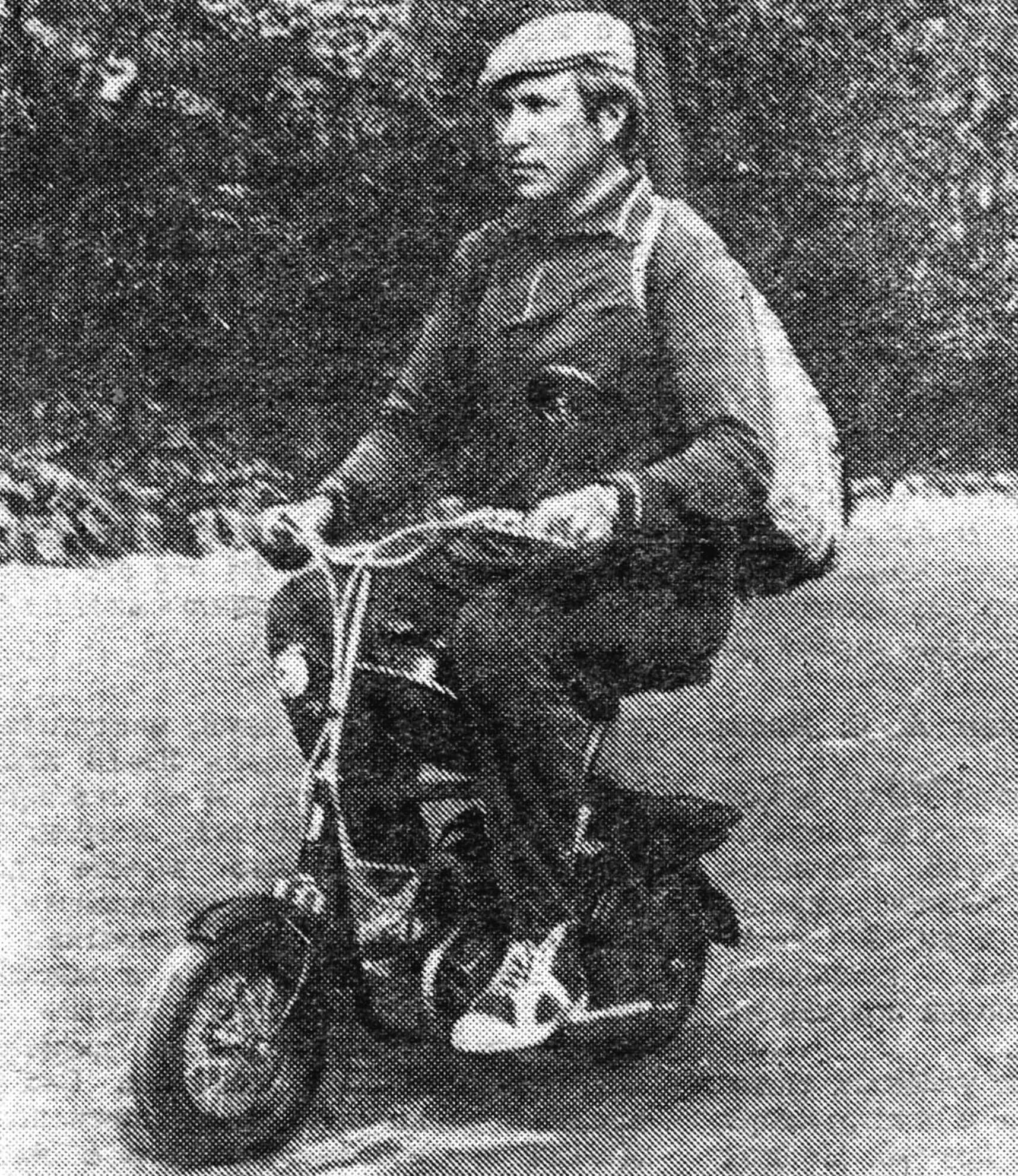
Maximum simplicity of design and minimal complexity of manufacturing – these are the principles that were used as the basis for the creation of the Gnome micromotorcycle (see photo).
The frame is made from parts of a scooter and a frame from a road bike (see Fig. 1, 2 and general view). The connected horizontal and rear links (part A) are cut from the bicycle frame, and lengths of 60 mm, 65 mm and 120 mm are cut from the front link. Then, from a tube Ø 22 mm, cut lengthwise, three rings are sawed off with a hacksaw and put on a piece of the same tube 340 mm long. A brake pedal with a lever, made of a 4 mm thick steel strip, is attached to the middle one. The outer rings, placed close to the middle one, play the role of a sliding bearing for it, then this entire bracket is installed on the frame and rubber footpegs from a motorcycle are put on its ends. All fastenings are made by brass soldering.
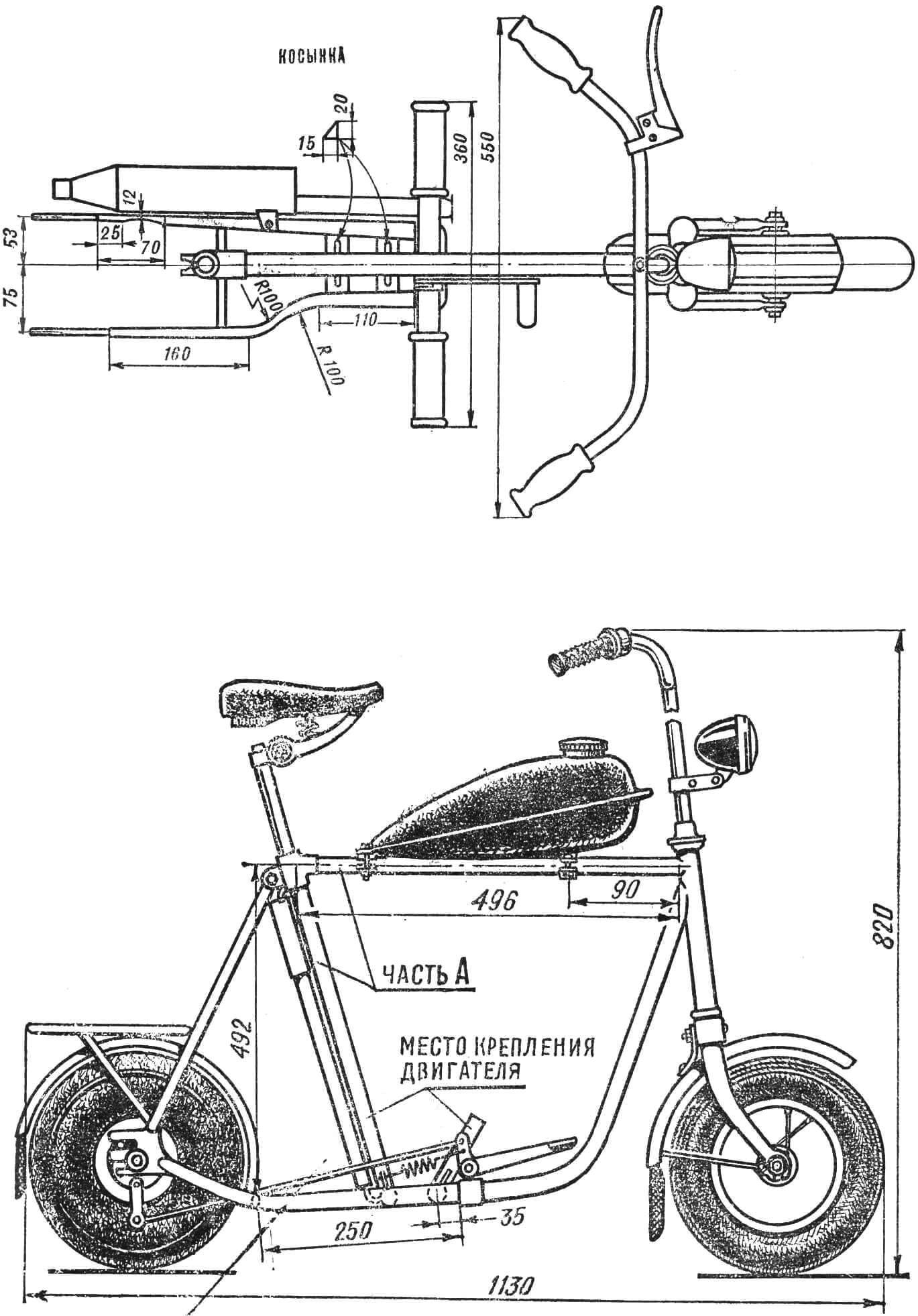
Sections 60 and 65 mm long are welded between the halves of the rear fork of the scooter. A 120 mm long section is welded to the front of them and to the middle of the micromotorcycle footrest pipe, forming the front mounting bracket for the D-6 engine.
Part A rests on the rear section, to which the rear engine assembly is attached, a tank from a “Verkhovina-3” or “Verkhovina-4” moped and a saddle from a “Riga-7” moped are installed. This is the best saddle of this type. It has a place for keys, and its spring serves as a good shock absorber; In addition, it is possible to adjust the saddle height. The right half of the scooter’s rear fork bends as shown in Figure 1.
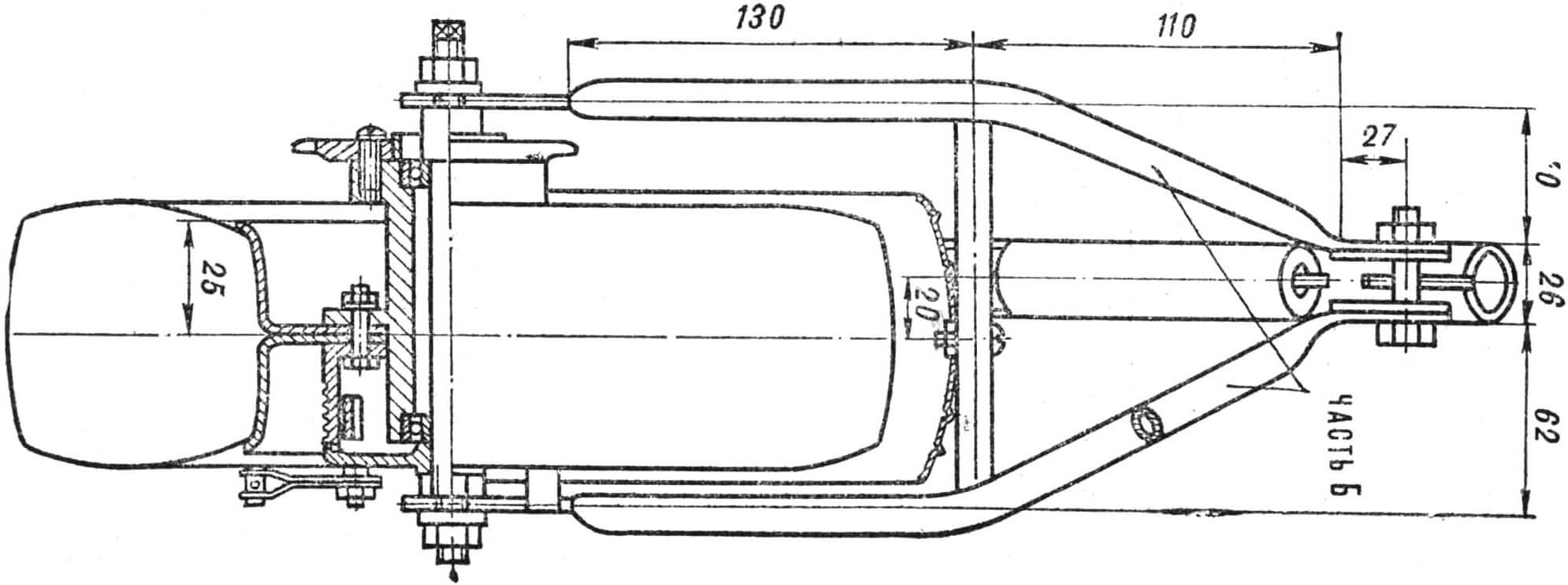
Eyelets are made from sheet steel 4 mm thick (Fig. 5), which have slots for the axle, and in the right one a slot is made for the locking pin of the brake disc. The lugs are welded into the fork to replace the old ones.
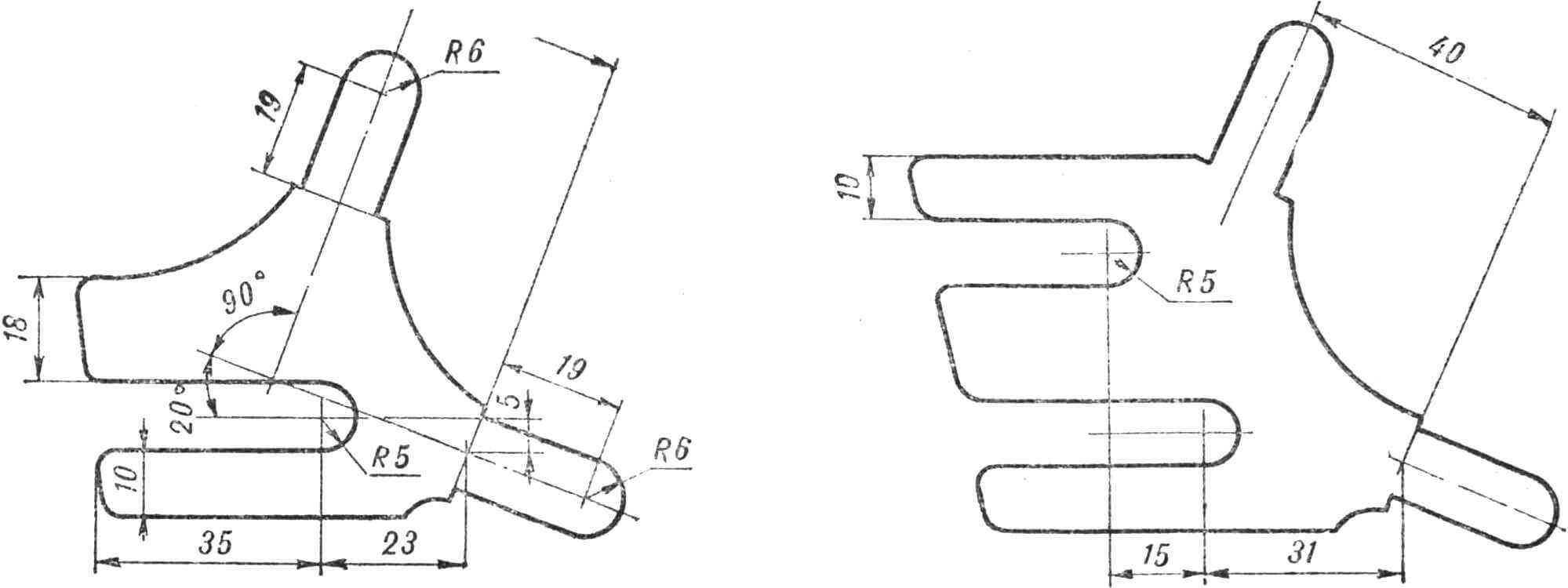
The section of the left half of the fork on the inside is flattened, as shown in the drawing, for the passage of the chain. Then the halves of the rear strut are cut off from the bicycle frame, made flat on the inside, bent as shown in the drawing, and attached to the lugs by welding (part B). Pieces of tube are welded between them and the rear fork halves to increase rigidity and secure the rear fender.
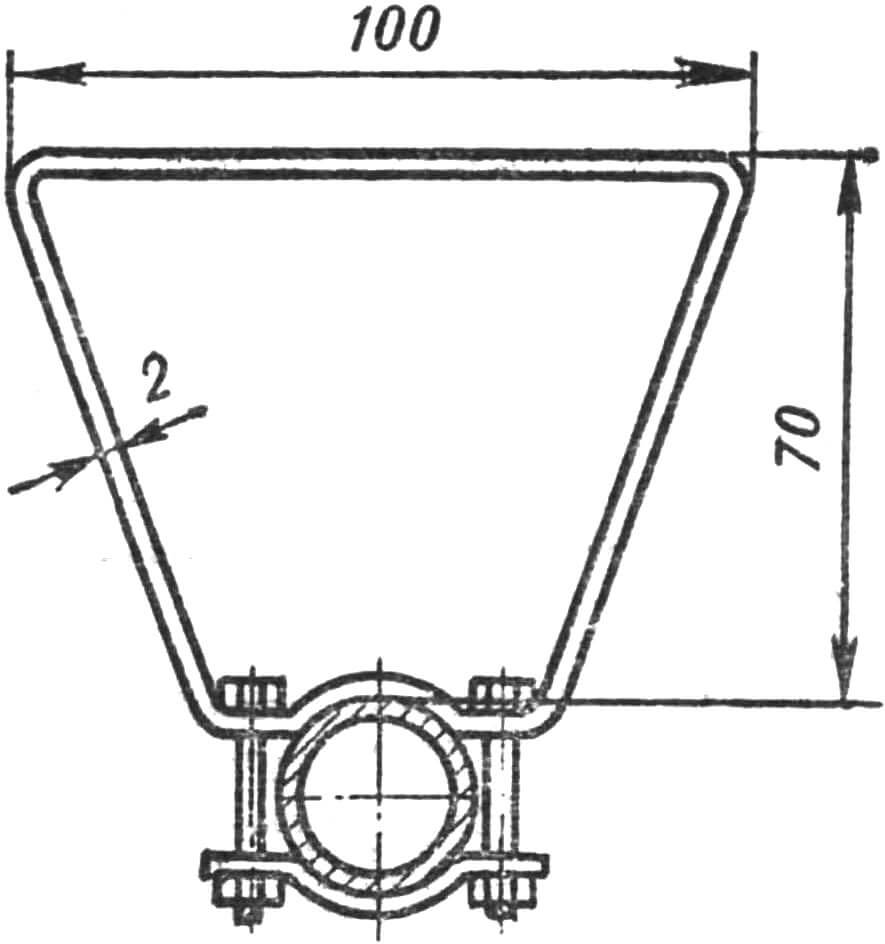
The front bike rack is used for transporting cargo.
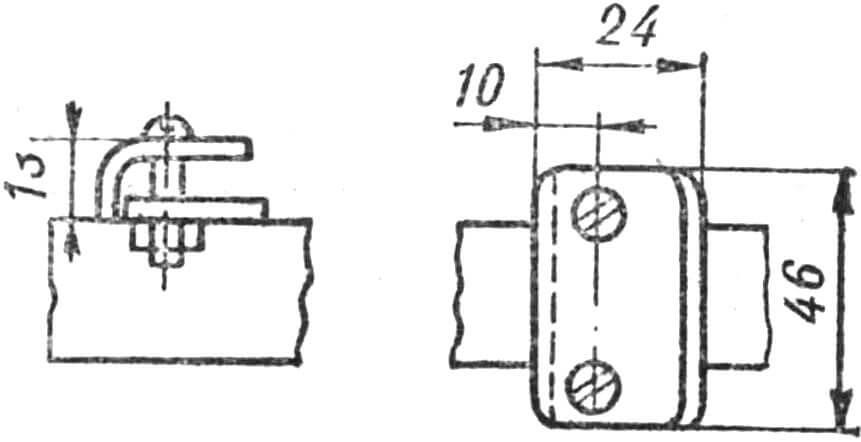
The holders for the pump are welded to the vertical link of part A from the back, and the rear mounting plate of the tank is welded to the horizontal link (Fig. 4). Here, a palm-width area remains on the frame for carrying a micromotorcycle.
The frame is ready. All that remains is to paint it to match the color of the tank with Moto-Java nitro enamel.
Wheels. The front one, size 300X60 mm, is from a scooter. To increase strength, you need to double the number of spokes (taken from the rear wheel of the scooter) by drilling holes for the nipples in the rim. The ball bearing separators are removed and more balls are added.
To prevent the tire from self-breaking, the contact point between the tire and the rim must be taped with a strip of rubber bandage.
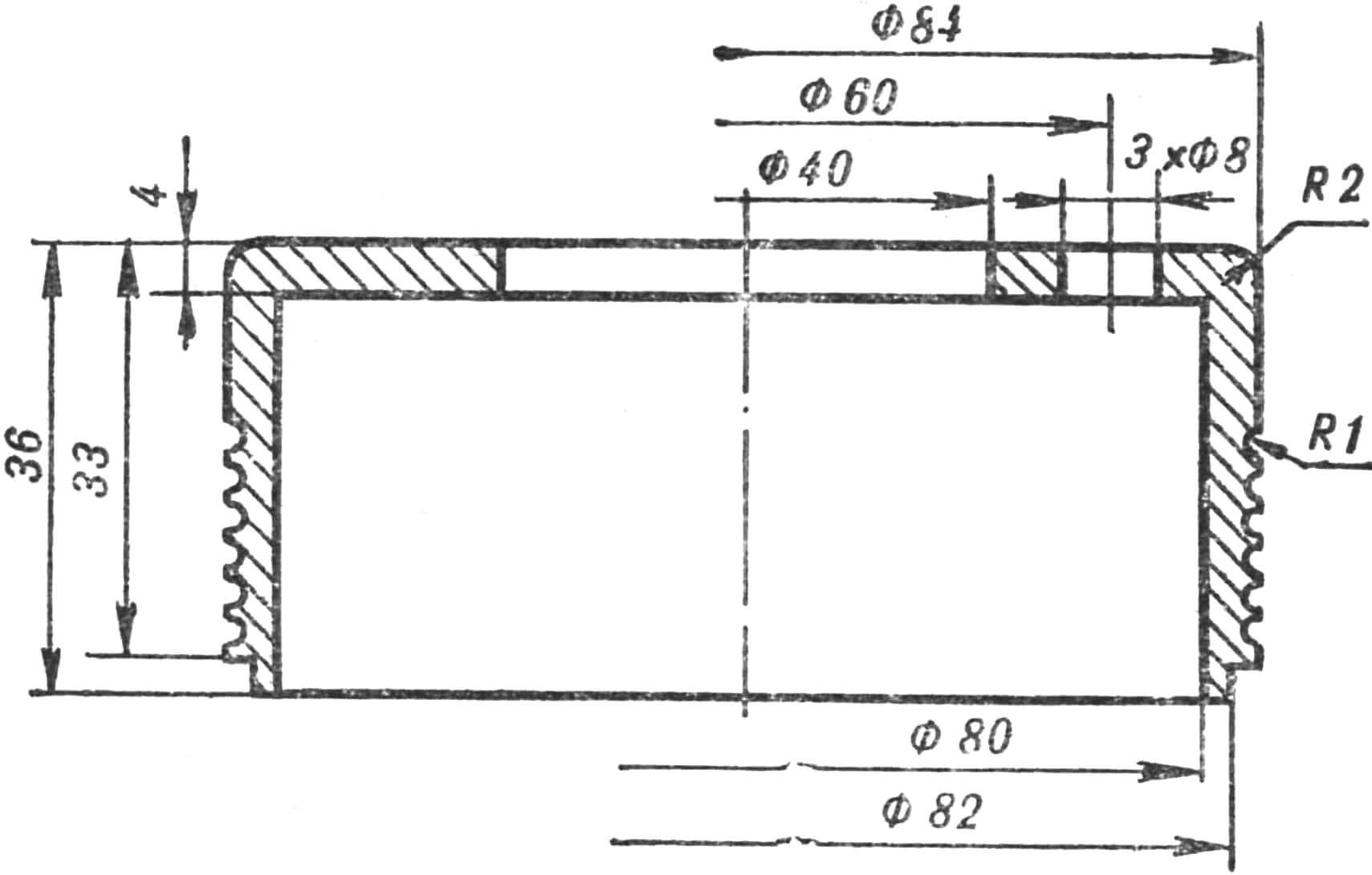
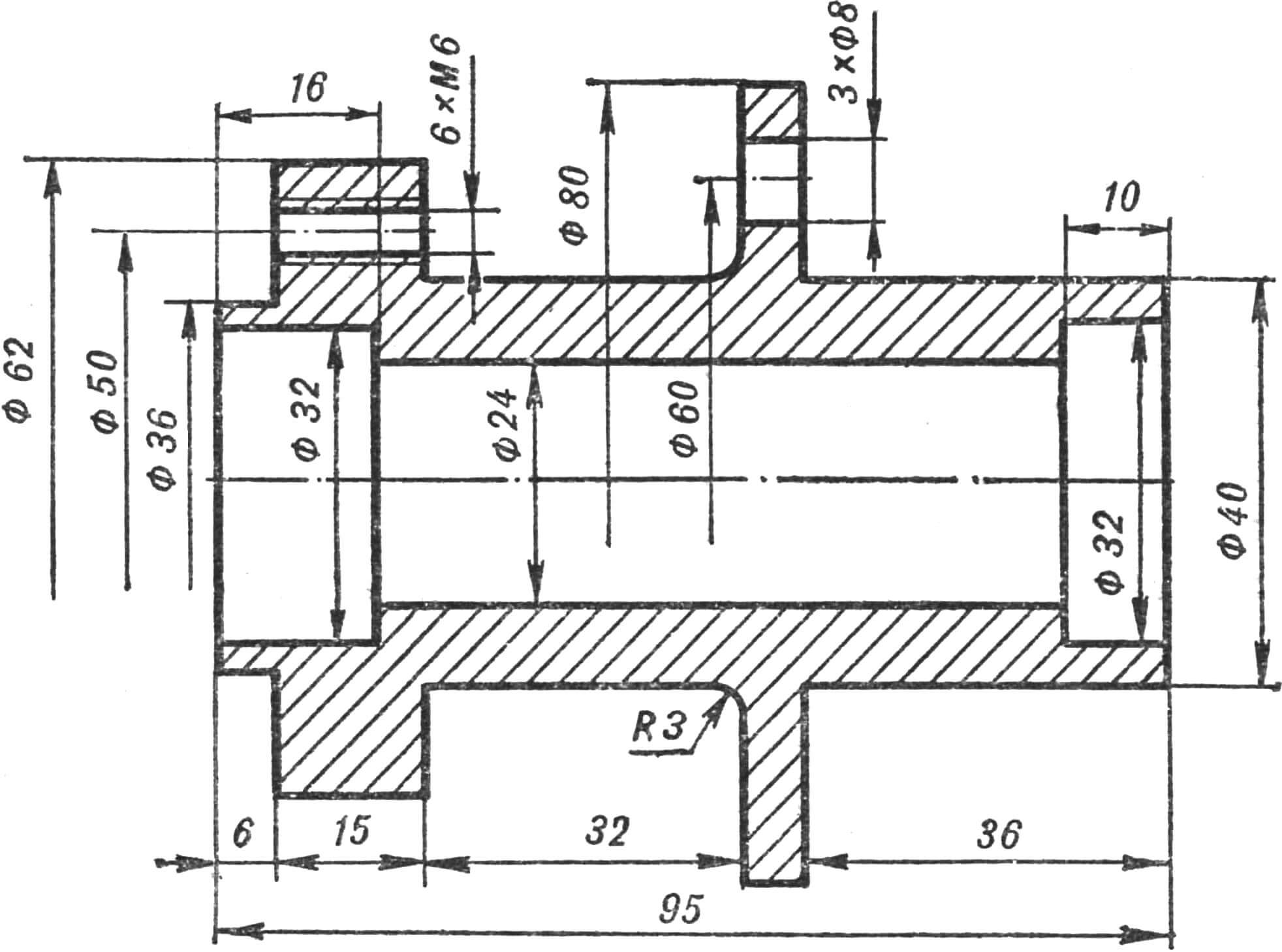
The rear wheel measures 280X85 mm (B-29) – from a kart. The axle is steel, the hub (Fig. 9) is made of duralumin. The latter has a cylindrical protrusion on the left for seating the sprocket and a thickened flange with threaded holes for fastening it. The 19-tooth sprocket is from a road bike. Its body has holes for mounting screws. With such an asterisk, the Gnome reaches a speed of 50 km/h on a flat road. To drive on very rough terrain, you need to install a sprocket with 21 teeth. There is enough space on the flange for new mounting holes, and the size of the eyes ensures normal chain tension without changing its length.
Between the central flange of the hub and the brake drum, the wheel discs with the camera and tire mounted on them are clamped using three bolts (see Fig. 2). One of the methods for making disks is described in “M-K” No. 6 for 1974. You can also turn them from a duralumin blank or casting.
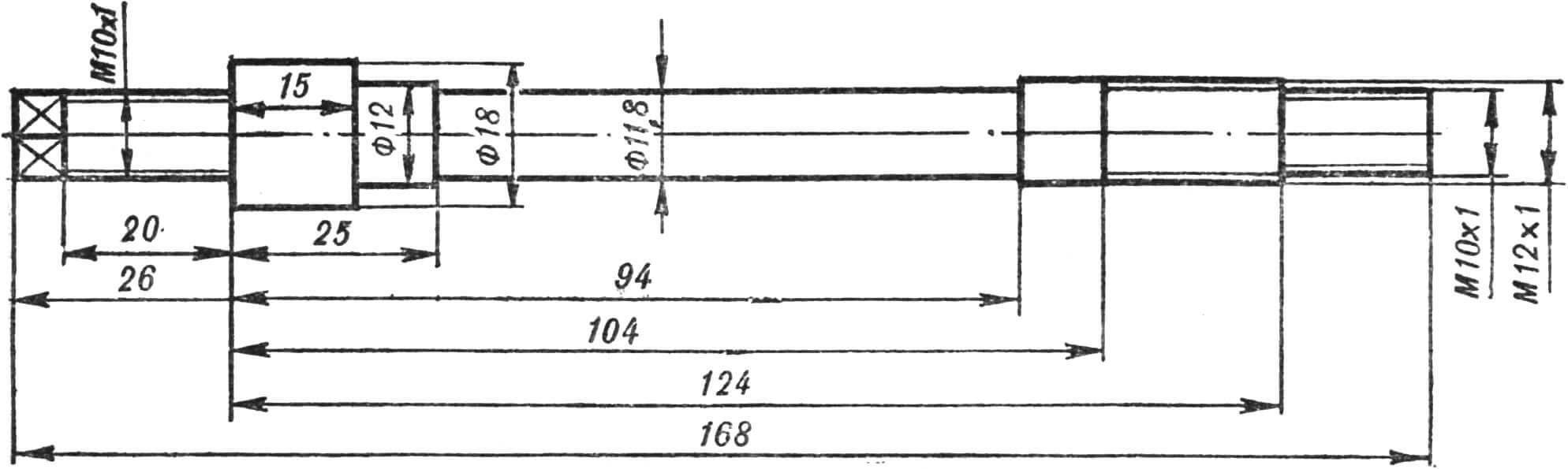
The length of the right half of the hub and the dimensions of the brake drum are given for the case of using a brake pad Ø 79-80 mm (from the Yavetta or Stadium moped). With other pads, these dimensions and the shape of the right eye change. To avoid splashes from the front wheel, the scooter’s wing must be moved forward in a circular arc by 120-130 mm, for which the wing mounting angle is riveted.
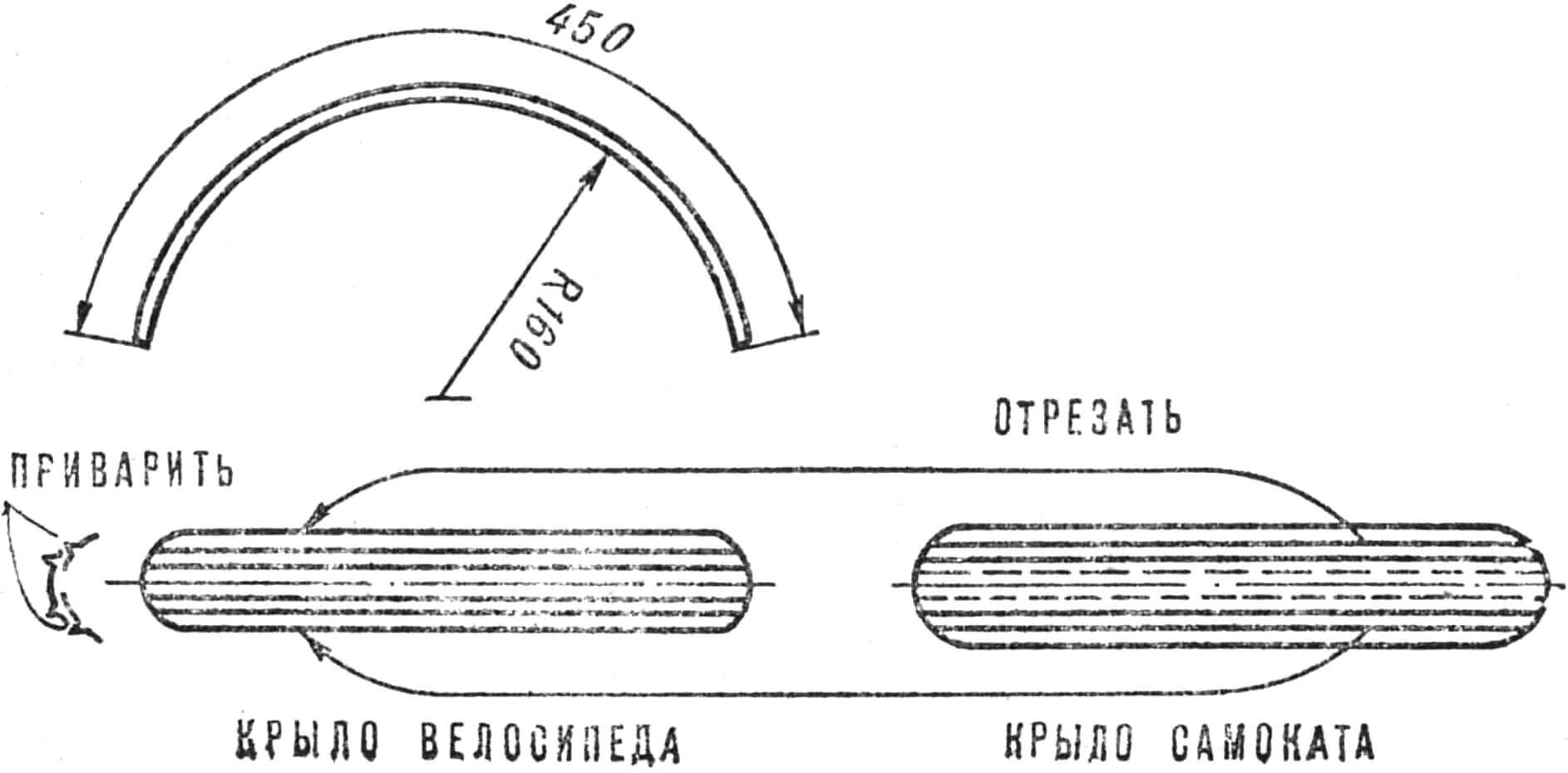
To make the middle part of the rear fender, you need to make a piece of the fender from a road bike flatter in cross section, and then bend it in an arc with a radius of 160 mm. The side parts along with the stiffeners are cut off from the rear wing of the scooter and welded to the prepared central part, as shown in Figure 3. Rubber mud deflectors are placed at the rear ends of the wings.
The micromotorcycle engine starts with acceleration. With good ignition adjustment, a distance of two to three meters is quite enough. To get moving, you need to make one or two pushes with your foot. Maintaining balance when riding a Gnome is initially somewhat more difficult than when riding a bicycle. To increase stability, it is desirable to increase the fork offset (see “M-K” 1974, No. 5, p. 15).
For teenagers, a micromotorcycle can be made in a significantly simplified version. The rear wheel hub of the scooter is replaced with the rear hub from the Shkolnik bicycle. Double the number of spokes from the moped is installed. To do this, they are cut from the “cap” side to the required length, then their ends are bent again, and the holes in the sleeve are enlarged.
Instead of the drive sprocket, a brake lever is installed. The new sprocket is fastened like a motorbike: using steel half-rings and rubber gaskets, on the left side.
The tire is treated in the same way as the front one. There is no need to bend the scooter fork for such a wheel; You just need to weld the eyes with slots for the Ø 8 mm axle.
To store and transport a micromotorcycle in public transport (without gasoline), a cover measuring 1700X1500 mm is sewn from thick fabric. “Gnome” also fits in the trunk of a car.

BRIEF TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Overall dimensions, mm:
length… 1130
width … 550
transport width (steering wheel turned at 90°) … 360
height… 820
Engine…D-6
Weight (dry), kg … 25
Speed, km/h … 50
Payload, kg… up to 120
G. KNYSHEV