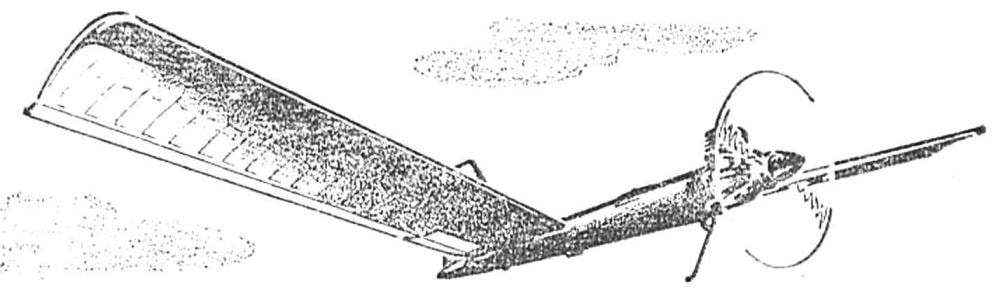
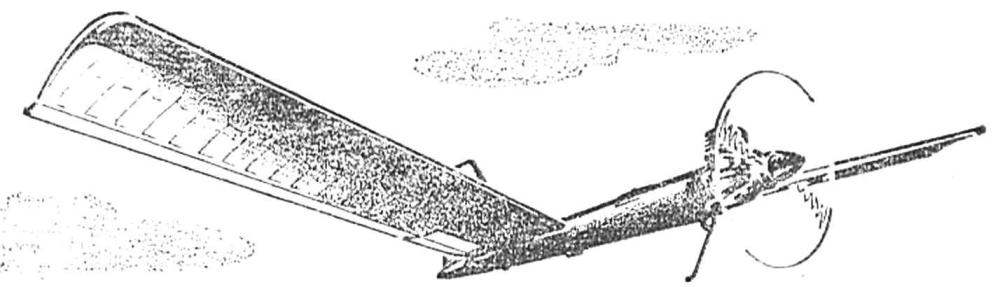
 Attract the attention of athletes and spectators time the model is tailless. Most of them presented in the traditional competition “Experiment” in recent years, has a wing to direct the sweep and power system tractor or pusher propeller. However, this scheme has a number of inherent disadvantages. So, with the engine in front of the wing there is a need for additional balancing weight for balancing the tail model, the tail boom has to greatly increase to ensure a sufficient efficiency of the vertical stabilizer. And when using a power plant with pusher propeller there is a significant probability of hitting the hands of the athlete during the spinning propeller when starting Tierney.
Attract the attention of athletes and spectators time the model is tailless. Most of them presented in the traditional competition “Experiment” in recent years, has a wing to direct the sweep and power system tractor or pusher propeller. However, this scheme has a number of inherent disadvantages. So, with the engine in front of the wing there is a need for additional balancing weight for balancing the tail model, the tail boom has to greatly increase to ensure a sufficient efficiency of the vertical stabilizer. And when using a power plant with pusher propeller there is a significant probability of hitting the hands of the athlete during the spinning propeller when starting Tierney.
From these drawbacks could be eliminated by the scheme with forward-swept wing. It also allows you to get the model high flight performance. Thus, we propose timername “wing” consistently had three relatives on the geometry options, and they all helped the designer every time to become the winner of the competition “Experiment”. Studies have shown — to ensure that longitudinal balance of the machine with forward-swept wings rather small uniform positive twist and 4.5° (the profile of the wing is concave with a bent up tail, modified from the profile of Kupffer). The increase in the twist gives rise to losses for balancing model, which ultimately reduces its aerodynamic quality. The use of split two-piece wing with different angles of zaklinanie sections requires a lot of stability (i.e., greater aerodynamic twist), since the breakdown of the flow occurs in all sections simultaneously unlike the wing with a uniform twist. In the latter case, the failure gradually extends in size and the model manages to exit at small angles of attack before stalling at the corkscrew.