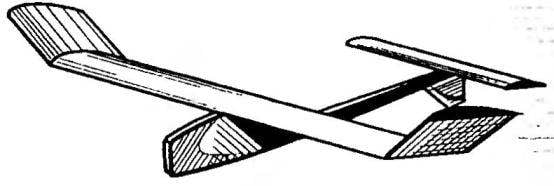
Design models for traditional training gliders, if not to take into account the singularity of the transverse frame of the wing (rarely a very powerful set of ribs) and profiling. High flight performance is likely obtained due to the successful combination of the profile of the wing, his cross “V” and the area of the bearing planes. A short, badly up ears not only give the glider greater stability even in turbulent air, but also increase the efficiency of the Central area of the wing to create maximum lift at relatively low value of drag. Have very short wing (for which the new model got the name “Compact”), even with its enhanced design moment of inertia in roll is much smaller compared to pure samples of the championship with a wingspan up to 1.5 m. Therefore, it is likely that the glider was very sensitive to upward flow, good holding, even in the narrow “thermals”. Short fuselage with light weight tail (including the keel and stabilizer) provides a low value of the moment of inertia in pitch, allowing for sufficient effectiveness of the horizontal tail to the high stability of the flight even with a strong gusty wind, which is clearly not typical of the subclass of the gliders of type A-1.
The manufacture of such models is simple. The main requirement is high-quality raw materials, precise machining, fit of parts, and accurate Assembly of the entire frame. Used for bonding plasticized epoxy, which gives not comparable with any other glue results.
Svobodnaya model glider “school” class:
1 — fuselage (nose), 2 — pin for the front rubber band wing mounting, 3 — pin rear, 4 — beam tail, 5 — keel 6 — tool tray-stabilizer, 7 — lodgment of the wing, 8 — hook tow, 9 — “eye” wing, 10 — fender (Central part), 11 — stabilizer.
The fuselage (fore and aft):
1 — insert the nose (lime plate, s8), 2 — the load balance weight (lead shot filled after the adjustment of the model epoxy), 3 — tube, 4 — bow Board (plywood, s1,2), 5 — pin for the front rubber band wing mounting (bamboo rod Ø4), 6 — a fillet reinforcement (epoxy resin), 7 — the frame of the wing (plywood with a transverse direction of the layers “shirts”, s1,5, C40), 8 — pin back (bamboo rod Ø4), 9 — beam Kostova (pine rack 13×8; to the rear end section to reduce to 6×4), 10 — adjustable tow hook (wire Ø2 OBC), 11 — cover plate (stainless steel, sheet, s0,8… 1), 12 — stud fastening M3 (to glue on the epoxy in the fuselage), 13 — keel (balsa plate, s2), 14 — pin rubber belt stabilizer attachment (bamboo rod Ø3), 15 — emphasis (profiled fake rack), 16—the outline of the profile of the stabilizer, 17 — hook wick of determinator (OVS wire Ø1,5), 18 — boss support adjustment (Linden), 19 — turn the adjusting wheel (stands out from the keel only when necessary kompensera VAT inaccuracies of the model), 20 — trim the keel (pine or the Linden rail 3×2), 21 — tool insert of the stabilizer (plywood, s1,5).
Wing:
1 – solitaire (plywood, sl). 2 – ending (fake rack 9×4), 3 – rib (fake plate, s2) 4 – solitaire front (plywood, s1,5), 5 — Polonnaruwa (fake plate, s2). 6 – edge front (pine rack 6×4), 7 – rib joint oblique (fake plate, s4), 8 — auxiliary gusset (plywood, s 1). 9 — stringer (pine rail 3×2), 10 — spar (team detail of the two shelves: the top is pine rack 5×2. 5, bottom — 4×3), 11 — Klondike support shank ribs (plywood, s1), 12 — edge of the rear (raked pine 9×3), 13 — strengthening the edges of the Central (pine rail 5×4), 14 insert (plywood, 1.5 s), 15 — Polonnaruwa Central (Linden plate, s5), 16 — zone designation mounting wall of the spar of lime plates (s1,5).
Stabilizer:
1, 3,11 — scarves (plywood, s 1), 2 — rib zakonczona (purple plate, s3), 4—rib (fake plate, s0,8… 1), 5 — Polonnaruwa (fake plate, s0,8), 6 — spar (pine rail 5×2), 7 — pad (Linden), 8 — edge front (pine rail 3×3), 9 — rib Central (Linden plate, s3) 10 — edge of the rear (raked pine 6×2,5).
Profiles of the wing and stabilizer:
A — cross section of the Central wing, B — wing section of the intermediate, In — cross section of the stabilizer intermediate.
Scheme of cutting of the workpiece, made in the form of profiled sections of the wing, the oblique rib joint “ears” and a Central part.
Although in the drawings for most parts specified materials such as pine and basswood, the choice of wood should be approached very carefully. Even high-quality pine, if possible, should be replaced by spruce — the latter is easier to process and, most importantly, it produces less massive frames with increased strength and rigidity. Lime in connection with its porosity (durable varieties too heavy) it is better to replace wasp: it is more difficult to process and is very fragile, but with equal strength of the parts of aspen and Linden first almost two times lighter.
Cover all bearing surfaces of the airframe — quality macalintal paper, glued and topped with a homemade “amelita” — nitrocellulose adhesive for leather, diluted with solvent No. 646. Unlike modern domestic dopes binder such good pulls the paper practically does not age and does not yellow.
Model “Compact” is extremely simple to operate, which is very important as when teaching beginners and Junior competition. In particular, the airframe is completely absent now newfangled mechanics, from the most complicated multi-part tow hooks and ending with the clockwork of time limit of planning (more practical appeared a simple matchlock device).
On our model tow hook — less common side type. The displacement of the suspension point of the glider on the rail sideways is about 12 mm. straightness of the takeoff is provided by a positive twist of the wing in the side of the hook. The both “ears” have the same negative twist in the range of 8 mm at the tip. Such an asymmetrical wing allows the model immediately after leaving the Leer go a turn without loss of height, even when towing according to the type of dynastart. With a little practice manage to disperse the “Compact” in the final phases of takeoff to speeds comparable with the speed of the gliders international championship class F1A. Estimations for optical measurements of height and calculations of time planning allowed us to determine that benefit from a “shot” of the rail is 10 m additionally recruited during takeoff altitude.
V. COSSACKS
the head of a circle of aircraft modeling
Recommend to read YOUR E-PSYCHOLOGIST A set of electronic devices that use psychologists is constantly expanding. In addition to the "Polygraph" (the"lie detector"), there are other devices to test the emotional state of... TABLE-FUNGUS Its round tabletop and the same support can be of different diameters depending on the purpose of table: to be coffee, chess, or stand for flowers. Here for the latter and proposed a... 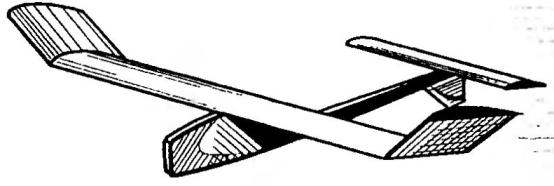 This svobodnymi glider — simple, durable, reliable and moderately “volatile” — was created as a training. It was assumed that newcomers in the process of its manufacture and operation will quickly master techniques of the work with the model aircraft materials and will gain the skills to adjust and run the model. However, tests have shown that among its advantages is joined by terrific “volatility” on the level of specialized osakryl models championship.
This svobodnymi glider — simple, durable, reliable and moderately “volatile” — was created as a training. It was assumed that newcomers in the process of its manufacture and operation will quickly master techniques of the work with the model aircraft materials and will gain the skills to adjust and run the model. However, tests have shown that among its advantages is joined by terrific “volatility” on the level of specialized osakryl models championship.