Electronics today referred to as the catalyst of scientific-technical progress. It is really hard to find the field of science or engineering, not electronic engineering. Natural popularity that are mugs e-direction in students. As a rule, syut they have a narrow specialization, for example, radio club, club automation, etc. is quite justified. The enduring nature of the lessons (1-3 years) allows students to acquire a deep enough knowledge of the theory and the necessary practical skills by working in any one field of electronics.
Electronics today referred to as the catalyst of scientific-technical progress. It is really hard to find the field of science or engineering, not electronic engineering. Natural popularity that are mugs e-direction in students. As a rule, syut they have a narrow specialization, for example, radio club, club automation, etc. is quite justified. The enduring nature of the lessons (1-3 years) allows students to acquire a deep enough knowledge of the theory and the necessary practical skills by working in any one field of electronics.
In the camp circle is in the other conditions. Only 6-8 sessions, no pre-training of the majority of guys of different age composition and some other factors make meaningless the construction of the circle according to the scheme used on the suit.
The specificity of the pioneer camp suggests the creation of a wide circle, whose main task is not the design of complex devices, and the popularization of knowledge on the largest and most promising areas of electronics. But summer camp has more possibilities to reach of children technical creativity: the year a large number of students through its clubs, will receive vouchers for syut in accordance with its vocation.
The above considerations formed the basis of the circle of radio electronics pioneer camp “Artek”.
As practice shows, the age structure and level of initial training boys is very different. This determines the style of the group: a differentiated approach to various groups of children. In the simplest case, we create two groups:
1. Design (guys, having some basic training);
2. Beginners, not previously involved in the groups.
Because of the short duration shifts in the first group it is inappropriate to give the children individual tasks — they just do not have time to complete complex devices. Therefore, we resort to the technique of the collective Assembly of electronic devices. The success of the joint work depends on each participant, therefore a special role acquires the proper organization of children, the distribution of loads taking into account the readiness of each. This system of training has prompted us, and modular Assembly.
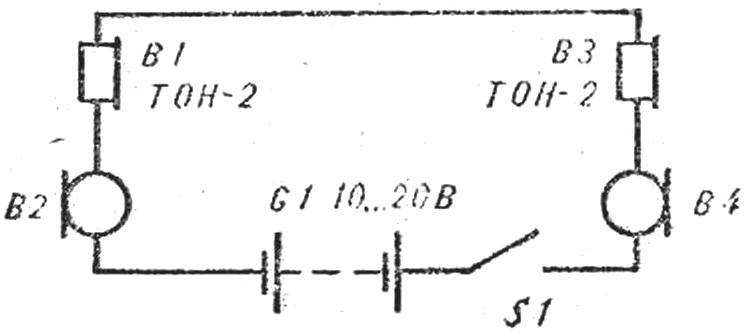
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the phone.
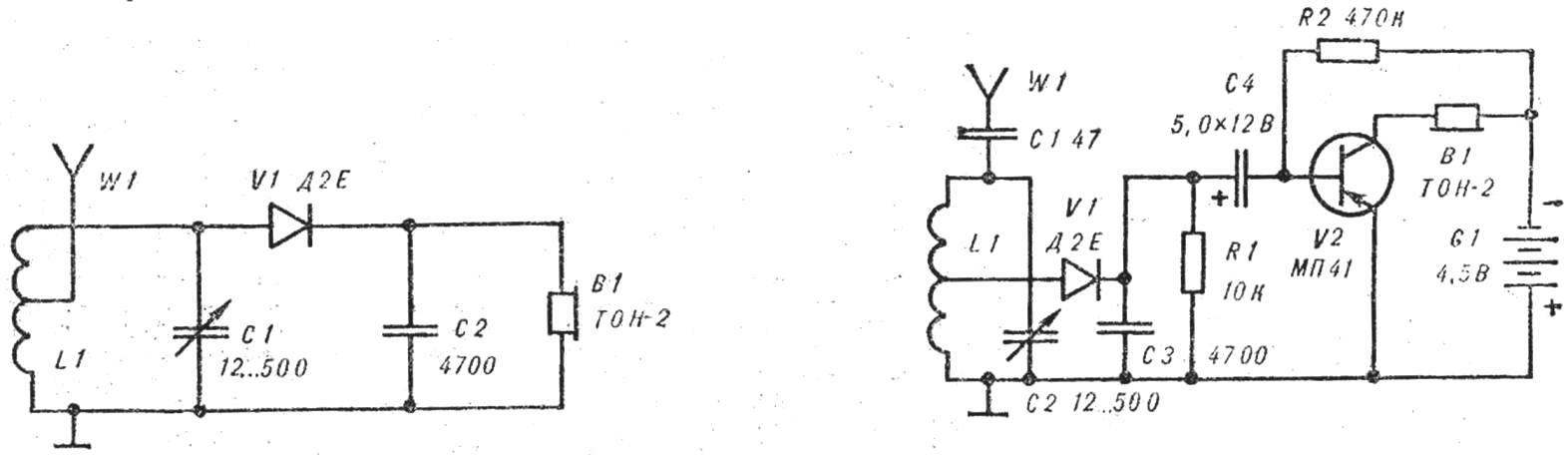
Fig. 2. The schematic diagram of the detector and transistor receivers (L1—2X100 = 200 turns of wire PEL of 0.31 on the frame Ø 20 mm).
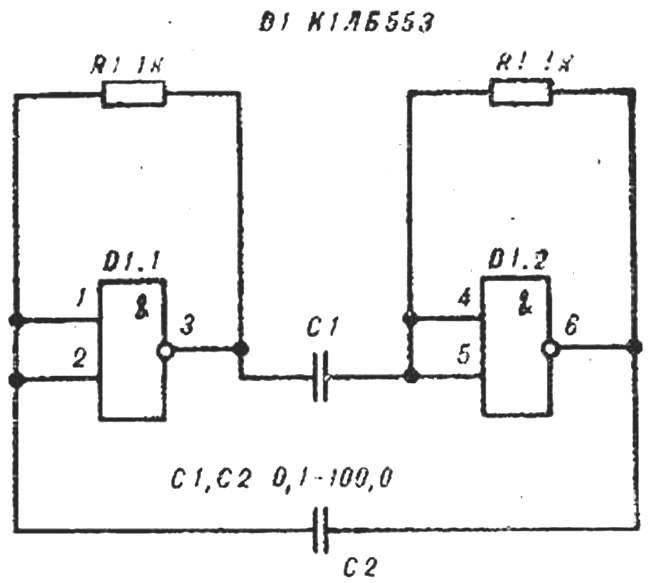
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the multivibrator
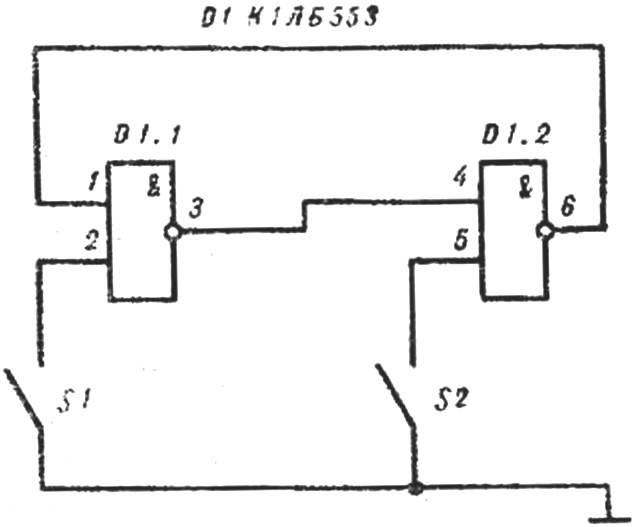
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of the indicator

Fig. 5. Schematic diagram of the trigger.
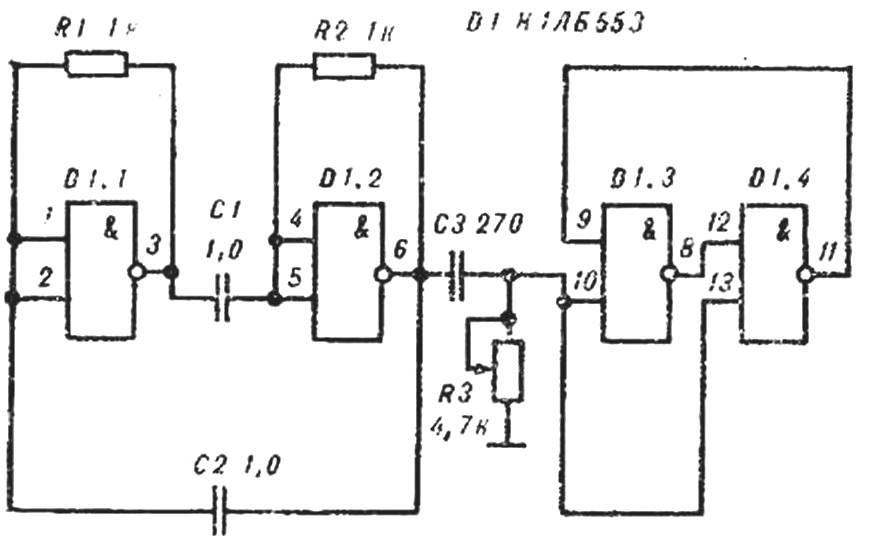
Fig. 6. Schematic diagram of the counting trigger.
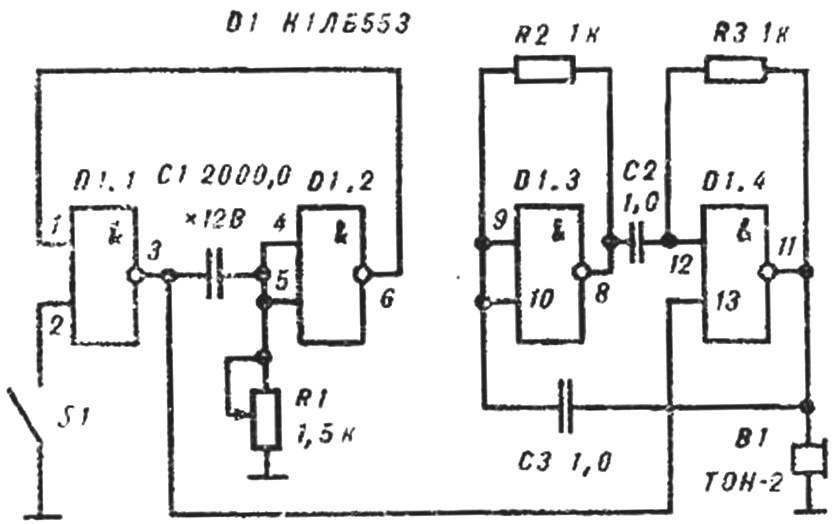
Fig. 7. The time relay.
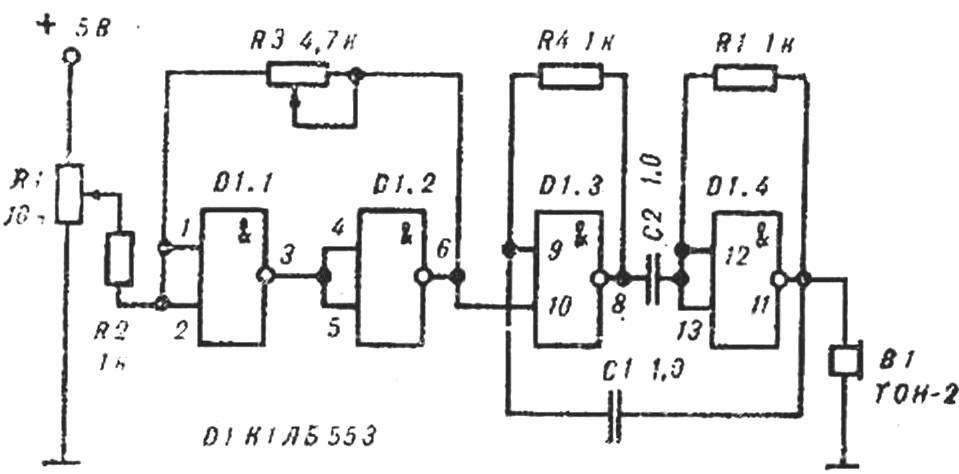
Fig. 8. The Schmitt Trigger.
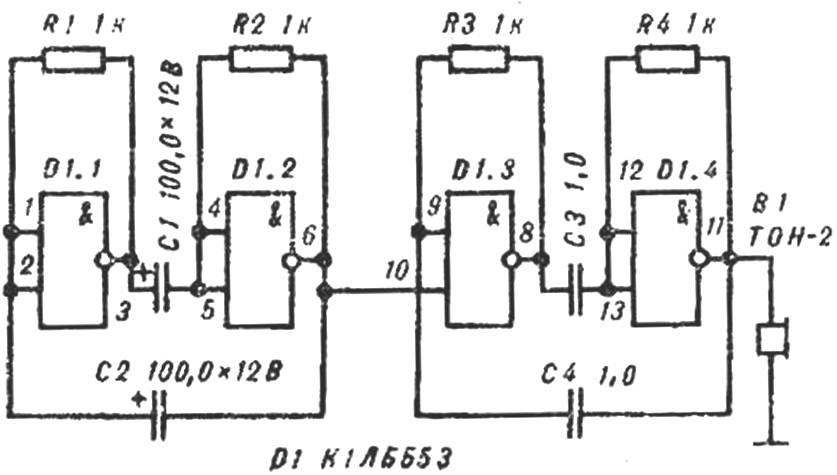
Fig. 9. Siren.
The work of the design team starts with the selection scheme. Then she breaks into containing one or two transistor modules, which produce is possible in one or two classes. The result will be a merging modules into a single, rather complex design.
High benefits of the transition to a new kind of modules — integrated circuits. Practice has shown that the work with the chips interesting for the members. Given the great prospects of integrated circuitry, we can say that this is the future of electronics, with which the kids are introduced today.
The task of the leader is the breakdown of the scheme and assistance in developing modules. His participation should not hamper the creative initiative of young technicians.
Form of work with the second group of children is, as noted above, the nature of the promotion. One of the options of the program for eight sessions is given below: it is based on the principles set out in the introductory part of the article.
Program mug
 The program is designed for children of 12-14 years, are unfamiliar with electronics. During the shift are 8 classes, two academic hours each.
The program is designed for children of 12-14 years, are unfamiliar with electronics. During the shift are 8 classes, two academic hours each. INTRODUCTORY LESSON. The boys get acquainted with the history of electronics and its achievements. Communicate basic information about the electric current, the techniques work safely with electrical equipment.
LESSON 2. the First half is given to familiarize with elements of electronic devices, memorization of symbols. Where possible, the characteristics of the elements are justified experimentally.
In the remaining time, children learn the techniques of soldering and Assembly.
LESSON 3. introduction one of the major directions of electronics — communications. Guys get acquainted with the history of the development of means of communication. Studied the principle of transmission of sound, image over wires. Describes existing means of communication: telephone, Telegraph, Videophone, etc. In the practical part included the Assembly of a simple telephone with a carbon microphone and head phones (Fig. 1).
LESSON 4. another Studied the principle of transmission of information — radio. Members acquainted with the history of the development of radio engineering with the operation of the radio transmitter and receiver.
The second part of the lesson is devoted to the Assembly of the detector of the receiver and its base — transistor (Fig. 2).
LESSON 5. the kids are introduced to the world of microelectronics, in particular with digital circuits. Experimentally established the basic properties of elements AND, OR, NOT, AND NOT etc.
Going to the flop with two inverters AND chips К1ЛБ553 (Fig. 3). Changing the values of R1, R2 and capacitors C1, C2 achieve change of pulse duration, repetition period, duty cycle. Monitoring the condition of the multivibrator is made with an oscilloscope or indicator device, depicted in figure 4.
LESSON 6. Sixth teaching computer science. Guys get acquainted with the principle of operation of digital computer, its structural scheme. Collect the schema of the trigger memory element CVM (Fig. 5). Closing (short) free inputs of the inverters on a common wire, transfer (dump) the trigger is in a different state that is controlled by the tester or indicator (Fig. 4). Trigger in the counting mode going the circuit shown in figure 6. Connecting an oscilloscope or headphones alternately to the output of the multivibrator and the trigger is adjustable by a variable resistor R3 until the output trigger pulses of twice the duration, or current in the headphones twice lower frequency than the output of the multivibrator.
LESSON 7. the Pioneers familiar with automatics, learn about “simple automatic devices and automatic control systems. Discusses the prospects of development of the industry.
Is the Assembly time relay (Fig. 7) and Schmitt trigger (Fig. 8). Rotate the potentiometer R1, find the threshold of the trigger, rotate the potentiometer R3 and resistor R2 picking up, set the desired threshold and hysteresis. As an indicator, in both cases, a multivibrator, shown in figure 3, or tester.
At the end of class to discuss possible options for the use of time relay and Schmitt trigger in the economy.
Session 8-e, final. The design team presents their work to the judgment of all members of the group, discusses the advantages and disadvantages of the devices. The second group participates in competitions but high-speed Assembly siren (generator intermittent signals).
In conclusion, is awarding the winners with diplomas.
POZHARSKY