In preparing attack on South East Asia command of the Japanese armed forces imagined the difficulties associated with overcoming the army of the numerous water hazards on the territory of China and island States. Plans combat operations in the specific conditions of the far East and Pacific regions has necessitated the creation of amphibious tanks in accordance with the developed then the concept of “tanks – in close cooperation with the infantry”.
In preparing attack on South East Asia command of the Japanese armed forces imagined the difficulties associated with overcoming the army of the numerous water hazards on the territory of China and island States. Plans combat operations in the specific conditions of the far East and Pacific regions has necessitated the creation of amphibious tanks in accordance with the developed then the concept of “tanks – in close cooperation with the infantry”.
In 1933 the firm “Mitsubishi”, and in 1935 the firm “Sikvdila” were alternately presented and tested samples experienced amphibious tank SR-I “Ro-I” (“First model”), SK-II “Ro-Go” (“Second model”). They were later joined by SR-III (the”Third model”).
The most successful was “Horns”. It was a 4-ton vehicle with a length of 5100 mm, width – 1900 mm height – 2400 mm. In its armament consisted of two 6.5-mm machine guns: one in the hull and the other in the tower. The crew consisted of three people.
The top of the body and turret was welded from 6 mm armour plate, the bottom of the case is the same thickness – proclaimers. The undercarriage had four track roller, combined in two carts, with horizontal coil springs; driving wheel – front. Engine mounted 70-strong carburetor, allows you to develop speed on the highway to 40 km/h and on the water – to 9.3 km/h.
The buoyancy of the machine provides not only displacement of the body and removable side pontoons, the movement afloat – two propellers placed in the stern.
Note, however, that the prototype of the “Ro-Go” was the English Vickers amphibious tanks А4Е11/А4Е12.
SR-III was somewhat easier, had a crew of two people. The front gun was removed, the thickness of the armor was brought to 10 mm. engine Power increased to 72 HP Test tank was finished in 1937, but found them unsuccessful and further work in this direction ceased.
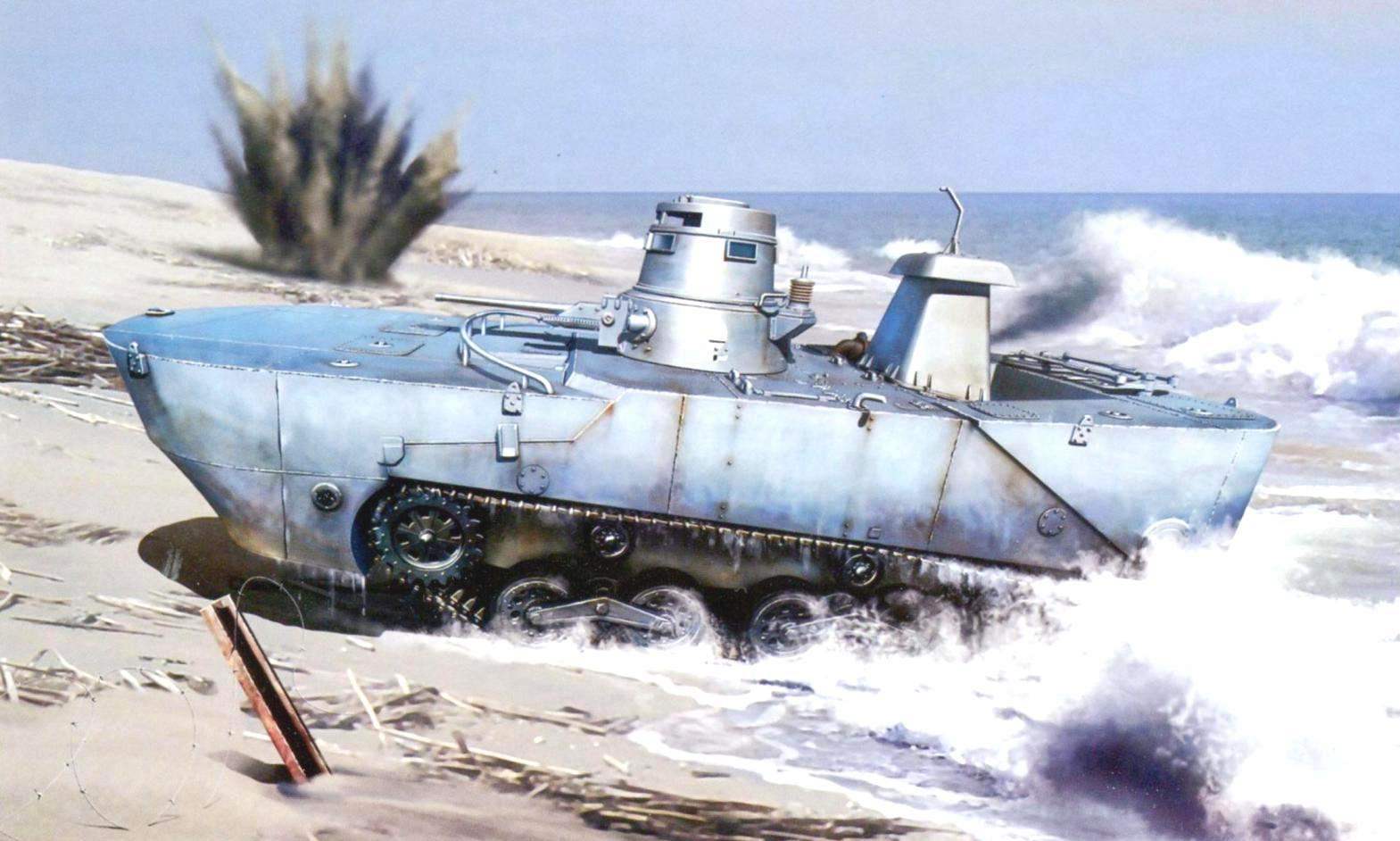
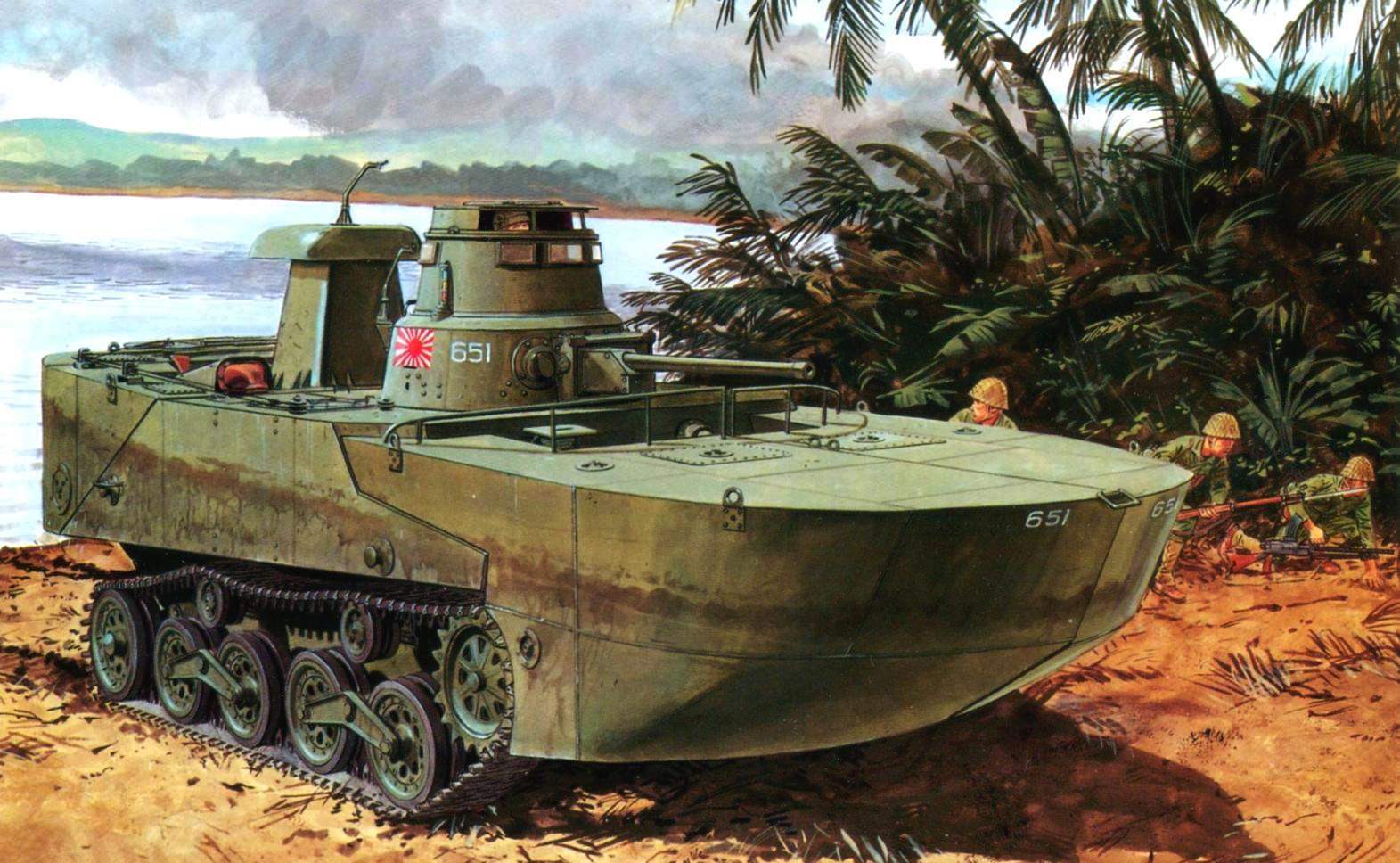
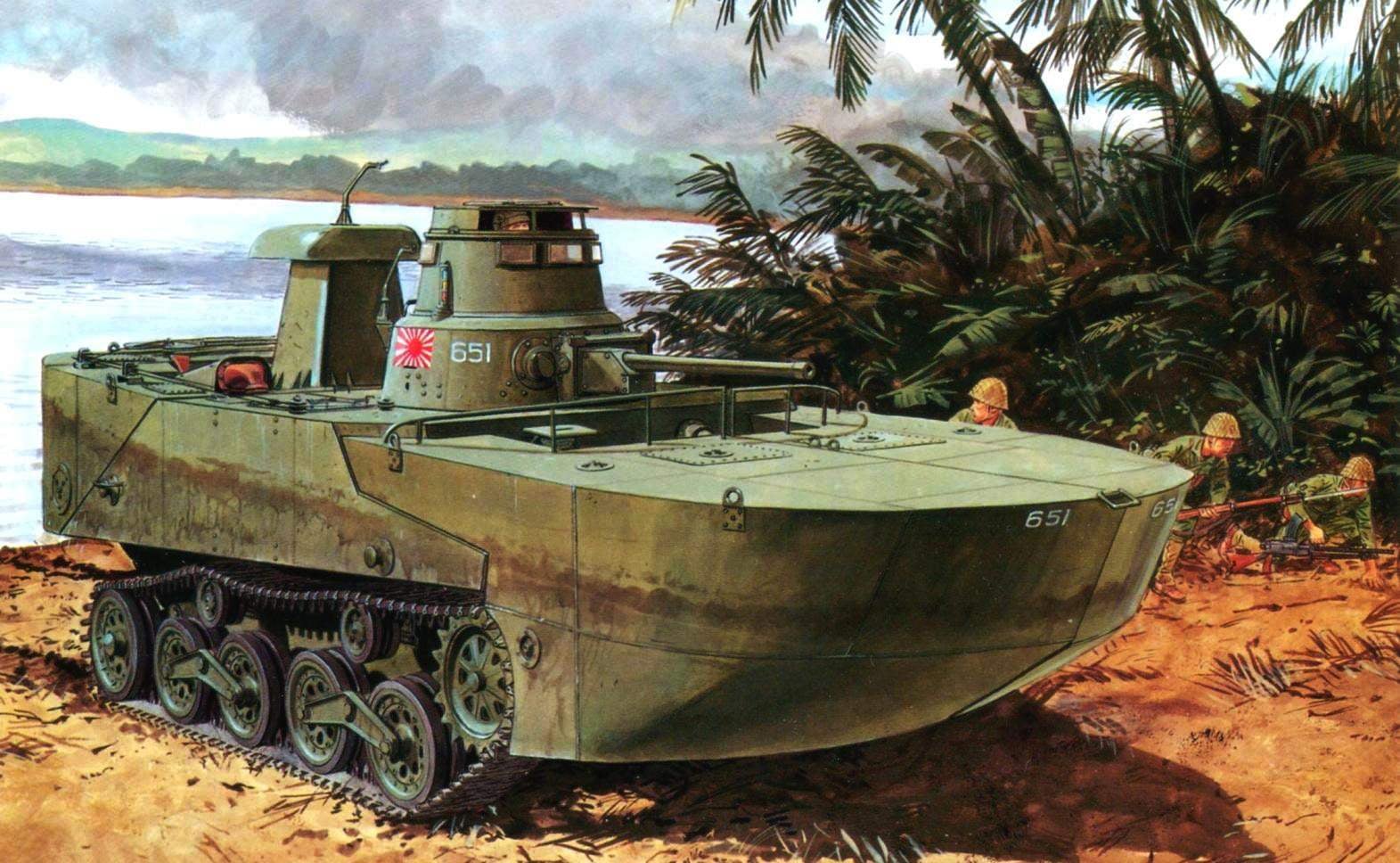
Amphibious tank “Ka-Mi” was commissioned by the Imperial Navy
The Japanese military returned to the subject of amphibious tanks in 1940, rather, it was the naval leadership of the Imperial Navy. Such machines have required them to provide amphibious operations in the Pacific ocean. The fact that armed special naval troops then there were only the usual armor.
And then the tank builders began to follow their previous concept to give the tank the necessary buoyancy. They went through the already previously proven path improvements vehicles boats, instead of creating special tanks, provide the required vodorodnoe characteristics.
In 1941, again firm Mitsubishi has developed light amphibious tank Ka-Mi (“Ka-Mi” Ka “floating”, Mi-from the name of the company), equipped with pontoons. Without them the car could not stay on the water.
Be transported to the combat area “Ka-Mi” were on the landing ship. When approaching the destination they went aboard, did swim to land, where he was engaged in that battle, after dropping the pontoons. However, to exit the water, they had a solid bottom and fairly shallow beach. However, good seakeeping, large reserve buoyancy allowed the tank to be tested in the turbulent waters of the long voyage. Since 1942 began its mass production.
The steel pontoons were installed in front and aft “Ka-Mi”. Using the front pontoon is composed of metal sheets, the car was given a streamlined “gruposura” hydrodynamic shape to reduce water resistance. In addition, the sheet it bottoms in the front was sloped for better and smooth “germination” into the oncoming wave, in this case on top of the body gets low water.
The volume of the front pontoon – 6.2 m3. In the first samples, it was manufactured in one piece, but then proceeded to divide it in two part to facilitate the passage of the car after dropping it.
The rear pontoon is formed by vertically set sheets, had a volume of 2.9 m3.
Both pontoons mounted on the body of special locks clips, which are opened in a spiral mechanisms inside the housing without exit of a crew from a tank. In the event of damage during the shelling they had a waterproof section in the front there were six, back to five. Lots of pontoons equal to 3.0 t, and their installation increased vehicle weight from 9.5 t to 12.5 t
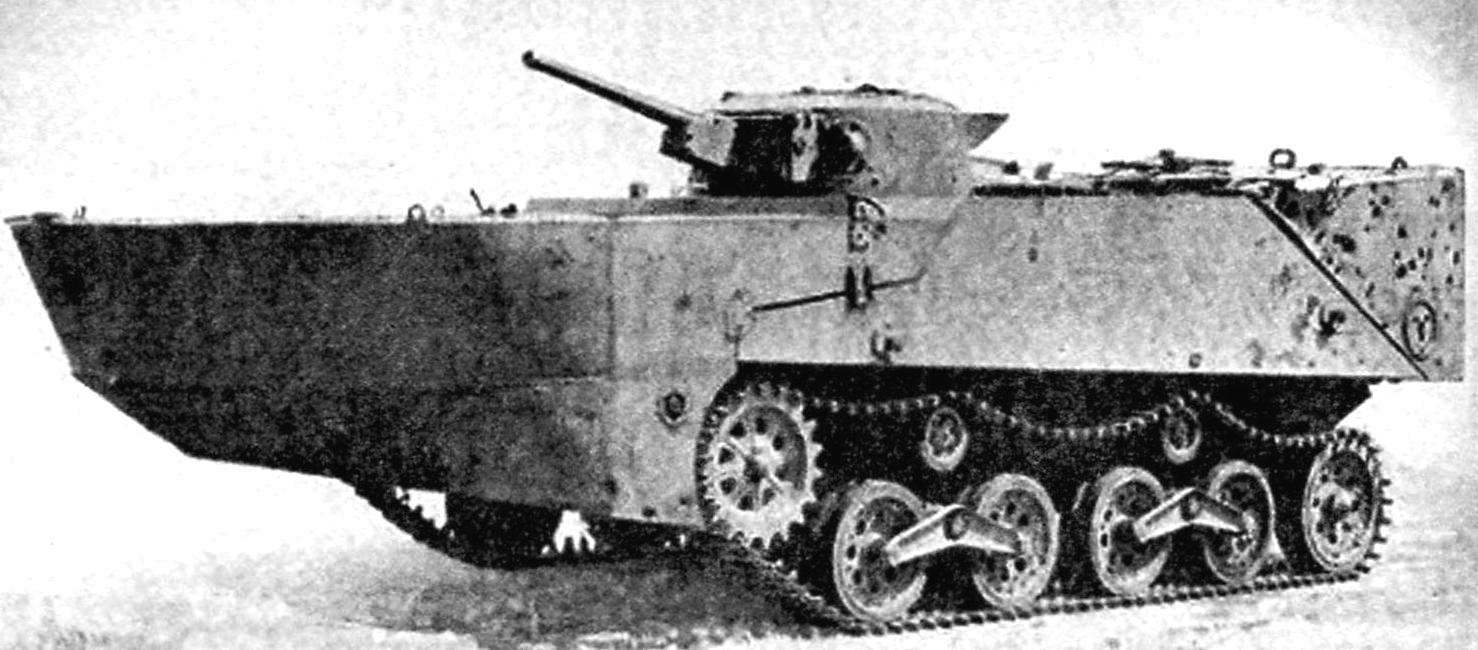

Japanese amphibious tank “Ka-Mi”, equipped with front and rear pontoons
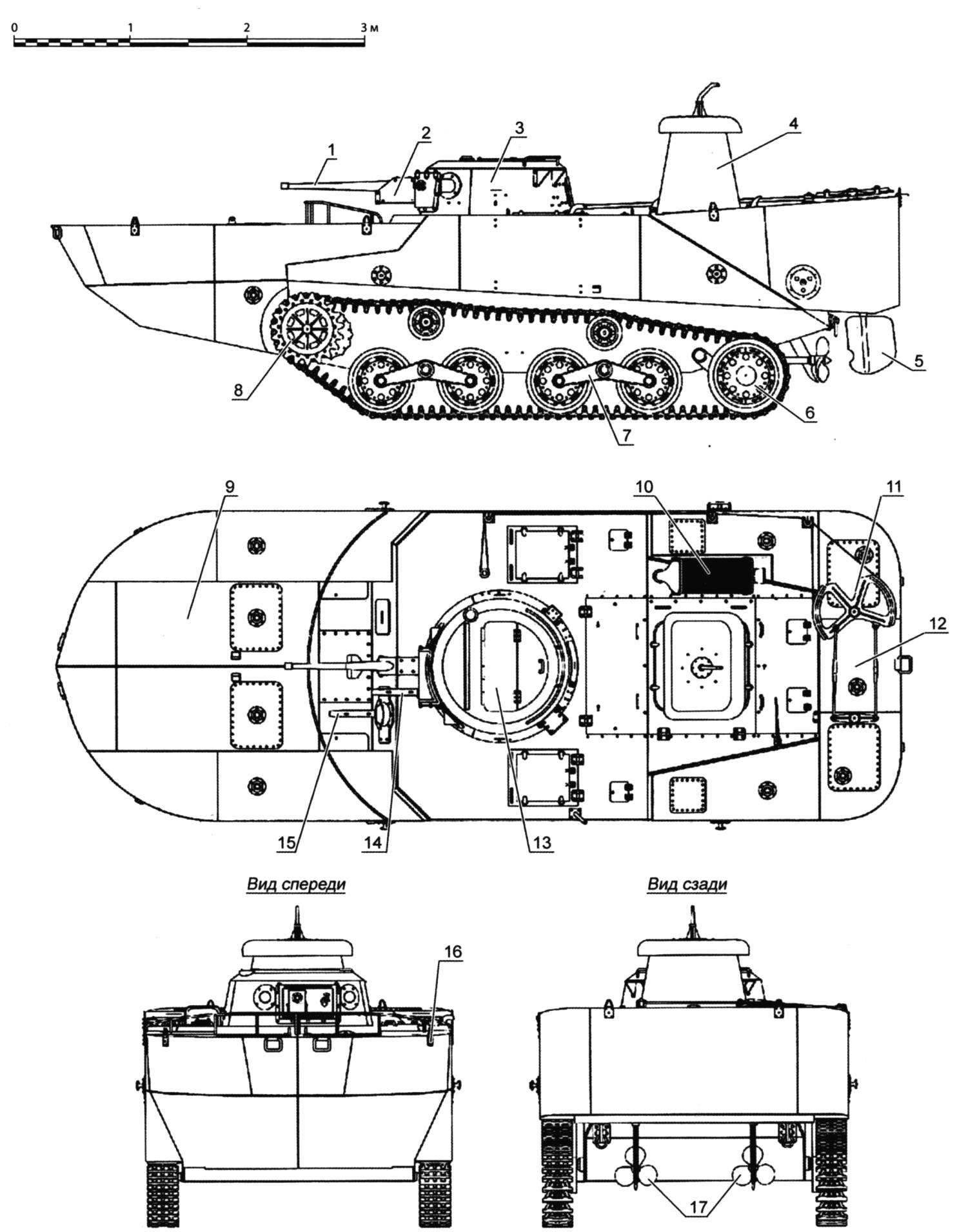
Tank “Ka-Mi” with the pontoons:
1 – 37-mm gun “Type I”; 2 – the mask guns; 3 – turret; 4 – air intake duct of the engine; 5 – drive; 6 – output gear; 7 – cart rollers; 8 – driving wheel; 9 – the front pontoon; 10 – exhaust pipe of the engine; 11 – the steering sector; 12 – rear pontoon; 13 – closed turret hatch; 14 – coaxial 7.7 mm machine gun “Type 97”; 15 – course 7.7 mm machine gun “Type 97”; 16 – the castle of the pontoon; 17 – three-bladed propellers
With a light hand of Japanese tankers such legkousvaivaemyh pontoons called “hakama” – the so-called traditional pants and skirts.
For the carriage of one set of pontoons for a single tank is needed, one three-ton truck. On the March of such tank units formed a convoy of going ahead “Ka-Mi” and the following vehicles with the “boats”.
Good seaworthiness of the machine, in particular, its stability was also ensured by a ratio of body length to its width. If the body of the tank is equal to 1.73 (length – 4830 mm, width – 2790 mm), with pontoons by increasing the length of the machine to 7420 mm, this ratio has changed to 2.66.
He sealed the case of “Ka-Mi” was a box-like shape with front and aft the sheets, placed under small angles to the vertical, broad almost horizontal front sheet-deck and developed only niches. The body was made of welded armor plates, riveting was used only in some places. The armor thickness varied from 6 mm at the top to 14 mm on the sides and 16 mm on the front sheet.
Arrangement traditional: in front of the transmission and the driving compartment, in the center – the fighting compartment in the stern – the engine. Transmission-manual, transmission with eight forward and two back. The propeller shaft passed through the hull.
The engine is mounted 6-cylinder 110-horsepower Mitsubishi NVD 6120 (“Mitsubishi”), two-stroke diesel air-cooled. His exhaust pipe is displayed above the engine compartment, the grille-shutters were on the roof at the rear.
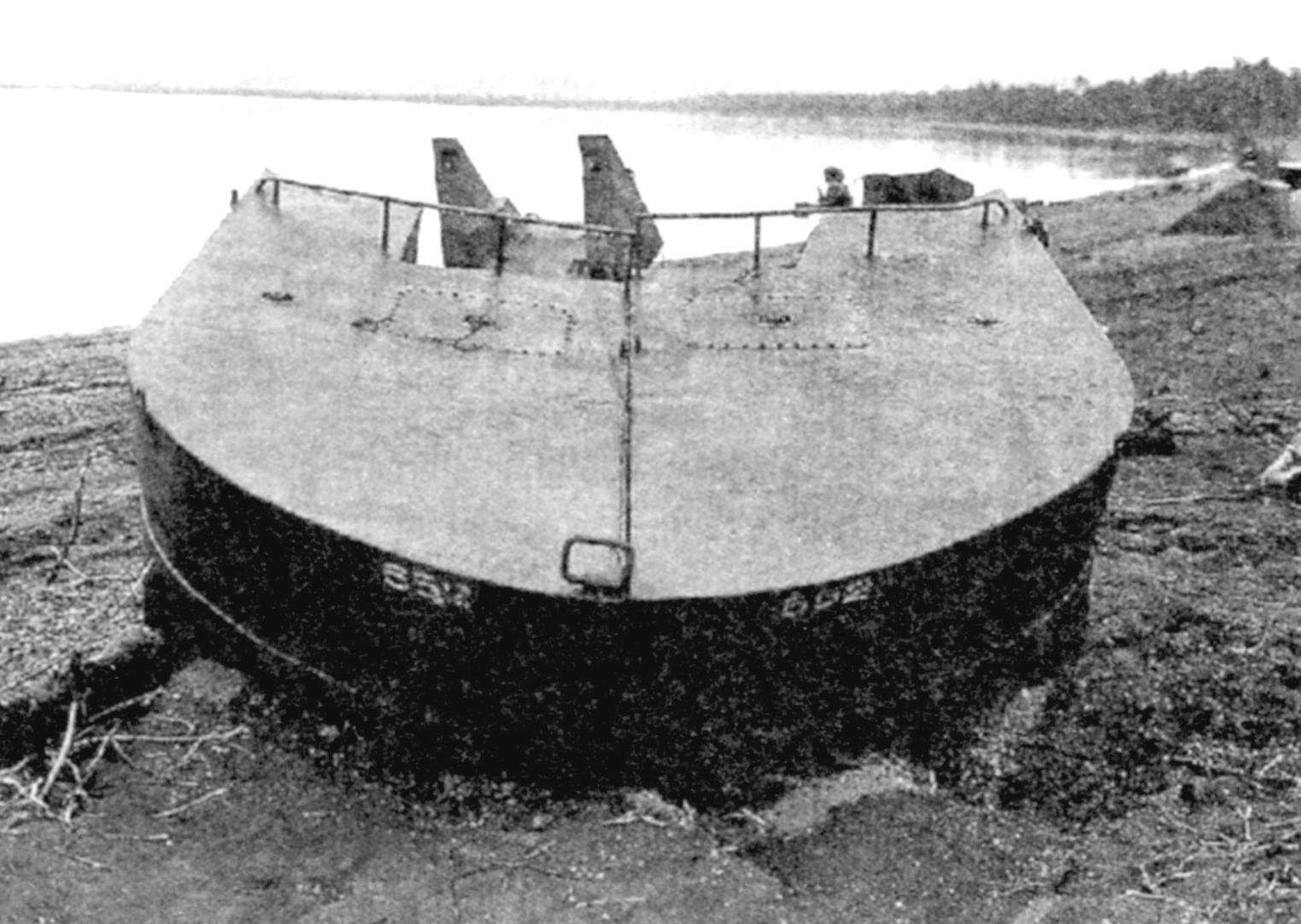
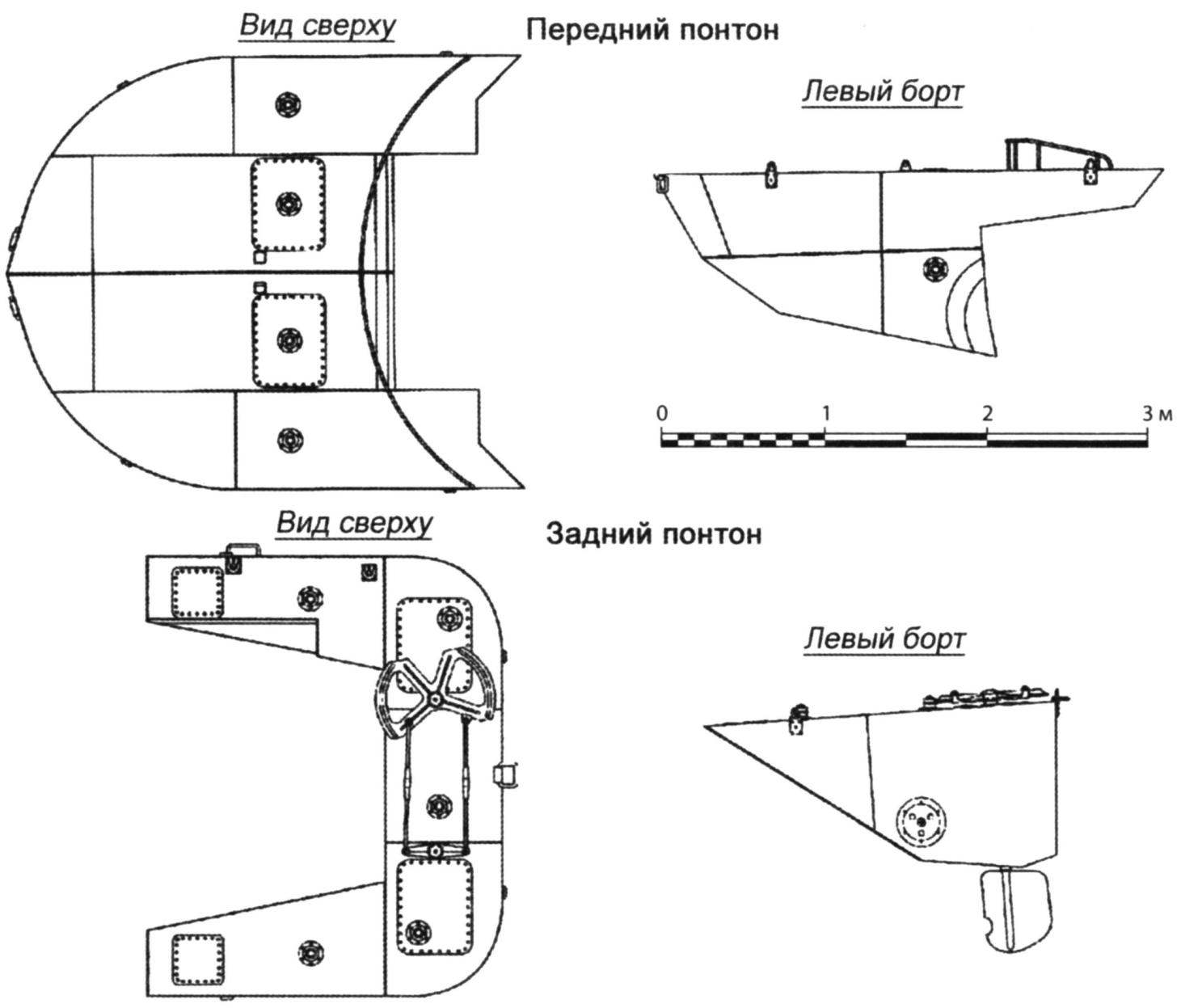

Front and rear pontoons of the tank. The pontoons weight about 3 tons
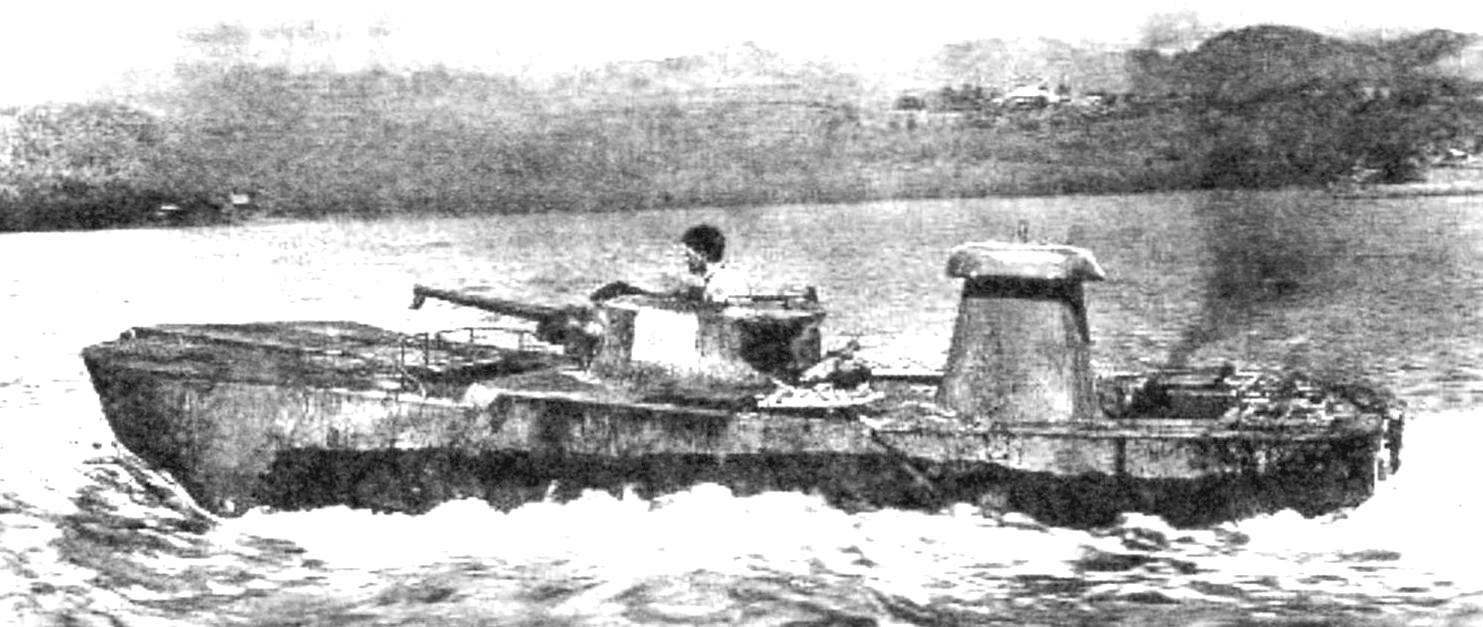
The speed of the tank afloat was 10 km/h
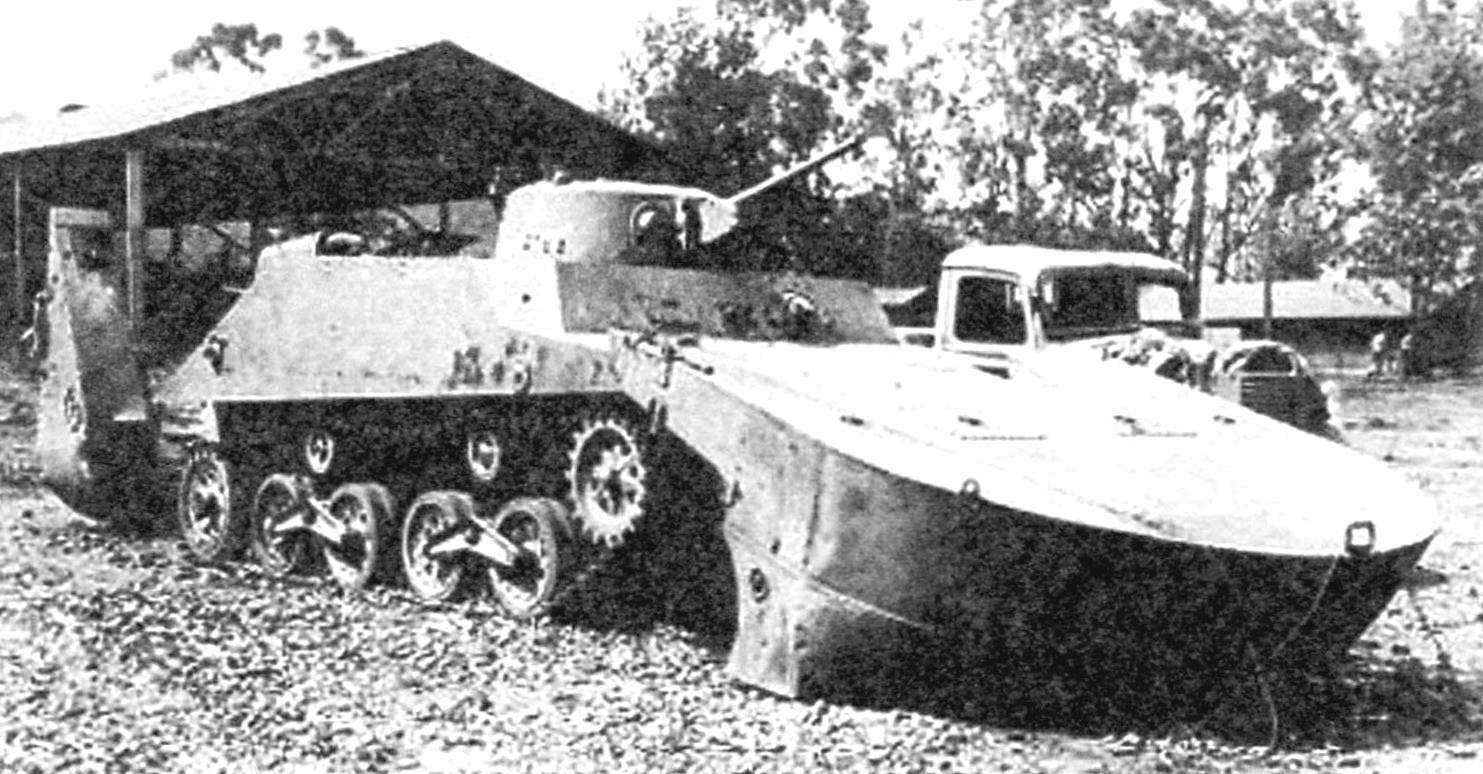

“Ka-Mi” resets the pontoons
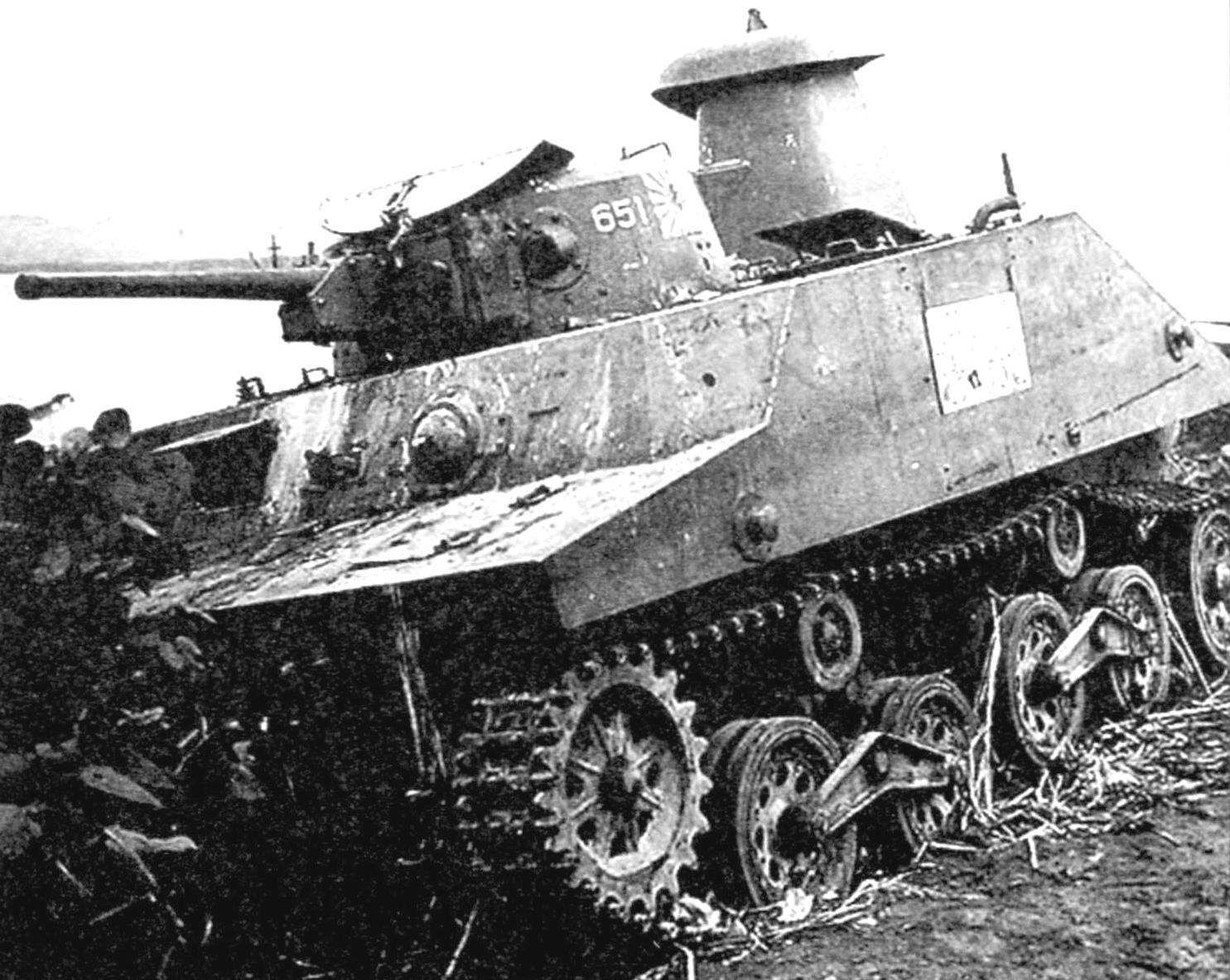

Tank “Ka-Mi”, to get rid of the pontoons, enters the fray. The island of Luzon, Philippines, January 1945
Suspension consisted of four road wheels on Board, interlocked in pairs in the truck with horizontal coil springs, cleaned the inside of the case, unlike the land version of the tank. Drive sprocket front and idler in the rear lowered to the ground to increase the area of contact. Each caterpillar had 103 melkopilchatye odnoklubnik truck with a width of 305 mm. Is left its imprint on the difficulty of going on shore with a weak ground. However, specific ground pressure of the machine was very high and was equal to 0,77 kg/cm2 (without pontoons -0,63 kg/cm2), for comparison the same characteristics for our 14-ton floating PT-76 mod. 1951 – it was 0.5 kg/cm2.
The movement on the water was provided by two three-bladed propellers under the hull in the stern, an engine-driven tank. Turns were carried out by the rudders, linked through sector steering cables from the helm of the commander who drove the car afloat. Speed on the water – up to 10 km/h.
The main armament of the “Ka Mi” was the 37-mm gun “Type I” with a barrel length of 45.9 per klb. In the tower it was mounted in a frame on vertical and horizontal axles. It is possible to download it without the rotation of the tower within ±100; the maximum angle of traverse was +240. The gun had a recoil device with hydraulic brake and spring lakatnik. Suggests only a shoulder rest. To fire was used telescopic optical sight.
In gun ammunition “Type I” were unitary shots with armor-piercing shells. Weight 700 g, having an initial velocity of 675 m/s, these shells from a distance of 500 m and could penetrate the armor thickness up to 25 mm.
In addition to guns, the tank was armed with two 7.7 mm machine guns “Type 97”. One of them was paired with a gun, the other mounted in the hull.
The ammo in the car was 132 37-mm shot, and 3500 7.7 mm rounds.
Conical tower mounted on the housing, had a front a mask a gun, according to her sides and then along the sides to the stern – peepholes have “triplexes” and three loopholes for firing personal weapons, equipped with closed bronezaslonkami. In the roof was a double leaf hatch, which served as the main entrance and exit of the crew. The thickness of the armor of the tower from 6 mm on the roof to 13.2 mm in the frontal part and the sides.
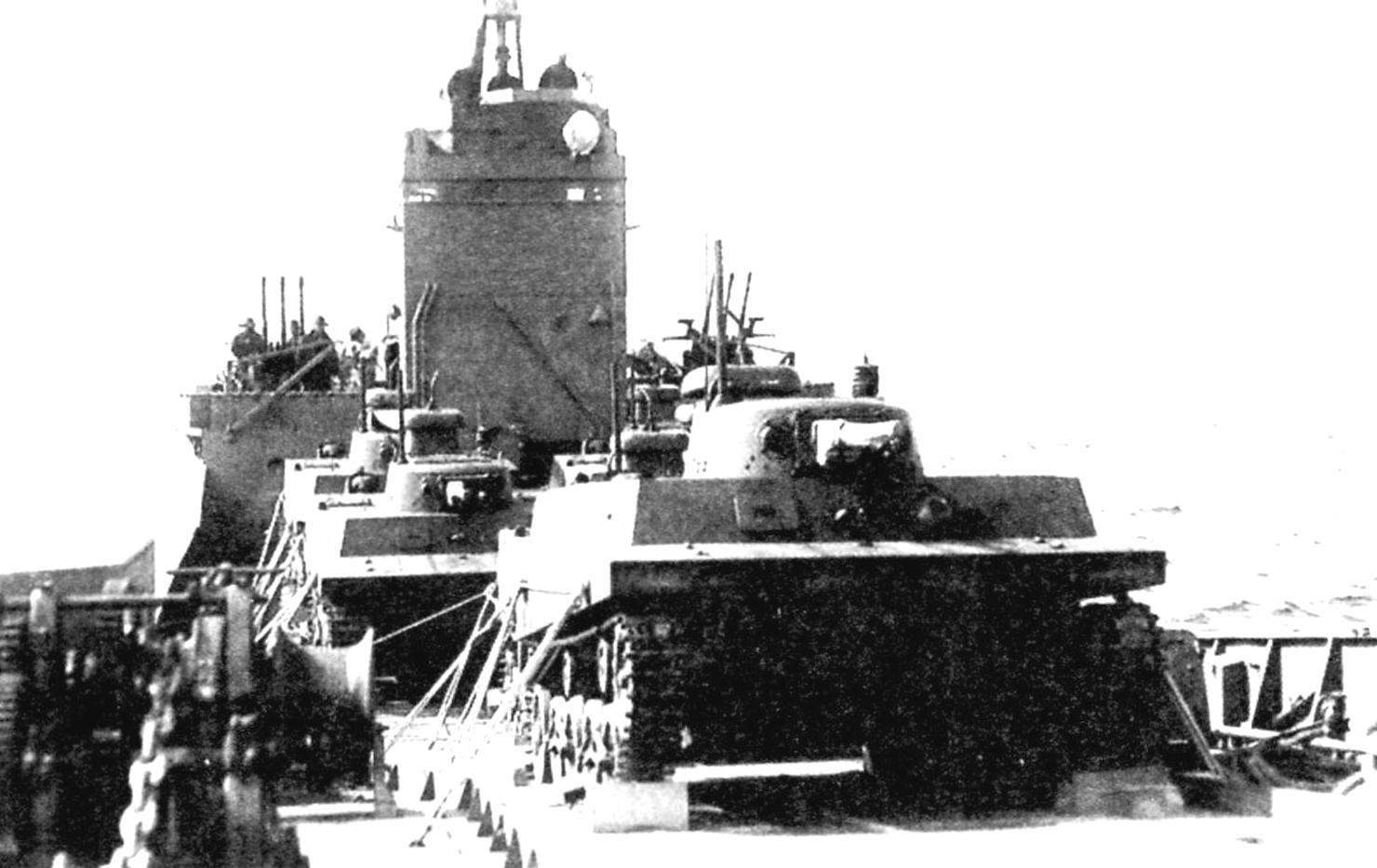
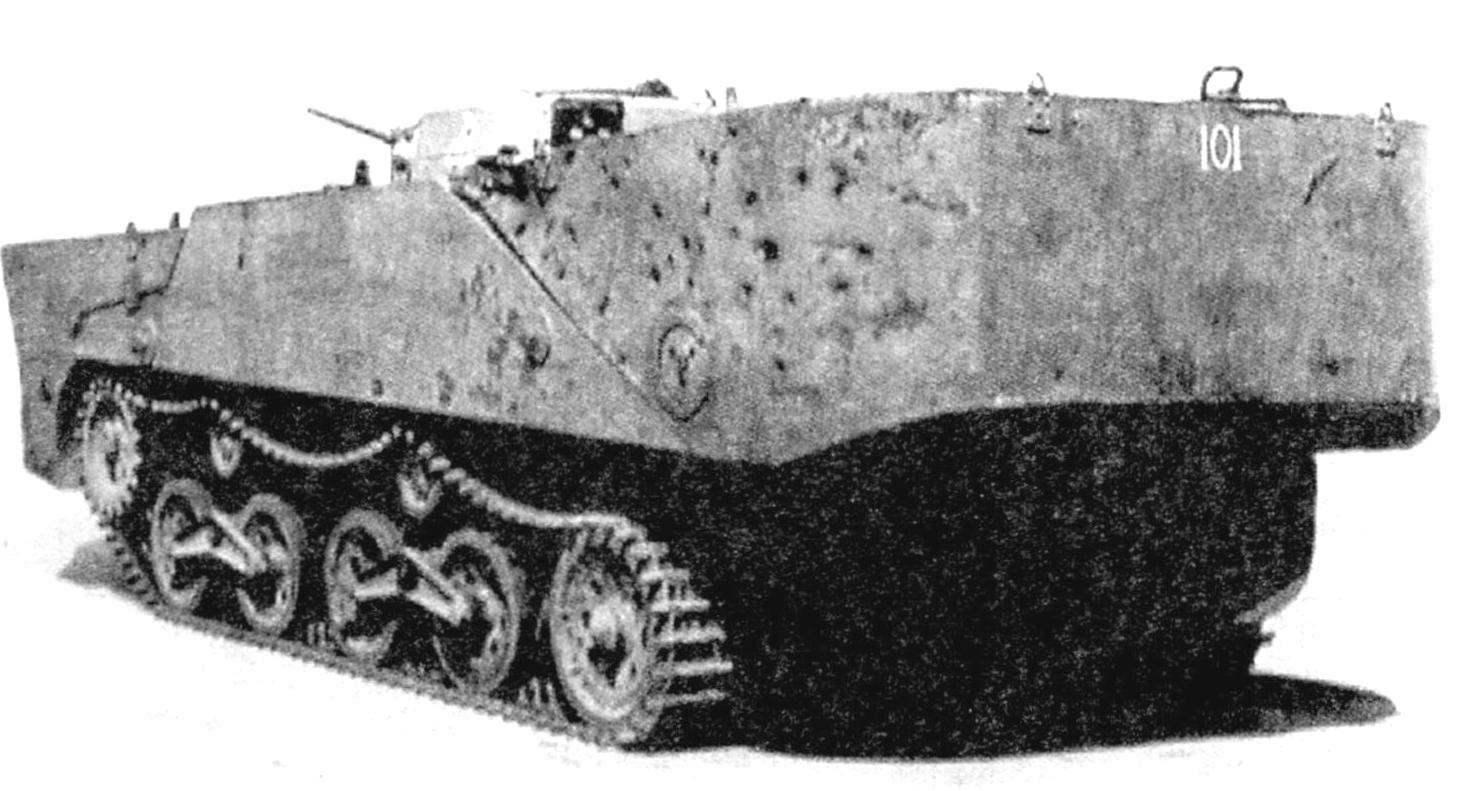
Japanese floating tank “Ka-Mi” from the 101st special naval landing party with removed pontoons on Board of transport. The pontoons in such cases, were laid on the stern of the ship. Delivery of landing on the island of Saipan. Mariana Islands, June 1944
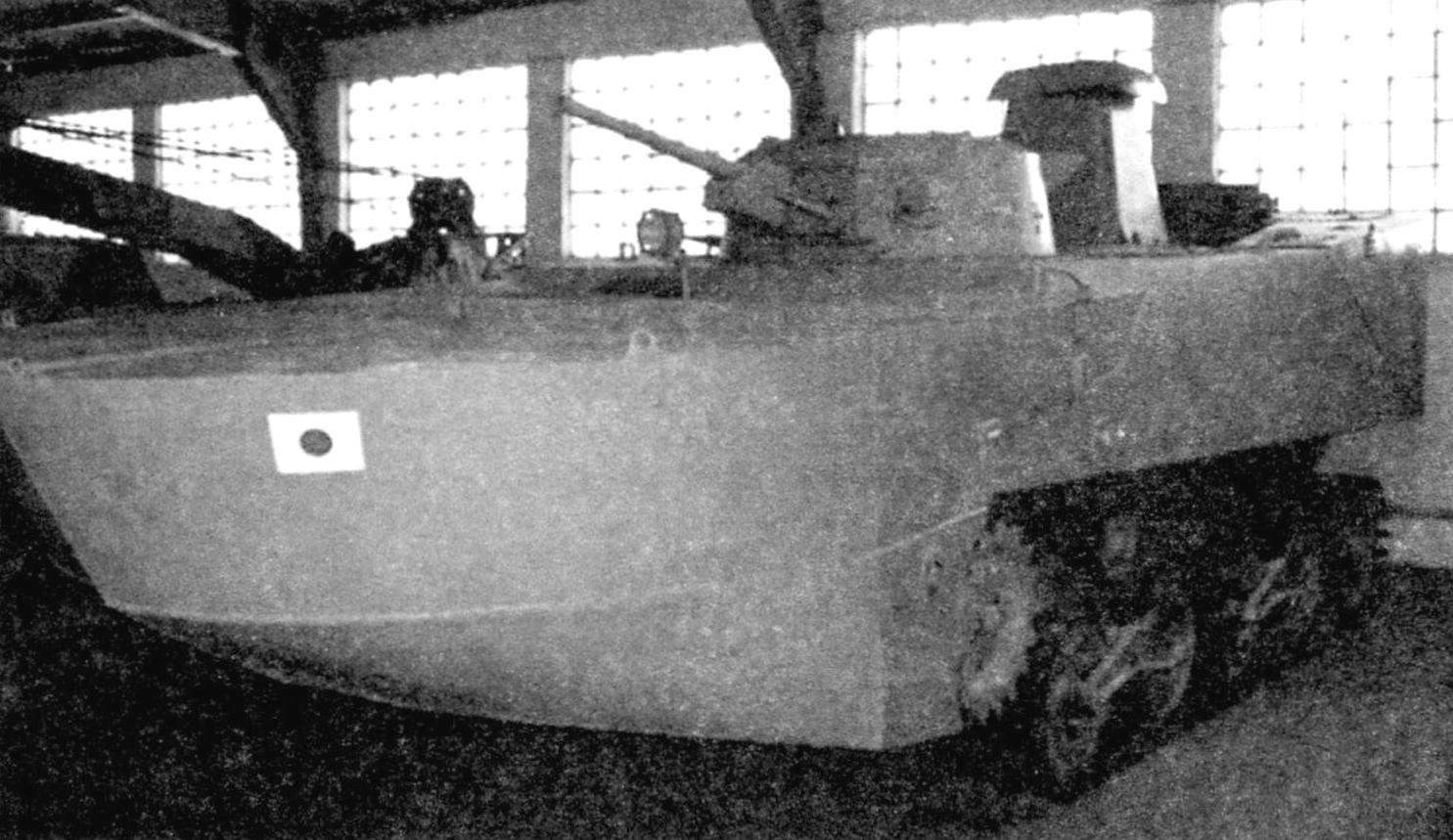
Amphibious tank “Ka-Mi” in the exposition of the Military historical Museum of armored arms and equipment in Kubinka
Tanks, the latest release of the tower was strengthened splash guard with sight window for better observation by the commander, and the hull mounted swivel spotlight.
The crew of “Ka-Mi” consisted of five people – the driver, the mechanic and loader had their jobs in the hull, gunner and commander were seated in the turret. However, its volume was insufficient for working together, they were in March.
It should be noted that before entering the water gap and the turret was to be sealed with rubber gaskets. To spray or water-saturated air is not trapped in the engine compartment, on the aft vent began to establish a streamlined air intake duct pipe with a mushroom cap.
“Ka-Mi” the first of the Japanese tanks got internal communication of crew-tank intercom TPU, as well as radio.
From mid-1941 to the summer of 1942, produced only prototypes of the tank, then started the mass production. In 1943 began production of the modernized version of the “Type II” with uprated to 120 HP engine. Capacity two fuel tanks brought to 250 l, which increased the reserve on land up to 170 km and afloat up to 150 km.
Only by the summer of 1945 was released 182 amphibious tank “Ka-Mi” (not counting pre-production), although the initial order was calculated for 300 units.
All these tanks were used in world war II in the Pacific theater of war, they were used in the advanced echelon to capture the beachhead and then its expansion in the interior of the captured Islands. However, they are often used in defense.
Part in the war for “Ka-Mi” began with the battle of Guadalcanal (Solomon Islands) at the end of 1942, where he sent a few more pre-production machines. More tanks were used EN masse in 1944 during the defense of the garrisons in the Marshall Islands, in the defense of the Philippines, the landing operation on the island of Saipan (Mariana Islands).
The idea of a Japanese tank builders use pontoons-skirts to create samples of amphibious armored vehicles was picked up by the designers of other countries. For example, in the United States were developed lightweight floating 3-ton armored personnel carriers and М29С M29 Weasel (“Weasel”) and 4-ton M76 Otter (“Otter”), also used in the Pacific theater.
There were attempts of the Americans to establish such pontoons on tanks M3 “Steward”, M4 “Sheridan”, M24 “Chaffee”. The test seemingly passed, however, to maintain such heavy machinery pontoons were extremely large sizes.
P. S. recently in the magazine “Military review” reported on the development of one of the Italian companies “special set of enhancing amphibious capabilities crawler transporters”. The set is called “sea” and is intended including for “overcoming water obstacles in the operations of the ship-to-shore”. It consists of a bow, having a hydrodynamic shape, and two aft – all of them “dress up” on the body with the aim of increasing the buoyancy of the machine.
As you can see, the “new” averse to repeating the “old” – almost seventy years.
The PERFORMANCE characteristics of the amphibious TANK “KA-MI Type II”
Weight with pontoons kg………………….12 500
Crew…………………………………………5
The length of the pontoons, mm…………………..7420
Width, mm……………………………………2790
Height, mm……………………………………..2340
Ground clearance, mm……………………………………..355
The thickness of armor, mm:
the frontal part…………………………………..16
Board……………………………………………….14
feed…………………………………………………8
roof……………………………………………….6
the bottom…………………………………………….8,5
The thickness of the armor of the tower, mm:
the forehead and sides……………………………………13,2
roof……………………………………………….6
mask guns……………………………………14
Weapons………………………37-mm gun “Type I” 45, 9 klb, two 7,7-mm machine gun “Type 97”
Ammo……………37-mm shots – 132, ammunition 7.7 mm – 3500
Engine………………………6-cylinder 120-horsepower Mitsubishi NVD6120, two-stroke diesel air-cooled
Suspension……..four anchor roller, interlocked in two carts, and three supporting roller Board, driving wheel – front
Crawler chain……..103 melkopilchatye odnoklubnik tracks with a width of 305 mm
Vodorodnoe mover………………..two three-bladed propeller
Speed km/h
on land……………………………………………37
afloat…………………………………………..10
Specific pressure, kg/cm2………………..0,77
Tank capacity, l……………………………….250
Reserve, km
on the highway………………………………………..170
afloat…………………………………………150
Width of overcome ditch, m………..2,0
Wall height, m……………………………..0,75
V. TALANOV