysuke described in "MK" (see: 1969, № 6, 1970, № 3,... IN A QUARTER OF A BRICK Partitions of brick in construction are widely distributed. Without them it is difficult to do even in houses built of wood. In many cases, for example, in the construction of sanitary...  The conduct of hostilities rivers are a serious obstacle to the attacking side. Not accidentally during the Second world war, a powerful defensive lines were built on their shores; suffice it to recall the well-known German Eastern wall, an important part of which became the Narva river, Sozh, Dnieper and Dairy. It is significant that after the victorious conclusion of the Battle of the Dnieper which lasted from August to December 1943 for heroism 2438 most distinguished soldiers, sergeants and officers all the armed forces was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union (in just four years of the great Patriotic war awarded the gold Star medal were 11 603 warrior).
The conduct of hostilities rivers are a serious obstacle to the attacking side. Not accidentally during the Second world war, a powerful defensive lines were built on their shores; suffice it to recall the well-known German Eastern wall, an important part of which became the Narva river, Sozh, Dnieper and Dairy. It is significant that after the victorious conclusion of the Battle of the Dnieper which lasted from August to December 1943 for heroism 2438 most distinguished soldiers, sergeants and officers all the armed forces was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union (in just four years of the great Patriotic war awarded the gold Star medal were 11 603 warrior).