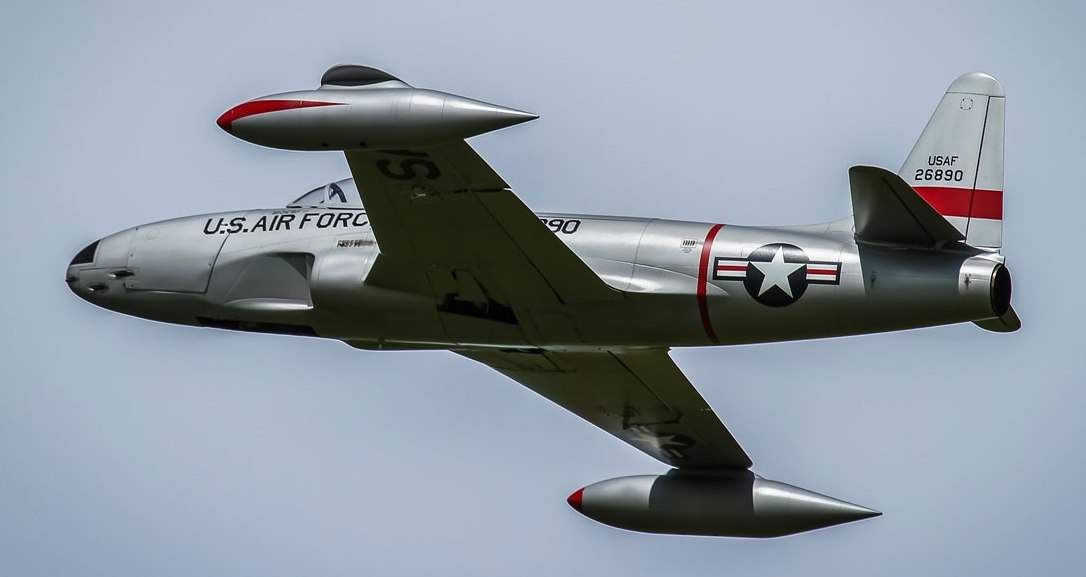
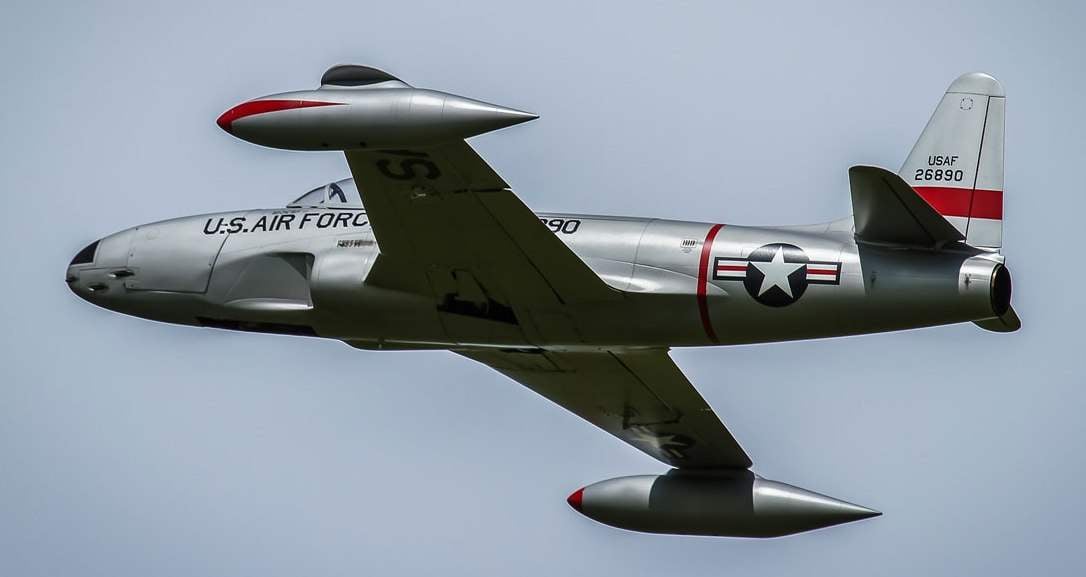
THE F-80 SHOOTING STAR. The story of the creation of the F-80 started in late spring of 1943 at Wright field, where the main designer firms Lockheed (Lockheed), Daniel Russ (Russ Daniel) met with representatives of the command of the U.S. air force. The meeting resulted in an official letter in which the firm was asked to develop a fighter jet under the English engine.1B “Goblin” company Havilland De (De Havilland.) These engines are planned to produce on the industrial base of the American company Allis Chalmers (Allis Chalmers). Last long time was trying to develop his engine, but 1943 she abandoned her fruitless attempts and have purchased a license for the construction of N. 1B.
THE F-80 SHOOTING STAR. The story of the creation of the F-80 started in late spring of 1943 at Wright field, where the main designer firms Lockheed (Lockheed), Daniel Russ (Russ Daniel) met with representatives of the command of the U.S. air force. The meeting resulted in an official letter in which the firm was asked to develop a fighter jet under the English engine.1B “Goblin” company Havilland De (De Havilland.) These engines are planned to produce on the industrial base of the American company Allis Chalmers (Allis Chalmers). Last long time was trying to develop his engine, but 1943 she abandoned her fruitless attempts and have purchased a license for the construction of N. 1B.
23 June 1943 before the air force presented a preliminary design of a jet fighter under the trade designation L-140. Approved the project and signed a firm contract for the production of three experimental aircraft and 13 pre-production machines. The contract States that the company should develop and build the first copy of the 180-day period. The aircraft was assigned the designation XP-80. By the beginning of September, the military had planned to send the UK’s first squadron of new jet fighters.
The Lockheed major project work L-140 was headed by little-known engineer, Clarence Johnson (Clarence Johnson). Under his leadership, 35 designers worked 10 hours a day. Wooden model airplane was built in a month. All the time, while there was the Assembly of the first model of fighter, the workers slept in the Assembly shop. Finally, after 143 days after signing the contract the aircraft was built. It was called “Lovely Lulu” (Lulu Belle).
On November 14, “Lulu” was dismantled and transferred to the airbase Muroc, where he planned to begin flight tests. However, malfunctions in the power plant is not allowed to make its first flight until January 1944. Finally, problems with the engine somehow settled, and January 8, 1944, at 9 a.m., the machine rose into the air. Following the flight of the XP-80 made in an hour. Began an intense program of testing.
10 June 1944 to the first plane joins the second prototype. The tests were quite successful, and Lockheed was ready for serial production. The only serious obstacle was the engine. Allis Chalmers tightened terms of delivery of engines and the whole program was in jeopardy. Lockheed decides to put on a production aircraft engines I-40 firm General electric (General Electric). Subsequently, their production will transfer to the firm, Allison (Allison), and they are known under the designation J-33. And while one of the prototypes began to remodel for the new power plant. The length of the fuselage is increased to 51 cm, changing the shape of the air intakes and in front of it put a razor edge layer. Wingspan increased to 60 cm. At the request of the military in the armament added another gun. Before on the XP-80 was a five M2 machine guns of 12.7 mm. To increase the flight range at the wing tips provided a suspension of additional fuel tanks.
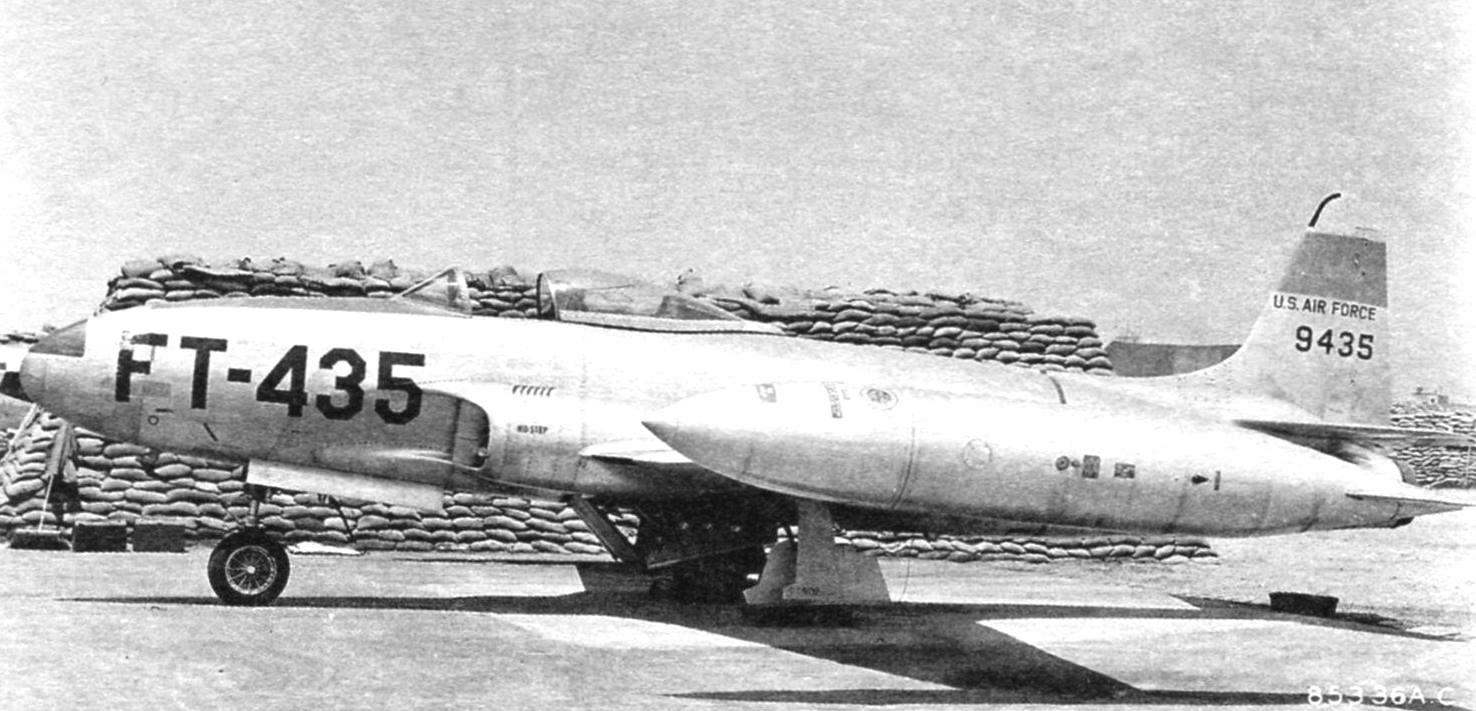
The F-80C
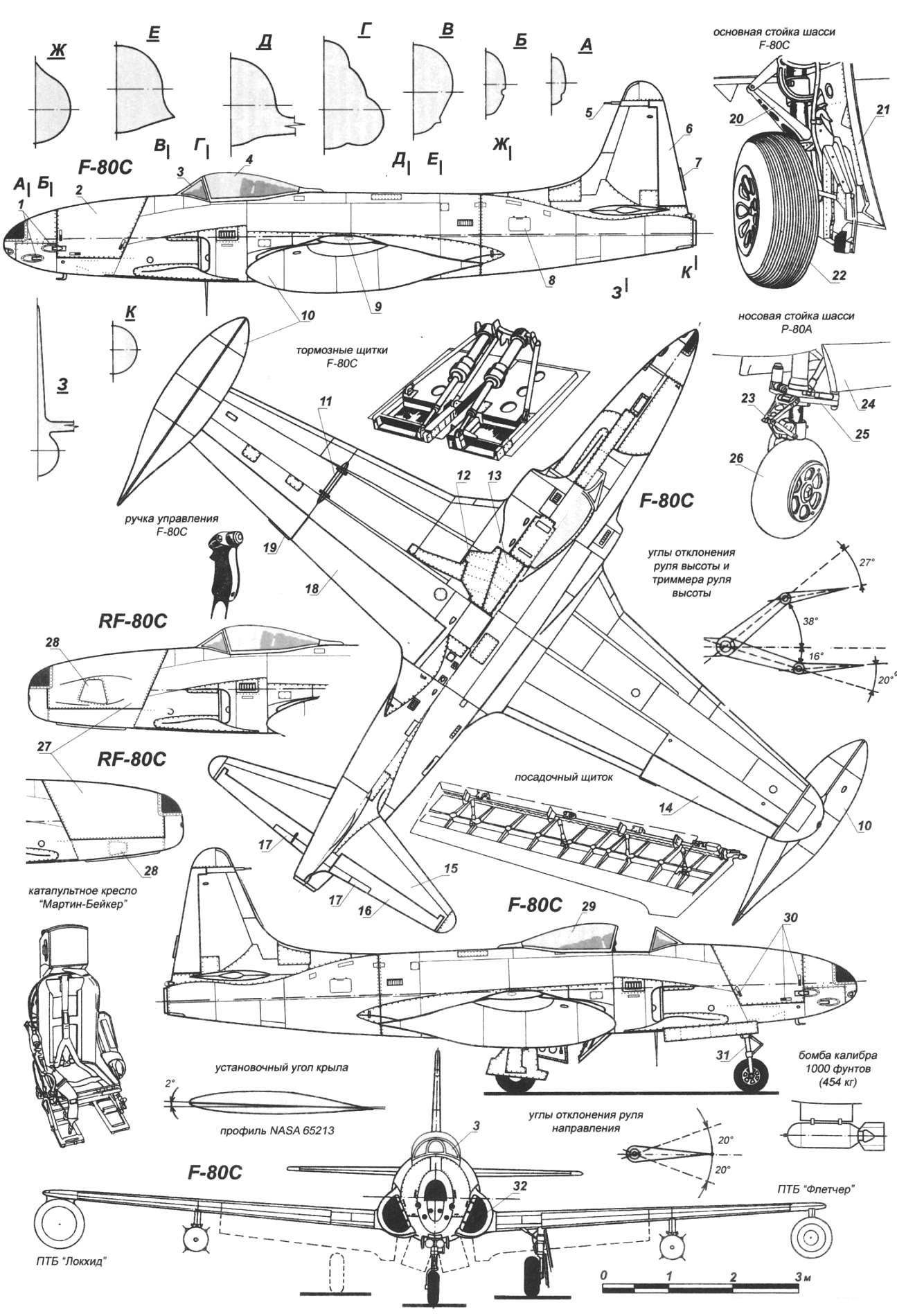
F-80:
1 – machine guns; 2 – hood compartment of arms; 3 – the canopy the canopy; 4 – movable part of the lamp in the closed position; 5 – LDPE; 6 – rudder; 7 – trimmer of the rudder; 8 – maintenance hatch motor; 9 – NGO; 10 – end of the wing outboard fuel tank; 11 – wing pylon; 12 – shield main landing gear; 13 – the panel of the niche of the cleaning wheels; 14 – Aileron; 15 – the stabilizer; 16 – steering wheel height; 17 trimmer rudder; 18 – the landing brake flap; 19 – Aileron trimmer; 20 – dvuhsvetny; 21 – plate rack; 22 – wheel of the main stand; 23 – dvuhsvetny; 24 — plate niche cleaning stand; 25 – wheel turning mechanism; 26 – wheel; 27 – hood photographic equipment; 28 – illuminator; 29 – the movable part of the lamp in open position; 30 – locks of a cowl; 31 – front; 32, the air intake
The new engine had a higher performance. Its maximum thrust was 1750 kg, 580 kg more than the N. 1B. The first flight of the upgraded aircraft took place on 16 February 1944. Take-off weight of the machine increased by 25% and amounted to 5000 kg.
On the model of the upgraded prototype was built ordered thirteen pre-production aircraft YP-80A. The first of them took to the air on 13 September 1944. The test was successful, and at the front the pilots increasingly began to meet the German jet aircraft. Air force began to rush the firm with mass production required for the front of the plane, dubbed Shooting Star, literally English -“shooting star”.
Realizing that the best test of any plane is its participation in combat operations, the air force sent four YP-80 in the European theater of operations. Two aircraft aboard the aircraft carrier arrived in the UK and two in Italy. Unfortunately, neither one of these fighters failed to meet with the enemy.
Meanwhile, in the United States developed the serial production of aircraft engine J33-GE-9, the first car rolled off the Assembly line just nine months after the release of the pre-production aircraft. In March 1945, the first production aircraft entered the 412 fighter wing airbase in March in California. Came the first loss, so on 6 August 1945, during the flyby of another series of the P-80A killed major Richard Bong (Richard Bong).
The first modification “Shuting old” was a P-80A-1 engine J33-GE-11, issued in the amount of 345 units. Then followed a P-80A-5 (with the engine J33-A-17) – 218 pieces. Total built 677 fighter jets, P-80A. In January 1946, serial P-80A has set a national speed record, breaking the distance between new York and Los Angeles in 4 hours 13 minutes 26 seconds. On the basis of the P-80A mass production reconnaissance aircraft FP-80A (RF-80A).
The next version of the fighter received the designation R-80V. In its construction were taken into account and fixed some of the shortcomings of previous versions. So, at high speed, P-80 tended to delay the dive. To counter this phenomenon, the designers have changed the profile of the wing, decreasing its relative thickness and thereby increasing the critical Mach number.
The machines were installed engines J33-A-21 with a thrust of 1820 kg. mass production of the R-80V began in 1946. The armed fighters have changed, and now the enemy threatened six advanced guns M3. Complete avionics radar appeared rangefinder, he stood in the place of the landing-taxi lights in the nose of the fuselage. The designers have thought about the possible use of R-80 from unprepared airfields and provided for suspension of the rocket boosters, which reduces the takeoff distance. The main innovation was the ejection seat of the pilot, created in collaboration with German designers.
The firm has built a 240 instances of R-80V, and located in parts “A” is altered according to the new standard. Specifically for Arctic conditions built fighter 31 P-80B-5-LO. The engines of these aircraft worked on a mixture of kerosene with petrol (fuel JP-3), the wheels were a special frost-resistant Pneumatics, and cabin has been insulated.
New American jet fighters began to appear in various parts of the world. In 1947, with a P-80 became acquainted Western Europe. Back on Board the escort carrier “Sicilia” (Sicily) came 36th fighter wing. In 1947, after changing the notation in the U.S. air force when the letter R of Pursuit – “the hunter” was replaced by the F Fighter is “fighter”, “Shuting Old” received a new designation – F-80.
In the postwar years, except for training and demonstration of power on other continents, American pilots were involved in all sorts of celebrations. May 15, 1948 in the United States celebrated the 30th anniversary of airmail. This significant event captain Harrison Vermont (Vermont Harrison) timed the flight from new York to Washington – in the cockpit of his F-80B, he put the bag with the mail. In 1947 air force base Yuma formed the first aerobatic team of the U.S. air force – Aero Jets. She often performed in front of an enthusiastic American public.
The last mass modification of F-80C began in February 1948. It has established an even more powerful engine – J33-A-23 with a thrust of 2080 kg Significantly increased the combat capabilities of the machine. Under the wing there were two pylons to mount bombs or rockets. Serial production of the aircraft ceased in the summer of 1950. The last batch of 200 F-80C was equipped with engines J33-A-35 with a thrust of 2450 kg. the Engine accelerates the plane to a speed of 950 km/h Takeoff weight was 7,000 lbs. Total built 798 F-80C.
On the basis of the F-80C was built double combat training aircraft TF-80 (T-33). The first aircraft of this modification took to the air on 25 August 1947.
In 1949, all aircraft have installed a new ejection seat company Martin-Backer. The chair provided a safe evacuation of the airplane at a speed of 960 km/h On the seat established a special stabilizing surfaces, good protection of the knees and a device that allows you to open the parachute manually and automatically. The tests were performed on the Lockheed T-33. The chair had its own parachute with a diameter of 4.88 m, to prevent the possibility of collision chair with a pilot.
Separately want to talk about the various experimental fighter variants “Shuting Old”.
In 1950-ies the main armament of the fighter-interceptor of the U.S. air force was considered to be rockets, which are housed in the outboard launchers. Big drag launchers were forced to look for designers new options for placing and launching rockets. On one of the P-80A was tested automatic launcher, NUR flow from the drum to a single trunk. The installation occupied the entire nose part of the fighter, and the trunk stood out far ahead. Large mass and low rate of the device is not allowed to take it on Board.
For testing ramjet engines have used another P-80A. At the wing tips of the plane secured two pulsating ramjet engine With 30 firms Marquardt diameter 76,2 cm In January, 1946 pilot Herman salmon (Herman Salmon), nicknamed “Fish” lifted the plane into the air. At a speed of 800 km/h it included the RAMJET and turn off the main engine. Thus, the P-80 became the first manned plane to fly some RAMJET.
By order of the air force, the American firm Stanley was researching the effect of large overloads on the pilot, with the aim of finding the optimal placement of the crew maneuvering the aircraft. Studies performed with the fighter P-80 with a small cockpit in the forward fuselage. In this cabin, lying on a nylon rug, was a test.
One of the aircraft equipped with a radio system, was used for air sampling of radioactive clouds during and after a nuclear explosion.
Five aircraft served as test platforms for equipment and guidance system supersonic Intercontinental cruise missile RASCAL.
Finally, most of the planes after their write-off were used as radio controlled target QF-80.
The Navy used a modification of the DF-80 to control the targets of Regulus.
Specifically, for setting the world speed record in a P-80A-1 was equipped with an engine J33-A-23 with the forcing (injection into the compressor Vodopyanova mixture). August 19, 1947, under the designation of XP-80R, the plane accelerated to a speed of 1000 km/h In the cabin were Colonel albert Boyd (Albert Boyd), head of testing center of the U.S. air force at Wright field.
COMBAT USE
By the beginning of the Korean war the U.S. air force in the far East consisted of a total of 1172 of the aircraft. 5th air army, stationed in Japan, is conventionally divided into three sectors. The Northern sector had the airbase in Misawa, medium – Yokota and South in Itazuke. “Shuting Old” were armed with five groups of aircraft. Three of them were based in Japan. 49th FBG, composed of 7th, 8th, 9th FBS (fighter bomber squadron), located at the airbase in Misawa, 8 FBG (35, 36, 80 FBS) in Itazuke, 35 FIG in the composition of the 39th, 40th, 41st FIS (fighter squadron interceptor) was stationed in Yokota. By the 35th FIG organizationally belonged to the 8th reconnaissance squadron RF-80A. In total, the us air force in the future theater of war, there were 360 “Shuting Old” of various modifications. In addition, from the Philippines to Okinawa was transferred to the 51st wing of fighter-interceptors. All of these units received the F-80, to personnel operated the fighter P-51 Mustang.
The fate of the F-80 was the first jet aircraft, took part in the Korean war. From June 27, 1950 they, with the F-82 Twin Mustang was escorted transport aircraft C-54, which was evacuated from Korea civilian personnel American institutions. It was expected that the North Korean fighters will try to intercept transport aircraft.
But the aggressiveness of the Americans changed the course of events. Four “shuting the old” eight intercepted the Il-10 bound rate at Kimpo airfield. The fight lasted less than a minute, as a result, the Koreans were missing four Il-10. Two of the aircraft was recorded at his own expense Lieutenant Robert Wayne (Robert Wayne), one captain R. Schillereff (Raymond E. Schillereff) and Lieutenant Robert Duvall (Robert N. Dewald). The remaining North Korean attack aircraft at low altitude headed North. Duvall in his memoirs described this battle: “I noticed straight ahead a dark green piston aircraft flying along the river… We passed over the suspect aircraft above, turned around and went in the opposite direction. I quickly drove one plane into the reticle – that is North Korean, I have no doubt remained. I have identified the aircraft as single-seat fighter. Suddenly from the cabin “single fighter” to my car reached the track – there are air shooter and he’s shooting at me! I released a long burst from all six guns at the cockpit of the enemy. Apparently, the pilot was not injured, as the plane continued flying steadily. However, the enemy did not attempt to maneuver away from the blow. I attacked him the second time – now the light at the cockpit of the enemy machines was not pulsing. Apparently I brought down the shooter. No one bothered me, so I put a long line in the area of the engine. I hit, but the enemy as if nothing had happened continued their flight: no smoke, no messy of the crash was not observed. He was teasing me. The third time I walked up to the maximum distance and fired, while it was possible. Again, I do not seen any damage. At this time, my fighter suddenly neither from that nor from this began to perk up, and the windshield poured streams of oil, oil seemed on the slats. Trouble! The mood lifted thrown on the radio the phrase of the commander: “You hit!” I still managed to hold on to Itazuki due to clearance and a favorable wind. The film fotokinopulemeta showed that I shot down the Il-10. To me this victory is exceptionally difficult”.
On the same day, North Korean Yak-9P and Il-10 were attacking Suwon airfield. Rescue of the F-80 engaged them in battle. This time the victory went to Lieutenant Orrin Fox (Orrin R. Fox) from the 80th FBS shot down two Il-10. Two Yak-9 downed pilots from the 35th FBS Sandlin Harry (Harry T. Sandlin) and Richard burns (Richard J. Burns). The rest of the day pilots “Shuting Old” shot down one Il-10.
28 June, aircraft of the 8th FBG for the first time struck at ground targets North Korean tank columns coming to Seoul. Distance of target from ground-based (500 km) forced the pilots to use external fuel tanks, making it impossible to use bombers and missiles. All this is not allowed “Shuting Star” to effectively deal with tanks and armored personnel carriers, for which six heavy machine guns of F-80-x posed no danger.
Already the first days of the war revealed many shortcomings in the design of aircraft and training pilots. Right on the airfields had to reinforce the underwing pylons that were broken and could not be used for suspension of the fuel tanks, missiles and bombs. For this reason, a significant number of F-80, had just become disabled. Constantly felt the lack of external fuel tanks and oxygen masks. In the end, technical problems resolved quickly, and the supply has established.
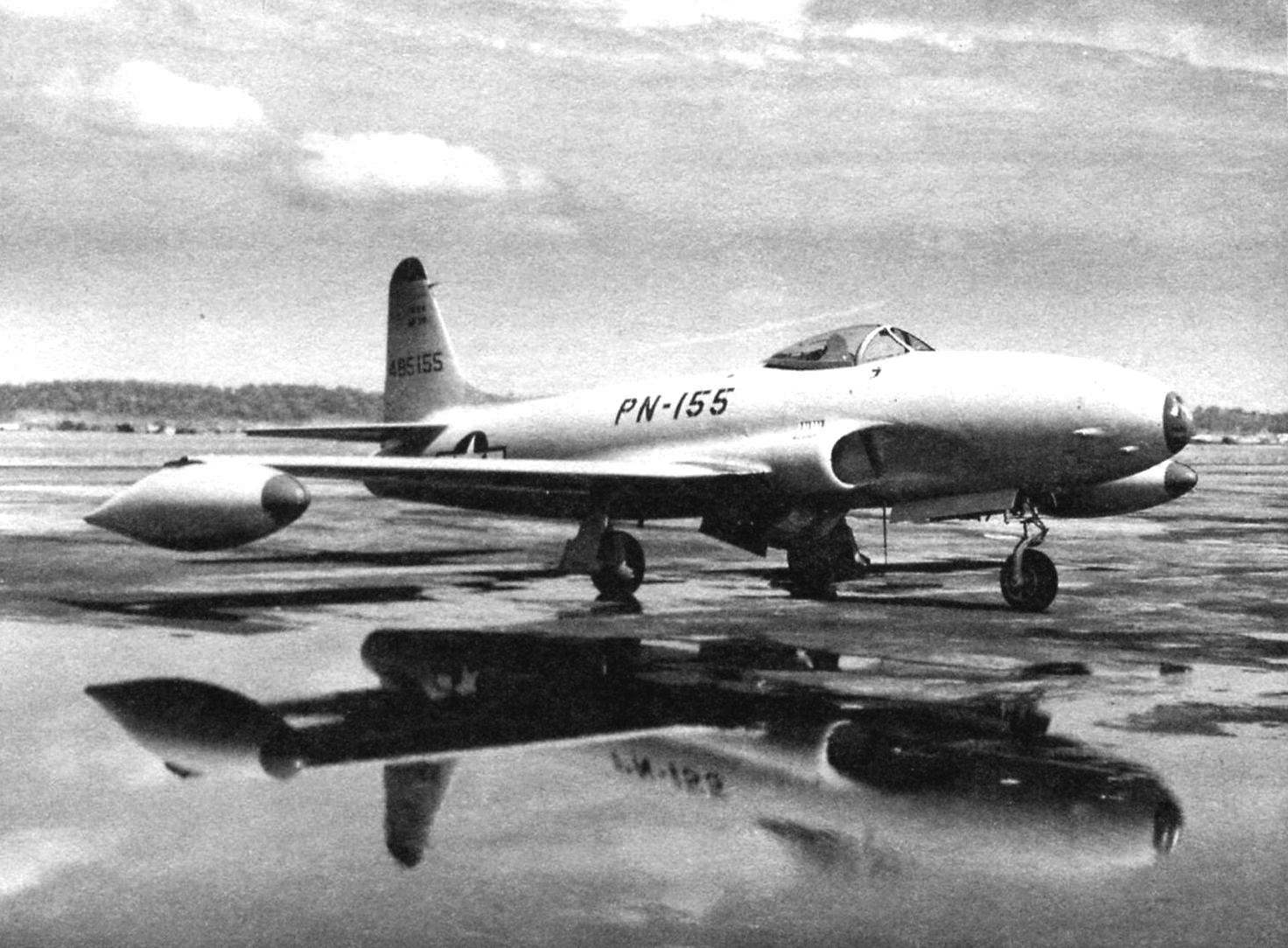

The F-80A
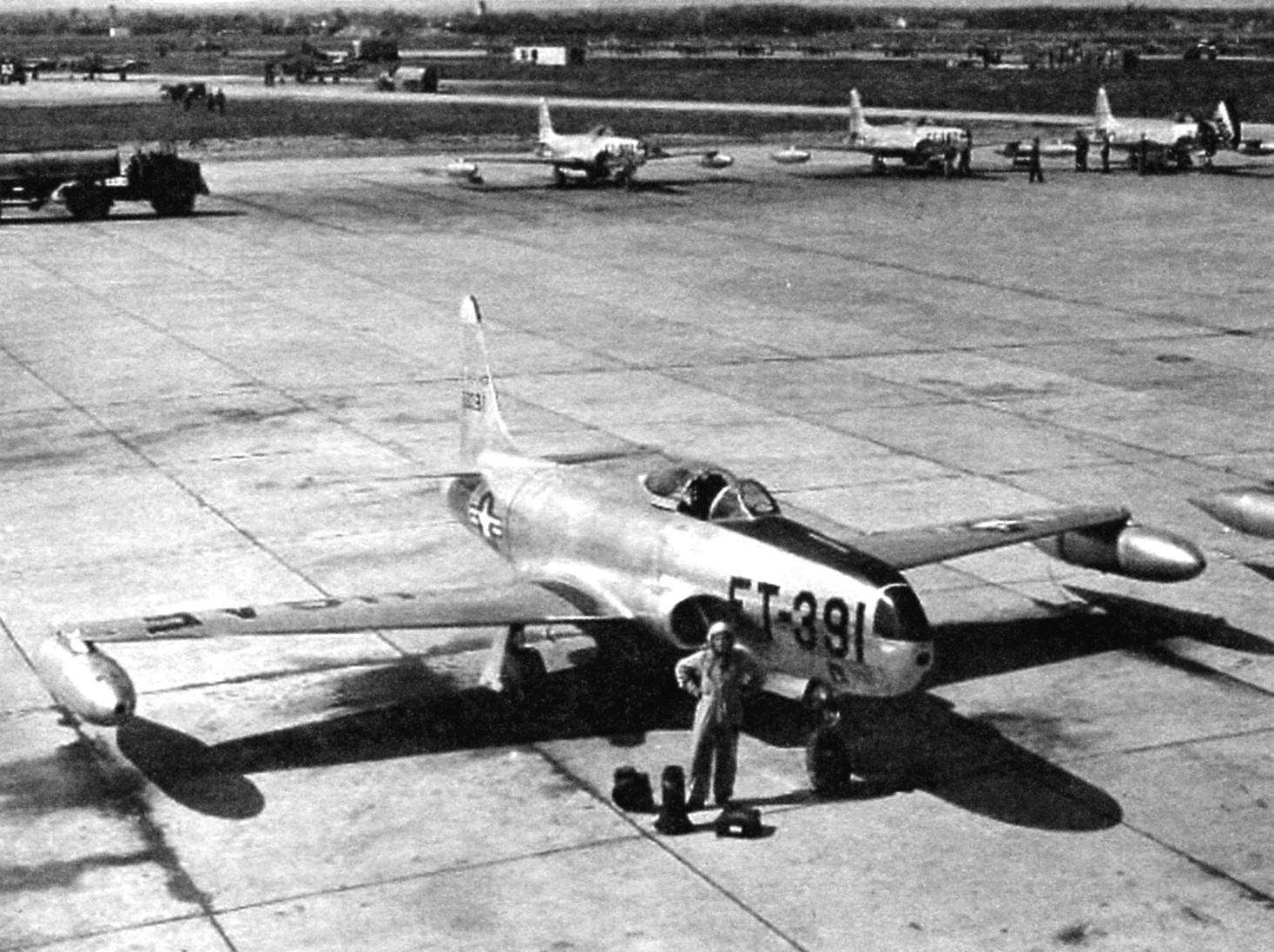

Reconnaissance aircraft RF-80A
The hardest thing was to address the shortcomings in the training of pilots. After the end of world war attention to the training of flight crews has shrunk. The squadron prospered simplism. It was believed that, and so the American pilots the best in the world. In fighter-bomber squadrons fully excluded from the basic training flights at the maximum range for unknown routes. The pilots performed the flights on familiar routes between the bases of Japan to the permanent navigation support from the ground. With the outbreak of hostilities, even for experienced pilots began to encounter difficulties in flying over the territory, inadequate navigation AIDS. When it was necessary to maintain the aircraft on the way number of way, few were prepared for this. With difficulty the pilots have survived for long flights to limit the range.
It’s hard to believe, but the year before the outbreak of war in Korea in the squadrons of the F-80 was not conducted firing HVAR rockets on ground targets, which could not impact on the effectiveness of the use of fighter aircraft in the first months of the conflict. Of course, the command knew what was happening in parts of the aircraft. Air force commander General George Stratemeyer (George E. Stratemeyer) has repeatedly reported to Washington about their problems, but Congress reduced the military budget did not allow to conduct full-fledged training and maintain the entire fleet of combat aircraft. Sometimes you just do not have enough kerosene to fly.
Still, squadrons of F-80s was actively used by the American command for solving a variety of problems. June 30, four F-80C of the 36th FBS has conducted air battle with a group of North Korean Yak-9, covering the Il-10 over the Suwon airfield. Junior lieutenants Thomas (John V. Thomas), and Worcester (Charles A. Wurster) shot down one aircraft. July 19, RF-80A of the member of the 8th PRS found in the area of Pyongyang previously unknown airfield of the enemy, which was more than 25 piston aircraft. In the same day “shuting old” from the 8th FBG struck the bomb. The results of the blow out sent the spy plane, the photos were seen destroyed 14 enemy aircraft.
The intensity of use of aircraft “Shuting star” in the first days of the war can be traced on the example of the 35 squadron aircraft which made 737 sorties (held in the air 1535 hours) for the first month of the war. Before the outbreak of hostilities the squadron pilots carried out by only 103 of departure and had only 218 hours of flying time.
By mid-July, as a result of blows of the American aircraft on the major North Korean airfields were destroyed around 50 planes on the ground, 9 of machinery in the air and about 30 enemy vehicles were damaged. From that moment the remnants of the North Korean aviation began to spread ourselves out on a small, well-camouflaged runways near the front line. From there they made an unexpected “outing” acting mainly at low altitudes. But it no longer represented a serious threat to aviation and ground forces of the Americans.
Since the end of July “shuting old” switched to action against ground targets. Special attention to the F-80 was paid to tank columns. In the fight against tanks the greatest efficiency was shown incendiary Napalm tanks. Other weapons could disable T-34 tanks, bombs did not possess sufficient accuracy, the rockets HVAR pierced tank armor, but the fiery tank destroyed everything in the area of 50 m2. Burning Napalm instantly burned all the oxygen in the air and a large part of the enemy hit by the attack, died not from burns, but from asphyxiation.
In the first months of the war, 70% of all sorties were F-80. A great influence on the efficacy of “shuting old” had errors in the guidance and the almost complete lack of information on the objectives. Often pilots are not have found at the specified location and dropped bombs anywhere. However, this did not prevent the Americans to declare that their aircraft from July to October 1950 destroyed: 39 of thousands of soldiers, 452 tank, 6000 vehicles, 1300 cars, 250 locomotives and 75 bridges.
The distance of the airbases the F-80 has led to the fact that even with the use of external fuel tanks over the target they could be only 15 minutes. This time was clearly insufficient for its destruction. The problem was solved pretty quickly. In Korea sent a 130-th engineering brigade of the air force, reinforced the engineering units of the army. At the end of July, the brigade was prepared airfield K-2 at Taegu and K-3 at Pohang to receive jet aircraft. This increased the length of the runway and covering it with steel gratings such as a PSP. Parking areas aircraft equipped with revetments of sand bags.
The rapid onset of the enemy did not allow the pilots to appreciate the work of the builders. In August, the “SCHU-ting old” left my new base and flew back to Japan. Before the command again there was a problem with a small radius of the F-80. From external fuel tanks had to be abandoned and free up hardpoints for weapons. The use of external fuel tanks on the wing tips with a capacity of 625 litres (teardrop) or 757 liters of the firm Fletcher did not solve the problem. Even the action with the nearest Japanese airfield in Itazuke plane with eight NUR HVAR had a radius of only 350 miles, and if the suspension of the two 454 kg bombs radius was reduced to 160 km. To the rescue came the ingenuity of the technical staff of the 49th FBG. Lieutenants E. Johnson (Jonson) and R. Egan (Egan) made new fuel tanks, adding tanks to Fletcher another compartment and bringing the total tank volume up to 1003 liters. The range of “Shuting old” increased to 563 km, with a full bomb load. New tanks received the informal name “Misawa”. Japanese entrepreneurs quickly established a serial production of new items.
Successful solution of the problem generated another. At sharp maneuvers of the aircraft with “Misawa-tanks” began to fall off the wings. In combat conditions the pilots were forced to refrain from maneuvers and the appearance of enemy fighters try to get rid of payload. However, the overall efficacy of the F-80 has grown, and the enemy began to notice the F-80, where before about them and not heard. Thus, the aircraft “Shuting Old” 8 FBS found to the North of Seoul a large column of enemy troops and attacked her. Part-time hours were destroyed 117 trucks, 38 tanks and a large number of manpower of the opponent. Such successful missions after the invention of the new tanks was a lot. From the air it was clearly seen that the roadsides piled with burned-out tanks, armored personnel carriers and trucks. Ultimately, the troops of the enemy, suffering heavy losses on the March, reduced the rate of occurrence. Napalm, bombs and missiles did their work.
In late August 1950, reconnaissance aircraft RF-80A of the member of the 8th PRS made a thorough exploration Inconscio port, chosen by General Douglas MacArthur (Douglas MacArthur) as paragraph landing. Its significance in the Korean war Inchon occupies the same place, which is Stalingrad during the Second world war. In the process of preparation of the operation, there was a lot of issues, one of which was the determination of the height of coastal concrete walls, which have to climb the infantry. In one day “shuting star” with a height of 60 meters has made several visits to the photography. The images were analyzed by a special group composed of one air force officer and two civilian experts, they were able to detect an excess of wall of sea level at different stages of the tide with an accuracy to several centimeters.
With the beginning of landing on Incheon appeared and the F-80. At this time, not without loss. 9 Sep anti-aircraft fire shot down three F-80. September 30, the Americans lost another two “shuting old”.
A successful landing airfields in Kimpo, Taegu, and Pohang once again became available to the U.S. air force. “Shuting old” began to use the tactics of Shuttle flights. Flying from airfields in Japan, F-80s attacked targets in Korea and landed in Daegu. Small group service level of 46 FBS produced aircraft refueling and mount weapons, and then released the machine in the reverse way. After the attack on North Korean troops planes returning to their bases in Japan. Such flights have become a necessary measure, as the Korean air bases did not have enough tanks to store fuel and necessary equipment.
Came winter, the first cold spell brought a lot of trouble to the engine-builders of the F-80. It turned out that at temperatures below 0° C the engine will not start. To start I had to use a 140-octane gasoline from the Mustangs. To the technical staff of the winter was a real horror. After all, unaccustomed to the cold Americans lived in small houses made of boxes and in tents.
Despite the difficulties, the pace of the F-80 was not reduced. In September from the airport to Daegu was committed 750 sorties. During this period, the F-80 began to make night flights. As a rule, the flight was conducted alone, at least a couple, in order to apply the “harassing attacks” on convoys of troops and enemy communications. Experienced pilots with a simple navigation instruments F-80 was able to penetrate to the army headquarters and concentrations of enemy troops in the rear of the combat area and keep them in constant tension. For causing “anxiety” to the whole area it was necessary to make several sorties during the night. At the same manpower and equipment of the enemy were inflicted considerable damage, although, as acknowledged by the Americans themselves, in the course of such raids perished and the civilians. Unpunished night raids undermine the North Korean soldiers faith in the effectiveness of its aircraft and air defense systems.
According to American sources, 8 November 1950 held the first meeting of the F-80 jet fighters MiG-15. Four “shuting old” of the 16th FIS was escorted by b-29 bombers striking blow on the bridge over the river Yalu. Before the approach to the target they were attacked by six MiGs. F-80 turned and took the fight. As a result of brief maneuvering one of the “MiGs” were corrupted and fell. The victory was chalked Lieutenant Russell brown (Russell Braun). This battle in the West is considered the first combat jet fighters in aviation history.
Pilot F-80 Jack Smith describes this battle: “… on the radio … warned: from the North on the approach of eight MiGs. Lieutenant brown visually detected enemy. “MiGs” was approaching rapidly – now the Americans were in the shoes of a pilot piston Yakov. Break away from the enemy was not possible. Brown moved his fighter into a gentle dive and ahead of the aircraft commander. The Lieutenant managed to catch the moment and he rushed to the attack. The presenter covered the slave. Stephens made the snake to examine the airspace – do not chase the “MiGs” for the closing couple:
– I looked around – if there were any MiGs? I saw one, and where! The enemy fighter hung on my tail!
Stevens managed to break away from “MiG” sharp transition into a dive, and brown is still “got” his “bandit”, despite the fact that his plane was denied five guns out of six!”
From our side the loss “MiG-15” this day deny it. How it actually is difficult to say, it may be true. But very soon the bitter mood in pilots of the F-80 has stopped, the pilots realized that “shuting Starov” had a serious opponent. 27 Dec pilots 177th IAP intercepted a group of F-80s from the 48th RVS. Captains J. M. Fomin and M. G. Andryushin knocked one “Shuting Star”. 3-th and 6-th of January the Americans lost in aerial combat five “shuting Starov”. January 24, 177-th IAP full structure had a fight with a large group of F-80 and F-84. Captain Belikov shot down one F-80. Ten days later, MiGs intercepted the five “shuting Starov” and shot down two of them. On this day the Americans lost and the T-33, which was sometimes used as aerial command post and relay data about the tactical situation with ground-based radar aboard fighters. It was intercepted over the river Yalu.

The loss of “shuting Starov” irresistibly grew, but the number of sorties these machines is not reduced. Over the described period, they made 736 sorties against the advancing Chinese army. But the advent of the Chinese has been developing rapidly. December 15 is the front line approached Kimpo on 20 km Now based there F-80s of the 49th FBG did several sorties a day, helping to keep the defense. The departure time was only 10-15 minutes, maximum aircraft loaded with bombs and missiles. Only one squadron of these days has recorded 817 sorties. Despite all efforts, February 2 airfield Kimpo surrendered Chinese troops. Rising on this day from the airfield planes throwing bombs and flew to Japan on the air base Jensen, where they were based until mid-1951.
Retaliatory counterattack the Americans demanded a powerful air support, and again the main burden fell on the F-80, which until the end of February has made more than all sorties – 750. February 23, 1951 a pair of “shuting Starov” from the 35th FBS attacked the strong point of Chinese troops in Inina. Napalm literally burned the 170 soldiers and officers. When this district was occupied by American troops, their eyes opened a terrible picture – all the equipment that was in the paragraph, completely burned and melted. Around it lay the mutilated corpses of soldiers.
Successfully passed and the RAID aircraft from the 8th and 49th FBG at the airfield Sinai. Most of the being there of the aircraft “Yak-9” and “Il-10” (about 40 pieces) were destroyed. All F-80 back to their bases.
In the second half of the war begins a gradual replacement of the F-80 on more modern machines the F-84 and F-86F variant of the fighter-bomber. Every month the F-80 less and less appeared over the battlefield. 12 September 1951 can be considered the most tragic day for the F-80. On this day, North Korea’s “MiG-15” managed to shoot down 15 F-80 in one dogfight. However, only three of the MiG was damaged.
In late September 1951, the 49th fighter-bomber group passed F-80s and moved to R-84. “Shuting old” was transferred to the 8th FBG, which continued to participate in the fighting. Now the F-80 did not fly in large groups, and operated at 4 to 8 aircraft. Increased tactical skill of the pilots allowed fewer aircraft to achieve good results. This was facilitated by more precise control of the aircraft from the ground. This was deployed 18 posts pointing to ground targets. Widely used advanced air controllers and airborne command posts. As the last used light aircraft T-6. Particularly well T-6 helped with the rapid moving front line.
The longest F-80C was delayed in part of the 80th FBS. His last sortie they made April 24, 1953. On this day, the planes carried out 120 sorties and dropped on the enemy, about 100 tons of bombs.
6 months before the end of the war all “shuting old” were taken from the combat units. At the front there are only scouts left RF-80 of 8th, 15th and 45th TRS. One of the main tasks of the scouts were reconnaissance of North Korean airfields, roads and Railways, surveillance of bridges and crossings over the river Yalu. With the advent of “MiG-15” the work of the scouts has increased, because the RB-29 and RB-26 could not perform exploration of the Northern regions of Korea, which was covered by enemy fighters. Since the end of 1951 became scarce RF-80. This forced air command to go to the conversion part of F-80S in the scouts. The work of remodeling was carried out directly in the field by the technical staff of the 67th TRG. With forty F-80S was shot all weapons and installed the camera from the RF-80A. The “new” aircraft received the designation RF-80S. To some extent this has reduced the need for high-speed scouts. RF-80S flew to the end of the war, was quite successful in carrying out their tasks. Based these planes at the air base K-14 Kimpo.
The use of reconnaissance aircraft command made a lot of mistakes. The main one was the duplication of tasks. Often to perform a exploration of the same objects flew as an RF-80 and RB-29. Sometimes lining the same happened with the aircraft carrier-based aircraft. Clear cooperation in this matter between the branches of the armed forces was not established.
In July 1951, was first performed air refueling of three RF-80A from the tanker aircraft KB-29. At the end of the right wing RF-80A mounted fuel consumer boom, similar to the F-84. The task of these aircraft was photographing the airfields on the river Yalu. Refueling was carried out on the Gulf of Wonsan. This gave an opportunity for the scouts to fly at maximum speed and avoid encounters with enemy fighters. A few days later, refueling was carried out and the F-80C.
“Shuting Old” was distinguished by its great structural strength. A legend of the Korean war was the case with the F-80C of 49th FBG, when he was performing the attack at low altitude, struck the ground, ricocheted up and flew back to their base. Known and the case when one of the F-80 crashed into a cable of a high voltage power line, ripped it and returned to base.
For the entire period of the Korean war “shuting old” has completed 98 of 515 sorties, dropped on the enemy 30 179 tons of bombs, 7554 tons of Napalm and released 80 935 rockets. The Americans acknowledged the loss of 143 F-80, 14 of them were shot down by fighters “MiG-15”.
DESIGN DESCRIPTION
The F-80 “Shuting Old” was a monoplane with straight low wing and single-fin tail. Structurally, the fuselage consisted of three parts. In the bow housed a pressurized cockpit, weapons and equipment. In the first modification in the bow mounted boarding-taxiway spotlight, and the modification and radar rangefinder AN/ARN-6. The middle part of the fuselage was occupied by fuel tank and inlet channels. In the back was the engine, and it is attached to the tail feathers. At the bottom of the fuselage directly under the cockpit, installed the brake pads with hydraulic drive. Calculated overloading of the airframe was equal to 11 d. air Inlets-side, with vertical blade boundary layer.
The wing had a NACA 65213 profile. The internal volume of the wing was occupied by the fuel tank. The mechanization of the wing consisted of flaps (max. deflection angle of 60°) and ailerons.
The tail unit was symmetrical profile NACA 652010. At the top of the keel was fixed to the radio antenna AN/ARC-3. The elevators had trim tabs. The scope of the stabilizer – 4,75 m.
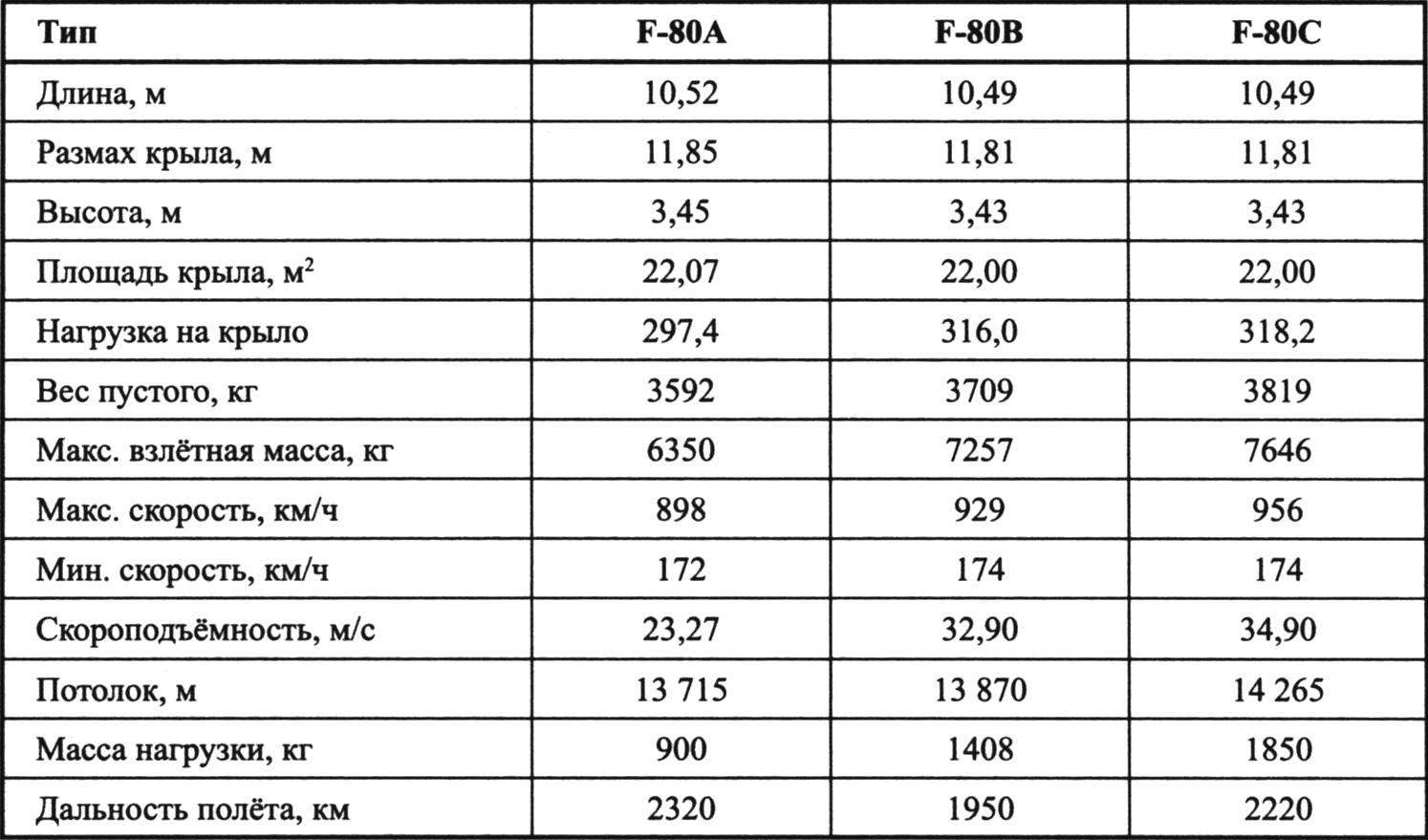
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Landing gear is tricycle, with the nose wheel. The cleaning mechanism -hydraulic. Main legs retracted into the fuselage.
Jets latest series to install the engine company Allison J33-A-35 centrifugal compressor. With water injection in the compressor the engine thrust reached 2450 kg Maximum fuel inside the fuselage – 2487 L.
Built-in armament consisted of six machine guns M-3 12.7 mm. Maximum rate of fire – 1200 rounds per minute. Ammunition – 297 rounds per gun. In the cockpit was set the scope To-14. Under the wing of the F-80B by two pylons suspended two bombs caliber 454 kg, or 8 NUR HVAR caliber 127 mm, or two incendiary tank with a capacity of 416 liters with Napalm. On the F-80C has established two additional pylons under the wing. The maximum load of the fighter increased up to 1850 kg. Check shooting results was carried out by shot-method N-6.
A. CHECHIN, N. Food reserve was