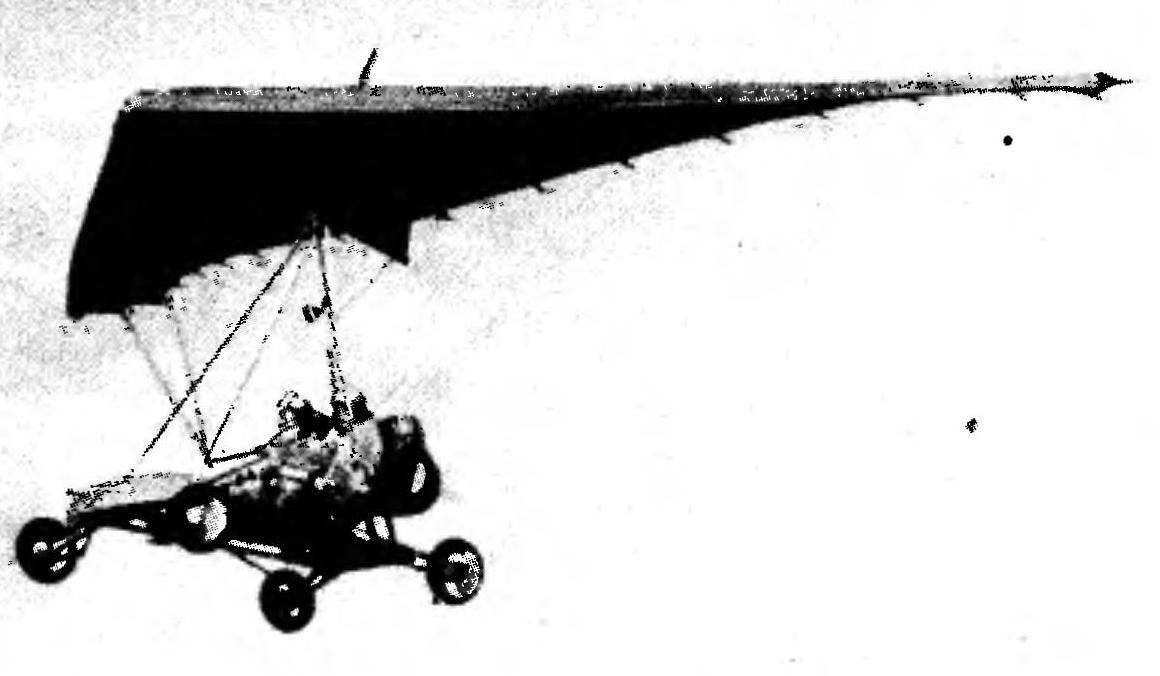
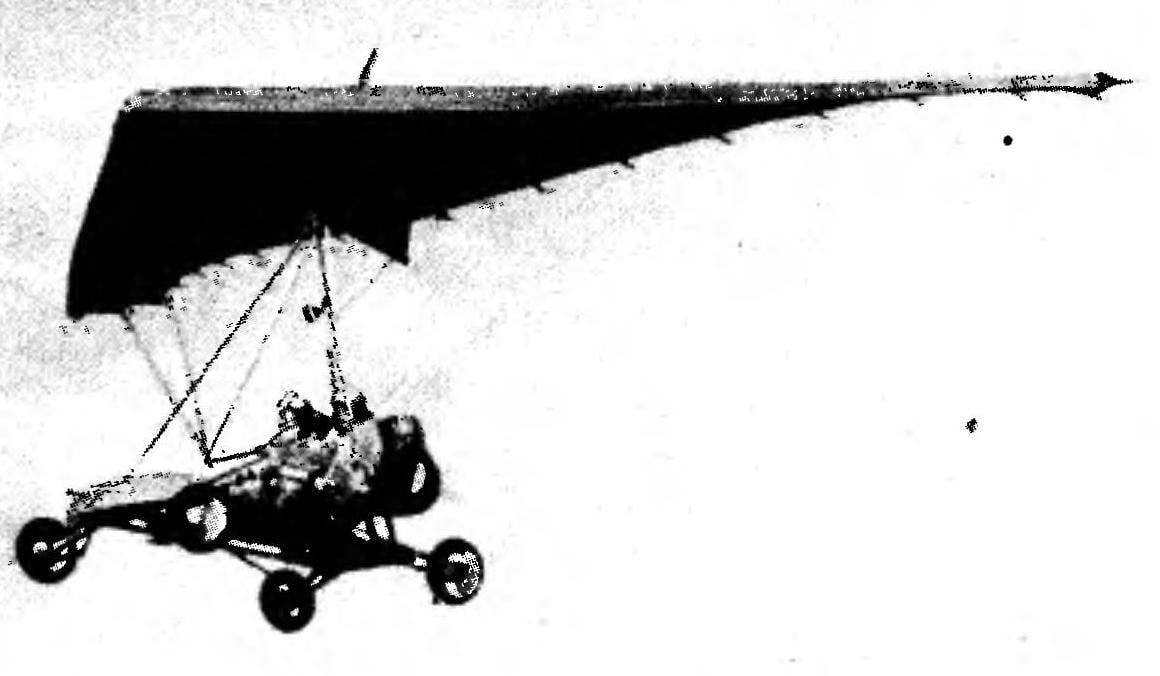
The design of the front suspension wheel ultralights is a little different from the rear. The same reinforced pipe, titanium bonded bridges and steel hollow rivets in the root, the same bolt with the head — end. Join the suspension to the axles is also the same: tubular struts and springs — bars of steel 55S2 size 236x44x16 mm, hardened after machining to HRC 50.
the collapse at 4° taking into account the future load — crew and engine), the assignment of wheels (front — steering, the rear — brake) and as a result the design of the hubs, wheels and axles (have front steering knuckles — axles with screwed in pins in them, the rear — brake drum-type).
In the winter instead of skis wheels are used (figure below left). The right ski differs from the left only by the location of the loops that are on the other half of snake and is designed for attachment of safety-adjusting cable with a length of about 640 mm. Around the middle rope attached to the steel plate with a hole, with the installation of skis it fits over the head bolt of the appropriate suspension. The exact position of the plate is levelled while suspended from the ceiling trike: the front half of the cable must be of such length that when landing ski not dug a toe into the snow. Parallel to the front half of the cord stretched rubber band, which in the air holding a ski with the toe above the horizon. The elastic band should be tight so that air flow was not able to deploy the ski with the toe down.
Ski made of sheet aluminum with a thickness of 1,5 mm. Collected using spot welding. In its absence you can use rivets.
Operating experience on the “Bug” showed that the width of the rear of the ski should be increased to 240 mm.
There is also the use of floats. Two float length 3400 mm, width 450 mm front and 300 mm rear, with a step height of 50 mm deltalyo easy to take off when fully loaded and to sit on the surface of almost any body of water.
But back to the wheeled version. Before you get in the air, it is necessary to check whether the device is balanced. For this, a curb trike hanging from the ceiling
for the abutment with wing, to achieve such a position it in space (pilot) to the front wheels was 150 mm higher than the rear. This difference in height should not change when replanting passenger.
The abutment of the mast a wing is a parallelepiped made of caprolactam, are clamped by bolts between the two dural cheeks. To the upper pole of the mast of the trike node is attached to the eyebolt with nut-“Barash-kom”. In the center of the box has a hole in which is inserted the keel of the wing. The location of the node on the keel is determined empirically.
The engine “Bug” attached to the motor frame, docked with the rear struts of the mast. The frame is a U-shaped rectangle, welded thin-walled (1.5 mm) SVEL lerov. With the struts of the mast and tie-rods suspension it connects at four points with bolts M8, for which the frame provides power units with shock-absorbing rubber and metal bushings.
The side channels are welded inside four boxes of clipanime in them “moskovichevskoe” rubber cushions shock absorbers. The design of the dampers slightly modified — “ears” of the mount bent back at 90°, and the two front faces of the cushions cut at a 45° angle (for greater mobility it bolted to the support beams). To the latter screwed a plate to the engine mounts.
This publication ends the story of deltarate “beetle-42”, which began in previous issues of “Modeler-con-structor”. Then it was about the design of the trike. Now consider all that relates to the power plant.
Power unit (SU) “Bug”, like most aircraft of this class, located on the mast of the trike behind the crew. It consists of motor, gear drive, a pusher propeller, power systems, cooling, monitoring and control.
Heart SOUS — engine PM3-640, manufactured by the Rybinsk engine plant and designed for snowmobiles “Buran”. He is unpretentious, develops considerable power and also weighs a little. The last argument in favor of the RMZ-640 makes it quite suitable to use and deltagate. But, of course, in a modernized form, since pure “snowmobile” motor could not provide “Beetle” reasonable speeds in different flight modes.
What was the upgrade?
First, to increase the capacity:
for each of the cylinders have been installed the carb К62И (from a motorcycle “IZH-Planeta-5”) and a homemade resonator. This has led to some increase of the propeller thrust.
Second, the translation engine with the air to liquid cooling, so a new mode of operation did not lead to the increase of operating temperature in the cylinders and they will not overheat.
Liquid cooling system required installation of the radiator (from a car VAZ-2108), hoses (rubber and plastic internal diameter about 20 mm), surge tank (capacity 1 l) with bleeder pump (from avtoelektroniki NC-300), inlet and outlet manifolds, connecting pipes, tees and clamps. In addition, it was necessary to modify the head and upper part of the cylinders of the engine is to supply them with their backs to cool. First, each cylinder drilled six upper cooling fins (holes in the top and then stirred up, the rest are now more channels for the coolant, in this case antifreeze). Then the ribs from the second to the sixth inclusive sawed from all sides and shut case “shirt” — a well customized aluminum strip 2-mm thickness, is welded to the first and the seventh rib (counting from the top) arc welding in argon. The band has warily two pipes for inlet and outlet of the antifreeze.
Modification of the cylinder head was a bit more complicated. Cooling ribs she had removed altogether. Instead, case made of aluminum sheet of 2 mm thickness — case “shirt” with inlet and outlet nozzles. The holes for the studs to cylinder reamed and warily aluminum sleeve with a stepped hole.
In addition, one of the heads have a threaded bushing — seat for the temperature sensor.
Assembled cooling system operates as follows. Pump, attached to the shaft of fan, pump antifreeze (2.5 l) in the “shirt” heads and cylinders. From there, the hot fluid enters the radiator placed in the nose cone, the trike and thoroughly blown RAM air. what in the front and rear walls of the fairing is provided with a rectangular opening and is closed by a metal grid with small cells. Cooled in the radiator antifreeze again rushes into the pump, and the excess in the expansion tank located above the engine.
The temperature and circulation of the coolant is controlled by a temperature gauge and a simple indicator (made from the neck of the bottle, two brass meshes and bulb) installed on the dashboard.
Modernization, of course, led to the complication and weighting of the power plant “Bug.” However, in the end, everything is justified by the fact that the engine is running in
optimal thermal mode, and its increased power will more than compensate for the weight of additional equipment.
To the frame, and more specifically to a notched plate lying on the support beams, the engine is hung from the same eight vertical studs that connect his head, cylinders and crankcase. Only instead of the top nuts on the studs screwed a long threaded sleeve. Itself the plate has eleven holes, eight of which are located respectively to the studs on the engine. Through these holes in the threaded sleeve screwed the bolts tractor engine to the frame.
Now for the drive of a propulsion — propeller. Torque from the crankshaft is transmitted to the screw wide timing belt is Kevlar. In
unlike traditional gear, belt less complicated due to the lack of oil bath and more reliable. And opting the timing belt done due to its benefits perebyjnis wedge: it is not slipping on the gears and has a high efficiency.
Gear ratio — 1:2,2. Its pinion gear is mounted on the shank of the crankshaft, not directly, but through the keyed bushing. Led, conversely, rotates in bearings (No. 7205 and N° 204) mounted on shaft fixedly attached to the notched plate clamps. To prevent slippage of the belt back (for flight) the ends of both gears is provided with a restrictive cheeks made of aluminum.
In the development of the power plant ultralights much attention was paid to the mover. Tested propellers of various designs and made of different materials. Preference was given to a lightweight and durable stack-aplastica, allowing you to change the pitch of the blades and thus to choose the optimal mode of operation of the engine at maximum thrust. However, this publication describes a wooden propeller as the most simple, available and cheap.
Driven gear screw spontannyi connected by bolts through rubber bushes-dampers.
It should be noted that when the trike is used as the Aero-mobile, snowmobile or aerocamera, around the air screw is installed a safety fence of steel rods. In the embodiment of ultralights, it is removed to reduce the weight of the apparatus.
Fuel for the engine (a mixture of gasoline And-76 with the oil) is contained in two aluminum tanks with total capacity of 34 liters, installed behind the seats of the crew, and served in the carburetors regular fuel pump.
Engine starts with a special handle. It hangs above the pilot’s head on the rope, which from the block on the upper pole of the mast extends down to the regular launcher device.
The powerplant pilot controls, as already mentioned, instrument panel nose cone: tachometer, temperature gauge toso-La and the indicator of its circulation in the cooling system. And controls the motor using the electric switch mounted on the tube of the spar under the seat and the gas pedal under your right foot.
Here, perhaps, and all. It remains to say that the realization of a long-standing dream of human free flight, the most noticeable behind the wheel of a trike. With the separation of the wheels from the ground feeling new and unknown burst into the consciousness along with the oncoming wind. Climbing higher, I notice that houses and cars are smaller, and with them… our everyday problems. Having absorbed the energy of the universe, land then updated, as if rejuvenated, and most importantly, confident.