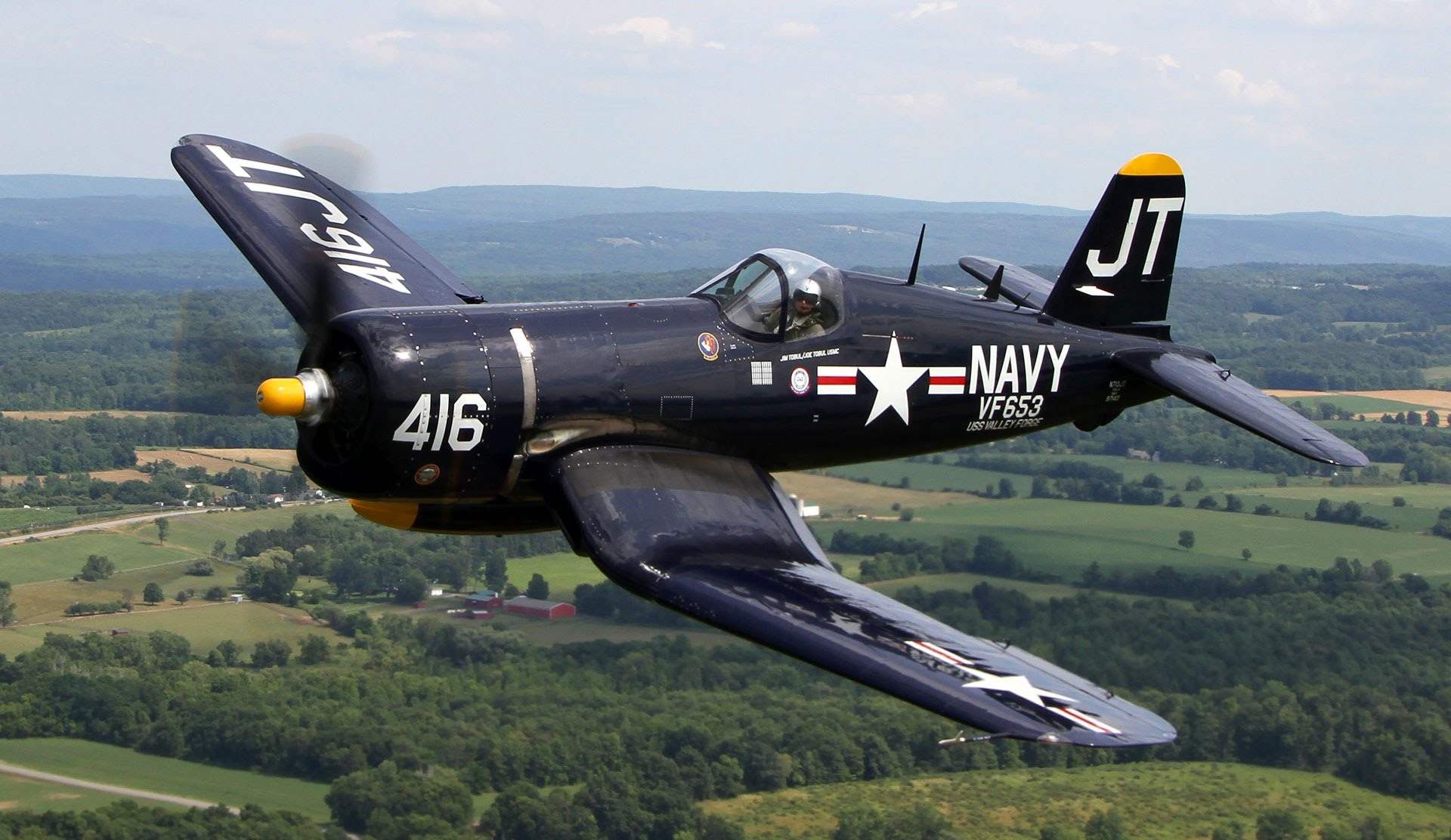
 Carrier-based fighter F4U-5/7 CORSAIR. In the annals of aviation are not many aircraft left in her mark. But it is to such aircraft include the American fighter F4U CORSAIR the Chance Vought company, which had a great influence on the outcome of the air battles over the Pacific.
Carrier-based fighter F4U-5/7 CORSAIR. In the annals of aviation are not many aircraft left in her mark. But it is to such aircraft include the American fighter F4U CORSAIR the Chance Vought company, which had a great influence on the outcome of the air battles over the Pacific.
During the Second world war aircraft F4U was armed with 19 fighter squadrons of marine corps aircraft and six squadrons of carrier-based aircraft. In the Pacific, from 13 February 1943 until the end of the war F4U CORSAIR performed 64 051 sortie.
According to American data, F4U shot down in aerial combat was 2,140 Japanese aircraft, while it lost a total of 189 cars. The loss ratio in aerial combat for these fighters was 11.3:1 in favor of the Americans.
It should be noted that counting their losses from the Americans was quite peculiar. They did not include planes unaccounted for, has not held up to their airfields, written off as a result of combat damage and crashed on landing. In total, the sea dogs gained 1435 such “non-combat” losses. And if you calculate the ratio of downed Japanese aircraft and “Le Corsaire” with the “non-combat” losses, it will be 1.48:1. But despite this F4U CORSAIR is deservedly considered one of the best carrier-based fighter of the Second world war.
Released in 1942, it remained in service until the end of 1957 and thus became the last piston fighter in the American fleet. In other countries, “Le Corsaire” fly for even longer. For example, France has written off the last F4U only in 1964. Until the beginning of 1960-ies these planes was in the air force of El Salvador, Honduras and Argentina.
The history of creation
F4U CORSAIR was created under the leadership of chief designer of the company Chance Vought Rex Beisel. In the draft went to the two fighters, previously developed by Chance Vought —V-166A and V-166B.
June 11, 1938, the Navy gave Chance Vought firm commissioned to build the first prototype of the fighter under the designation XF4U-1.11 February 1939, representatives of the Navy was shown the full-scale layout of the aircraft, and may 29, 1940, test pilot Lyman A. Bullard raised built the car in the air. During testing of the XF4U-1 reached a speed of 651,7 km/h (in a dive was overclocked to 885 km/h), which was the highest rate among the US fighters of the time.
On 30 June 1941 the Navy ordered the carrier-based aircraft and aircraft marine corps aircraft 584. The first production CORSAIR (serial number 02153) with the motor company Wright R2800-8 power 1970’s HP took to the air on 25 June 1942. The fighter reached a max speed 638 km/h at an altitude of 7545 m and rate of climb of 15.23 m/s. an Official ceremony F4U-1 to the customer took place in six days. 7 September 1942 the first fighters entered service with squadrons VMF-124. All the planes of the first series had a takeoff weight of 5388 kg, and the mass of the design was 4028 lbs. At the request of the Navy in the course of serial production of the fuel tank capacity has been increased several times; take-off weight of F4U-1 reached 6286 kg.
The following modification of the aircraft was the F4U-1A was increased to 650 km/h speed and better maneuvering characteristics. To improve visibility during landing on a flight deck the cockpit of a fighter was raised to 220 mm, and the lantern received a new glazing.
On the F4U-1A, in contrast to the predecessor, can be suspended 454 kg of bombs or two additional fuel tank, containing 736 liters of fuel. This fuel allowed the F4U-1A to remain airborne for 4.5 hours. From November 1943, the CORSAIR began to install the new engine R2800-8W with power of 2250 HP with water injection system.
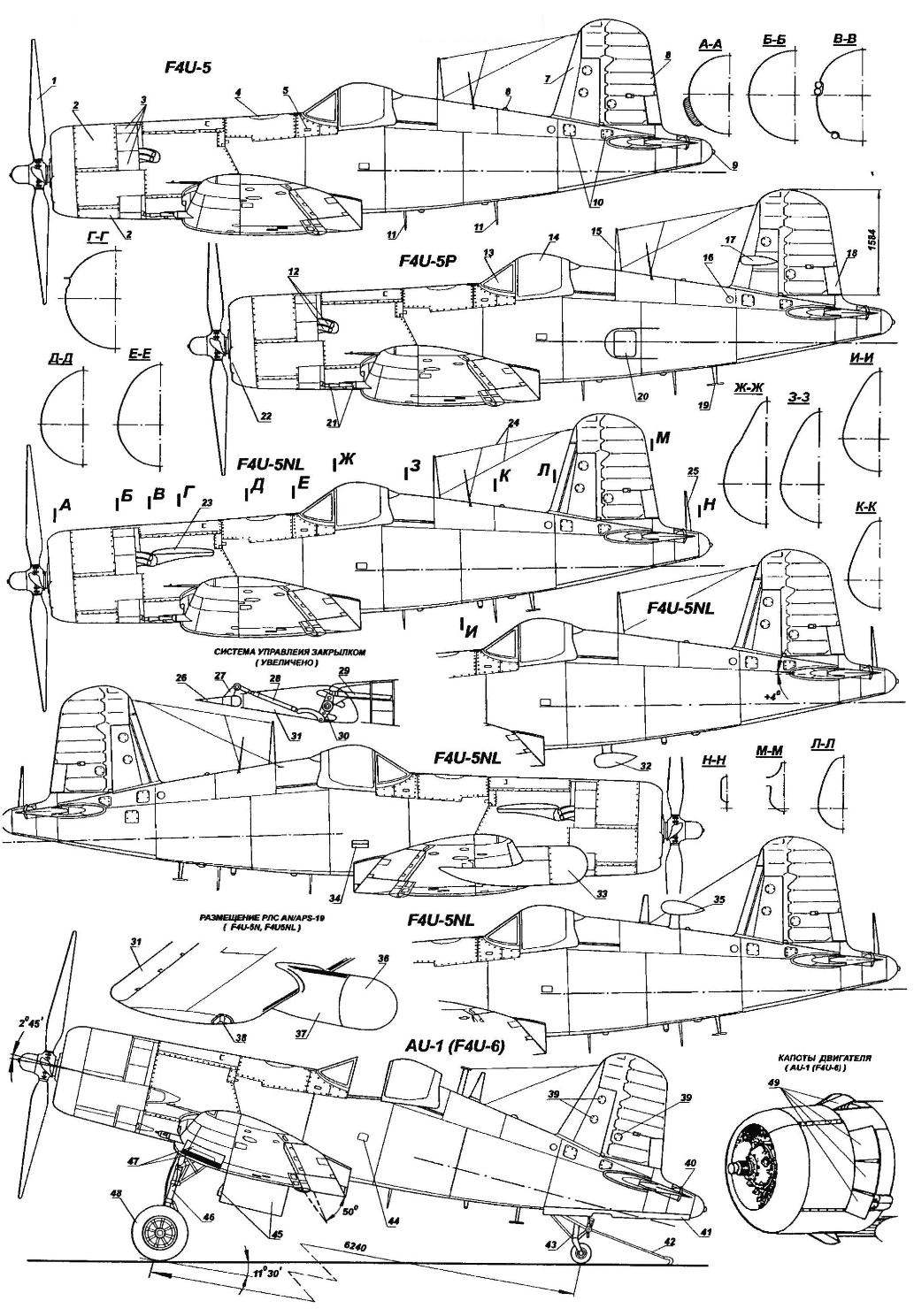

Carrier-based fighter F4U CORSAIR:
1 — four-bladed variable-pitch propeller Hamilton Standard, diameter 4013 mm; 2 — detachable hood; 3 — fold of the cooling system of the engine; 4 — fuel tank cap; 5 — grab handle with spring-loaded lid; 6 — identification of fire; 7 — keel; 8 — rudder; 9 — dimensional navigation-fire; 10 maintenance access doors control system control surfaces; II — antenna radar altimeter; 12—exhaust pipes; 13 — visor canopy; 14 — movable part of the lamp; 15 — antenna radios; 16 — lifting unit; 17 — antenna direction finder; 18 — trimmer of the rudder; 19— antenna radar altimeter; 20 — a cover of the camera; 21 — gun M3 calibre of 20 mm with flame arresters; 22 — intake system naturally aspirated; 23 — protivovospalitelnym shield over the exhaust pipe of the engine; 24 — a cable the radio antenna; 25 — antenna; 26 — trimmer Aileron; 27 — rocking chair trimmer; 28 — control rod trimmer; 29— control rod Aileron; 30 rocking Aileron; 31 — Aileron; 32 — antenna direction finder (bottom location); 33— radar AN/APS-19; 34 — grab handle with spring-loaded cover; 35— antenna direction finder (upper location); 36— radiotransparent Radome of the radar; 37 — the case of the radar; 38 — right ANO (red); 39 maintenance access doors control system rudder; 40 rocking the trimmer of the Elevator; 41 — fold niche cleaning tail wheel; 42— brake hook; 43 — strut tail wheel; 44— footboard; 45 — fold niches of the main cleaning wheel; 46 — front of the main wheels; 47 — reinforced wing pylons; 48 — wheel main landing gear; 49—fold of the engine cooling system in the open position; 50 — fuel selector; 51 —switch for the cabin light; 52 — light alarm production of fuel tanks; 53 — oxygen regulator; 54—arm control arms; 55 power button microphone; 56—switch control the oil cooling system and lighting system; 57 position indicator, landing gear and flaps; 58— crane landing gear; 59 — the pressure gauge in the hydraulic system; 60—position canopy; 61 — toggle switches control the trim tabs and indicators of their position; 62 — tumblers selection shooting; 63 — indicator and control handle de-icing system; 64— the locking latch wing; 65 — handle reset external fuel tanks; 66— ignition switch; 67 — light alarm temperature in the carburetor; 68— pressure in the fuel system; 69— speed indicator; 70 — altimeter and the guide roll; 71 —pointer vertical speed; 72—toggle-select missile launch; 73 switch work frequency of the radar; 74 — compass; 75 — spindle pedals; 76 hour 77 — accelerometer; 78— indicator reserve fuel remaining; 79— a pointer to roll and slip; 80 — an index of fuel consumption; 81 — indicator gyrocompass R-3; 82 — a combined oil pressure indicator and fuel; 83 — altimeter; 84 — the temperature gauge in the cylinders of the engine; 85 — pointer of the engine speed; 86— ANO switch; 87 — voltmeter; 88 switch elektrobatarei; 89 — AZS inclusion of ANO; 90 — lighting controller; 91 regulator cooling of the engine; 92 panel of the radio; 93 castle canopy; 94 — lever relocation of the wing; 95 — a first aid kit; 96 — fire hydrant; 97 regulator oxygen supply; 98 — the adjustment knob of the air intake; 99— block gas station; 100 controller podstepki devices; 101 —the nest check of the voltmeter; 102—release handle brake hook; 103 — the inner section of the flap; 104— external section zakrutka; 105 — socks wing with installed de-icing system; 106 — cap filler fuel tank; 107 is an access hatch to the guns; 108—panel cartridge boxes; 109— right ANO (red); A footrest with a spring-loaded cover; III —the steering wheel height; 112 — trimmer of the Elevator; 113 — flaps main landing gear struts; 114 — variant guns without flame arresters; 115—gilt-extractors; 116 — landing light; 117 — rod LDPE; 118 left ANO (green); 119 — stabilizer; 120 — fairings rocking of the flaps; 121 — a niche cleaning main wheels; a 122 guide the air intake duct system pressurization; 123 engine; 124 — removable pylons; 125 — oil cooler
Simultaneously with the production of the F4U-1A was the release of several modifications. F4U-1B — fighter with short 360 mm outer-wing panels, built specifically for the UK. F4U-1C cannon fighter; armament of this aircraft consisted of four 20-mm guns M-2 with ammunition 120 rounds for each gun. F4U-1D — strike fighter, differing from the F4U-1A is the possibility of a suspension of two 727-kg bombs; latest machine of this modification was armed with eight 57-mm or 122-mm NUR and their takeoff weight reached 6442 kg, and maximum speed due to more powerful engine decreased by only 2 km/h F4U-1P — reconnaissance modification fighter CORSAIR with a camera K-21, located in the cabin compartment. F4U-2 — night fighter issued by the firm in 12 copies. The order is executed at the end of 1942, by aircraft F4U-1: on the right wing set the container with the antenna of the radar AN/APS-6, with the machine removed two machine guns. Blocks of the radar station were in the outside compartment. The range of detection of air targets was 8 km.
In the second half of 1943, was carried out a radical modernization of the aircraft. The first copy of the updated fighter aircraft, designated XF4U-4A, flew on 19 April 1944. The second sample with the designation F4U-4B took to the air July 12, 1944. The design has made many changes, which affected mainly the power plant. The flight speed of the fourth modification has reached 717 km/h Significantly reorganised its radio equipment and weapons. Fighter F4U-4 began to arrive in the combat units in 1945. Until the end of the war, the Americans managed to build the 1912 aircraft modifications. Most of the “fours” took part in the recent air battles over the Pacific.
At the end of the war, the firm began manufacturing cannon series — F4U-4B. Cannon CORSAIR was armed with four 20 mm guns M-3 with ammunition, 220 rounds per gun. The index “V” In the revision designation indicates that these machines were intended for the Royal Navy. But, by coincidence, all 296 of cars left in the deck of the US air force under the designation F4U-4C, although this designation did not stick, and in parts cannon “dogs” were still referred F4U-4B.
During 1945, the firm built another 300 F4U-4B with a more rapid-fire guns T-31 and nine fighters-times-medicow F4U-4P with cameras K-21. Under the Central fuselage pylon all “fours” could be suspended an additional fuel tank or 454-kg bomb. Instead some bombs F4U-4P bore 248 mm NUR “tiny Tim”. Under the wing was fixed with eight small pylons for HVAR NUR. The location of the pylons was such that the rocket does not interfere with the flight of cannon shells. Serial production of the F4U-4 was continued until 1947.
Fighter F4U was made and other firms. Under the designation FG they were built by Goodyear And Brewster produced by the firm was assigned the designation F3A. On the basis of the F41M firm Vought has developed several experimental aircraft: F4U-4E — interceptor with radar AN/APS-4; F41MN — night interceptor with radar AN/APS-6; F4U-4K — drone with a radio system for use as suggestive of the projectile and the target.
Firm Chance Vought after the war, when she was busy working on a new jet aircraft, had continued to improve ITS releasing its next version — the F4U-5. At that, Chance Vought was able to increase flight speed, improve handling and visibility from the cockpit, and also to reduce the weight of the structure.
First, it established a new engine R2800-32W power 2450 HP with two-stage supercharger. The new motor required the lengthening of the engine compartment to 254 mm. changes were made in the design of air intakes — the bottom one is how it was on the F4U-4, designed the two side stands the so-called “cheek”. Setting the side air intakes led to the increase in movement of the fuselage for 205 mm. has Been completely redesigned fold of the cooling system of the engine on the skirt of the hood. Now it was ruled by the automation, and the pilot can focus on piloting. To improve visibility from the cockpit during takeoff and landing, the whole nose tipped down relative to the longitudinal axis by 2.75 degrees. At the same time it improved the longitudinal stability of the aircraft.
Second, a significant alteration has been the wing and aerodynamic controls of the aircraft. Finally they got rid of archaic fabric and got the lining from a thin sheet of aluminum. The horizontal stabilizers are made of the newest, exceptionally rigid and lightweight material, patented by the firm Vought, — metalit, representing a kind of “sandwich” of two aluminum sheets between which is a layer of ultra-light wood — balsa.
Under the fuselage of the F4U-5 in the Central reinforced pole you can hang a bomb caliber up to 908 kg. Basic built-in equipment has not changed — it still consisted of four 20-mm guns M-3. The prototype of the F4U-5 took to the air in December 1945. The new engine increased the maximum flight speed of up to 725 km/h. the First production aircraft handed over to the Navy in 1947, the last in 1951. Just built a 223 machine. There were the following modifications of this aircraft: F4U-5N night fighter for air defense aircraft carrier connections; F4U-5NL, a winter version of the night fighter, F4U-5P reconnaissance. Night fighters released 315 instances, the scouts built a much less — 30 copies.
Specifically for the war in Korea was developed several simplified, but armored strike aircraft F4U-6, received in aviation of the marine Corps (ILC) designation AU-1. The first AU-1 firm built on the production F4U-5NL. New attack soared 31 Jan 1951. It was built 110 aircraft. On the AU-1 was installed engine R2800-83WA (2800 HP). For a single stage turbocharger this engine no longer needed two intakes, and they were removed. Built-in armament consisted of four guns of M-3 with ammunition 215 shells.
On all previous “dogs” the firing of guns was only a volley of four guns, and on the AU-1 pilot could shoot at a time of two guns, which increased the duration of the shooting. The plane had increased bookings bottom of the fuselage (25 armor plates) and carrying 1615 kg payload in three ventral and ten underwing hardpoints. Maximum takeoff weight was 8800 kg. With outside foot speed AU-1 was reduced to 384 km/h.
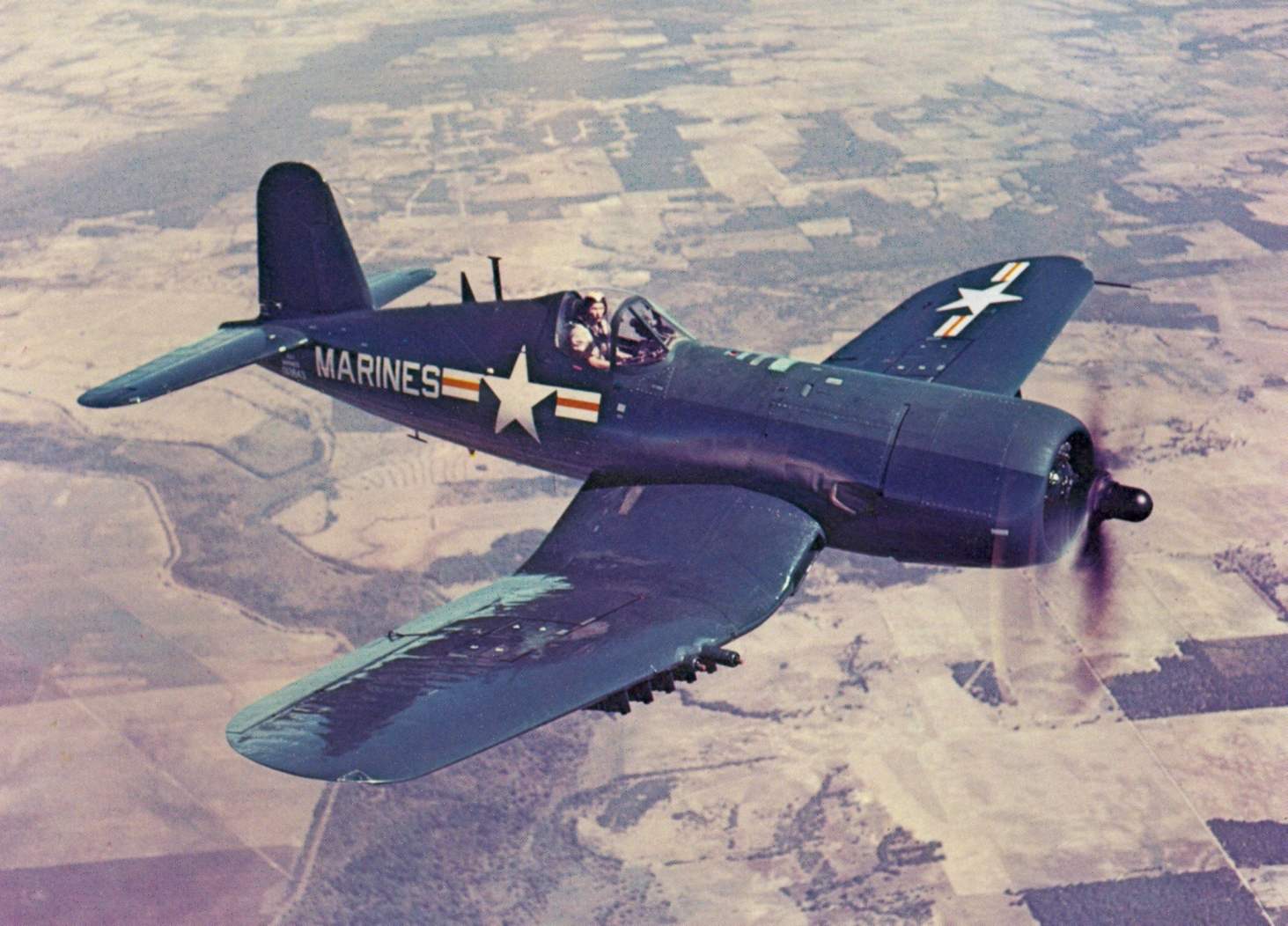

Attack AU-1 in flight
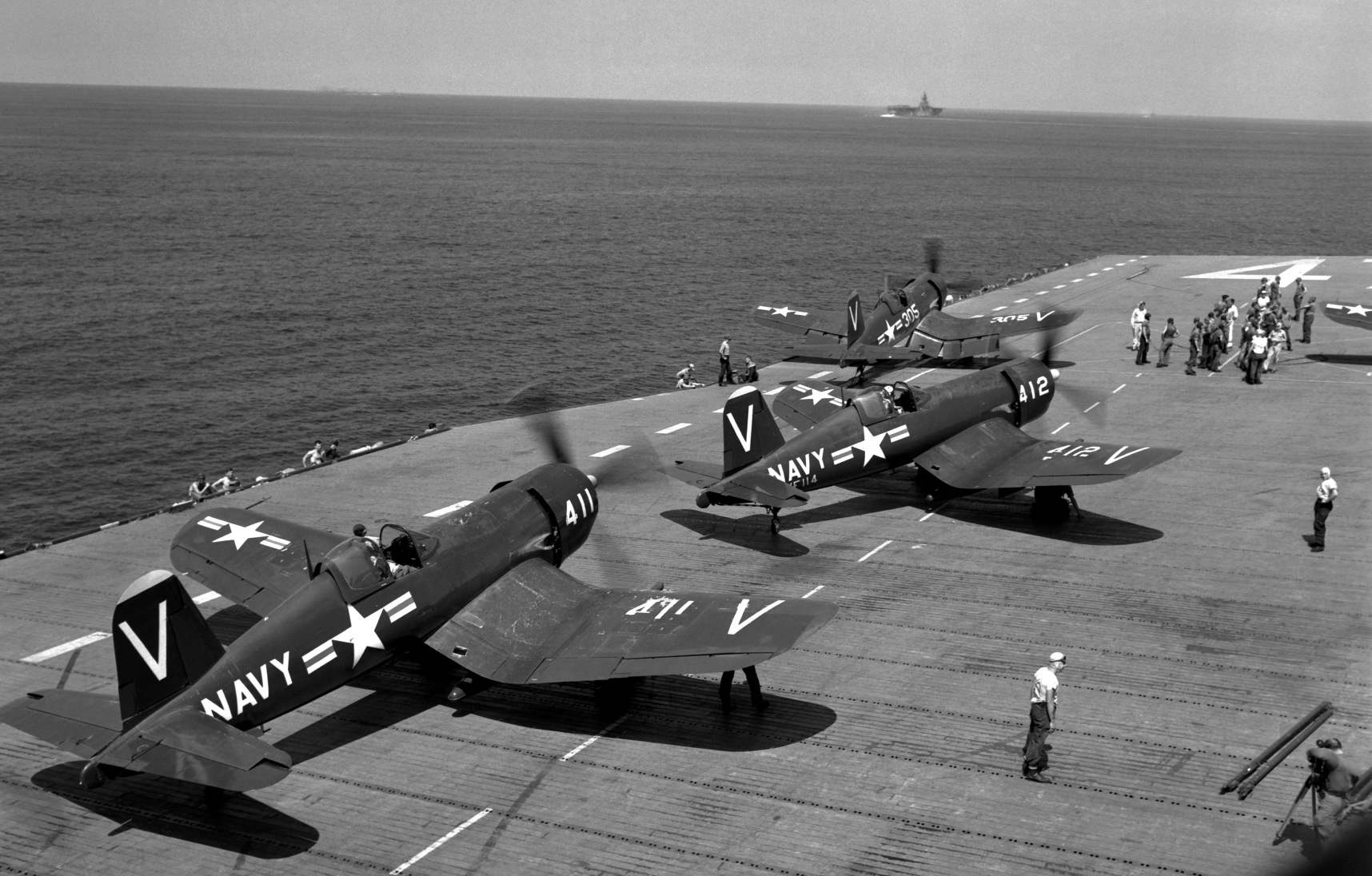

Night fighter F4U-5N on the deck of an aircraft carrier
Specifically for the French carrier-based aircraft firm Vought built CORSAIR plane 94 of the modification of the F4U-7. The design of put the glider from the F4U-4B, which is to improve visibility has been changed in the cockpit. As the power plant used engine R2800-18W power of 2100 HP the First flight of the F4U-7 was held on July 2, 1952. Serial production began in late summer of 1952. Retraining of French pilots was held at the “Ocean” (Seapa) in Virginia in October 1952. The first production vehicles entered service with squadron 14.F under the command of Pierre Mentee. The division was based in Tunisia.
In the autumn of 1953 the French troops who fought in Vietnam and experienced an acute shortage of fighter planes, turned for help to the Americans. A large-scale offensive the North Vietnamese army did not leave time for selection of appropriate technology, and French annuals gave what was at hand, aircraft AU-1 from squadron VMA-211. Most of these cars are in a failed state. 18 APR 1954 attack aircraft were delivered to the port of Annam. Two days of hard work the technical staff managed to put into operation only received 16 out of 24 cars. The intensity of the use of AU-1 of the French can be judged by the statistics of the sorties. Over the 11 weeks of fighting “corsairs” flown 1235 hours, dropping 700 tons of bombs, fired 300 NUR HVAR and shot of guns on Board 70,000 shells.
After the Vietnam war, the arrival F4U-7 French Navy continued. It was formed three squadrons. The aircraft was permanently based on aircraft carriers Arromanches and La Fayette. Until 1962, F4U-7 was used in Algeria.
In the autumn of 1964 CORSAIR fighters started to withdraw from service. In their place came a jet machine F-8FN Crusader and Etendard IVM. The last flight of a French F4U-7 was held on 28 September 1964.
Combat use in Korea
In the late 1940-ies of the piston “dogs” stopped playing the role of the main carrier-based fighter of the United States, which remained for them directly after the Second world war. F4U inferior to their successors in the jet speed, rate of climb and ceiling. Gradually winding machine began to transfer to the class of attack aircraft, and since 1948 their number has been continuously reduced. By the beginning of the Korean war, the air group for each type carrier of the Essex consisted of 35 F4U, SKYRAIDER 23, 30 F9F PANTHER jet and two helicopters H03S.
For “Le Corsaire” the war began on 3 July 1950 at 6.00 am when 16 fighter F4U-4 squadron VF-54 in the strike group aircraft carrier Valley Forge (CV-45) attacked the Pyongyang airfield. Being in the second wave of attackers, F4U-4 CORSAIR approached the airfield when the hangar, and the runway was already destroyed by SKYRAIDER attack aircraft and jet fighter PANTHER. The F4U was shot at surviving enemy aircraft in Parking lots. In the reports of the annuals return to aircraft carriers, reported the destruction and damage 38 27 aircraft of various types
Strikes of carrier-based aircraft allowed the Americans to gain full control of the air and hold it until the appearance of the MiG-15. During July, the F4U flew at the call of the land forces, restraining the advancing of the North Koreans. Typical ammunition “Le Corsaire” in such flights were 800 shells to the guns, one 450-kg bombs and eight 127-mm HVAR rockets.
In early August 1950 over the Korean Peninsula, there were “dogs” that belonged to the aviation Corps of the marine corps. At that time Americans did not have ground airfields and aircraft of the marine corps, flew with the escort carriers Sicily (CVE-118) and Badoeng Strait (CVE-116). 28 days Aug “dogs” made 1359 sorties. Targeting the aircraft was carried out by advanced group guidance, which were in each battalion of the ILC. During the fighting often happened that two squadrons of F4U (48 cars) had to support one of the advancing battalion!
After the end of fighting on the beachhead Bosanskom “dogs” got a job to support the landing at Inchon. The main purpose of aviation was the small island of Wolmido 700 m from the shore. On the island were camouflaged artillery battery North Koreans. To determine their coordinates succeeded only after a close approach to the island two destroyers, the decks of which were placed straw effigies in the form of American sailors. The Koreans could not stand such impudence and opened fire, issuing thus, the coordinates of batteries.
10 Sep 48 “pirates” attacked the exposed gun emplacements on the island, dropping 95 tanks of Napalm. The fire destroyed 39 buildings and a military camp. Using the fact that the North Korean position was not anti-aircraft guns, the Americans, with impunity, attacked the island during the day. In the result of devastating air strikes, the island managed to capture just over half an hour.
September 15, “dogs” bombed Incheon. Smoke and dust hid the sun, the visibility dropped so much that landing had to use the ship’s floodlights.
After entering the war, China’s status of us troops has sharply deteriorated. On the night of 27 November 1950 the 1st marine division encircled six Chinese divisions. Surrounded by a rescued “dogs” of the 1st wing of the PCM, which on 30 November managed to stave off the powerful attack of the enemy. Time to find about two thousand Chinese soldiers, annuals dive threw their tanks with Napalm. Terrified, they fled.
All summer 1951 “dogs” hunting for cars in the area of the 38th parallel. Day fighters worked in the daytime, dropping to the roads of bombs with delayed-action fuses. After sunset flew night fighter F4U-5N — using their radar, they discovered a convoy of the enemy and shoot them from on-Board weapons.
However, every month of the war the air defense of North Korean troops increased, and losses in the American aviation grew. Beginning in April 1952, based aircraft and aircraft of the marine corps, if allowed the distance to the target, began to act with the support of naval artillery.
The first combined aviationauthority the blow was struck on April 13 in the city of Chongjin. F4U in the strike groups of aircraft carriers attacked the factory of artificial silk and steel mills. For two flights of these aircraft dropped over 200 tons of bombs. Thanks to the cover of naval artillery, the casualties among the strike aircraft was not.
The MiG-15 is rarely found in the air with the “dogs”. But if that happened, then the outcome of the battle was not a foregone conclusion. Piston F4U CORSAIR was still a very serious opponent. Exceptional horizontal maneuverability and powerful armament gave pilots “pirates” a chance, even with the numerical superiority of the enemy.
Of course, in combat with a jet fighter F4U pilots find it difficult to exercise their advantage in maneuver, but when meeting with piston aircraft “dogs” demonstrated a complete superiority. Especially notable in these air battles Lieutenant guy P. Bordelon flew the night fighter F4U-5N. In just three weeks he was from an ordinary pilot, the Navy became the only ACE of naval aviation in the Korean war. Squadron VC-3, which, Bordelon arrived in Korea, flying from the aircraft carrier Princeton (CV-37).
During the final months of the war “dogs” continued to trouble the front edge of enemy defenses with their precise and sudden attacks. Their last combat missions F4U made on may 27, 1953.
Description of the design of aircraft F4U-5 and AU-1
Aircraft F4U-5 — single, single-engine all-metal fighter with a wing of type “reverse gull”. The fuselage — semi-monocoque with aluminum shell, supported by frames and stringers. Sheathing was attached to the frames and stringers are spot welded. The fuselage consisted of four parts: motor, front, middle and back. Motor part end the firewall plays the role of the first power frame. To it was attached the steel engine mount tube design, which is installed on the engine. In the engine compartment housed: reducer, fire extinguishing system, supercharger, oil tank. To prevent blinding the pilot in night flying on the F4U-5N and F4U-5NL exhaust pipes of the engine were covered with visors.
The front part of the fuselage is of circular cross-section. It has a main and reserve fuel tanks and the cockpit. The cabin had air conditioning and heated windscreen. Front fixed hood canopy, made of Plexiglas with a thickness of 38 mm. the Cup and the seat back of the pilot were made of armor steel.
In the middle part of the fuselage is a compartment with radio and navigation equipment. Aircraft reconnaissance modifications in this part of the fuselage mounted camera K-21 or S-75. In contrast to the reconnaissance modification of the F4U-4P, F4U-5P window under the camera made bottom, left and right sides of the fuselage. To avoid getting on the optics of oil or gasoline, they are covered by sliding lids.

The composition of equipment on the fighter collection F4U-5 was part of autopilot P-1 radar altimeter AN/APN-1 and also radio AN/ARC-28 and identification system AN/APX-2. Indicator radar was mounted in the center of the dashboard. On the night fighter F4U-5N and F4U-5NL on the right console fairing mounted radar AN/APS-19A or APS-6. In the rear (tail) of the fuselage was located the tail wheel, landing brake hook and a niche cleaning tail wheel.
The two-spar wing, all metal construction, made on a “reverse gull”. This form of the wing allowed to use the shorter uprights of the main chassis, and when making a forced landing without landing gear Chayka reduced damage to the fuselage. Wing profile NACA 230018 at the root and NACA 23009 in the terminal part. The thickness of the wing 18 per cent at the root and 15 in the area of the fold and 9 — at the end. Maximum wing chord 2688 mm, minimum mm. 1776 Structurally the wing consisted of three parts: a center section and two folding up to the fuselage of the console. The main spar is joined to the front power frames. In the center section of the wing mounted oil coolers with a diameter of 300 mm and the guide device of the inlet of the supercharger. On the right wing of the plane includes a shot-method for fixation of the results of the shooting.
On the trailing edge across the span of the wing was located flaps — four sections to the center section and two folding wing consoles. The total area of the flaps-flaps 3,38 m2. The maximum deflection angle of all sections — 50°. The ailerons in a big way 2304 mm took the trailing edge of the wing tips and were suspended at three points on the horns. The deflection angles of the Aileron up 19° down 14°. The area of the ailerons to 1.68 m2. Trimmers were installed on both sections of the Aileron.
On the front edge of the left wing was installed LDPE. On the upper parts of the console were located hatches for access to the guns and cartridge boxes. On the lower surface of the wing were cut out of the window to pillsoverseas. On the center section of an airplane wing could be mounted two removable pylons (one to the right and left) that were used for the suspension of weapons or additional standards.
Vertical tail unit all-metal, normal scheme. The power set consisted of stamped profiled stringers and ribs. The dural covering. To compensate for the torque of screw the keel was installed with an angle of 2° to the left relative to the plane of symmetry of the aircraft. The area of the keel — 2.03 m2. The area of the rudder is 1.20 m2. The deflection direction 25° in both directions. On the modification of the F4U-5P on the tail mounted antenna of the radio compass, which was a characteristic feature of this modification. Stabilizers monocoque construction with a shell made of metalit. The installation angle of the stabilizer 1° 25′. Area of 2.66 m2 scope 5088 mm. the area of the elevators of 0.68 m2. Deviation elevators: 23° 30′ up and 17° down. Steering direction and height — hard, from the control stick and pedals. Trimmers were driven by a knob on the left side of the cab.
Landing gear is retractable, tricycle, tailwheel. In flight the main stand was located in special niches in the center section of the wing. When cleaning they turned back on the flight, the wheels were turned by 90°. Track — 3792 mm. Diameter pneumatic wheels — 813 mm, width— 203 mm Wheelbase — 7430 mm. the Tail wheel with Pneumatics with a diameter of 317 mm and a width of 114 mm were cleaned in a fuselage on the flight back and was kinematically connected with the brake hook. The system of harvesting and the landing gear is hydraulic.
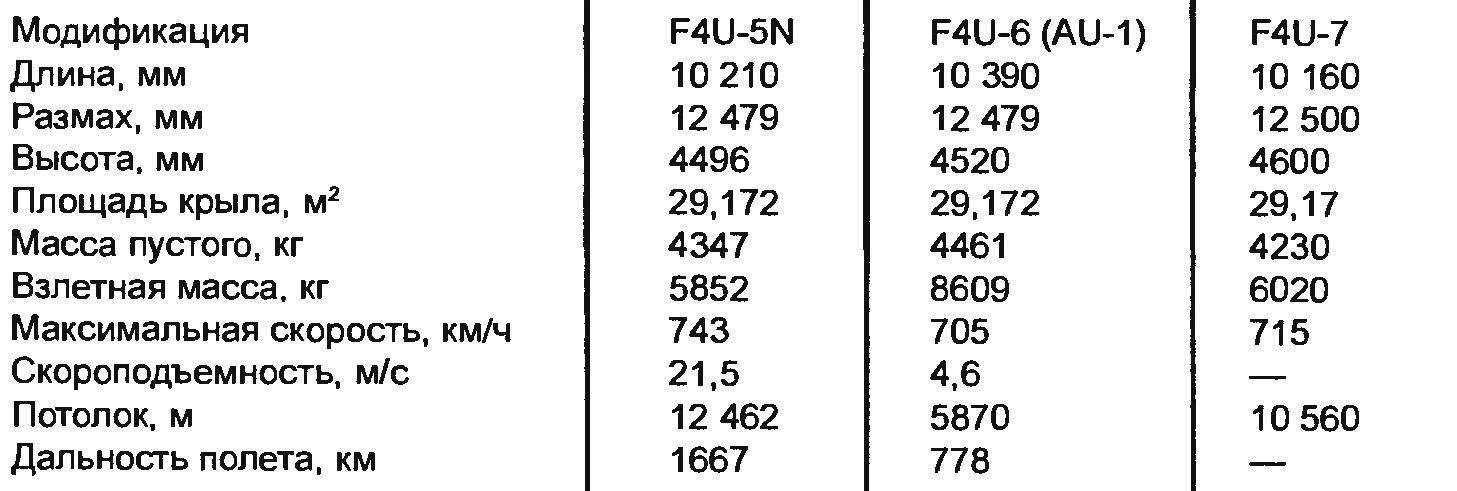
Flight performance of aircraft CORSAIR post-war modifications
The power plant consisted of the engine, oil and fuel systems units to ensure their sustainable work. On all models F4U-5 was installed 18-cylinder radial engine is air-cooled Pratt & Whitney R-2800-32W, with a capacity of 2550 HP in afterburner. The engine was equipped with a two-stage two-speed supercharger, followed by cooling of the air and direct water injection. Hamilton standard propeller with a diameter of 4125 mm four-bladed metal variable pitch. The hood of the engine was carried out in a quick-detachable duralumin panels and provide convenient access to the power plant and its units.
The aircraft was equipped with a new automatic system of oil cooling and controlling the air supply to the blowers. Louvers on the hood regulate air flow depending on the mode of engine operation and oil temperature. AU-1 was equipped with an engine Pratt & Whitney R-2800-83W power HP 2550 (2800 HP afterburner) with single-stage supercharger.
Armament consisted of four 20-mm guns M3 or T-31 with a total complement of 924 shells that were installed in the wing outside area, rotor swept. On the night fighter F4U-5N and F4U-5NL guns were equipped with flame arresters. On a Central pylon under the fuselage can be suspended 908-kg bomb. Centroplane reinforced the wing pylons was designed for bombs weighing up to 1,000 pounds (454 kg). On wing pylons were installed ten unmanaged 127-mm HVAR rockets. Aircraft AU-1 had a reinforced wing pylons, on which are mounted bombs weighing up to 250 pounds (113.4 kg). In addition, on the inner, middle and outer pylons could also be suspended from a 500-lb (226,8-kg) bombs. On the ventral and two centroplane pylon, if necessary, is attached to the tanks with bombs or external fuel tanks.
A. CHECHIN, N. Food reserve was



