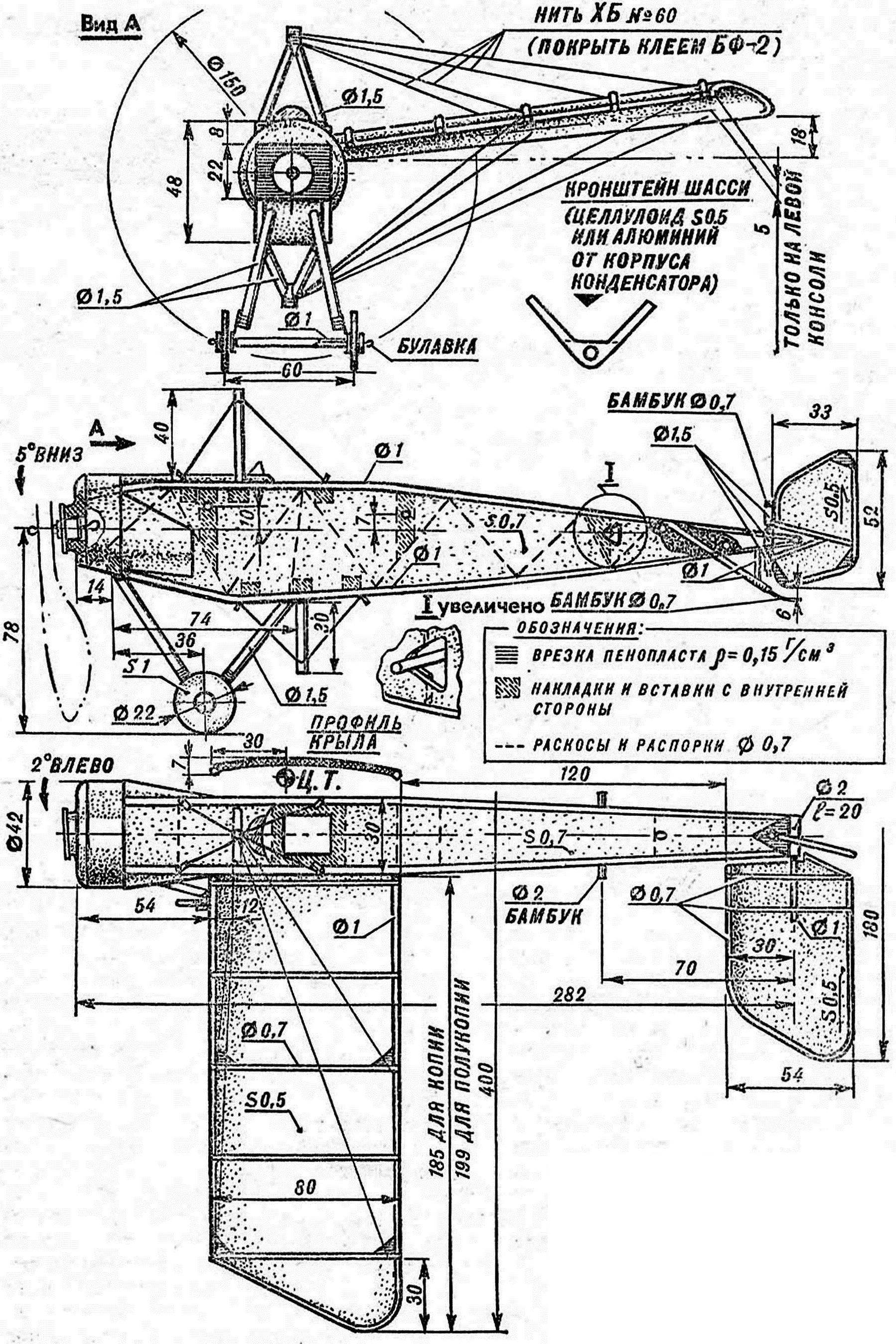
The fuselage is formed by two copies of Bo kominami, upper and lower “skins”. All these parts are cut from lightweight foam with a thickness of 0.7—1 mm. On the inner surface of the sidewall feature bracing made of grass d of 0.7 mm, and the contour of the pattern — stems d of 1 mm, and the “butt” of the stem must always be from the side of the forward fuselage.
The inner side of the horizontal plates of the fuselage increase the same struts. They should be placed so that after Assembly with the side walls of the point of convergence of the side braces match.
In the forward part of the box of the fuselage contained a boss of dense foam with a thickness of 5 mm with bore d 12 mm under the sleeve of the propeller. The latter is also foam on all edges glued plastic washers with holes for the shaft screws. Sleeve length — 6 mm d: 12 mm, thickness 0,5 mm washers Front is thecontour sleeve 2 mm — to focus on the boss.
R and S. 2. The forward fuselage simulation of the engine hood.
In places seal rubber motor, install the wing, tail, landing gear and “add-ins” is enhanced by the fuselage being glued to the internal plates of dense foam with a thickness of 1 mm. it should be Done before Assembly of the fuselage, and overlays and inserts must be in contact with elements of straw frame. In the fixation edge of the wing through the sidewall of the straw d are 1 mm, they will enter the pin edges.
The design of the tail, flat profile similar to the wing. Turning the stabilizer has a longitudinal d 1 mm, used for swivel mounting of the console on a straw tube in the tail of the fuselage. Fixation of the stabilizer angle of attack — thin bamboo splinter, passing through the flanges and additional through the straw, the jumper of the fuselage.
The propeller blades about 1 mm thick, planed from a dense foam and visseren. On the hub glued a plastic washer ø 8 mm (the thickness of plastic is 0.5 mm) to amplify under the tree. The last bend of stationery pins with annealed for bending the hook end of the rubber motor. The bearing of the propeller — two Teflon washers with a thickness of 1 mm, d 2 and d 4 mm. Closer to the screw is smaller. PTFE moleno to replace other plastics, for example, the roll in several layers.
Due to the high elasticity of the material of the blades, the breakage of the propeller in collisions with obstacles were not.
Wheels are cut from plates of dense Styrofoam mm thickness. In the center is glued straw with an internal diameter of about 0.5 mm, cut flush with the wheel. After the glue dries it acts as a bearing. On the through axis (also straw taped to the ends of the wire inserts) wheels are fixed with small plastic washers. Landing gear (d stems 1.5—2 mm) onto bamboo rods within the insets of the fuselage.
In the manufacture of the hood first, cut the front part of a lightweight foam thickness of 4 mm. Butt her stick pre-bent sides of two-millimeter plate. The edges of the front portion are rounded. In the front wall of the finished hood cutout is provided at the front end of the fuselage box, which is mounted on the adhesive the hood. Number of copies per cell of the model can be significantly improved through the installation of the lugs with simulated engine cylinders. One way to simulate a set of alternating washers of different diameter from foam and paper, dyed by immersion in the ink.
The fuselage for the model-polyopia cut from a plate thickness of 1.5 mm with framing foam billet stems 1 mm. In d neck plate affixed to the tube under the rubber motor. She received a spiral wrapped “tapes” with a width of 25 mm mm of lightweight foam. In the loaded sections of the tube is enhanced by the inset rings of dense foam (a width of 5 mm at the ends of the tube and 10 mm in the middle).
Fig. 3. The node setup of the wing to the fuselage.
To increase the rigidity of the contour of the fuselage in the sheet light side in some places, embedded elements from a foam density of 0.15 g/cm3 of the appropriate thickness. And in the area, loaded by a system of braces of the wing, installed stacked frame from separate corners, framed by stems. The rest of the process of building polyopia repeats work on the copy.
The mass of each model (and they are made with some surplus strength) amounted to 9 and 6 g (the latter refers to polyopia). Accordingly, the specific load on the bearing surface 2.2 and 1.5 g/dm2. It should be noted that the characteristics of the copy close to celebarty, covered with paper.
At these scales, even the rubber motor from end of rubber thread d 1,2 (“Hungarian”) provides a flight duration of 15-20 s. To copy the wiring is composed of four strands, with a length of 200 mm, polocaine — three.
R and S. 4. Insertion of the pins for mounting the superstructure on the fuselage.
The smooth surface of the models (it is easy to put markings) can be obtained by using a condenser paper, which is covered skeleton made of straw. However, in this embodiment, the total mass is obtained more copies — have to strengthen the frame to hold tension on the paper sheeting. Yes, and the relative ease of paper compared to the thin foam is not so significant (0.17 g/DM 2 vs. 0.3 foam). Advantage in weight disappears after covering the paper Amalita: according to our data, paint nitrocellulose lacquer increases the weight of 1 dm2 of plating of 6.2 g.
Proposed constructive solutions allow you to build and copy an enlarged size for flying in the open air with a mass of 15-20 g with a scale of about 1 : 20.
FEATURES MANUFACTURING AND TESTING OF THE MODEL
As already mentioned, the tube of the fuselage polyopia received a spiral-wound foam strips on the cylindrical rod. It is pre-wrapped cushioning layer of two coils of condenser paper. The end and the beginning of coiling the tubing secure them with a thread, cut after the glue dries. The binder is applied to the edges of the foam strips as they wrap on the rod. After drying, the adhesive rod is removed, the tube is placed folded double wand with grip — it can help extract, gradually reeling, gasket paper. In places sticking paper separated long pointed wire.
R and S. 5.Propeller models
Braces on the inner surfaces of the sidewalls of the model-copy set with a small margin along the length of the straw pieces. After the glue dries the braces are cut along the contour of the foam sidewalls. Similarly glued struts and horizontal panels.
Edging the rounded contours of the fenders and elements of the tail — a task not so simple. Wings need before starting work to squeeze processed on the profile of the foam template to the slipway. Banding is conducted by gradually pressing against the contour of the wing stalk of straw with pins, stick in the stocks (stalks puncturing is impossible, pins have only to draw the straw from the external side). It is helpful to first give the stems a rough profile of the bend on the soldering iron.
Rib of the wing is obtained by bending flat pack thin stems on the heated soldering iron. The pack is easily formed with greasing the ends of the blanks with glue. After giving the required profile in the place of the package corresponding to the overall length of the ribs, cuts with a razor. Alternately attestative from the package, they are glued to the wing.
Fig. 6. Fuselage and stabilizer models polyopia with a contoured performance of the fuselage.
Symbols and designations of items from straw correspond to figure 1.
For vystragivanija propeller should be used only sharpened knives. Removed the minimum chip thickness. The final finishing dimensions and surface of the blades — skins with medium and fine abrasive coating.
Adjustment start with debugging planning. Instead of the screw with the bushing is mounted is equal to the mass of the ballast of a piece of clay and pin to hold the rubber motor. The model should decrease smoothly, with a turn caused by the twisting of the wing. The rudder at the first stage in a neutral position. Quality planning is achieved by permutation of the stabilizer (his console is better not to turn in the hinges, and each time it is removed from the straw tubes of the fuselage).
R and S. 7. Chassis and power node of the fuselage of the model-polyopia.
The next stage of the overflight — trial run with the rubber motor, spin consistently at 50, 100 and 150 rpm with a propeller. Flight manifested in the tendency to dive or pitch up eliminate the selection of the position of the axis of the propeller, cutting the top or bottom landing of the end lugs of the fuselage. The proper model comes with a bend radius of about 3 m (adjustment via permutation of the rudder). After resii twist motor 100 rpm more and may experience the tendency to dive. Remove it by lifting up the front edge of the stabilizer or a small shifting of the center of gravity of the model. The total flight time procopii more than copies. An additional increase in duration can be achieved by selection of the-rotor with the increase of the diameter of the propeller. However, the chassis becomes purely ornamental value (as in many other models). It should be noted that debugging of flight copies without chassis is much easier and faster.
* * *
If you will be able to ensure particularly careful handling of the model, it can be alleviated by switching to a thin straw the frame member. So, edging the feathers are made of the stems d of 0.5 mm or less, the ribs of the wing — also the straw d is 0.5 mm. the thickness of the foam panels is brought to 0.5 mm copies and 1 mm for polycopy. When you run lightweight vehicles keep them for the rear rubber motor pin using the tool-fork.
In conclusion, I would like to note that such rezinobitumnye copies, as shown by the rich experience of group work, are the boys great success. Although traditional room fly much longer, they do not look like real airplanes. And the copies look more attractive and are made simply. The time of construction, for example, Prokopii about 4.5—6 hours.
0. MATHIS,head of the society, d. B o t K and K.
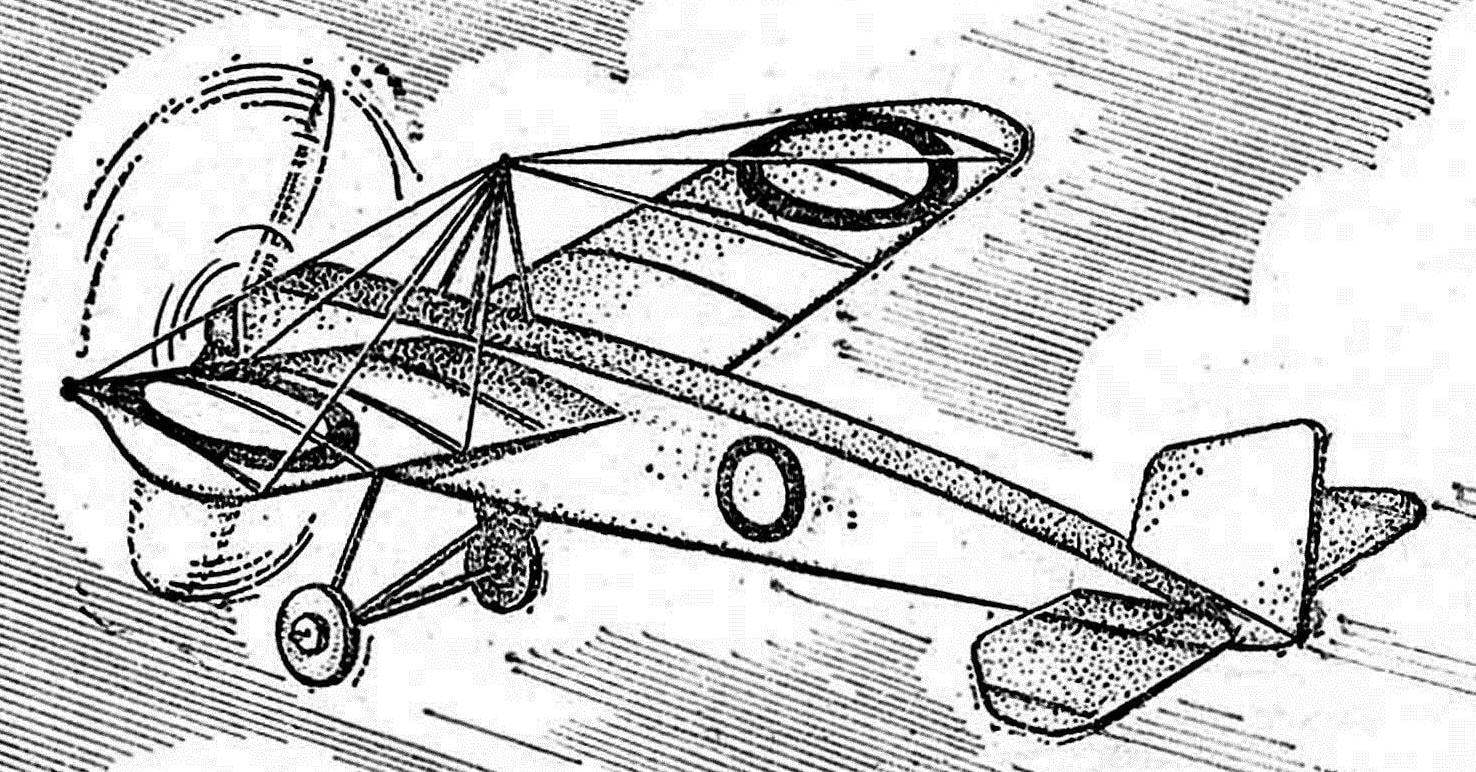
Recommend to read CLOTHESPIN ON A BED Until the seedlings, and it is easy to confuse what is planted in a particular bed. Arrange for your garden or summer cottage here such simple devices — and and plantings and sowings... INCREASE THE RELIABILITY OF THE “GRINDER” A master homebrew, working with metal, have in their Arsenal, angle grinder, called colloquially the "grinder" (the name originated in the old "stagnant" times, due to the fact that this... 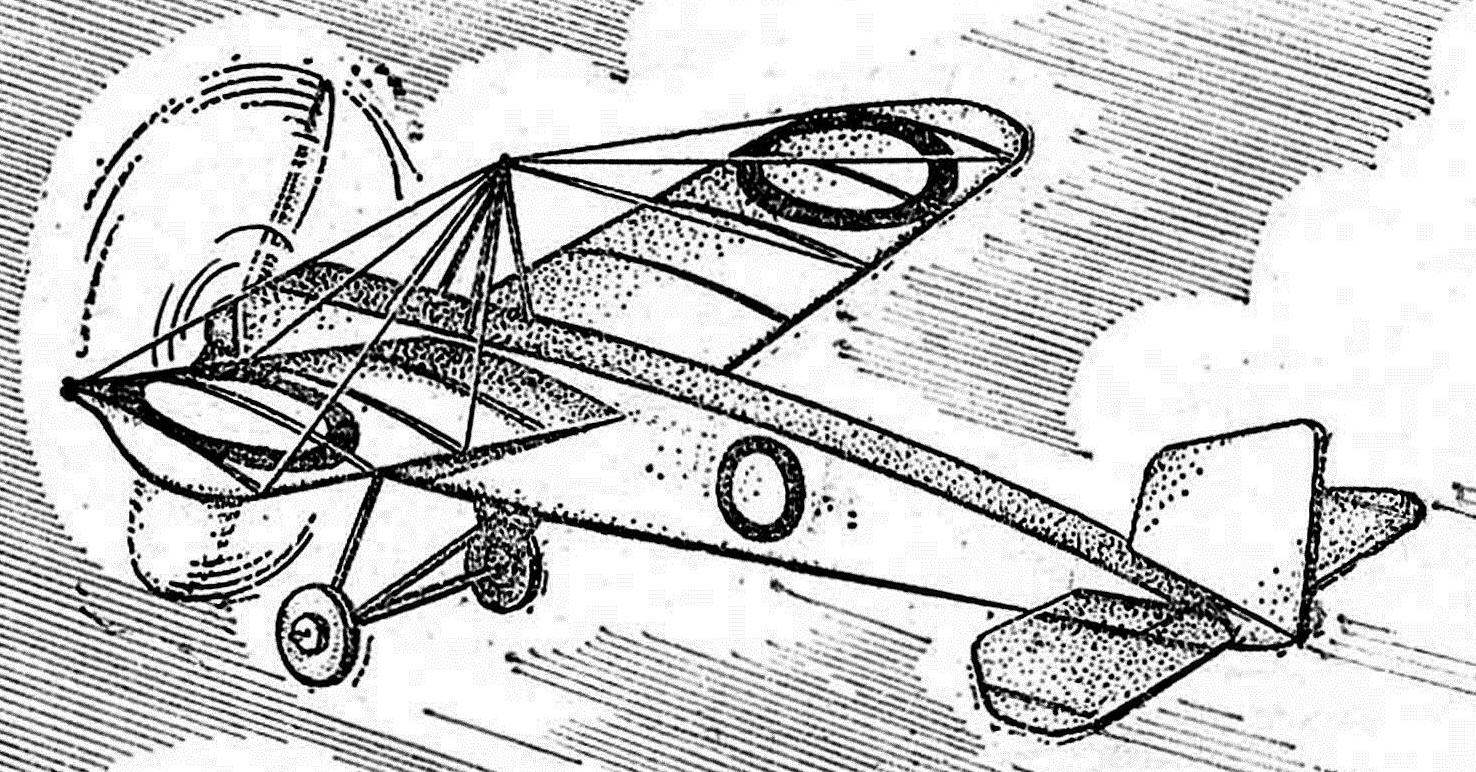 Readers rezinomotornaya a replica of a historic aircraft “Moran-G” in which famous Russian pilot P. N. Nesterov first in the world made air RAM .The model was created in two versions — “full” copy with a boxy fuselage and polyopia with a contoured fuselage. To achieve a satisfactory flying qualities, had to go to small deviations from the proportions of the prototype aircraft. The models are made entirely from common materials, the main of which was melkosortnyj packing foam density of 0.05—0.06 g/cm3, chopped termolabil for plate thickness 0.5—1.5 mm. By weight parameters of the model are comparable to the best balsa models. To make their students of 6-7 grades. Choosing a simple plane as a prototype to copy allows to make emphasis in students ‘ work and not to simulate individual elements, and the manufacturing quality of the device.
Readers rezinomotornaya a replica of a historic aircraft “Moran-G” in which famous Russian pilot P. N. Nesterov first in the world made air RAM .The model was created in two versions — “full” copy with a boxy fuselage and polyopia with a contoured fuselage. To achieve a satisfactory flying qualities, had to go to small deviations from the proportions of the prototype aircraft. The models are made entirely from common materials, the main of which was melkosortnyj packing foam density of 0.05—0.06 g/cm3, chopped termolabil for plate thickness 0.5—1.5 mm. By weight parameters of the model are comparable to the best balsa models. To make their students of 6-7 grades. Choosing a simple plane as a prototype to copy allows to make emphasis in students ‘ work and not to simulate individual elements, and the manufacturing quality of the device.