“Russo-Balt” C24-58 was fitted with the upgraded engine C24 (with the diameter of the cylinders increased from 105 to 107 mm and a stroke, brought from 130 to 140 mm).
Using the invention of the French engineer A. Kegress, who worked in St. Petersburg, a few cars models C24-40 factory equipped with half-track the progress of his design. Instead of the rear wheels on this car had a truck with rubber caterpillar tracks, reinforced cotton cord. The rotation of the axle shafts of the vehicle to the leading wheels of the truck passed the chains. The front wheels are winter equipped with skis. Preliminary calculations showed that the specific pressure of the tracks with a width of 385 mm at the snow or ground will be about 0.1 kgf/cm2.
The whole set was quite heavy – about 490 kg. But the possibility of movement on soft ground was obscured significant deficiencies in the design, especially noticeable when driving in the offseason. So, leading the drums to slip on the rubber band, and between them was Packed snow and mud. In the end, the caterpillar has torn or come off. However, on rolled snowy road half-track “Russo-Balt”, as the test showed, could reach the speed of 60 km/h and easily passed through the virgin snow.
In addition to the automobile bodies “Russo-Balta” family “With” was fitted with special bodies. It was the wagons for transporting the wounded, generator sets, ambulances, cargo bed for 1 ton of cargo, etc.
Very interesting was the car “Russo-Balt” E15-35, engineered to replace the C24-40 and the excellence of design superior to its predecessor. First of all, the engine is made in monoblock configuration of the cylinders; valves its (side, like the other machines release RBVS) were mounted only on the left. The timing was carried out silent plate chain instead of gears – a drive design has been revived in our country only in 1945 on the engine of the car ZIS-110.
In the cooling system of air supply, in addition to the four-bladed fan was also produced flywheel, equipped with spiral spokes. Was also modified and lubrication oil to all the friction couples filed a pump, and the oil reserve was not a separate oil tank, as well as in a modern engine, in the sump.
Four-speed transmission, clutch with reverse cone and worm steering gear used on E15-35, were widespread in automotive engineering. Less dated design of the propeller shaft, enclosed in a tube, which is rigidly, without joint, connected with the beam rear axle and transmit push forces directly on the crossmember of the frame. On the rear springs, these efforts have not passed, and the ends of each of the springs connected to the frame of the earrings. Another interesting element is also new for RBVS – use in the front suspension rubber dampers.
The width of the model E15-35 remains the same as the C24-40, although the track was increased to 1400 mm up To 3250 mm lengthened wheelbase, which allowed to comfortably accommodate the larger body three rows of seats.
Engine model E15-35 working volume 3684 cm3 developed capacity of 35 HP at engine speed 1500 Rev/min allowed the car, unladen weight of which does not exceed 1500 kg (recall, C24-40 – 1950 kg), to reach the speed of 75 km/h. in addition, the machine was 25% cheaper C24-40, spending 18 liters of gasoline per 100 km.
In addition to cars, RBFS was designed and trucks. The first was the M24-35 lifting capacity 2 tons, released at the end of 1912. Almost all parts of the vehicle except the engine, borrowed from the automobile model “C” series, were created anew – including transmission and radiator.
A year later, the truck has upgraded the capacity of the engine is brought up to 40 L. E., made a new radiator and installed the cockpit with awning. On the basis of the truck was also issued a 12-seater buses, tanks, and in the beginning of the First world war – armored with a machine gun.
Almost simultaneously with the family “M” on RBUS organized the production of cheaper truck chassis family “D”, is widely standardized across nodes with models Д24-35 and A24-35. However, the “Russo-Balt” Д24-35 had a completely different frame, and front and rear axles. Curb weight of the car with a loading platform was 1648 kg, speed – 40 km/h, the consumption of gasoline -26 liters per 100 km.
On the base of “Russo-Balta” Д24-35 (after the upgrade – Д24-40) was also produced cars with closed bodies, postal vans, health coaches and fire trucks.
RBWS in order to ensure stable sales of the vehicles responsive to the interests of the Ministry of war. The fact that in those years the further development of the auto industry on RBUS guaranteed first military orders. And when the army needed a powerful truck-tractor to transport 4-5 tonnes of military equipment, as well as for towing artillery limber and gun, a car rapidly established on RBUS, and in may 1913 the truck under the name “Russo-Balt” T40-65 enrolled in the trial. With a wheelbase 3650 mm track mm 1910 “Russo-Balt” T40-65 looked very solid NYM tractor – its curb weight was 4,320 kg, it can move in the speed range from 8 to 20 km/h, while consuming 56 liters of gasoline per 100 km.
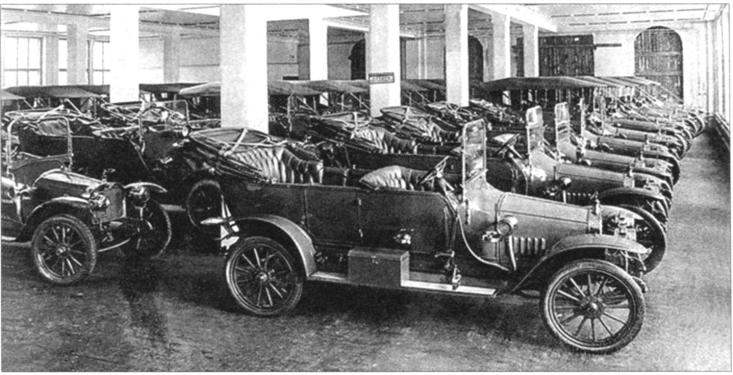
From June 1909 to September 1915 RBWS released 625 cars. Annually, the plant could give 300 – 350 cars, and the increasing demand to increase their production. It should be noted that annual production volumes RBWS almost did not depart from well known European factories.
“Russo-Balt” 10-24 – one of the first trucks release RBWS
The armored car on the chassis of the truck release RBVS with broncobeat Izhora plant
With the beginning of the First world war the tsarist government attended to the creation of the Russian armored car. To do this, planned the chassis of cars “Russo-Balt” to equip the hulls of production Izhora plant. However, when the front approached Riga, RBVZ had to evacuate – in particular, the automotive section of the plant was sent to Moscow. And in the empty shops RBWS during the period of the first Republic of Latvia settled numerous artisanal workshops. In 1990-e years in territory of the former RBUS appeared cooperative with the name “Russo-Balt” produces trailers to passenger cars.
However, back in 1916, when the Board of Directors RBWS purchased for evacuated plant near Moscow, the estate Pokrovskoe-Fili. And on July 1 opened a “Second automobile factory “Russo-Balt”. After a year the decree of the Council of people’s Commissars, the factory was nationalized and renamed “First state armored plant”. In 1922, the components of the backlog were collected five cars “Russo-Baltic”, and 29 January, 1923, the plant was transferred to the concession company “Junkers” that began there the production of all-metal aircraft, u-20 and u-21.
In 2002, automotive Atelier A:Level made an attempt to recreate namenity Russian car brand by launching a competition of design projects of car “based on” cars of the 1930 – 1940s. The winner of the competition was declared Zviad the tsikoliya – his project became the basis of the new car, called the Russo-Baltique Impression.
The concept car was created in 2006 in cooperation with the German company German Gerg GmbH. The car was shown in Europe at the competition Concorso d’eleganza Villa d’este 2006 and at the Geneva motor show in 2007. Some technical data of the car: 12-qi-lendrevie the power unit Mercedes-Benz with a double turbocharger with a capacity of 555 L. E., 6-speed automatic transmission, air suspension. The car was supposed to produce small batches: 10 – 15 copies per year at a price of 1.8 million dollars per copy. Unfortunately, the production car has not yet started.
Igor EBCTPATOB
Recommend to read
 THE DESTROYER “DARING”
THE DESTROYER “DARING”
By the beginning of world war II, Soviet destroyers and leaders in its combat performance characteristics superior to the best ships of the same class built in other countries.... “WELL, HARE, WAIT!”
“WELL, HARE, WAIT!”
With all the abundance of modern toys for children from a variety of soft to various Electromechanical and even RC — the kids are still popular favorite, and the simplest, especially if...
 The Russo-Baltic wagon factory (RBVZ) became the leader of Russian automobile industry in the early XX century. Founded in 1874 in Riga, is a large engineering company produced steam and horse threshing machines, seeders, plows, stationary oil and kerosene combustion engines, passenger and freight cars, trams, artillery limbers, and, later, cars and airplanes designed by I. I. Sikorsky. By 1912 the territory of the company, has a capital of 9.6 million rubles, was already 20 acres, and fifty shops of the plant worked 553 of the machine, which worked 4,000 people.
The Russo-Baltic wagon factory (RBVZ) became the leader of Russian automobile industry in the early XX century. Founded in 1874 in Riga, is a large engineering company produced steam and horse threshing machines, seeders, plows, stationary oil and kerosene combustion engines, passenger and freight cars, trams, artillery limbers, and, later, cars and airplanes designed by I. I. Sikorsky. By 1912 the territory of the company, has a capital of 9.6 million rubles, was already 20 acres, and fifty shops of the plant worked 553 of the machine, which worked 4,000 people.