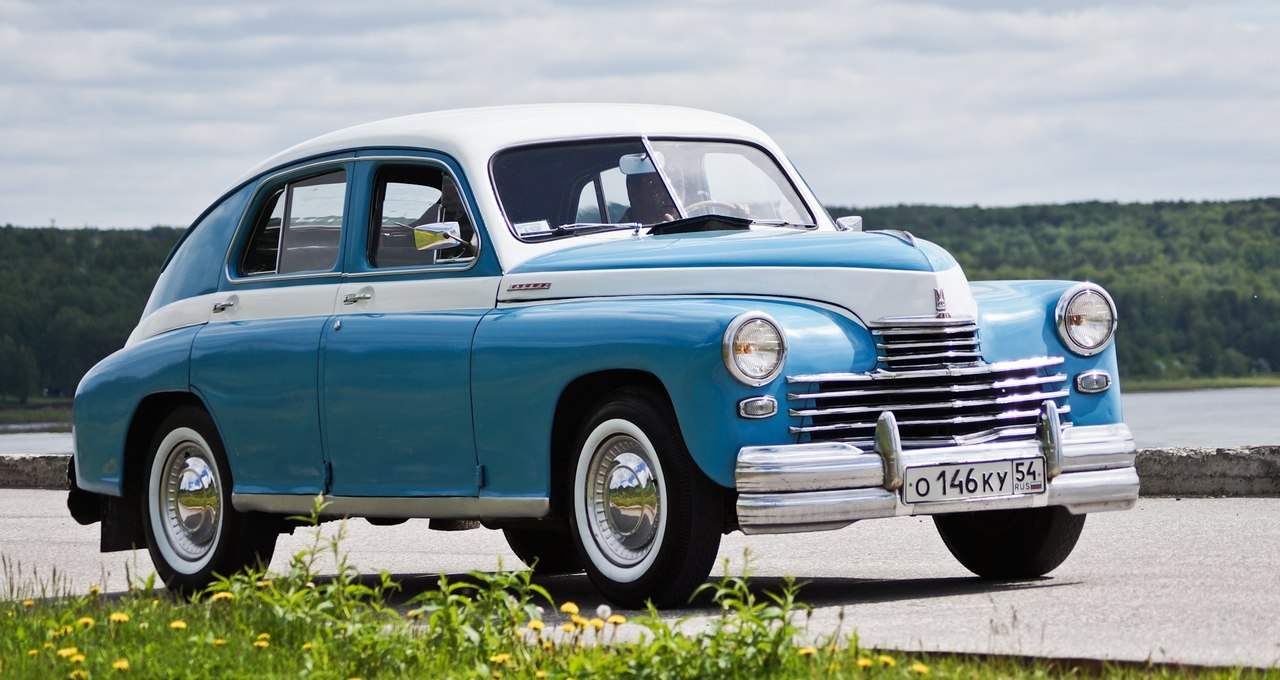
A Russian passenger car GAZ M20 “Pobeda”. This particularly civilian car was designed during the great Patriotic war. For a future peaceful life, she produced and assembled at the factory, almost completely destroyed by Nazi bombers and nevertheless producing light tanks T-60 and T-70 self-propelled guns SU-76M and armored cars BA-64. Finally, this machine was created by people who in this difficult time found the strength to work on the post-war future, then seemed incredibly far away…
A Russian passenger car GAZ M20 “Pobeda”. This particularly civilian car was designed during the great Patriotic war. For a future peaceful life, she produced and assembled at the factory, almost completely destroyed by Nazi bombers and nevertheless producing light tanks T-60 and T-70 self-propelled guns SU-76M and armored cars BA-64. Finally, this machine was created by people who in this difficult time found the strength to work on the post-war future, then seemed incredibly far away…
This is the first post-war car of the Gorky automobile plant named after Molotov — GAZ M20 Pobeda, which has produced a kind of technical revolution in the world of automotive engineering. It argued that the reason for this was, oddly enough, war, and ultimately uploaded our auto industry to military production and did not leave for managers at all levels opportunities for “petty” guidance to making useless, as it seemed to many civilian cars.
The creation of a huge, pre-war standards, the automobile plant in Nizhny Novgorod was the result of signing 31 may 1929 contract between the American firm Ford Motor Company and the Soviet government. The plant was constructed in just three and a half year — 29 Jan 1932 conveyor Nizhny Novgorod automobile plant (NAZ) came down the license polutoratonny truck NAZ-AA (FORD-AA), and in December of the same year, and the license of the car GAZ-a (FORD-A). In the same year, the Lower was renamed the town of Gorky, and the factory and, accordingly, mark its car — GAS.
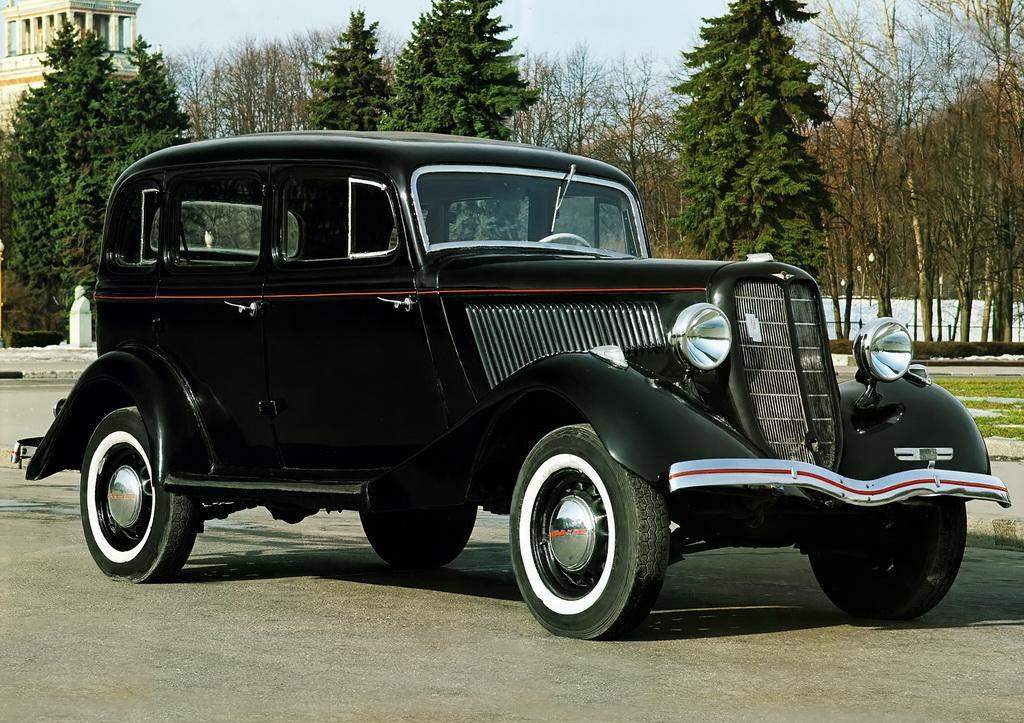

The famous “emka” Gorky automobile plant GAZ — M1 release 1936
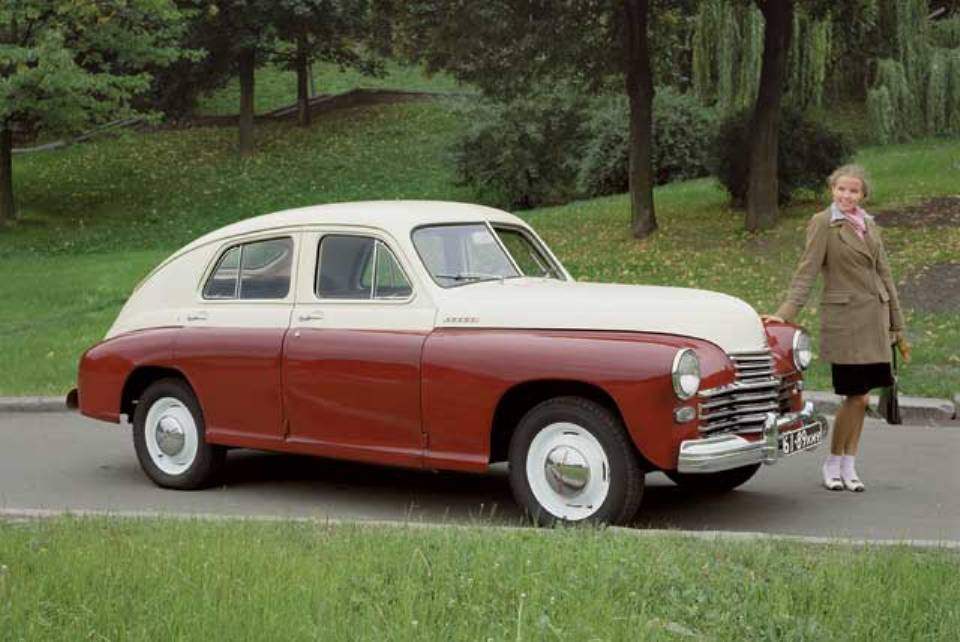

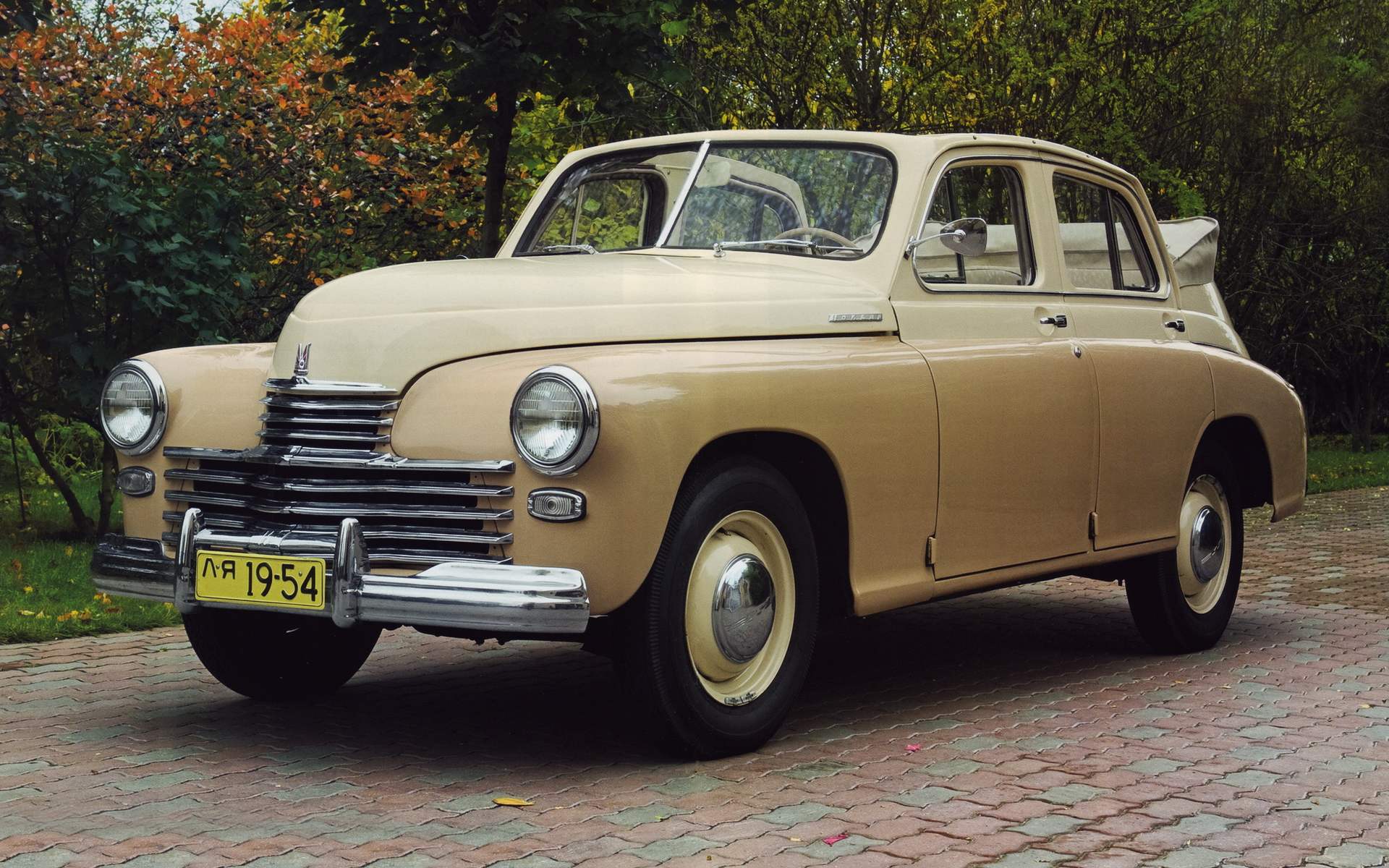
The first postwar passenger car GAZ — Pobeda GAZ-M20 edition 1946
The first models of Gas cars was the most unified: engine, clutch, gearbox and steering mechanisms in cars and the lorry was the same.
Passenger car GAZ-A was the body of a Phaeton type with a folding tent, equipped with four-stroke petrol engines working volume of 3.28 l (!) and with 40 HP Supply of fuel in the carburetor is produced by gravity from the fuel tank with a capacity of 45 L. the Gearbox was three-speed — three forward and one back. Brakes — drum, driven. As highlighted in the technical description of the machine — “on all four wheels”!
Transverse leaf springs, semi-elliptic. Shock absorbers are hydraulic. Wheel combo — steel rim and welded it thirty spokes. The car was equipped with starter, speedometer, fuel gauge in the tank, ammeter, pressure gauge, electric alarm, tinted laminated glass “triplex”, electric brush for the front glass (now called the wiper) and rear view mirror. The vehicle weight was 930 kg. the Car was able to accelerate to the speed of 85-100 km/h (depending on road), while spending on 100 km about 11 l of fuel.
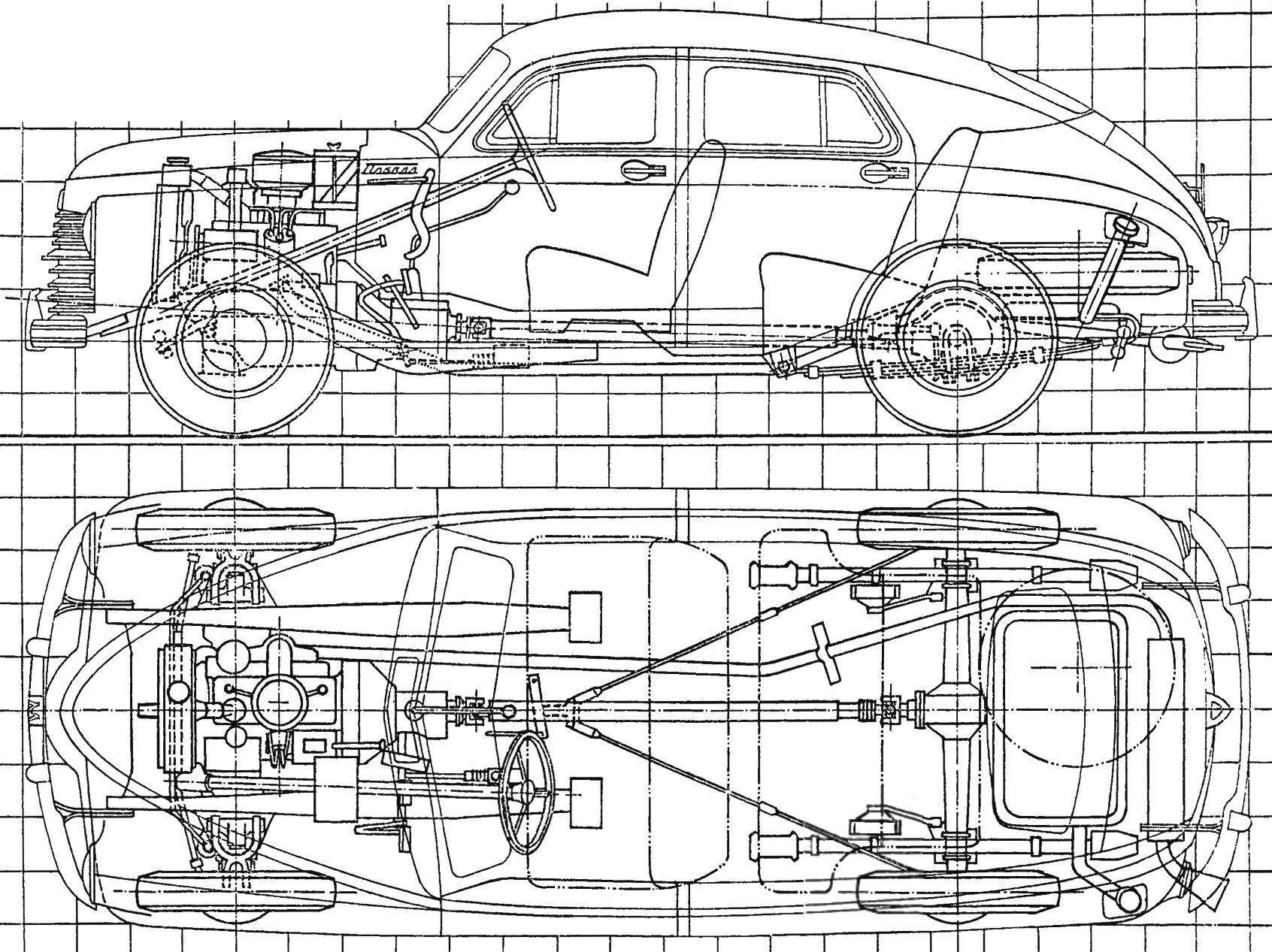
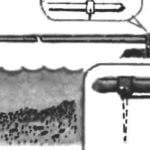
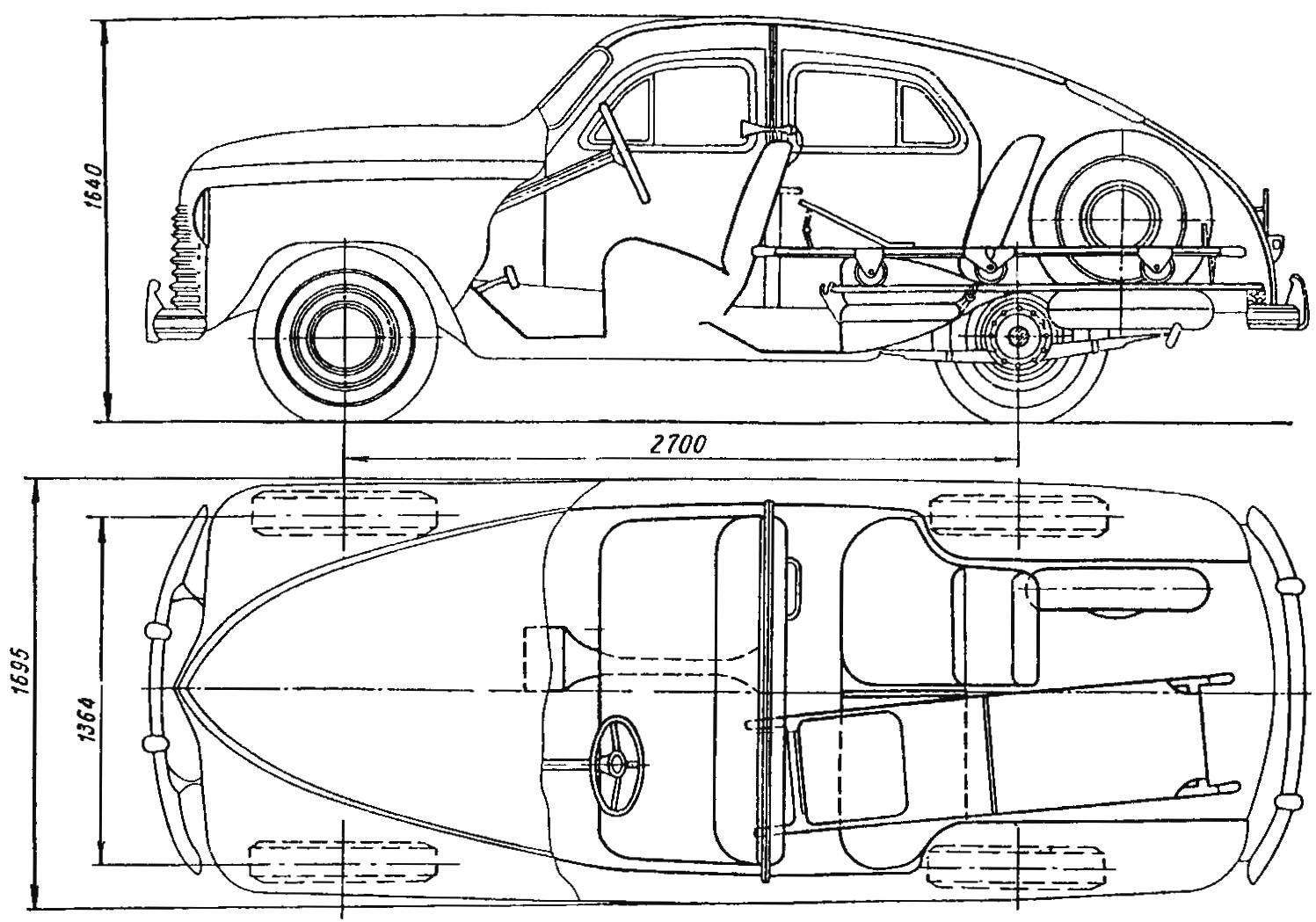
The layout of the car “Pobeda” GAZ-M20 of the first issue (the side of the grid is 200 mm)
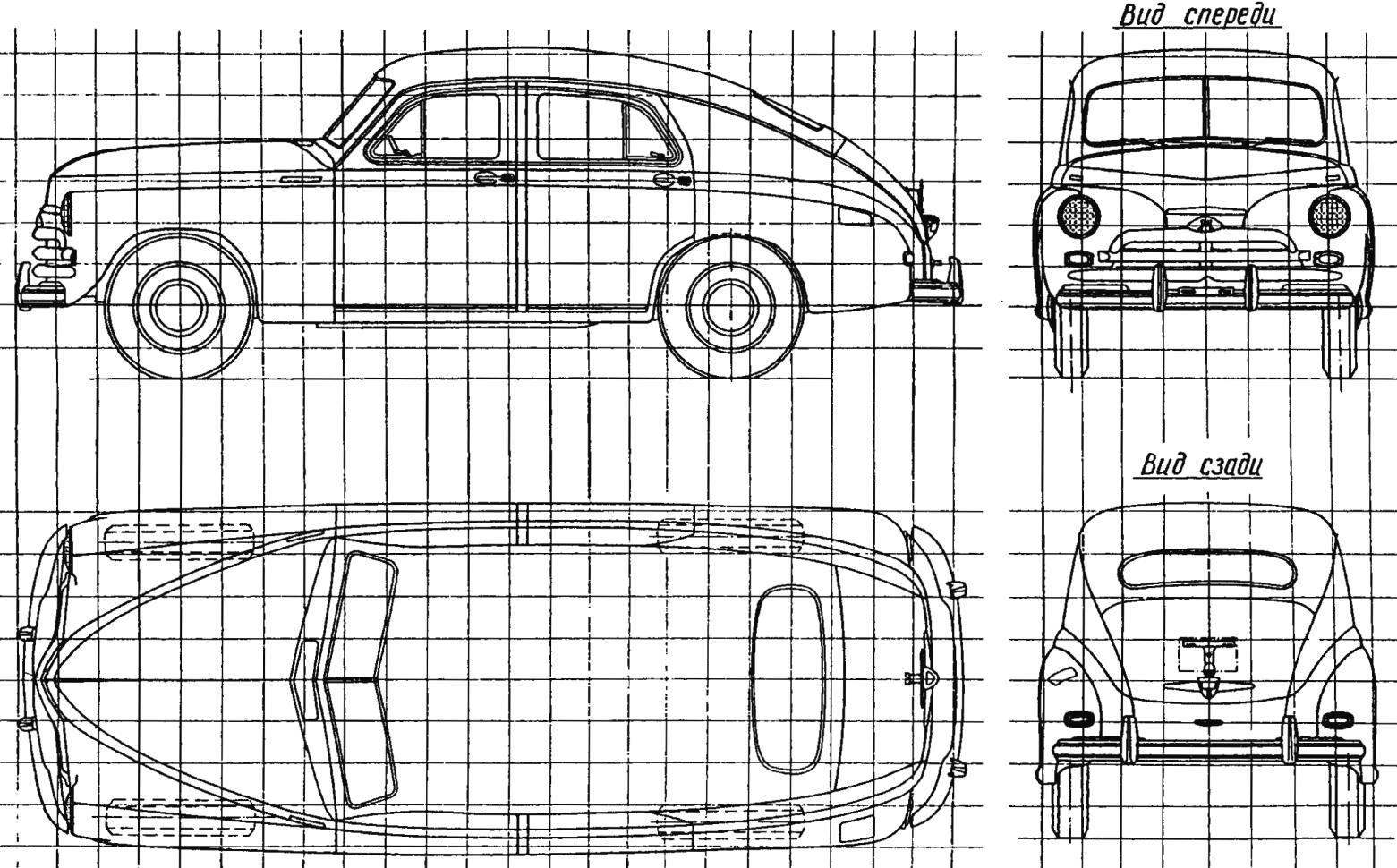
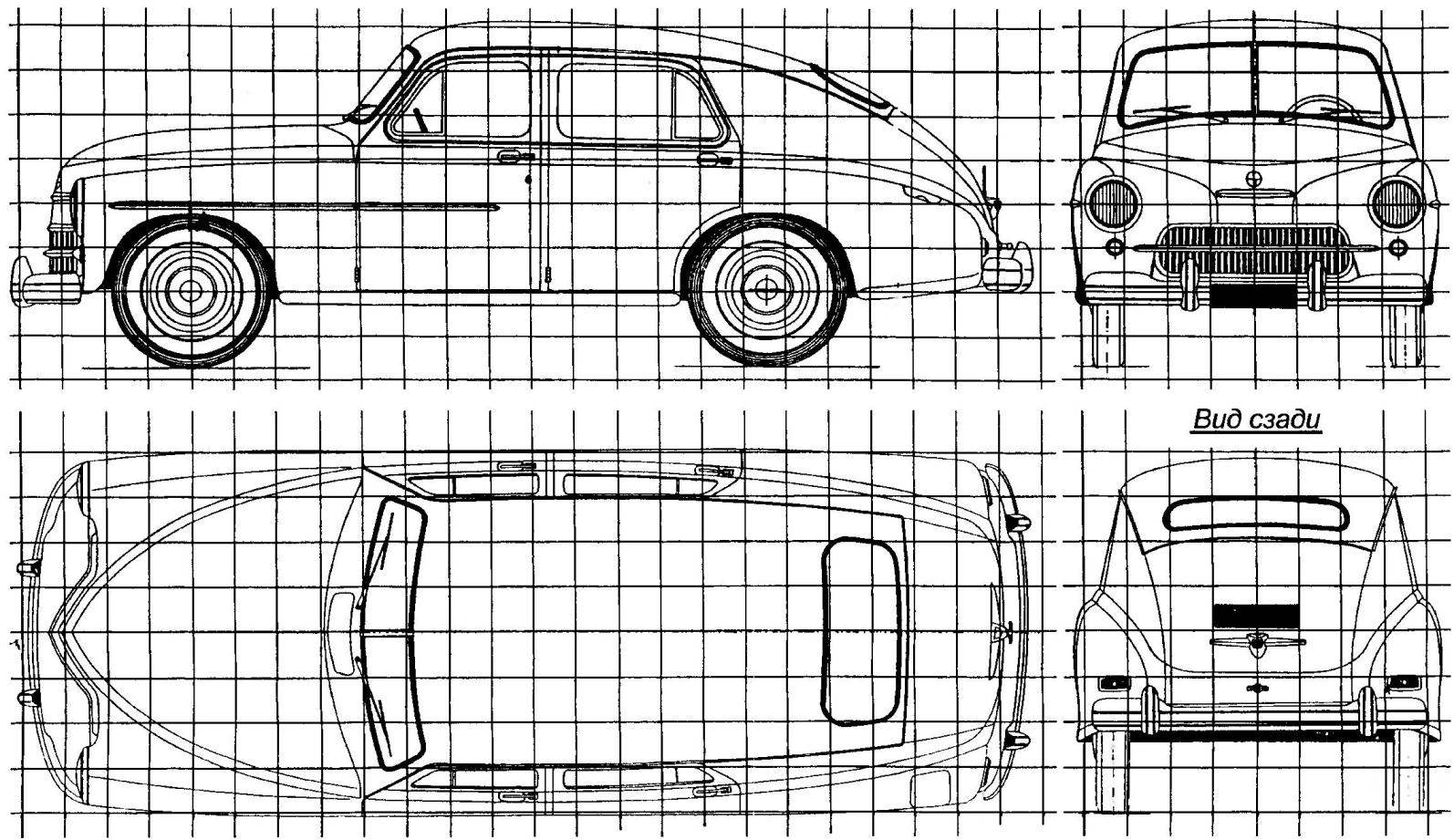
The geometric scheme of the car “Pobeda” GAZ-М20В (side of the square grid is 200 mm)
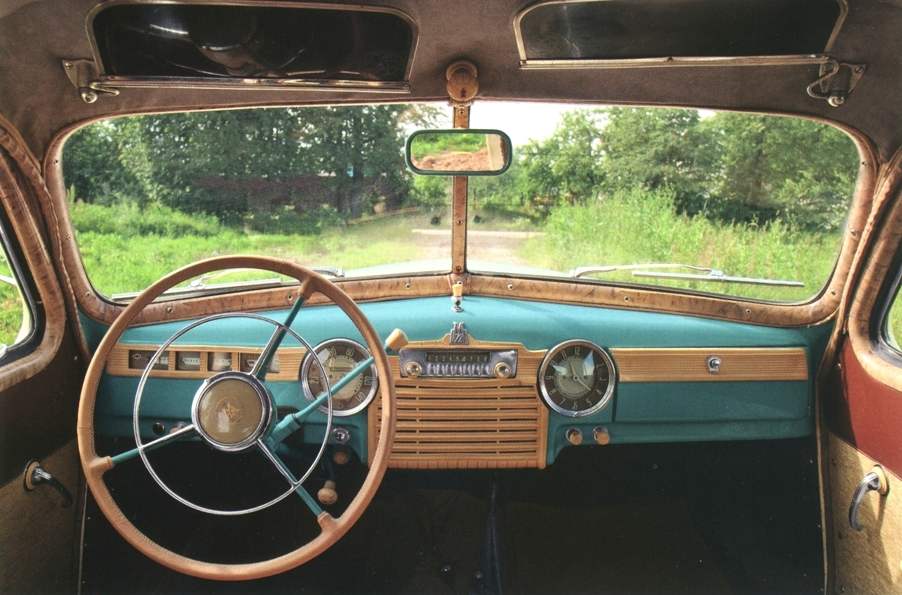

The interior cabin of the car “Pobeda” GAZ-М20В
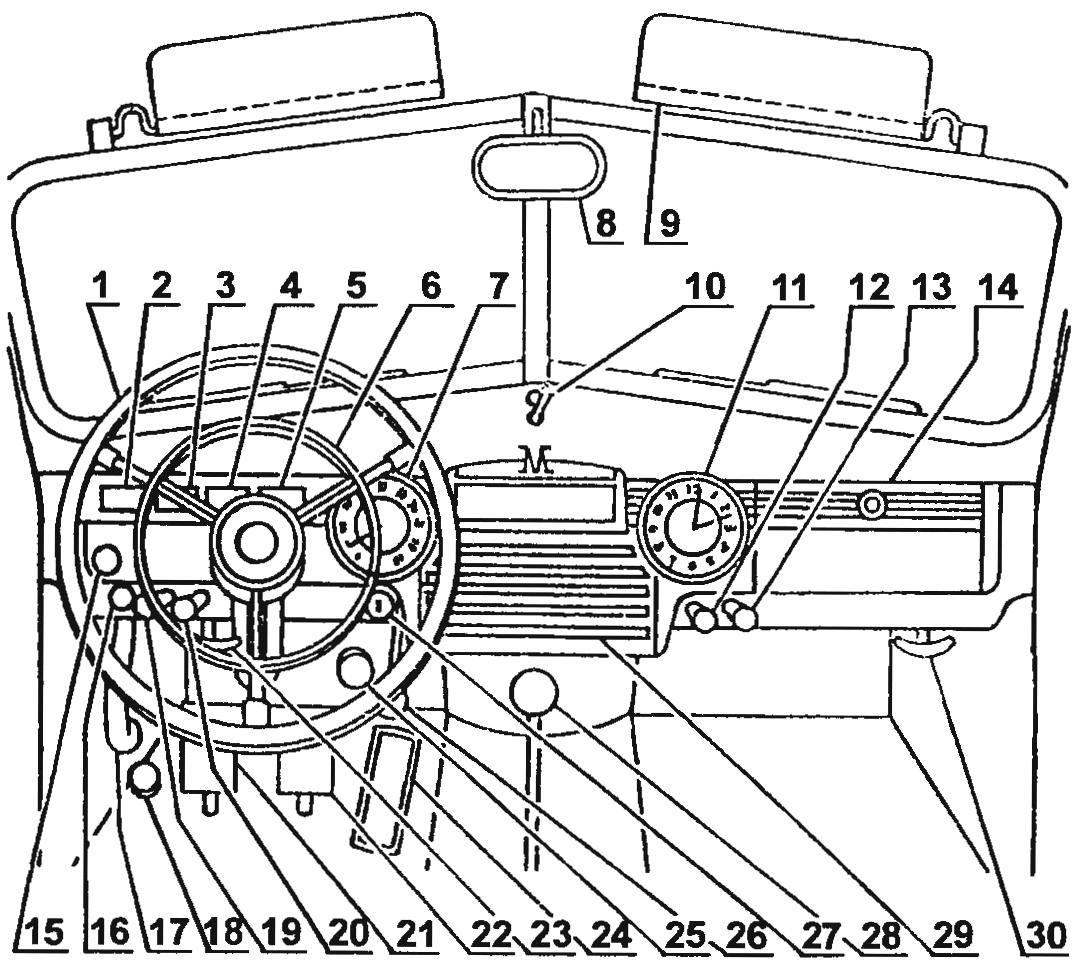
Controls and instruments car “Pobeda” GAZ-M20 the first issue:
1 — steering wheel; 2 — ammeter; 3 — fuel level indicator; 4—pointer water temperature; 5—oil pressure indicator; 6 — ring horn switch; 7—speedometer; 8 — mirror; 9 — sun visor; 10 — switch of turn indicators; 11 — Electromechanical clock; 12— button choke control carburetor; 13—cigarette lighter plug; 14—the glove box; 15 — warning lamp Parking brake; 16 — heater control; 17—Parking brake lever; 18 — foot dimmer switch “near—far”; 19 — Central light switch; 20—button control the throttle of the carburettor (“DC gas”); 21— a coupling pedal; 22 — a brake pedal; 23 — actuator lever grille; 24 — throttle; 25 control arm ventilation hatch; 26— / starter switch; 27 — ignition switch; 28 — shift lever; 29—place the radio (on the machines of the first issue was not established); 30—the handle of the hood lock
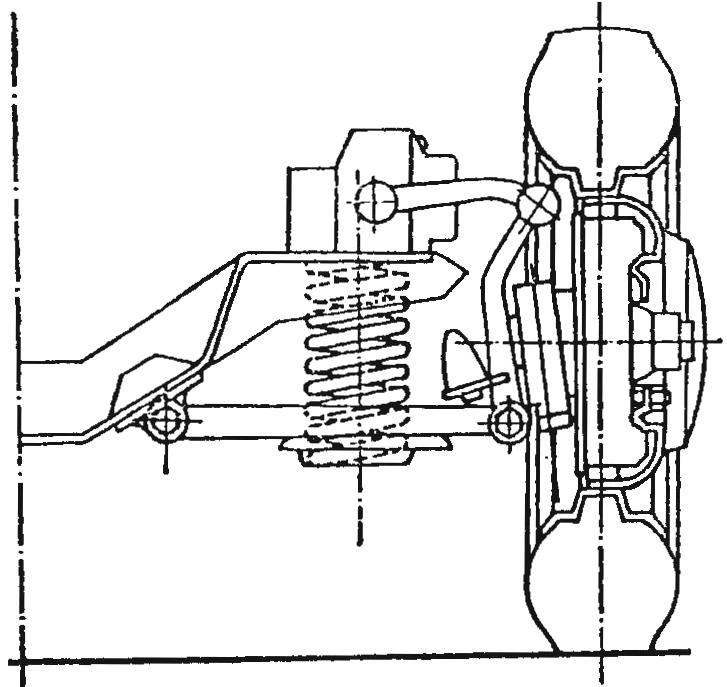
The front suspension of the car “Pobeda” GAZ-M20
The body of “Victory”
The car “Victory” in modification of “Ambulance”
The following passenger car, called the GAZ-M1 (“emka”), rolled off the Assembly line of the Gorky automobile plant in March 1936, replacing obsolete passenger car GAZ-A. the Basis of the new car was the FORD V8, which was replaced by the suspension (instead of Ford’s, transverse leaf springs, Gorky used longitudinal). The engine on the “emka” was still used, but after the upgrade he developed power of 50 HP and accelerates the car up to 105 km/h. unlike the previous model with an open body-a Phaeton with a folding tent, “emochka” was much more comfortable: she was a five-seater all-metal body-sedan.
The car is also a truck-pickup truck called GAZ-M-415. Further development of “emka” was released in 1940, the car GAZ-11-73 with the more powerful (76 HP) six-cylinder engine. The car got a new grille and a modified form of the vents on the hood sides.
A lot of “emok” was produced in the protective coating — before the great Patriotic war in the army, there were about 10 thousand of these machines. On the basis of GAZ-M-1 in 1936 produced light armored cars BA-20 with a 7.62 mm machine gun. And in 1941, on the basis of units “emka” was commercially produced four-wheel drive car-vehicle GAZ-61.
Work on the new car, later named GAZ M20, began in 1943. The first plaster model of this car in scale 1:5 was made in the factory sketches of the artist-designer Benjamin Smolin, who worked under the leadership of chief designer of the plant Andrei Lyphard. Design and layout of the study showed that the M20 is not another version of “emka” and a new design, largely forward the development of leading automotive firms.
I must say that the attempt to create a body without the traditional for that time of the fenders and foot pegs were already done, however, to construct a monocoque frameless body “pontoon”, as they said, improved aerodynamics (the drag coefficient of the car was 0.31) tried nobody here Gorky was the first. The fact that this time they did not use the traditional for the Soviet automobile industry, the method of borrowing and copying, and was able to summarize the world experience in the car industry and create on its basis a fundamentally new design and engineering concept that is not part of the technological differences with modest automobile.
The first prototype of the new car factory workers prepared for the November 6, 1944, followed by a small pilot batch. Before the start of production of GAZ M20 he was taken to the Kremlin in that time, no new car, no new aircraft and no new movie was not run of the series without the blessing of Stalin. Demonstration of the new machine took place on 19 June 1945. GAZ M20 has not made much of an impression on the President of the Council of Ministers of the USSR, and when the Director of the plant I.Rags asked Stalin for permission to call the car “Victory”, the answer came: “Not a big win but let it be a “Victory”.
A year later, in June 1946, started serial production of “Victory”. In its final form it was a four-door five-passenger car with a monocoque body, the type of which can be attributed more to the hatchback than the sedan. The machine was equipped with nizhnekayancha row “four” working volume of 2,111 liters and output of 50 HP. semi-detached with three-speed (three forward and one backward) transmission gear shift from “emka”. The front suspension of the car was spring, independent rear — spring, dependent, continuous beam. Brakes on all wheels drum, hydraulic. The maximum burst speed of “Victory” was 105 km/h.
Almost immediately after the release of GAS began to improve newborn car. In 1949, the car appeared improved clutch, rear axle, with increased gear ratio, improved carburettor. Also changed the design of leaf spring rear suspension and the location of the silencer. And one more “serious” revision, made on the observations of Stalin during a demonstration of the machine by 50 mm were omitted pillow back sofa. In 1950 was followed by another upgrade— car has a new synchronised gearbox, which replaced the one that got the M20 from the GAS withdrawn from the production of GAS M1, and instead of a floor shift lever stalk appeared.

“Victory”-a convertible with a folding top (1949-1953)

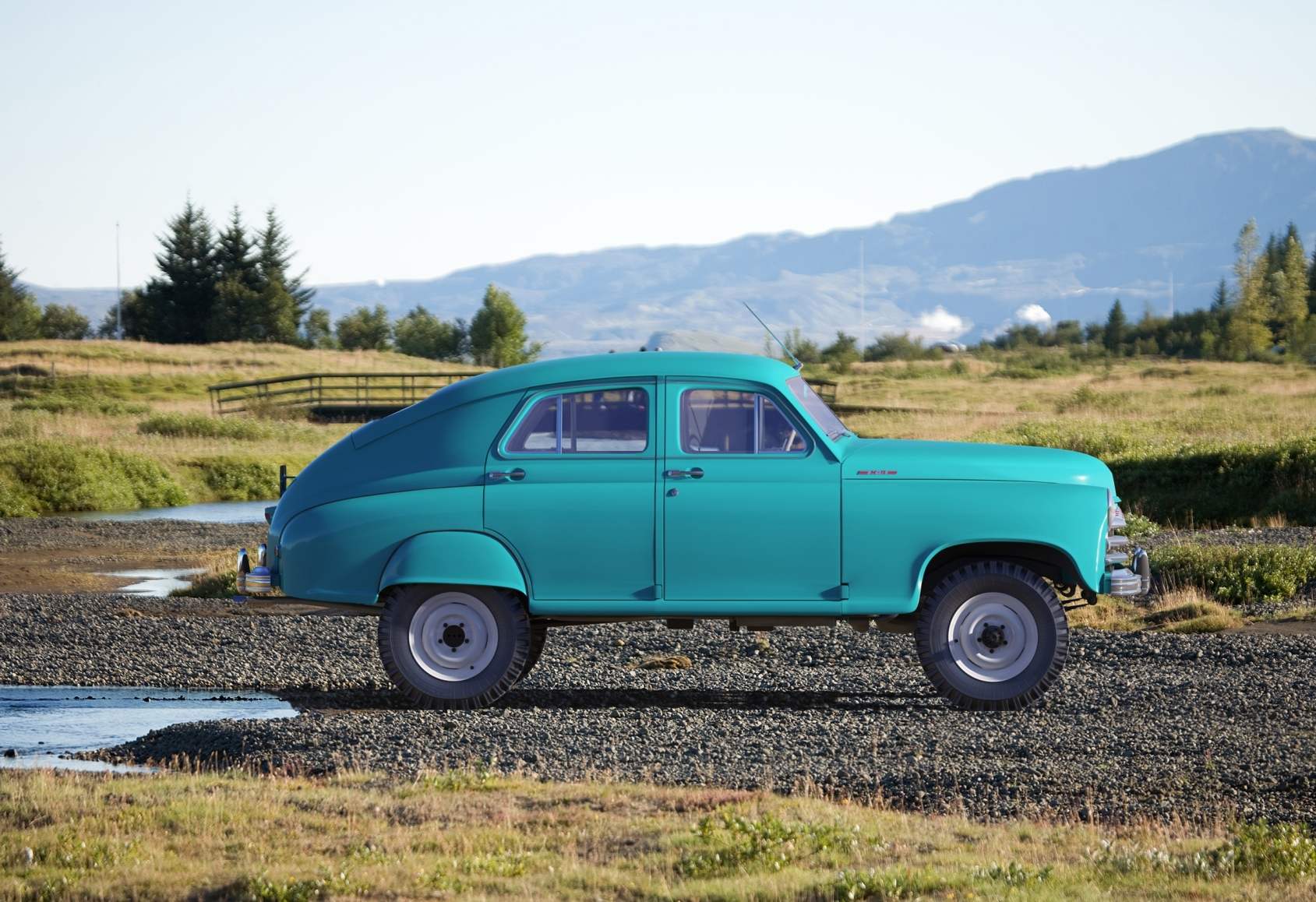
The car “Pobeda” GAZ-М20В (1955-1957)

Comfortable jeep GAZ-72 on the basis of units of “Victory” and the army SUV GAZ-69
The car WARSZAWA, produced under the Soviet license in the Polish FSO plant (side of the square grid is 200 mm)
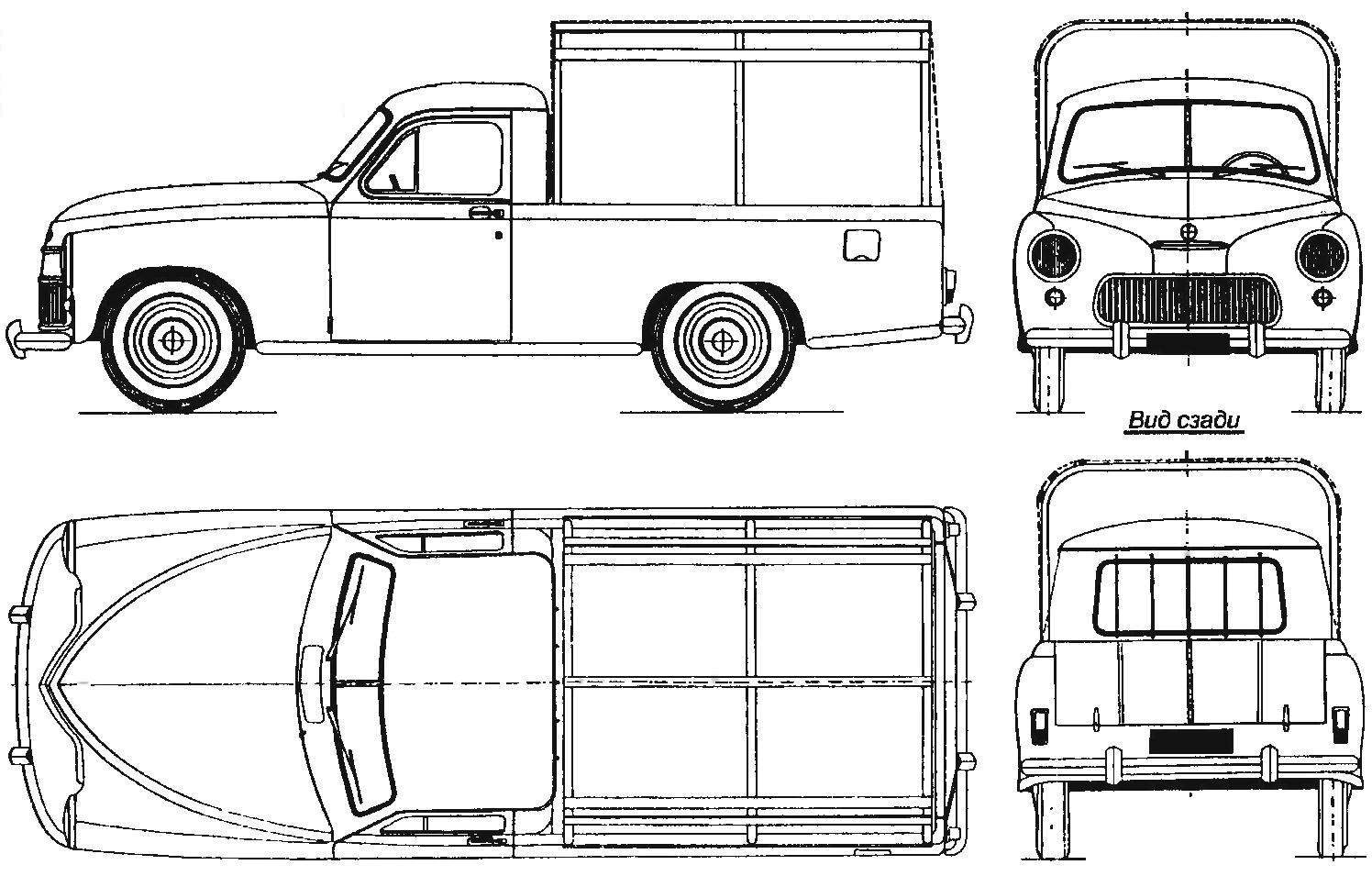
Cargo modification of the Polish “Victory” — WARSZAWA PICK-UP
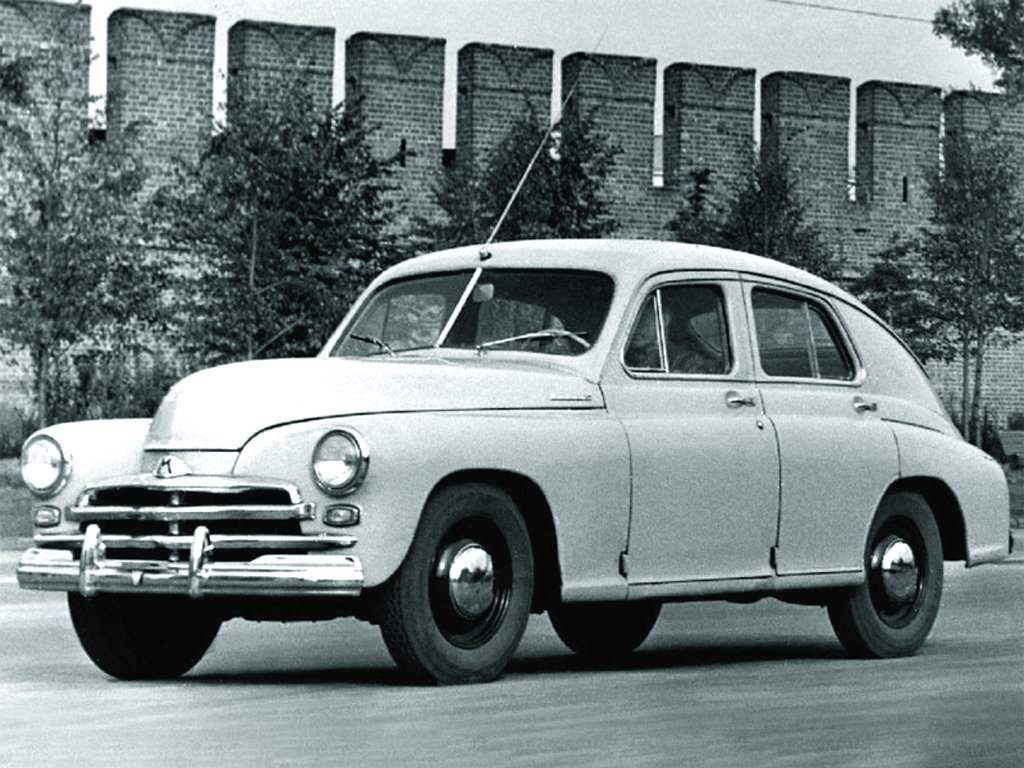
In 1955 he was made a regular upgrade of “Victory”, the designation GAS М20В. Externally, it differed from its predecessor only changed the grille. However, there was increased engine power, improved carburetor, upgraded water pump, front wheel bearings and the steering gear. In the lounge there is a radio (of course, the vacuum tube) equipment, at the time unthinkable for the domestic mass of the car.
In 1955, the plant produced version of “Victory” with a canvas-top convertible. Thus was formed the roof, and durable doorways provide the necessary rigidity to the body.
In addition to General-purpose vehicles, the plant produced specialized versions — taxi and “ambulance”. The first was distinguished by two-tone colouring (dark grey body with the hood and the roof of a milky color) with “checkered” along the entire side, green light in the corner of the windscreen and the taximeter; the second had a folding rear seat consisting of two parts, and equipped with folding stretcher, loaded into the car through the door.
The interior of the car was incredibly rich, of course, by the standards of the time. In the center of the dashboard, under the big chrome says “Automobile plant named after Molotov” — built-in radio receiver. The right and left of it are the same size and shape of numerals of the speedometer (left) and electro-mechanical watches (right). From behind the wheel with a thin plastic rim, ivory, in front of the driver — a combination of instruments: ammeter, fuel level in the tank, coolant temperature and oil pressure, as well as several warning lights.
Arm gearbox located under the steering wheel, approximately where most cars steering-column mounted lever for windshield wiper (on the first editions of the CAT from “emka”, the shift lever was on the floor). Control pedal “gas”, “brake” and “clutch” were outdoor. Parking brake handle red set to the left of the driver, under the instrument panel.
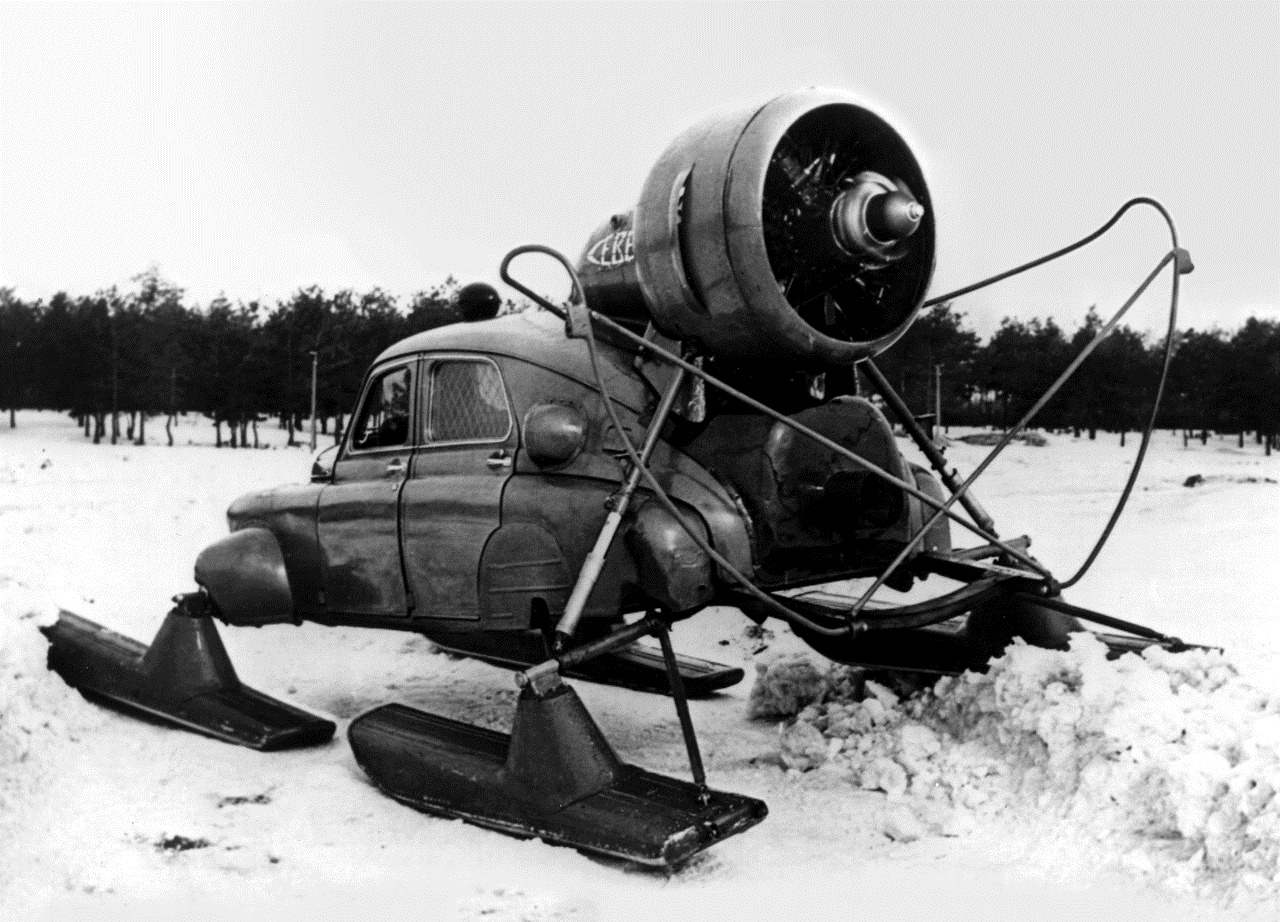

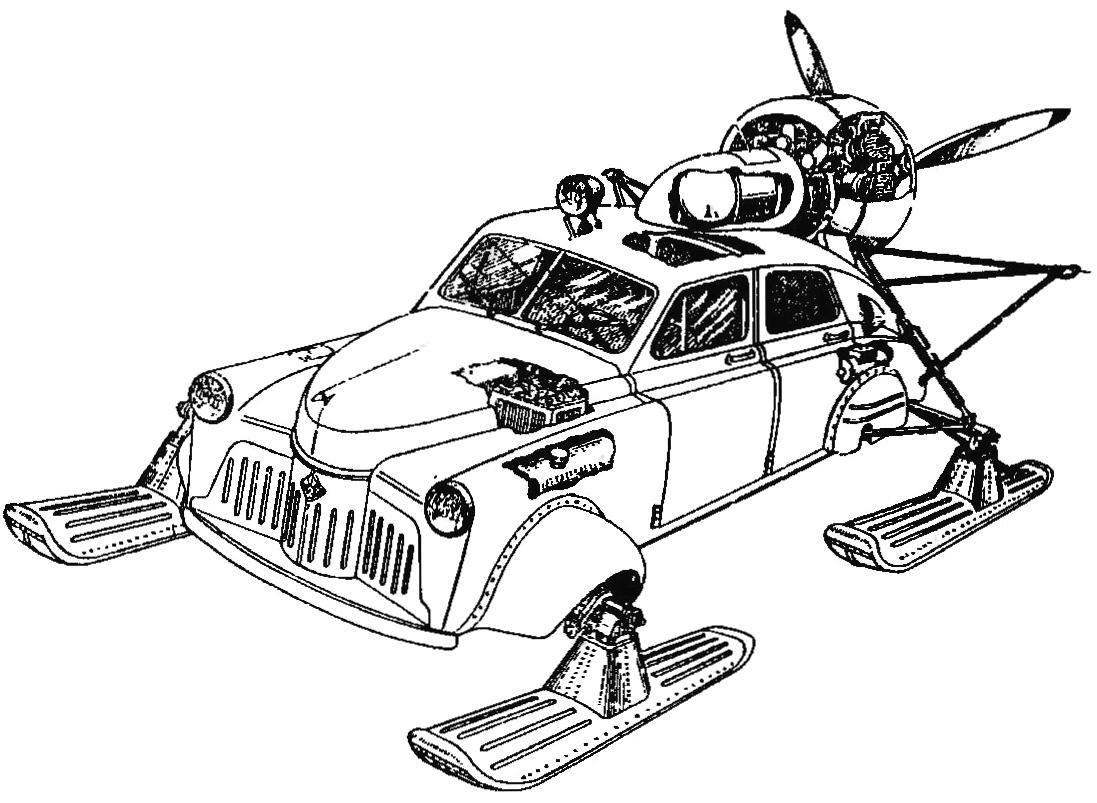
The post snowmobile “North-2”, created on the basis of a body of “Victory” in design Bureau N.And.Kamov
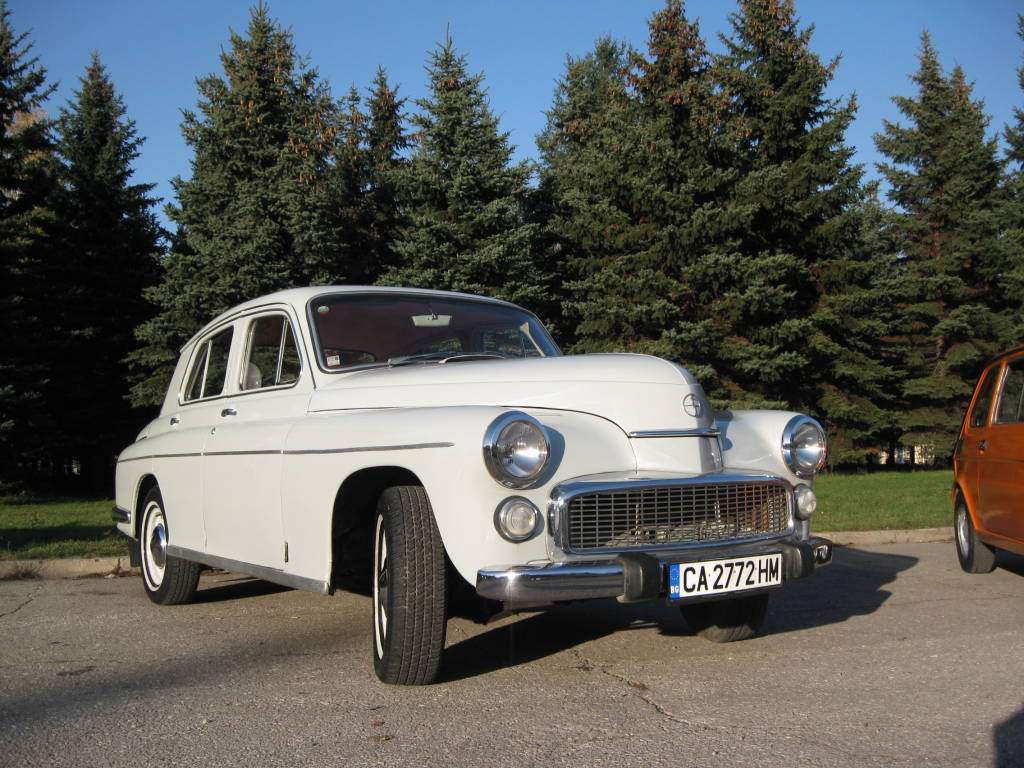

The last Polish modification of the “Victory”—WARSZAWA 223 with a notchback sedan and a panoramic windscreen
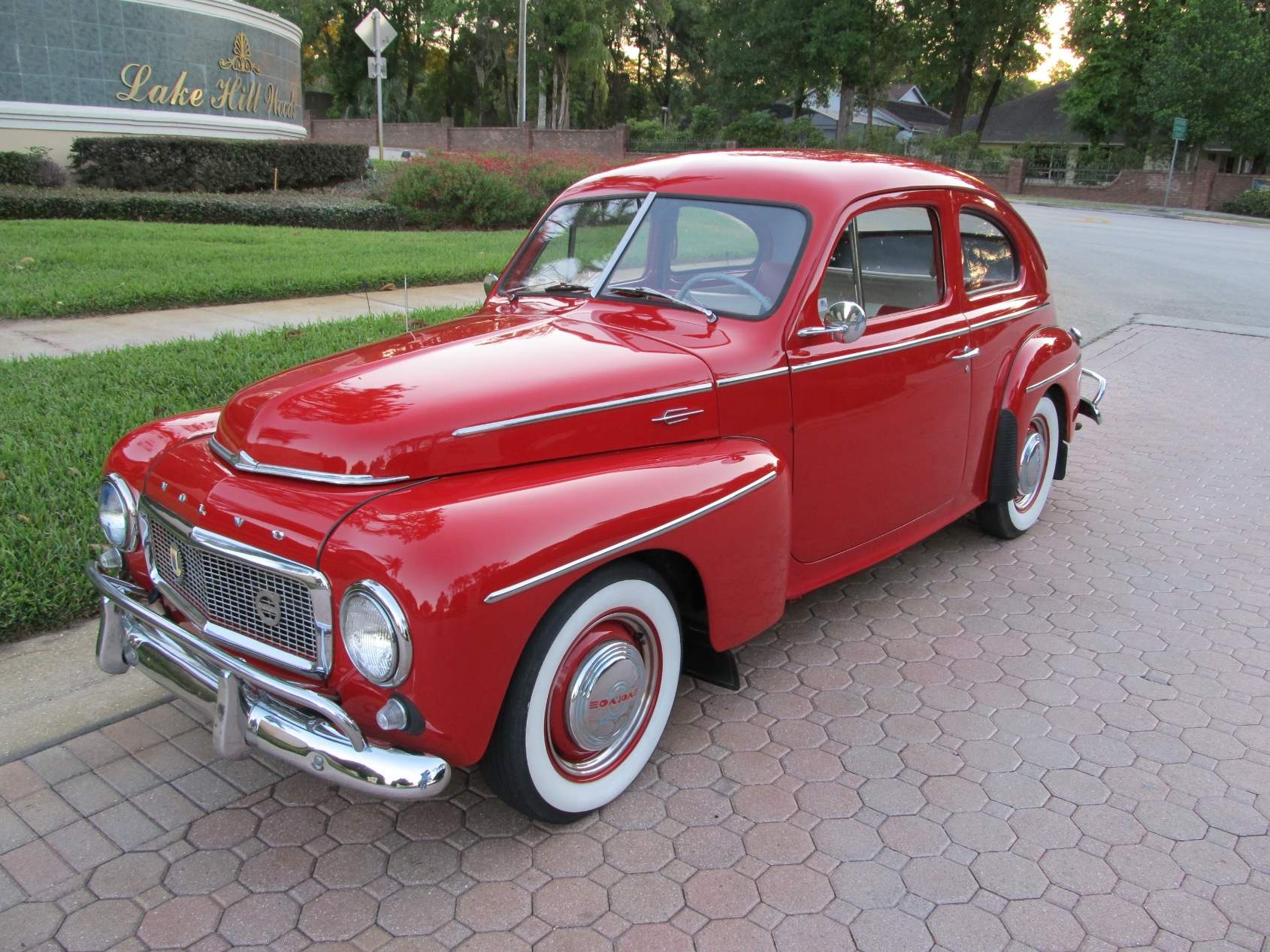

The Swedish equivalent of “Victory” — a two-door VOLVO PV-444
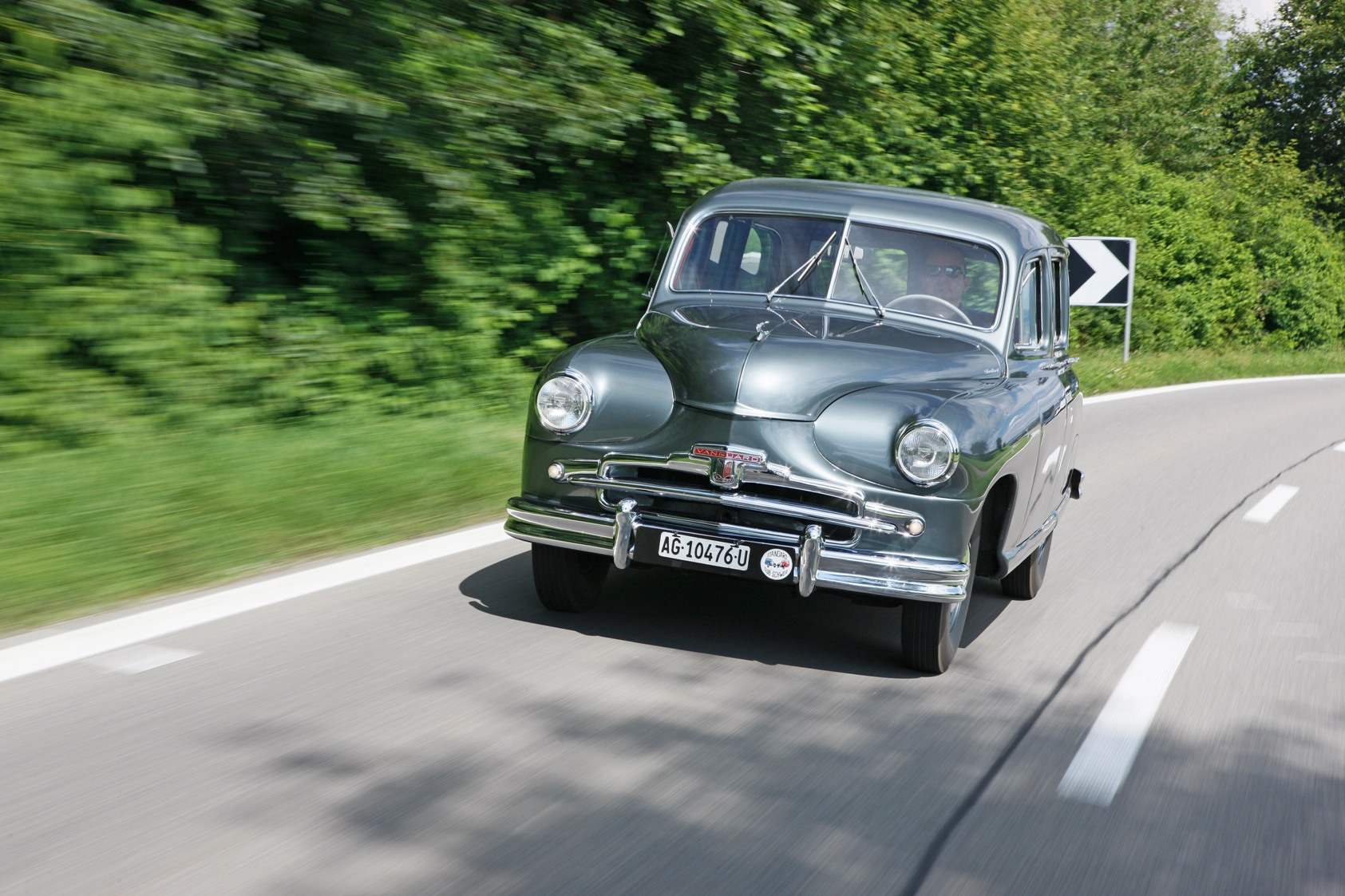

The English equivalent of “Victory” — a four-door STANDARD VANGUARD
The car was equipped with a ignition lock, however, it was only possible to include an electrician. The starter of “Victory” run with your foot on the pedal “gas” to this end was mounted button: the driver was hitting it with the toe of his Shoe, at the same time the heel adding “gas”.
Seat — divan type. The front can be moved forward or backward in accordance with the height of the driver, but adjust the backrest angle.
“Victory” became the first large domestic car equipped heater unit, it is necessary in the middle lane of the Soviet Union, where negative temperatures are dominated by about six months. In machines of the earlier releases of the driver is required in the winter to dress warmly and to carry a small bag of salt to wipe the glasses to avoid fogging and frosting.
“Victory” was produced by the factory until 1958. Total production of cars of all modifications made 235 of 999 copies.
In automotive publications describing this truly outstanding car, often published statements that a number of foreign automobile firms after the release of “Victory” put on the conveyors copies, passing them off as original designs. Studies have shown that the designers of these companies is likely to come to this decision. By the way, this view was held and the classic domestic car industry candidate of technical Sciences Y. Dolmatovsky, for many years worked in the editorial Board of the journal “modelist-Konstruktor”. Just Gorky, creating their “Victory”, was riding the crest of automotive science. And fine, that on the same crest rose and others — it merely meant that Gorky was the right way.
The number of machines — twins “Victory” — it’s usually two: English STANDARD VANGUARD and the Swedish VOLVO PV-444. The first being a four-seater convertible pontoon type, was presented to the public in 1947 — one year after the start of production of “Victory”. It seems that any avtostroitel confirms that to create tooling for the serial production of the new model in a year — it is a utopia!
Second car — VOLVO PV-444 — a copy of “Victory” can be called only conditionally. It was first shown to the public in 1944. All that, despite the clear “posadowsky” shit in her design, two-door VOLVO PV-444 had distinct wings, which are completely absent on “Victory.” In short, the coincidence in the appearance of “Victory”, STANDARD VANGUARD, VOLVO PV-444 show only that the us automakers were on the world stage!
The cessation of the production of “Victory” at the Gorky automobile plant has not stopped production of this car called WARSZAWA, it is still many years produced in Poland, while having undergone a number of upgrades.
The first WARSZAWA, does not differ from the “Victory” rolled off the Assembly line car company Fabryka Samochodow Osobowych (FSO) in November 1951. Initially WARSZAWA was a exact copy of the GAZ M20. But gradually it began to modernize, first by car has a new grille, and then assembled in Poland increased engine power (up to 57 HP). The following revision has made “paradowski” body in classic three-box sedan with a normal rear trunk — this car called WARSZAWA-203, appeared in 1964. Last modification of “Victory” — WARSZAWA-223 — was produced until 1973.
Leafing through the pages of history, “Victory”, we can not stay on the head about how this car became the progenitor of the concept of comfortable SUVs — the cars of foreign automotive firms at the time not even thought of. This SUV received the name of dry GAS M72, was established on the basis of a body of “Victory” and units of the army all-terrain vehicle GAZ-69. The vehicle was equipped with a transfer box with switchable and dual leading front axle. With 16-inch wheels with extended lugs (so now equipped with all-wheel drive Niva) machine had increased the ground clearance that it provided good flotation in mud, sand, snow, arable land and rough roads. The car was produced in small series from 1955 to 1958 and was intended mainly for rural economic and party managers. It is a pity that the line of such machines has not received a worthy continuation for our country, with its off-road a vehicle was priceless.
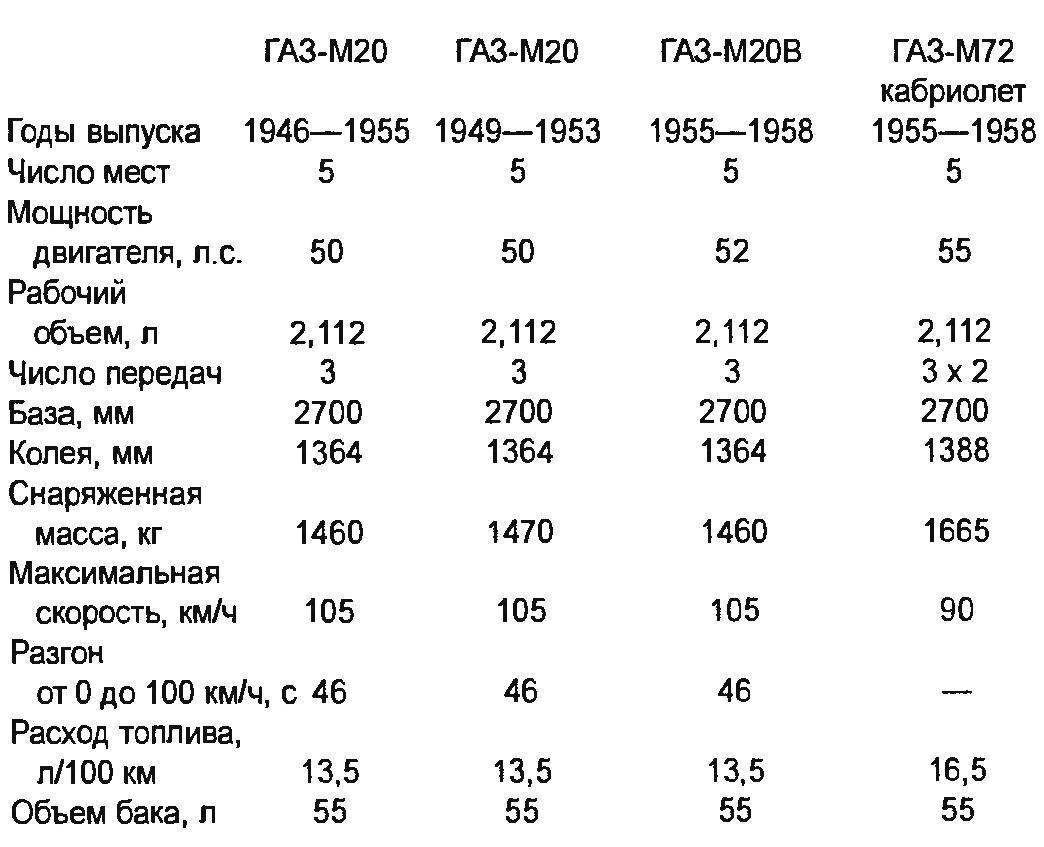
Technical specifications of cars “Victory” of various modifications
I want to mention about another incarnation, in which were all the same “Victory”. In the late fifties of the USSR Ministry of communications ordered the experimental design Bureau N.And.Kamov involved in the creation of helicopters of the coaxial scheme, the development of the post of the snowmobile to remote areas of the far North, Siberia, Kazakhstan and the Far East. A year later at the zip line received the first snowmobile “North-2”. It was chetyrehrazovoe vehicle with the body of the car “Victory” and rotor setup on the basis of a piston aircraft engine AI-14РС with power of 191 HP, designed by A. Ivchenko with a pusher three-blade propeller. Characteristically, the snowmobiles were supplied serial “Poberovskii” body, which was subjected to only minor modifications. The car was insulated and equipped with auxiliary heater, allowing it to operate at temperatures down to minus 55 degrees. The maximum speed for Aero-the”Victory” was 60 km/h, a cruising range reached 360 km Snowmobile “North-2” was produced from 1959 to 1963.
In automotive flows among domestic and foreign cars there, he catches a glimpse of a familiar silhouette of “Victory”. Yeah, no wonder the owners of this car believed to be neisnesamos of the body and the units “Victory”. There was even a legend that the body of this car was tinned. However, it is not so. Just one of the ways of elimination of defects of stamping of body parts was leveling the surface with solder. When the body repairs under the old paint were discovered shining tin zone, the presence of which gave rise to this legend. However, a lot of “wins” is perfectly preserved to our time as a kind of embodied a reproach to the domestic car-from designers and engineers of the forties, which in difficult conditions managed to create one of the most advanced cars of its time.
I. EVSTRATOV