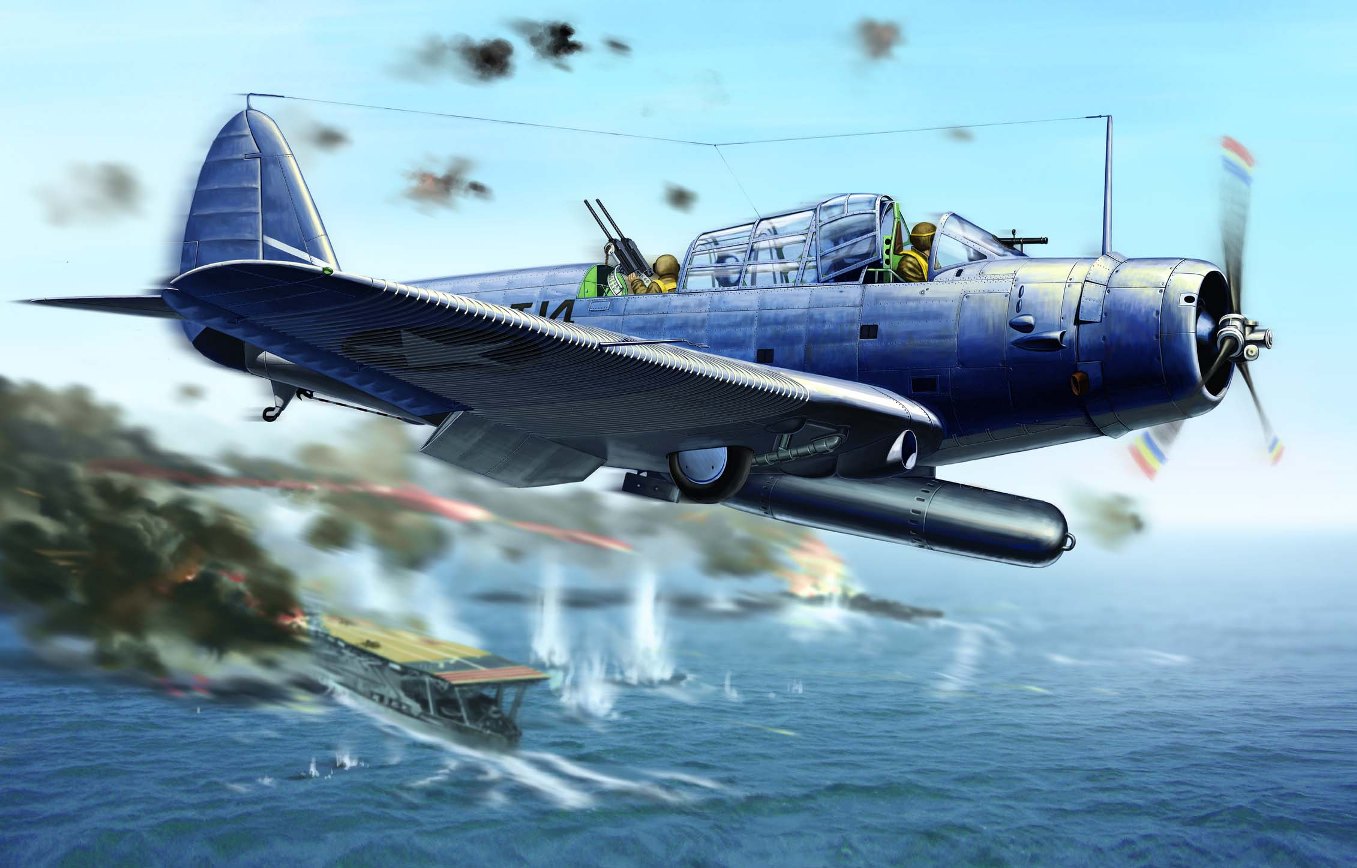
Torpedo bomber TBD-1 Devastator. In 1927, for service with the us Navy received the first aircraft carrier of special construction — the Lexington CV-2 and Saratoga CV-3. Then, in 1934, they were joined by “Ranger” CV-4. Began a large-scale program of rearmament of the fleet. Until the end of 1941 it was planned to build and put into operation four more ships: the “Yorktown” CV-5, enterprise CV-6, “Wasp” CV-7 and hornet CV-8. Their weapons required new advanced combat aircraft, because each was planned to accommodate up to 90 vehicles: fighters, dive bombers and torpedo bombers.
Torpedo bomber TBD-1 Devastator. In 1927, for service with the us Navy received the first aircraft carrier of special construction — the Lexington CV-2 and Saratoga CV-3. Then, in 1934, they were joined by “Ranger” CV-4. Began a large-scale program of rearmament of the fleet. Until the end of 1941 it was planned to build and put into operation four more ships: the “Yorktown” CV-5, enterprise CV-6, “Wasp” CV-7 and hornet CV-8. Their weapons required new advanced combat aircraft, because each was planned to accommodate up to 90 vehicles: fighters, dive bombers and torpedo bombers.
In June 1934, the Bureau of Aeronautics of the Navy (BuAer) asked the aviation firms to develop new bomber-torpedo bomber to replace the obsolete biplanes Т3М and Т4М Martin, developed under the contract of 1925. Needed replacement and bomber Martin BM-1, established in 1928. All of these aircraft were in service squadrons of aircraft carrier “Langley” CV-1, the “Lexington” and “Saratoga”. It was a biplane with many struts and braces, exposed radial engines R-1690 firms Pratt & Whitney and fixed landing gear. The maximum flight speed of these machines did not satisfy the military: the torpedo Т3М and Т4М it was 184 km/h and the bomber VM-1 — 236 km/h, at a time when the fighters had a top speed of over 400 km/h.
Such speeds were expected from the military and a new torpedo. They counted on aircraft with a greater combat load. The torpedo was supposed to be used with three variants pendant weapons: torpedoes Mk.XIII, three 227-kg bombs or a combination of the twelve 45-kg bombs and one 454-kg bombs. As the power plant was proposed to use the latest engine, the XR-1830-60 firm Pratt & Whitney power 800 HP, which has just been finishing the test and run in production.
In the competition participated company Great Lakes and Douglas. Both companies offered to build prototypes of their aircraft. Torpedo bomber and Great Lakes XTBG-1 (serial number 9723) was built according to the biplane scheme. The fuselage was of all-metal construction, and wings and tail tight fitting cloth. The Bombardier and the pilot was located one behind the other, and the front was a scorer who used a telescopic sight with a window, a door under the fuselage between the landing gear. In the process of testing a torpedo Great Lakes XTBG-1 revealed that it has mediocre flight performance in the air behaves erratically, and the design it requires major improvements. All of this was the reason that the biplane Great Lakes production was not adopted.
A different opinion has been formed about the monoplane XTBD-1 (number 9720) by Douglas. This aircraft was the first not only by its symbol but also the first all-metal carrier-based monoplane, the first carrier-based aircraft with a hydraulic folding mechanism of the wing, the first torpedo with the torpedo, half-hidden in the fuselage and, finally, the first carrier-based aircraft with the brakes of the main landing gear wheels.
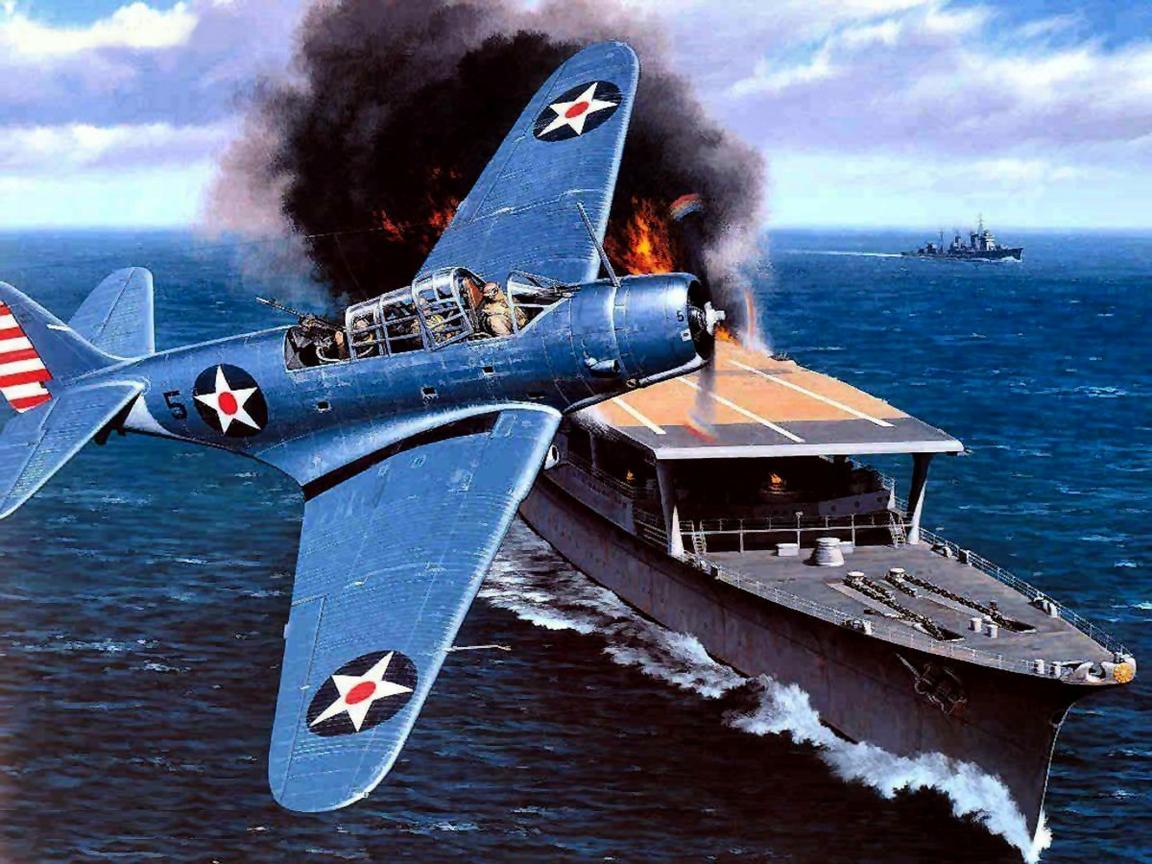

Carrier-based torpedo bomber TBD-1 DEVASTATOR by Douglas
The plane caused great surprise at the Commission’s fleet. He differed from project VT-VB with drawings that are familiar to the specialists of the fleet during the first stage of the competition. In a short time the project has been completely redesigned, and now before them stood a handsome all-metal low wing. Landing gear was cleaned only half, however, as did the representatives of the company, this design feature of the aircraft was more advantage than disadvantage: during a forced landing exposed wheel protects the fuselage from damage. Under the cabin were the latest optical sight of company Norden Mk.XV. Very long, the canopy has a few sliding sections and their appearance resembled the glazing of the greenhouse. The pilot sat in the front, gunner in the back, and in his possession was a turret with 7.62-mm machine gun “Colt-Browning M2” with six hundred rounds of ammunition.
Weighing of the aircraft before the first flight showed that the empty weight is 2371,5 kg and the maximum takeoff weight with a torpedo — 4018,5 kg. Fifteenth day of April 1935 XTBD-1 took to the air, and nine days later he was sent to naval base in Anacostia for military tests. Flying from the deck of the USS Lexington began on December 5, 1935. Marine pilots W. Davis, D. Anderson and S. Anderson has completed 13 take-offs and landings with the use of arresting gear. They put the final assessment of the aircraft— “excellent”. Landing speed was only 102 km/h Maximum speed of the aircraft — 324 km/h, with a full bomb load -194,4 km/h, and with the torpedo -162 km/h flight Range with a torpedo was 704 km and with a full bomb load is 1134 kg. testers were more restrained, but they were satisfied. Identified design flaws representatives of the firm Douglas has promised to eliminate on production aircraft.
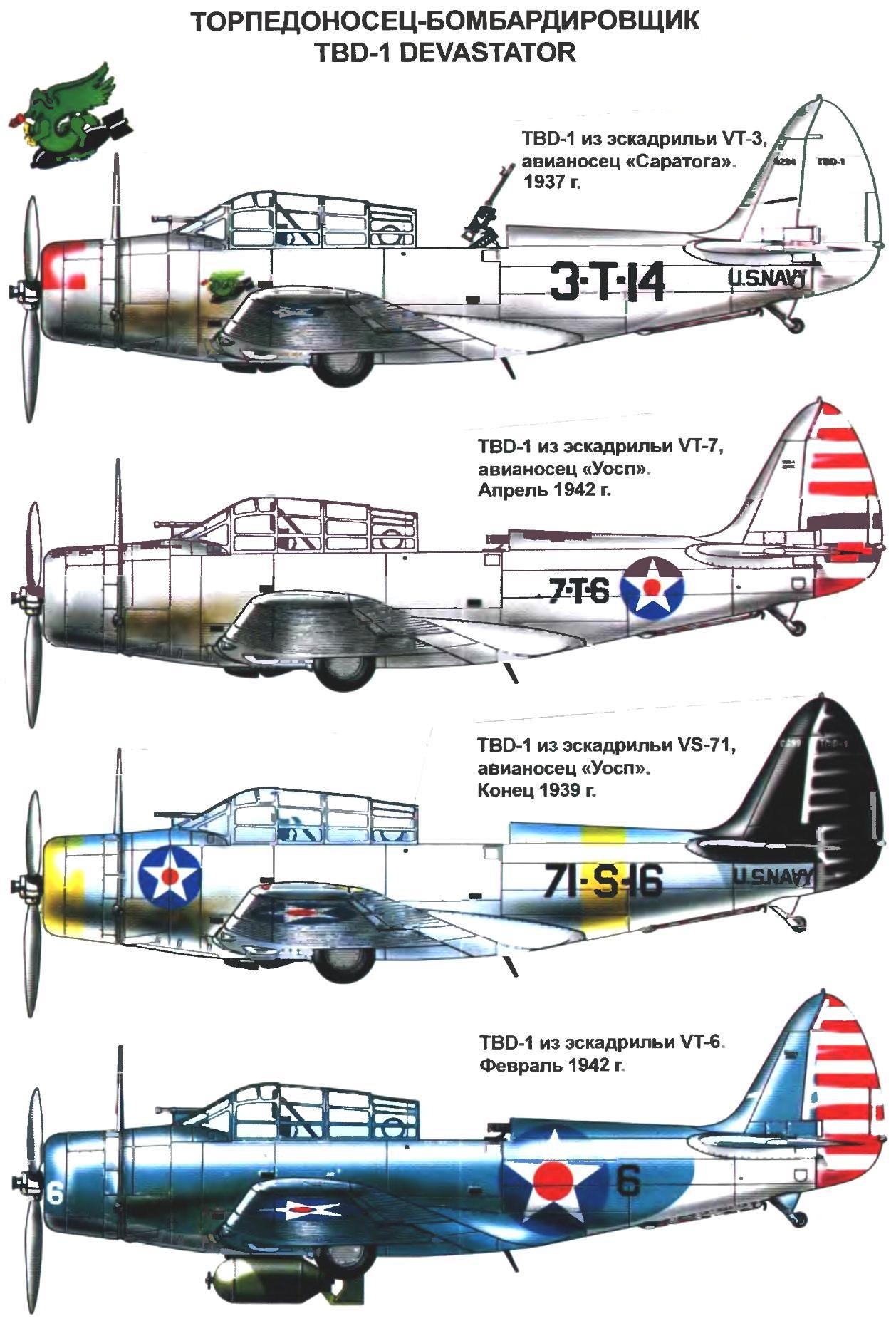
Torpedo adopted January 16, 1936, and February 3, with the firm Douglas signed a contract for the production of 114 aircraft (serial numbers with 0268 for 0381). The prototype remained at the firm for testing engines.
To improve visibility on production machines replaced the lamp on more convex. Now it consisted of seven sections, four of which are shifted. The oil cooler was moved from the lower surface of the fuselage on the right console wing, and he hid the carburetor air intake. From a retractable tail wheel refused.
The first production aircraft arrived at the military order of 27 June 1937. It was a more powerful engine Pratt & Whitney R-1830-64 power 900 HP with three blade propeller variable pitch. The area of the keel was increased. This and the second car remained at the base in Anacostia for the various tests. The new torpedo can perform all aerobatics including loop the loop and barrel rolls. Loaded with bombs, the plane managed a few sluggish.
To keep the machine afloat in case of a forced landing on water, the designers have provided a rubberized bags. Located in the wing, they can be inflated automatically or at the request of the pilot has in the cockpit was the valve from the balloon with carbon dioxide.
The third TBD-1 was transferred to fighting squadron VT-3 from USS Saratoga October 5, 1937. This unit played an important role in the fate of the plane, it was in VT-3 revealed the advantages and disadvantages of the machine. So, a lot of trouble caused by the system of folding the wing. According to the instructions the wing fixed in deployed position with locking pins with red flags. Before takeoff the pilot had to check their availability and reliability of fastening. One of the pilots died, forgetting to check the pins before flight. And during the maneuvers of 1937, which was simulated by a sudden torpedo attack on pearl Harbor, the wings of the cars suffered greatly from sea water, and in early 1938, the division had to replace the covering on the wings of aircraft.
Sixteenth of August, 1938, the Navy ordered 15 of the planes to replace the lost of disasters and training of flight personnel. This small series was distinguished by wider paths for walking on the wing and swapped in the new rear tail lights.
Enter the fleet of modern aircraft carriers have always received new torpedo. On each ship was based a squadron, consisting of 12—15самолетов. First TBD-1 were on all carriers, except the “Yorktown”, which had a shorter deck. In the end, and “Yorktown” still received his squadron VT-5, consisting of TBD-1, but using only these planes as bombers.
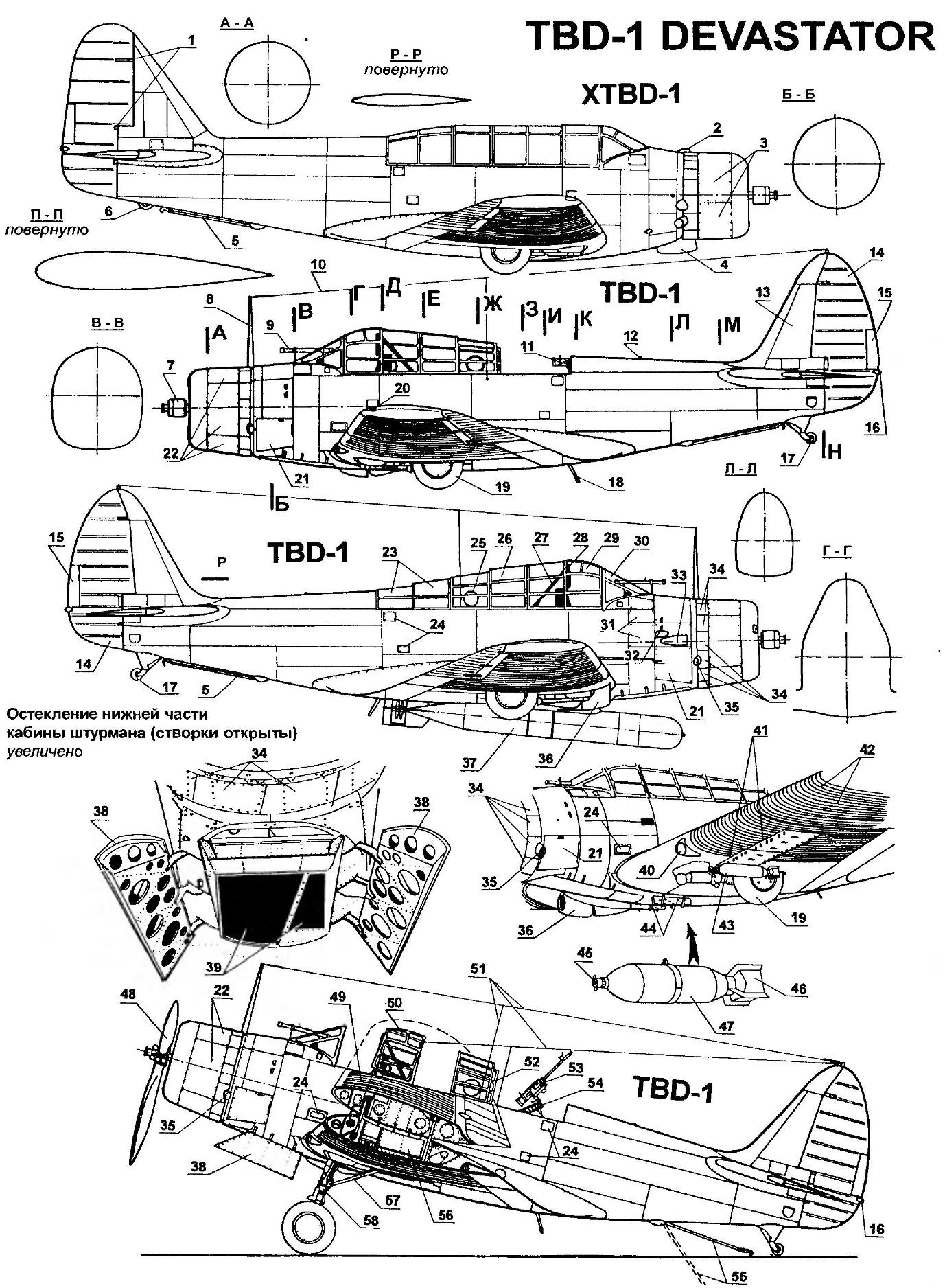
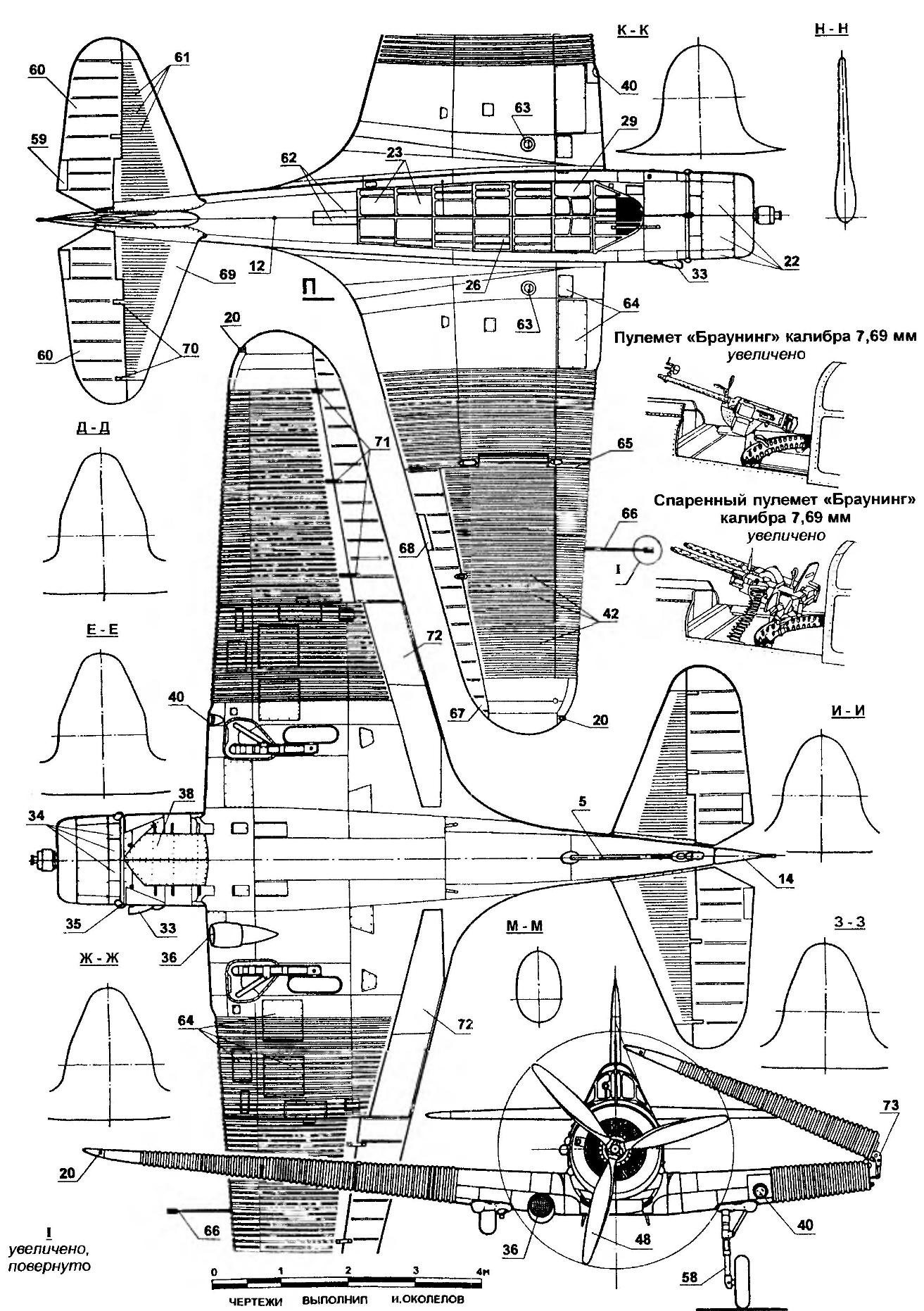
Carrier-based torpedo bomber TBD-1 DEVASTATOR:
1 — hinge of the rudder; 2,33 — carb intakes; 3 — removable hatches engine of the prototype; 4 — cooler; 5 — boarding plus; 6 — tail wheel in the retracted position; 7 — bushing of the propeller; 8 — the mast of the radio antenna; 9 — telescopic sight Mk.III; 10 — antenna; 11 — machine gun in the retracted position; 12 — drill-fire; 13 Kil; 14 — rudder; 15 — trimmer of the rudder; 16 — position light; 17 — the tail wheel; 18,24 footpegs; 19 — wheel main landing gear in the retracted position; 20 — ANO; 21,22 — hatches of the engine; 23 — section sliding canopy arrow; 25 — antenna radio compass; 26 — sliding canopy of the Navigator; 27 — protivokapotazhnoy frame; 28 — the pilot’s headrest of the chair; 29 — sliding the cockpit canopy; 30 — visor of the cockpit; 31 — detachable operating panel exchange machine gun; 32 — fairing machine gun; 34 — fold shirts fairing of the engine; 35 — exhaust pipes; 36 — oil cooler; 37 — torpedo Mk.XIII; 38 — fold lower cab glass Navigator; 39 — the lower cabin Windows Navigator; 40 — landing light; 41 — removable panel bomb racks (for three bombs); 42 — corrugated wing skin; 43 — 45-kg bomb; 44 — fuselage bomb racks; 45 — fuse bombs; 46 — stabilizer bombs; 47 — 227-kg bomb; 48 — the three-bladed steel propeller variable pitch; 49 — left wing tip of the wing in folded position; 50 — the cockpit canopy in the closed position; 51 — option cable radio antenna (in the later series); 52 — canopy arrow in closed position; 53 — 7,69-mm machine gun “Browning”; 54 — the turret ring; 55 — a boarding hook in the released position; 56 — end rib of the center section; 57 — strut main landing gear; 58 — the main landing gear; 59 — trimmer of the Elevator; 60 — blade pitch control; 61 — corrugated casing of the stabilizer; 62 — fold niche of cleaning the aft machine gun turret; 63 — cap filler centroplane fuel tanks; 64 maintenance hatches of the wing; 65 — line fold of the wing; 66—Pitot tube (Г1ВД); 67 —Aileron; 68 — trimmer Aileron; 69 — stabilizer; 70 — the hinge of the Elevator; 71 — hinge Aileron; 72 landing brake pads; 73 — node folding cantilever wing
In 1939, the US Navy began developing a float patrol bomber based on TBD-1; the modification was designated TBD-1A. This machine is the retractable landing gear under the fuselage by N-shaped struts were fixed duralumin floats with a length of 8.8 m. In the future, the Americans invited the government of the Netherlands to buy a plane. At the request of the Dutch, on the plane put the engine GR-1820-G105A company Wright power of 1200 HP, the same engine put on a fighter Buffalo, already delivered in the Netherlands. In addition, the aircraft increased the area of the rudder. Negotiating the purchase of cars stopped in 1940 after the capture of the Netherlands by the Germans. All attempts by Douglas to sell the float plane to someone else failed, and the project was closed. Seaplane TBD-1A remained at the disposal of the Navy, which used it for testing torpedoes at Newport torpedo station.
In 1940 the U.S. Navy conducted a variety of experiments to find the most effective painting of aircraft carrier-based aircraft. In these experiments, participated at least two squadrons of TBD-1; VT-3 and VT-5. It was supposed to develop a color scheme that mislead pilots of the enemy relative to the direction of flight and the spatial position of the machine. Testing ended in the fall of 1940, though, and showed the fallacy of the conception, but, nevertheless, helped the Navy to develop a standard color scheme.
October 1941—the day is very significant for torpedo aircraft of the United States. On this day, TBD-1, the first carrier-based torpedo bombers, got its official name DEVASTATOR (Devastator, destroyer — eng.). This formidable name reflected the mood of the time.
In late 1939, the aircraft TBD-1 began to take part in patrolling the Atlantic in search of German submarines, the so-called “Neutral patrol”. Cars that took part in these flights, were of a bright color with yellow wings and colorful bonnets. Later, with the deterioration of the international situation, the aircraft is painted in standard sea camouflage. In late 1940, with the wings of the TBD-1 began to dismantle the inflatable bags to prevent accidental capture by the Germans on modern aircraft.
Baptism of fire of the torpedo took place on 10 January 1942 — on this day four TBD-1 DEVASTATOR from the USS Lexington attacked with depth charges a Japanese submarine. Later, in March TBD-1 sank a small Japanese ship.
The following episode occurred on 7-8 may 1942 in the coral sea. Interestingly, in a naval battle, in which participated TBD-1 DEVASTATOR ships for the first time in history not exchanged a single artillery shot — all decided based aircraft. The seventh of may at 11.00 more than seventy American planes attacked the Japanese light aircraft carrier”, secho”, the ship was hit by 13 bombs and seven torpedoes. The carrier exploded and a quarter of an hour sank. The eighth of may at 11.20 seventy Japanese planes attacked the American aircraft carriers “Lexington” and “Yorktown”. The Lexington received a direct hit by two torpedoes and three bombs. Six hours later the ship started a huge fire and the Americans had to finish the aircraft carrier by five torpedoes. “Yorktown” was only one bomb, the aircraft carrier returned to pearl Harbor, where for two days they renovated and put to sea, having Medeuskogo to the beginning of the battle. In this battle, three torpedo bomber TBD-1 was shot down by anti-aircraft fire and squadron VT-2, consisting of 12 aircraft, was killed along with the “Lexington”. And yet here TBD-1 DEVASTATOR made a pretty good seven exact hits. As was stated by the pilots, hits could have been greater if not for the design flaws of the torpedoes MK.XIII. These statements of the pilots were well-founded. Some sources indicate and the shortcomings of the fuse, but now it became known that the main “culprit” turned out to be the casing of the warhead, miss sea water. The weight of the torpedo was increased, and she was in the deep, more calculated.

The main weapon of torpedo modified only by 1943. External difference between the upgraded torpedoes — ring stabilizer in the tail section.
It appears that these deficiencies coupled with the low maneuverability of the loaded torpedo aircraft resulted in huge losses among the TBD-1 DEVASTATOR during the battle of midway. In the course of only one attack aircraft carrier “Akagi” Japanese fighters managed to shoot down 14 flying machines from 26. All in all, the day of the 41 aircraft, only six returned. Losses can be ranked and two TBD-1, which made a forced landing in the sea after running out of fuel on the morning of 4 June. During the battle, there had been no contact torpedoes at enemy ships.
Large losses and low combat effectiveness forced the Navy to remove the TBD-1 from service. In combat formations, it was replaced by a more modern torpedo bomber AVENGER.
So far not survived a single aircraft TBD-1 —all the machines were lost in crashes or scrapped. Americans are desperately searching for the wreckage with tail number 0353, which on 2 September 1943 and she fell eight miles off the coast of Miami.
The design of the aircraft
Carrier-based torpedo bomber TBD-1 DEVASTATOR was a cantilever all-metal triple single-engine aircraft-the monoplane with low wing and retractable landing gear.
The fuselage truss. The power set consisted of frames, stringers and spars. Technologically, the fuselage was carried out in three sections: nose, Central and tail. The bow section ended with a fire shutter frame.
In the Central section housed a fully enclosed cockpit. Cockpit for improved visibility maximum forward and the pilot seat is installed with the elevation, compared to chairs of other crew members. All this gave the pilot excellent visibility on takeoff and landing. The chairs of the pilot and other crew members did not have a reservation.
The set equipment allows you to perform flights day and night, even in adverse weather conditions. All of the instrument panel in the cockpit, Bombardier-Navigator and the radio operator had illuminated, which provides flight at night and in the clouds. Front windshield visor of the cockpit, with a slight shift to the right was mounted a telescopic sight Mk.III exchange machine gun.
Behind the cockpit was a Navigator-Bombardier. In his cabin and navigation equipment and the latest bombsight the Norden Mark XV-C cabin Floor at gunpoint were glazed. In flight it was closed with two doors that could be opened only while aiming and dropping bombs.
In the cockpit the radio operator were in the control units, radio and 7,69-mm machine gun “Browning” (in the later series aircraft installed coaxial machine gun of the same caliber). In the stowed position the gun was cleaned in a special niche and closed the doors. Gunner was located in a comfortable seat, which was part of the design standard turret installation.
To tail section attached to the fin and stabilizer with the elevators and direction, as well as the tail wheel. Fuselage is dural, it consisted of panels of large size. The two-spar wing, free-bearing, of three sections — a center section and a pair of consoles, folding to the fuselage for storage of the aircraft on the aircraft carrier. The wing folding system is hydraulic. A large part of the wing and the wing had corrugated siding. Under the right side of the center section were located annular oil radiator fairing, on the left is attached to a landing light.
The entire rear edge of the folding wing panels held the ailerons, which had all-metal power set and a fabric covering. At the bottom of the center section across the span was placed flaps with hydraulic drive. To further reduce speed while landing on the aircraft carrier the ailerons could be deflected down and to work the flaps. In the center section were niches for cleaning the main landing gear wheels. The bottom of the center section could be installed removable panels (two on each half of the wing) with bomb racks for up to three 45-kg bombs. On the right wing mounted Pitot, and all the endings — navigation lights.
The tailplane, like the wing, it was dvuhlonzheronnoe. Power set — metal. Stabilizer and fin were trimmed with aluminum panels, and elevators and directions — cloth. Trim stabilizer — corrugated. On the rudders and height were trimmers, removing unnecessary effort from the handle control.
Control system misc: Elevator — hard, from the handle; the rudder, a flexible cable from the pedals. Trimmers were rejected when you turn the pilot knob.
Landing the device includes retractable tailwheel landing gear and landing hook. The main landing gear retracted into the fuselage on the flight back when the wheels were half of the niches. The system of harvesting and the landing gear is hydraulic. The main wheels were equipped with air brakes “Bendix”.
The power plant of the aircraft consisted of 14-cylinder air-cooled engine Pratt & Whitney R-1830-64 power of 900 HP, equipped with three-blade propeller variable pitch diameter of 3.12 m. On all models screw had no fairing.
Fuel tanks with a total capacity of 784 litres was placed in the center section of the wing.
Armament — simultaneous exchange 7,69-mm machine gun “Browning”, which in the later series of aircraft was replaced by a more powerful 12.7 mm machine gun. And the other was mounted on the starboard side of the aircraft, in front of the cockpit. The ammunition in the first case was 1000 rounds, and the second 500. In the cockpit, radio operator-gunner on the turret were 7,69-mm machine gun “Browning” with 600 rounds. In the later series of aircraft was located coaxial installation of two similar guns.
Bomb armament included to bombs weighing from 45 to 227 kg underwing and underfuselage bomb racks. The last could be suspended deep a 45 or 147 kg bombs. Under special ventral node was suspended aircraft torpedo Mk.XIII weighing 908 kg.
Performance characteristics of the torpedo bomber TBD-1 DEVASTATOR
Wingspan, mm………………………..15 240
Length, mm…………………………………..10 690
Height, mm……………………………………4590
Empty weight, kg………………………….2804
Takeoff weight, kg…………………………4473
Maximum takeoff weight, kg…..4623
Maximum speed
at a height of 2438 m, km/h………………….331
Cruising speed, km/h……………..205
Landing speed, km/h………………109
Practical ceiling, m………………6004
Flight range (with torpedo MK.XIII), km……………….700
N. Food reserve was, A. CHECHIN, Kharkov