Electric ПБ21-01 was not at the time. It was built in the time when electrified heavy mountain sections of Railways where the maximum speed was limited to brakes, and where driving passenger trains successful freight locomotives. Electrified suburban areas were still too short to enter them on locomotive traction. Fast ПБ21 in the 1930-ies was simply nowhere to show their speed. By the time when they electrified the direction of Leningrad-Moscow, Moscow – Kharkov, Moscow – Minsk and others, where exploitation of high-speed ПБ21 could be justified, he has already become obsolete.
ПБ21-01, unlike many other locomotives, such as the aforementioned high speed engine type 2-3-2, lucky not to turn into scrap metal. Along with a few unique locomotives, he received the status of a monument. A long time standing in depot Perm II, in 2003, the honored cars were transferred to Ekaterinburg, where on-site locomotive depot Sverdlovsk-sorting was organized by the Museum of the Sverdlovsk railway. Unfortunately, now ПБ21-01 is significantly different from its original appearance. Apparently, lost forever mechanical compressors. The original floodlights replaced by “pots” from the PL-54. Disappeared invoices, letters and numbers number and series, as well as name plates and unique star with the words “behalf of the Politburo of the Communist Bolshevik party” and portraits of members of the Central Committee. Removed buffers, screw couplers replaced with automatic couplers. Window openings are sewn up with iron. Nevertheless, we hope that the restorers would ever return to him his former appearance and it will become like the car that struck the imagination of our countrymen in the distant 1930-ies.
TECHNICAL DATA OF ELECTRIC ПБ21
Axial formula…………………………..2-S0-2
The nature of the service……………………..passenger
Hour power, kW…………………..2040
Continuous power,kW………………1800
Hour traction force, kgf……………………10500
Prolonged traction force, kgf……………….9000
Design speed, km/h……140
The coupling weight, t……………………………………67
Total weight, t…………………………………….131
Diameter of driving wheels, mm…………1850
Bedunkovich diameter of wheels, mm………..1050
The minimum radius
passable curve, m………………………150
Predatore number
traction reducer…………………………3,025
S. JEVAC
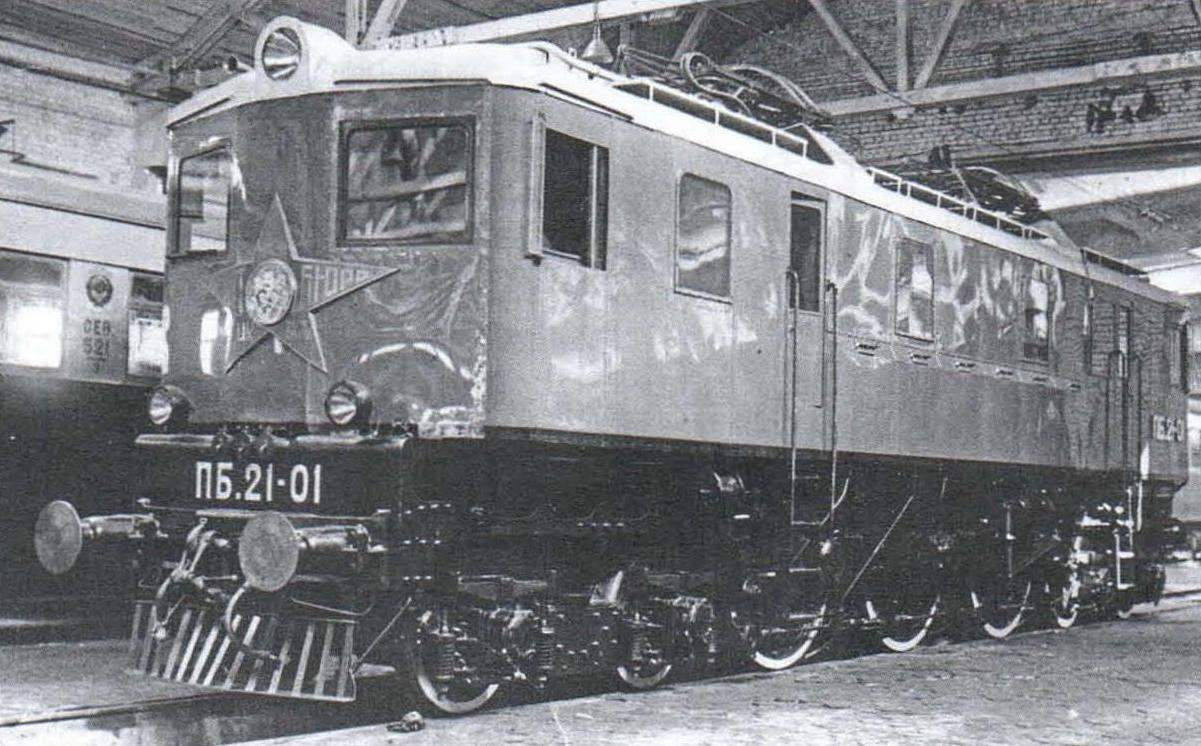 Locomotive PB-21 of issue, 1934. In the early 1930-ies the USSR had embarked on the reconstruction of Railways, in particular, the decision not to build cars with the number of axes less than four. Rolling stock was assumed to be equipped with automatic couplers and air brakes automatic. For the traction was designed and built powerful locomotives – freight and passenger FD IP. It was planned and the electrification of the Railways; it was built Сс11 electric locomotives, cargo and passenger vehicles ВЛ19. In addition, the Central lokomotivostroenie Bureau (CLPB) together with the plant “Dinamo” has designed a locomotive designed for pure passenger services. It was a very original car, not like any one of the locomotives of the time. Moreover, this engine was absolutely unique – a hitherto nothing of the kind in our country were not built.
Locomotive PB-21 of issue, 1934. In the early 1930-ies the USSR had embarked on the reconstruction of Railways, in particular, the decision not to build cars with the number of axes less than four. Rolling stock was assumed to be equipped with automatic couplers and air brakes automatic. For the traction was designed and built powerful locomotives – freight and passenger FD IP. It was planned and the electrification of the Railways; it was built Сс11 electric locomotives, cargo and passenger vehicles ВЛ19. In addition, the Central lokomotivostroenie Bureau (CLPB) together with the plant “Dinamo” has designed a locomotive designed for pure passenger services. It was a very original car, not like any one of the locomotives of the time. Moreover, this engine was absolutely unique – a hitherto nothing of the kind in our country were not built.