The rapid growth of car fleet in our country in the last decade has led to a number of problems, many of which do not find their solutions: many kilometers of traffic jams and fumes of city streets by automobile exhaust. The increase in the number of cars outstrips the pace of road construction and organizational measures to streamline the traffic. The transport problem for large cities is not new, and its decision of the Moscow authorities began almost eighty years ago. In 20-e years of the last century one of the ways to solve transport problems of Moscow, the leaders of the Soviet Russia has seen the development of public transport.
The rapid growth of car fleet in our country in the last decade has led to a number of problems, many of which do not find their solutions: many kilometers of traffic jams and fumes of city streets by automobile exhaust. The increase in the number of cars outstrips the pace of road construction and organizational measures to streamline the traffic. The transport problem for large cities is not new, and its decision of the Moscow authorities began almost eighty years ago. In 20-e years of the last century one of the ways to solve transport problems of Moscow, the leaders of the Soviet Russia has seen the development of public transport.
In these years, the main public transport of the Soviet capital were trams and a few buses could not cope with the ever-growing flow of passengers. In 1924, a proposal to organize a trolleybus from the Moscow circular railway to the holiday towns in the North-Western suburbs of Moscow. After numerous discussions in 1932 started the construction of the first trolleybus line from the Belarus station on the Leningrad highway to the village of all Saints (in the present area of metro station “Sokol”),
In December 1932 the people’s Commissariat of heavy industry ordered the creation of prototypes of new transport domestic enterprises chassis and body — all-Union tractor Association (vato), and electrical equipment all — Union electrotechnical Association (VEO). Six months later, the Yaroslavl automobile plant started production of chassis trolley, designed by the Institute of motor and tractor industry (NATI) on the basis of the truck I-6. In the fall after the factory test two finished chassis was transferred to the Moscow plant named after Stalin (now ZIL) for fitting bodies. By this time another capital factory “Dinamo” has started production of the American documentation two sets of electrical equipment. On the eve of the anniversary of the October revolution the plant employees gave the finished body of the Dynamo, who managed in a few days to install the equipment and test factory-prepared trolley. In parallel with the Assembly of trolleybuses for future highway started installation of supports of the contact network from the Belarus station to the intersection of Volokolamsk highway from Moscow ring railway. Stops on trolleybus route “Belorussky station”, “Run”, “the Stadium “Dynamo”, “the Academy of Air fleet”, “Ring road” laid asphalt, and in the village of all Saints began construction of the garage trolleybus Park.
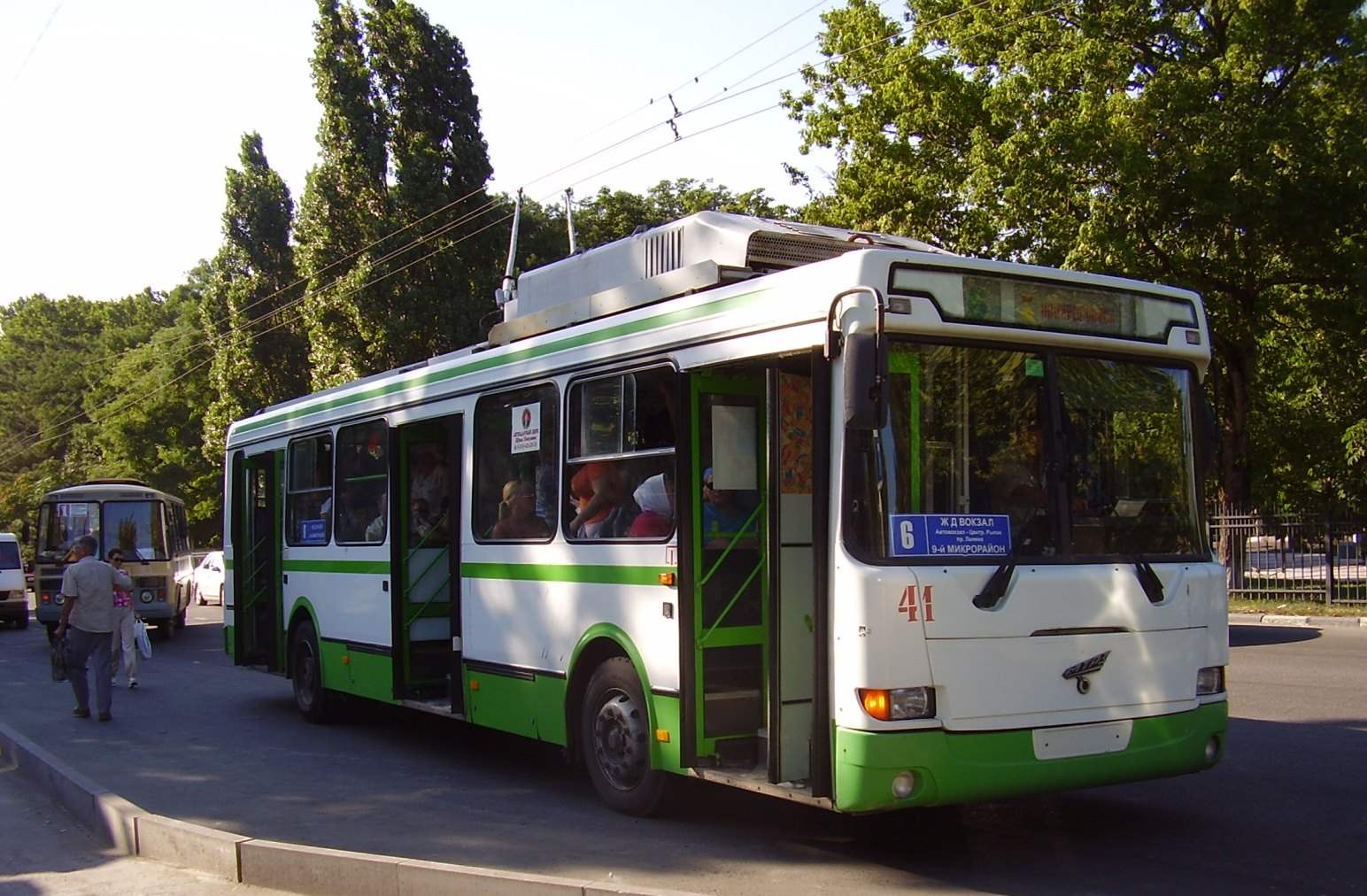
On the evening of 7 November, 1933 the first Moscow trolley bus LK-1 (in honor of “initiator trolleybus” — the first Secretary of the Moscow gorkom of the CPSU(b) Lazar Kaganovich) marked on the front body panel “From the workers, engineers and employees of the 1st state of the car factory Stalin factory “Dinamo”, Yaroslavl automobile plant NATI” went to trial run to the Belarus station. During the following two days took place the official acceptance of the trolley by the leaders of Moscow, on 15 November, the trolley began transferring residents. For the first two weeks the Moscow trolleybus carried 22,000 passengers.
The first Soviet trolley had hardwood (ash and Oak) body shell, covered with metal sheet mounted on a frame made out of channels. The cabin was 37 soft pas sagorski seats, only seats 45, and the cabin was heated by electric heaters placed under the seats. For transportation of small things was intended mesh shelves above the Windows. In the piers between the Windows housed the mirror. The motor power of 60 kW allowed the trolley with a mass of about 13 tons to reach a speed of 55 km/h the Trolleybus with the same engine had a throttle response comparable cars of the time.
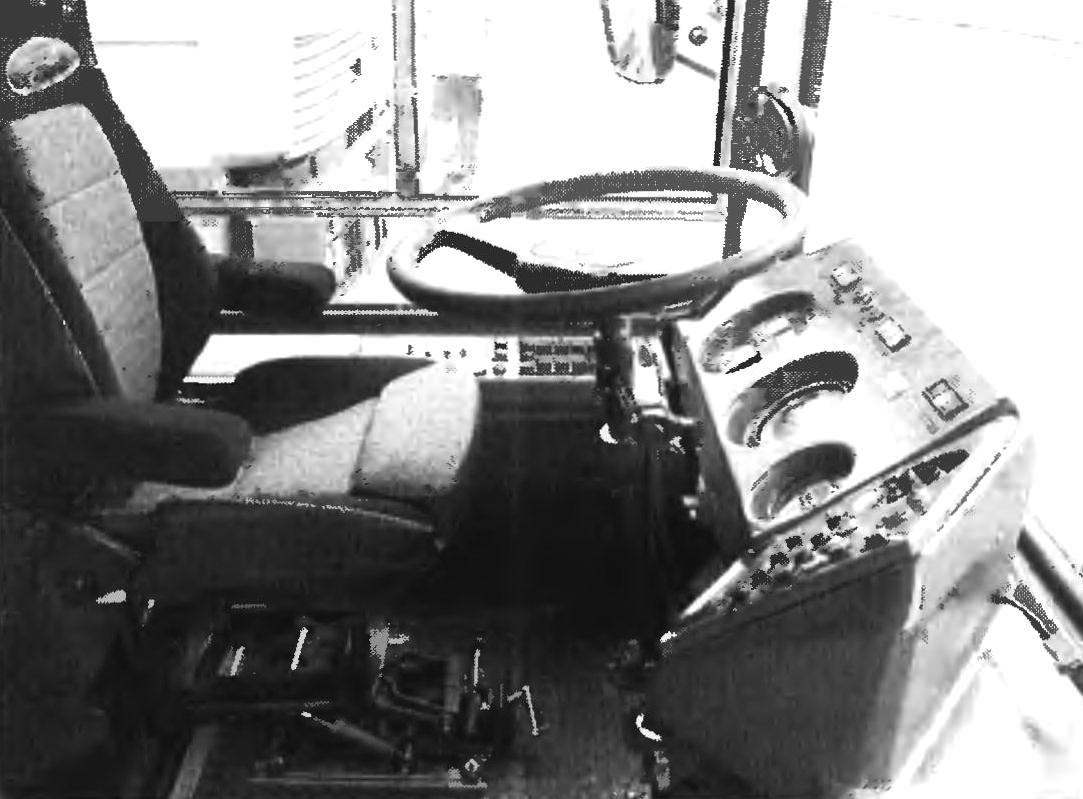

The driver of a trolley bus 5272.01 “Rus”
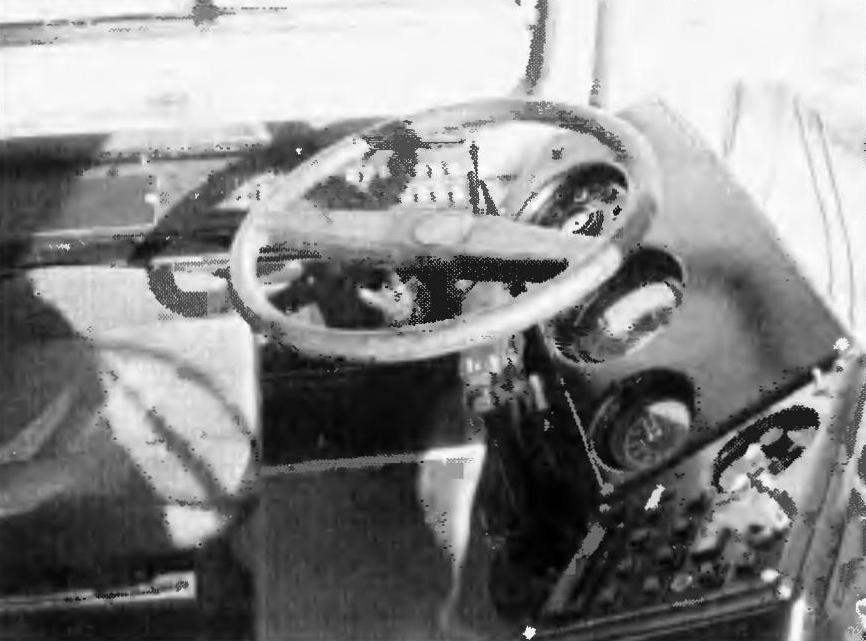

The driver of the trolley with RXU
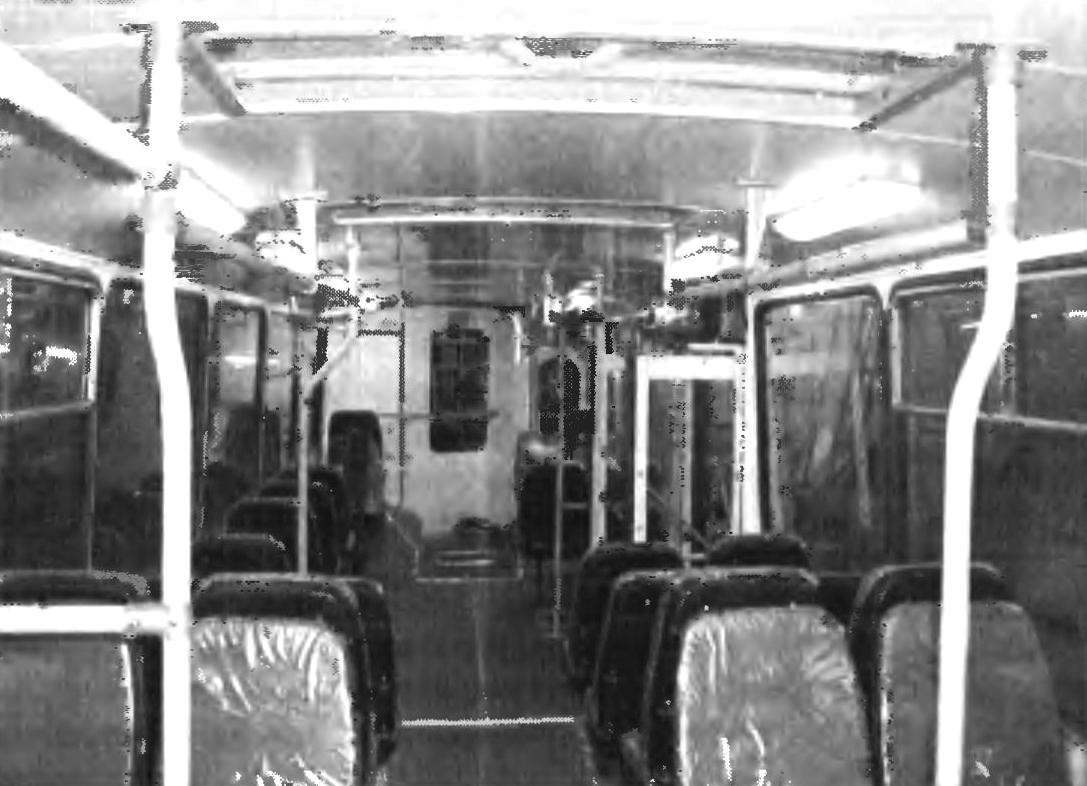

Salon trolley MTRS-5279.02
A new form of transportation met expectations, and the Moscow city Council has ordered another ten trolleybuses: Yaroslavl produced chassis, mechanical equipment, the Moscow car repair plant (AREMZ), body — ZIS, electrical equipment factory “Dinamo”, the final Assembly led Sokolniki carload and autoparametric plant (SVARZ) Trolleys of the second batch, starting with the third machine that’s assembled on Swarze, called the LK-2. The first trolleybus line was extended first to city Council, and in late 1933 to Sverdlov square. In the spring of 1935 trolley buses in the capital were served by two routes: № 1 — Sverdlov square — Pokrovskoye-Streshnevo and No. 2 Sverdlov square — Dorogomilovo. At the end of the year there was a route 3 — Sverdlov square — Rzhev (now Riga) station, and route 2 was extended to Rzhev station.
In 1934 in Moscow cruised 30 domestic trolley buses, and in 1936 trolleybus Park of the capital, there were 68 machines. The example of Moscow inspired the leaders of other large cities, and soon the trolley was carrying passengers in Leningrad, Kiev and Rostov-on-don.
Operation of the first trolleybuses has identified a number of deficiencies, the elimination of which in the summer of 1935, the specialists of NATA and the Yaroslavl automobile plant, developing a more sophisticated 50-seater trolleybus model, called YATB-1 (Yaroslavl bus — first model). With the development of the trolleybus traffic in the country, the brunt of their release had at the Yaroslavl automobile plant, where their production has organized a special workshop. The complexity of manufacture of the body was about 75% of the total work on the machine In the factory created a body design Bureau led by Vladimir Osepchook. In 1936, the citizens received from narkomtyazhprom an order for 250 machines. Until the end of the year in Yaroslavl has produced 152 YATB-1.
A characteristic feature of the trolley was the pneumatic brakes-Regenerative-rheostatic system of electric braking was allowed to slow down the trolley over the entire range of speeds. On LK-1 wheel brakes with a mechanical drive can be used at a speed of 20 km/h and below. The pneumatic actuator had a double-leaf entrance doors and the wipers. Softer suspension on an oil-pneumatic shock absorbers, reduced noise in the cabin. The latter has made the transition from gear-main gear to the worm. The displacement of the motor with a longitudinal axis of the machine to the left under the seat made it possible to lower the level of the floor of the cabin and get rid of stairs, which increased the stability of the machine and she swayed with the movement. Yaroslavl trolley was not devoid of faults on electrical equipment located in the front of the cabin was dirt and water, did not differ reliability of the worm gear. wore out quickly roller trolley head. The job of the driver was complicated by the lack of a partition between the driver and passenger compartment. These drawbacks have been removed in the model YATB-2, released in 1937. The new car had besides the enhanced transmission: expelled from it through drive shaft and the transmission disc brake. Channel cross member frame was replaced by tubular.
The latest model developed by the Yaroslavl automobile factory before world war II, became YATB-4. produced in 1938, differing from its predecessor by a more powerful engine with 74 kW, improved compressor, worm gearbox and window regulators. Only the latter produced until 1941 922 trolley, carrying passengers in 11 cities of the USSR.
The great Patriotic war stopped the development of public transport in the country In the years warriors, the trolley was the main mode of passenger transport in Moscow: buses mobilized for needs of red Army, and much of the tram tracks went for defense and, in particular, for the manufacture of anti-tank hedgehogs part of the trolley used for freight.
In February 1944, the Soviet government adopted a decision to organize in Moscow, close to Savyolovskaya station, on the Great lords of the street on the site of the 13th taxi company in Moscow trolleybus repair plant (MTRS) for the overhaul of trolleybuses, worn out over the years and damaged during the war.
In Moscow at this time, there were about 400 trolleybuses. A substantial portion of them were in a semi assembled state.
The weakest point of most pre-war trolleybuses appeared to be a wooden structure for their bodies are Extremely short-lived, it required constant monitoring of its technical condition, timely replacement of rotten structural members. During the four years of war repair trolley is in fact reduced to keeping them in more or less working state, so the physical wear of machines was almost complete. For this reason, has closed a number of trolleybus routes with a small number of passengers and where they were duplicated tram lines.
In the summer of 1944 the staff of the new facility began renovations in the maintenance base of passenger transport, and in October was repaired the first trolley. In August 1945, the plant has overhauled the first trolleybus YATB. In may 1946, the plant started mass overhaul of trolleybuses yatb-YATB 1 and-2. Over the next two months overhauled the first ten trolleybuses.
In 1945, the plant Director was appointed I. S. Efremova, who worked in the trust “Astrolabes” the chief engineer of the 2nd trolleybus Park. Yefremov was one of the most authoritative experts in the field of urban electric transport and has made a great contribution to the creation of semiconductor power systems for traction substations and electronic control systems all types of electric rolling stock of get. All traction substations of Moscow and other cities of the USSR were equipped with reliable and economical semiconductor rectifier units, developed under the direct supervision of doctor of technical Sciences I. S. Efremova.
Starting with the repair pre-war trolleybuses, later the plant mastered the overhaul of MTB-82 trolleybuses, production of which was established in early 1946 at the Tushino machine-building plant № 82 (TMZ). This trolley had a unitized body with a city bus ZIS-154 and tram MTV-82. The Tushino plant was part of the Ministry of aircraft production, so the body structure trolley is widely used parts from aluminum alloys. All-metal body of the trolley is trimmed with a 2-mm dural leaves are used in the same seats, Windows, doors, fittings. But full unification with the bus failed to achieve: unlike a bus with a monocoque body, the trolley had a traditional body with a bearing frame channels. So, in essence, a trolley represent a modernized version of the unrealized project of the Yaroslavl pre-war trolleybuses YATB-6.
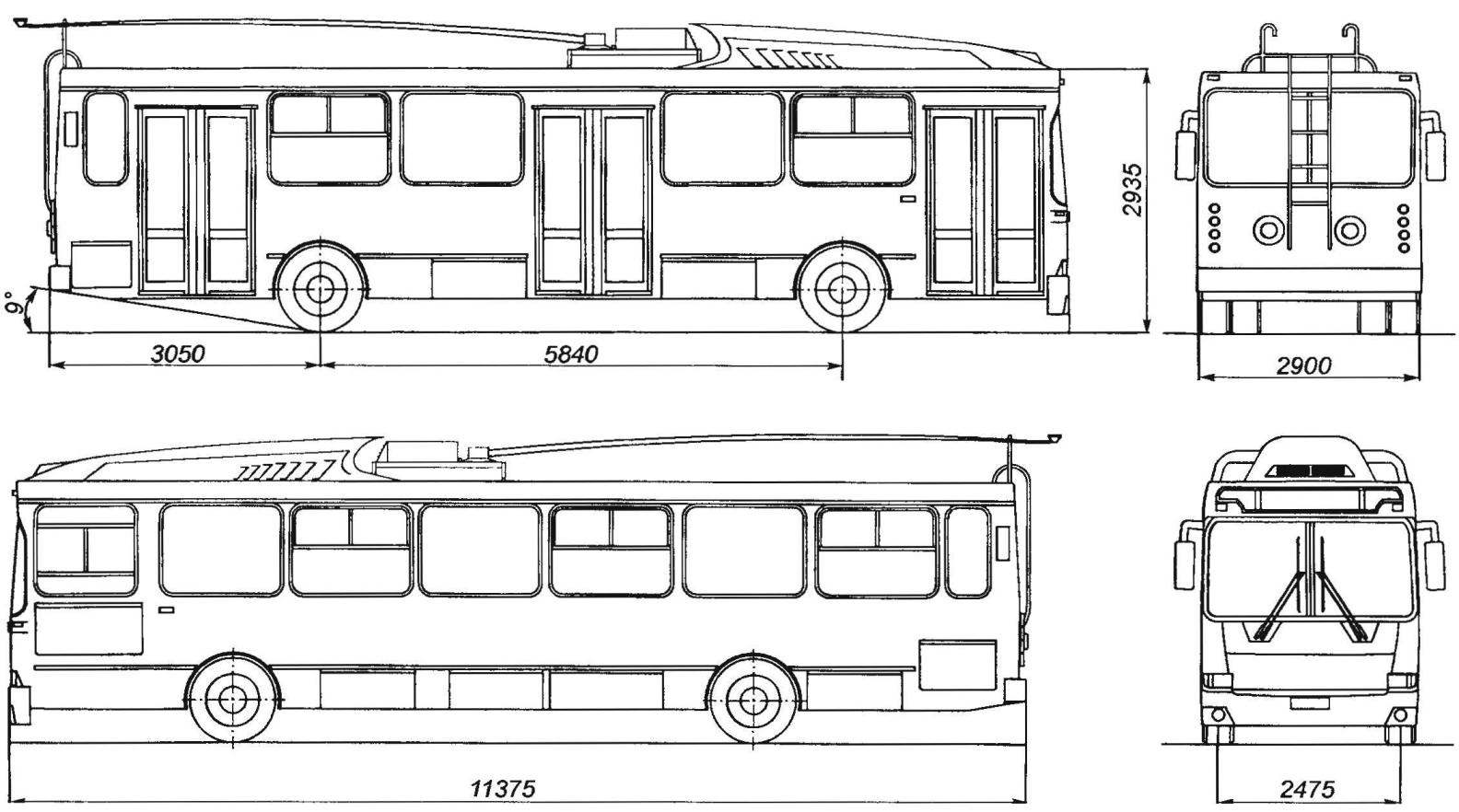
Trolley MTRZ-5279 “Rus”
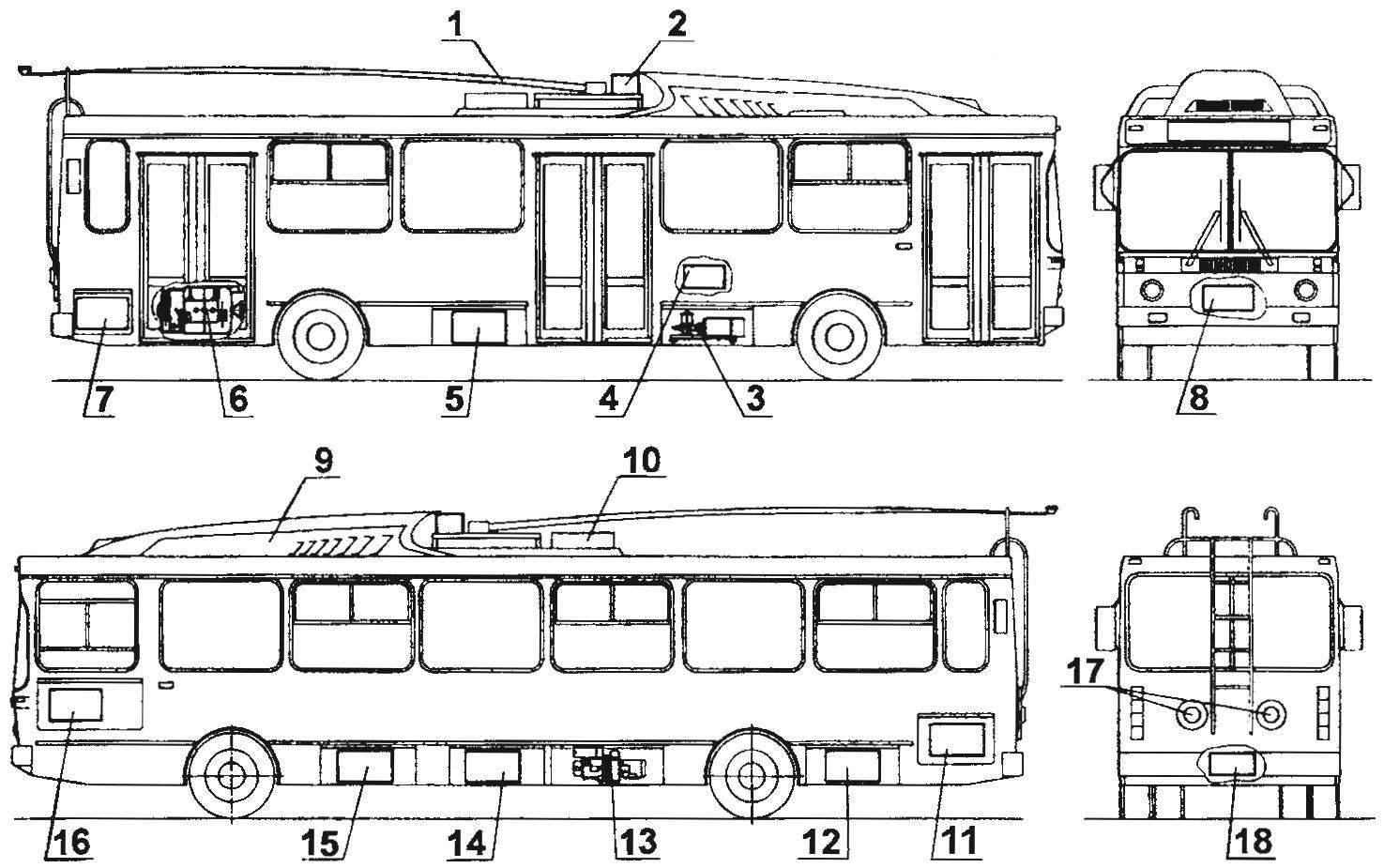
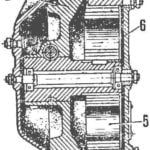
Location of main components on the trolley MTRZ-5279 with an electronic control system for the traction motor:
1 — rod pantograph; 2 — Converter and gazorazryadnoi; 3 — power steering; 4 — oven; 5 — batteries and remote control panel battery; 6 — drive motor; 7 — the control panel of the furnace; 8 — bake the driver’s cabin; 9 — traction Converter; 10 — redirector; 11 devices of measurement of leakage current and insulation resistance motorblade box; 12 oven interior; 13 — compressor; 14 — the inverter compressor, the oven interior, bar compressor; 15 — air balloons; 16 — low-voltage panel and fuse; 17 — strological; 18 — oil-water separator
In early 1947 at the Tushino mastered the production of an improved model of MTB-82Д. The trolley with the electric motor 86 kW could carry 65 passengers, 45 of them sitting, with a maximum speed of 47 km/h. Fabrication of the trolley on TMZ continued until 1951, when their manufacture was transferred to Zavod imeni Uritskogo (ZIU) in the city of Engels, Saratov region. In 1955, the plant Uritsky developed the first instance experienced, trolleybus TBU-1, which is since 1959 the factory produced commercially as ZIU-5. The trolley had forced ventilation of the cabin, power steering, a more powerful motor DK-207 capacity of 95 kW. ZiU-5 was carrying 78 passengers (40 seated) at speeds up to 68 km/h. This model was primary on the streets of Moscow. ZiU-5 is the most abundant domestic trolley: eleven years of these cars produced about 20 thousand.
In 1972 was replaced by the model ZIU-9B, repeating a constructive solution, proposed in the mid 1960-ies specialists of the Kiev electric transportation plant named after Dzerzhinsky, when you create a popular Ukrainian trolley bus “Kiev-6”.
An extensive network of trolleybus routes in the city ensures the development and significant loading MTRS: in 1974, the plant was repaired 710 trolleybuses, in 1985-1988— 2310. In 1988, the plant, along with the overhaul and modernization of trolley buses ZIU-9 and ZIU-682 began the production model “SVAR-Icarus”, developed on the basis of the chassis and bodywork of the city bus “Ikarus-280”, produced by TMZ. Until 1991 in MTRS produced 51 trolley this model.
In the autumn of 2002 out of the gate MTRS got the first trolleybus models 6223, manufactured by the factory using elements of body city bus LiAZ-5256. New comfortable car meets all modern requirements for urban public transport.
For increased electrical safety and improved conditions of service part of high voltage equipment and the static Converter is placed on the roof in a special container.
At one time there were complaints to the safety of passengers when travelling by trolley in rainy weather. To exclude the possibility of the slaughter of the passengers by trolley current to the insulated rod current collectors, wheel housing of the casing and foot pegs made of plastic, in addition, doorways has provided a special insulating plastic covers and insulated handles.
Cab driver operating on city streets in heavy traffic, equipped in accordance with the requirements of ergonomics; the seat is adjustable for height and backrest angle. Improved visibility from the driver’s seat is provided a panoramic front windshield and adjustable rear view mirrors with electric heating. New steering control scheme helped to reduce the effort for turning the steering wheel. Today, after testing for strength, reliability and safety, the machine works in a Moscow trolleybus parks.
The exhibition, held in autumn 2002 at the Expocentre on Krasnaya Presnya, work MTRS received a high rating Moscow leadership: the trolleybus is awarded a diploma.
In 2003, under the leadership of chief designer B. C. Gavrilova on MTRS designed and manufactured in cooperation with the TMZ new model trolley “Russia” on the basis of the bus LiAZ-5256 with an electronic control system for the traction motor (on IGBT-transistors) created by the Czech electrotechnical company “Skoda Ostrov”. “Skoda-Island” is a world leader in the production of trolleybuses and guarantees high quality, reliability and safety of their products and the lifetime of the system management for 15 years the control System was specially modified under the bodywork LiAZ-5256. As the traction engine used Czech DC motor 9AL2943rN of the company “Skoda” with nominal power of 100 kW. Transmission uses double-spaced main gear RABA 318.77-3300 — Central bevel gear and planetary wheel gears. The pneumatic system works from the Hungarian rotary compressor BRQ4/10/12T with electric.
On the frame in the middle part of the base susceptor with fiberglass rods and the heads of the susceptor, there is a DC / DC Converter IPT and gazorazryadnoi.
Unified monocoque Likino bus plant has an increased service life; for its production galvanized sheet is used, after Assembly, the housing is subjected to additional protective treatment against corrosion. Manufacture the body specialized enterprise allows both partners to reduce labor costs for its manufacture, due to the larger number of cars produced.
The trolley is equipped with a dual circuit brake system with a pneumatic actuator with anti-lock system ABS 2X4S/4K24V German company “Knorr-Bremse”. The allegations of factory experts, the share of domestic components, even at the initial stage of production will exceed 65%. The trolley has been successfully tested and runs on the streets of Moscow.
In an effort to reduce the cost of their primary products and thus expand their range of consumers, MTRS establishes contacts with domestic manufacturers of parts and components that can replace expensive imported ones. Therefore, the specialists of the plant designed on the basis of body bus LiAZ-5256 modification of the trolley with a domestic control system on IGBT-transistors, developed by specialists of St. Petersburg in NPP EPRO. In this model, a further development of constructive solutions used in the previous model. As the traction motor is an asynchronous ADT-3 with a capacity of 130 kW. Electric trolley is designed to work with a large drop of frequency. The use of the recovery system provided savings of up to 30% of electricity. Forced cooling pulse Converter with IGBT-module has improved the reliability of its work. Trolley equipped with built-in control system, the diagnosing of electric traction without the use of special measuring devices. The reverse gear switch actuator (forward and back) happens without current load, which increases the service life of the contactors. Design decisions used in the creation of this model, 50% have reduced the complexity of the service and 80% of the cost of spare parts.
The cabin trolley has 24 individual seats, with soft cover made by “Pilot-Russia”. The total number of seats in the passenger compartment — 89, the limit is 114. In the cabin trolley mounted scoreboard with a running line, duplicate the sound information.
With the new models there is a characteristic increase of the floor area at the back of the cabin, caused by the location of the bus motor on the rear overhang of the body. MTRS represented a modification of the “Rus ‘” with asynchronous motor and control system on IGBT-transistors at the Moscow exhibition “Passenger: transport, station complexes, and the services sector”, held in early March 2004 at the all-Russian exhibition centre.
In 2004 the government of Moscow ordered nine new trolleybuses with electronic control system. Guide passenger transport in the capital has high hopes for the trolley created MTRS, considering that new cars can be the hallmark of the Russian capital.
L. MALANKINA