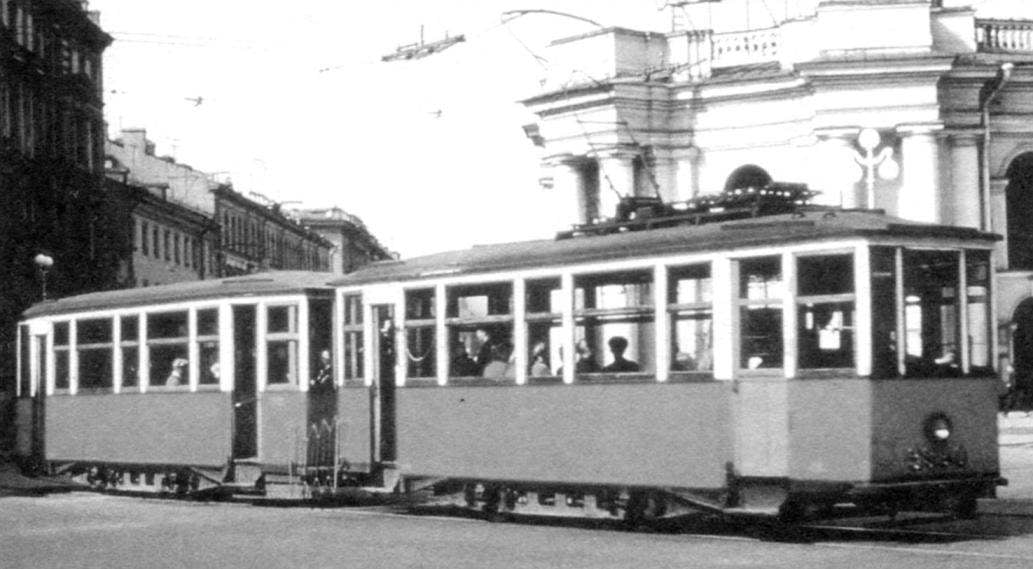
The first carriages of the MS received in the tram Park. Konyashina, where they began to work on the route No. 9, from the Narva gate up to the Polytechnic Institute.
Cars MS has released four, slightly different from other versions: MS-1 (1927 — 1931), MS-2 (1931), MS-3 (1931 — 1932) and MS-4 (1932 — 1933). End of cars MS-1 had a rounded shape in plan. Other modifications of the tip was more simple, angular. In cars, the MS-2 was missing the sliding doors between the salon and venues, so starting with this modification, the cars equipped with sliding glazed entrance doors.
In addition to motorcars MS, the plant “Red Putilovets” in 1929 released a trailer cars PS. They have no traction electrical equipment, control stations, and the chassis were the two free (not United into the cart) axis.
A number of motor cars in 1933 and was made without the traction electrical equipment and was used as a trailer — they received the designation of SMEs.
Of course, unlike a single car, two-car to coupling gear, consisting of motor and trailer cars, it was not easy to walk on routes without turns at the last stop. However, already in 1920-e years the tram network of Leningrad was optimized. Most of the radial routes with the end stops in the city centre was transformed into a diametrical, with end stops in the suburbs, equipped with pivot hinges. Movement on the routes of the couplers was not a problem.
Capacity two-axle wagon were 24 passengers, which was clearly inadequate in order to meet the growing transportation needs of Leningrad, and in the 1930-ies the MS tram walked the trails with a hook (sometimes two) cars.
Due to the fact that the “Red path-the catch” is more loaded with military orders, in particular, the production of tanks, in 1930, the plant stopped producing locomotives, and in 1933 it was the turn of tram cars.
Obsolete, it would seem, to 1940-th years of the cars MS proved to be extremely popular in the years of the siege of Leningrad. Due to the fact that a significant proportion of vehicles were mobilized to the front, the tram has become a very important form of urban transport, both passengers and freight.
In December 1941 without warning was removed the voltage from the contact network. All trams and trolleybuses stood where they were caught off. So they stood the hard winter of 1941/42, but in the spring the question was raised about the resumption of the tram traffic. In early March, in a network applied voltage. The lines went trams — first freight and special. With their help was restored the way and a contact network, which was destroyed by bombing and shelling, was removed from the paths of the snow and the wreckage of buildings, towed to the depot abandoned on the tracks the cars.
Motor car X (Mytishchi, Ust-Katavsky plants) 1927 — 1941
Motor car MC-1 (the Putilov factory) 1927 — 1930s
Motor car MC-2, MC-Z, MS-4 1930— 1933 years
And so, on 15 April 1942 Leningrad again heard the call of the tram. 116 cars MS went on five routes, then the number of routes was increased. For people who survived the nightmare of starvation and cold winter of the siege of 1941/42, tram calls in April 1942, meant that the hard part is done, the city comes alive, life is getting better…
German troops besieging Leningrad, could not help but notice the appearance on the streets of flashes from sparking tram pantographs. The news that in Leningrad resumed tram, shocked the Germans, who expected the imminent imminent surrender of the city.
With the resumption of the tram traffic in the city by the Nazis during the shelling began to strive to conduct aimed fire on the cars and tram stops to achieve the greatest possible number of victims. So they had from time to time to carry stops that it was impossible to zero in. And to reduce the sparking of the current collectors on the cars parallel to the main installed auxiliary current collectors. To increase the speed on the line was produced only motor cars without trailers.
The routes were deliberately released old “amasi”. The fact that damage to the contact network of the passengers were able to push out from the damaged section of small MS, in contrast to the heavier trams.
By the way, in the movie “Baltic sky” was shown very credible scene in which the passengers pushed the car MS for part of the way with undamaged contact wire.
After the war, in connection with the beginning of construction of a new tram LM-49, MS cars began to be transferred to tram system in other cities where passenger traffic was not so significant. Small batches “amasi” went to Minsk, Irkutsk, Sverdlovsk, Kalinin, Taganrog, Astrakhan, Krasnodar and some other cities. A number of cars MS altered at the same time on a narrow gauge.
Gradually, the MS cars have undergone significant changes. Since they no longer need to walk the trails without turning at the last stop, the cars were removed the rear control post, and the doors were left only on the right side.
Lattice entrance doors on cars MS-1 were replaced with sliding. Route lights from the roof were transferred under the cabin Windows and the air intakes were eliminated altogether. The driver’s area was figuratives improvised cabin and under the driver’s seat mounted electric heater. On some trams there is a rope tow trolleys were replaced by pantographia.
Currently, the number of cars is preserved in the MS collections of the Museum of urban electric transport in St. Petersburg, and some of them are maintained in working order. From the car of MS-1 No. 2066 in 1981 was made a car replica firm Brush (MB) No. 1028. And the car of MS-4 No. 2603 in 1970 was transferred to the tram Museum in Amsterdam.
Recommend to read ON “PLATE” — TV In many cases, it is convenient to mount the TV on the swivel stand. This device is easy to do on the basis of gymnastics "plate" — sports a rotating disk simulator. To turn it into a... LUNGING — SPEED A-1 Speed kordovye models are very popular among modelers of the USSR. According to the classification of models of the ships they are United in group a-and are divided into four classes:... 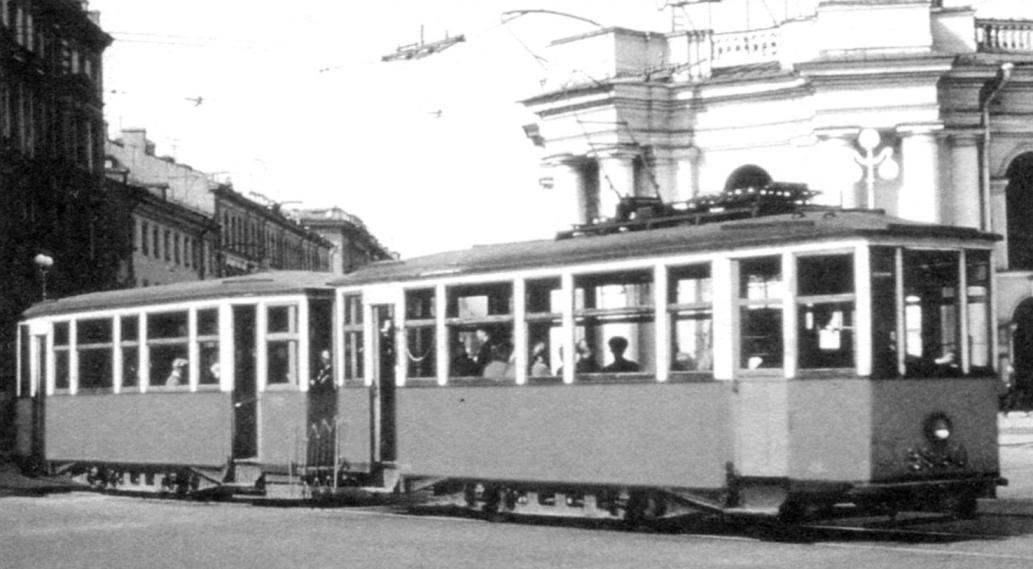 From the devastation of the civil war Petrograd began to rise by the middle of 1920-ies. Respectively, began to grow and the population of the city, considerably departing from 1918 to 1920. The only form of public transport in Petrograd was a tram, but the cars are too worn down and dilapidated over the years of the First world and Civil wars. Naturally, to return the city to normality was needed and the restoration of the tram system, which has taken a number of measures.
From the devastation of the civil war Petrograd began to rise by the middle of 1920-ies. Respectively, began to grow and the population of the city, considerably departing from 1918 to 1920. The only form of public transport in Petrograd was a tram, but the cars are too worn down and dilapidated over the years of the First world and Civil wars. Naturally, to return the city to normality was needed and the restoration of the tram system, which has taken a number of measures.